内核是如何运行ko文件的--insmod命令
内核是如何运行ko文件的–insmod命令
文章目录
- 内核是如何运行ko文件的--insmod命令
- insmod详细分析
- 在正点原子阿尔法开发板中查看insmod使用什么方法:
- 使用finit_module写一个自己的命令
- 使用init_module来实现自己的命令
insmod详细分析
insmod命令将文件加载到Linux系统中运行。那Linux系统是如何加载的文件呢?加载ko文件使用的是insmod命令,insmod命令做了哪些事情呢?实际上,命令本质上是一个可执行程序,也是有源码的。我们来看下insmod命令的源码。
打开busybox源码busybox/modutils/insmod.c文件,找到以下代码。
int insmod_main(int argc, char **argv) MAIN_EXTERNALLY_VISIBLE;
int insmod_main(int argc UNUSED_PARAM, char **argv)
{
char *filename;
int rc;
/* Compat note:
* 2.6 style insmod has no options and required filename
* (not module name - .ko can't be omitted).
* 2.4 style insmod can take module name without .o
* and performs module search in default directories
* or in $MODPATH.
*/
IF_FEATURE_2_4_MODULES(
getopt32(argv, INSMOD_OPTS INSMOD_ARGS);
argv += optind - 1;
);
filename = *++argv;
if (!filename)
bb_show_usage();
rc = bb_init_module(filename, parse_cmdline_module_options(argv, /*quote_spaces:*/ 0));
if (rc)
bb_error_msg("can't insert '%s': %s", filename, moderror(rc));
return rc;
}
int FAST_FUNC bb_init_module(const char *filename, const char *options)
{
size_t image_size;
char *image;
int rc;
bool mmaped;
if (!options)
options = "";
//TODO: audit bb_init_module_24 to match error code convention
#if ENABLE_FEATURE_2_4_MODULES
if (get_linux_version_code() < KERNEL_VERSION(2,6,0))
return bb_init_module_24(filename, options);
#endif
/*
* First we try finit_module if available. Some kernels are configured
* to only allow loading of modules off of secure storage (like a read-
* only rootfs) which needs the finit_module call. If it fails, we fall
* back to normal module loading to support compressed modules.
*/
# ifdef __NR_finit_module
{
int fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY | O_CLOEXEC);
if (fd >= 0) {
rc = finit_module(fd, options, 0) != 0;
close(fd);
if (rc == 0)
return rc;
}
}
# endif
image_size = INT_MAX - 4095;
mmaped = 0;
image = try_to_mmap_module(filename, &image_size);
if (image) {
mmaped = 1;
} else {
errno = ENOMEM; /* may be changed by e.g. open errors below */
image = xmalloc_open_zipped_read_close(filename, &image_size);
if (!image)
return -errno;
}
errno = 0;
init_module(image, image_size, options);
rc = errno;
if (mmaped)
munmap(image, image_size);
else
free(image);
return rc;
}
init_module与finit_module均为系统调用
#define init_module(mod, len, opts) syscall(__NR_init_module, mod, len, opts)
#if defined(__NR_finit_module)
# define finit_module(fd, uargs, flags) syscall(__NR_finit_module, fd, uargs, flags)
#endif
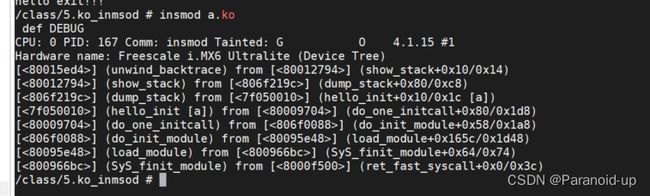
在正点原子阿尔法开发板中查看insmod使用什么方法:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
static int hello_init(void){
#ifndef DEBUG
printk("no def DEBUG\n");
#else
printk(" def DEBUG\n");
#endif
dump_stack();
return 0;
}
static void hello_exit(void){
printk("hello exit!!!\n");
}
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("Paranoid");
MODULE_VERSION("V1.0");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
所以可知使用的是finit_module
insmod命令流程
insmod_main->bb_init_module->finit_module
使用finit_module写一个自己的命令
myinsmod.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
# define finit_module(fd, uargs, flags) syscall(__NR_finit_module, fd, uargs, flags)
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
int fd;
int ret;
int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY | O_CLOEXEC);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("open error\n");
return -1;
}
ret = finit_module(fd, "", 0) ;
return ret;
}
交叉编译器编译
arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc myinsmod.c -o myinsmod
使用自己的命令来安装驱动
./myinsmod a.ko
结果与insmod相同
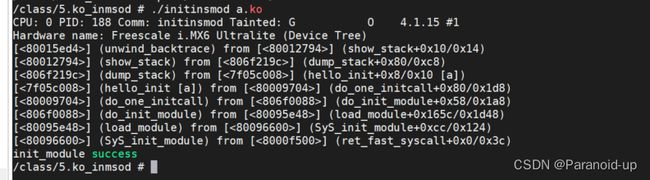
使用init_module来实现自己的命令
init_insmod.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define finit_module(fd, uargs, flags) syscall(__NR_finit_module, fd, uargs, flags)
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
int fd;
int ret;
size_t image_size;
char *image;
struct stat statbuf;
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY | O_CLOEXEC);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("open error\n");
return -1;
}
fstat(fd,&statbuf);
image_size = statbuf.st_size;
image = malloc(image_size);
read(fd,image,image_size);
ret = init_module(image, image_size, "");
if(ret <0){
printf("init_module errno\n");
}else{
printf("init_module success\n");
}
free(image);
return ret;
}
arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc init_insmod.c -o initinsmod