PG配置文件详解
文章目录
-
-
- 一、概述
- 二、pg_setting视图
- 三、数据库相关配置 postgresql.conf
- 四、客户端认证配置文件 pg_hba.conf
- 五、ident认证配置文件pg_ident.conf
- 六、详解postgresql.conf
-
- 6.1 文件位置(FILE LOCATION)
- 6.2 连接和验证(CONNECTIONS AND AUTHENTICATION)
-
- 6.2.1 连接设置(Connection Settings)
- 6.2.2 认证(Authentication)
- 6.2.3 SSL
- 6.3 资源使用(RESOURCE USAGE (except WAL))
-
- 6.3.1 内存(Memory)
- 6.3.2 磁盘(Disk)
- 6.3.3 内核资源(Kernel Resources)
- 6.3.4 基于成本的真空延迟( Cost-Based Vacuum Delay)
- 6.3.5 后台写入(Background Writer)
- 6.3.6 异步行为(Asynchronous Behavior)
- 6.4 预写日志(WRITE-AHEAD LOG)
-
- 6.4.1 设置(Settings)
- 6.4.2 检查点(Checkpoints)
- 6.4.3 存档(Archiving)
- 6.5 复制(REPLICATION)
-
- 6.5.1 发送服务器(Sending Servers)
- 6.5.2 主服务器(Master Server)
- 6.5.3 备用服务器(Standby Servers)
- 6.5.4 订阅者(Subscribers)
- 6.6 查询调优(QUERY TUNING)
-
- 6.6.1 计划方法配置(Planner Method Configuration)
- 6.6.3 查询优化器(Genetic Query Optimizer)
- 6.6.4 其他计划选项(Other Planner Options)
- 6.7 报告和记录(REPORTING AND LOGGING)
-
- 6.7.1 记录位置(Where to Log)
- 6.7.2 何时记录(When to Log)
- 6.7.3 记录什么(What to Log)
- 6.8 流程标题(PROCESS TITLE)
- 6.9 统计数据(STATISTICS)
-
- 6.9.1 查询和索引统计信息收集器(Query and Index Statistics Collector)
- 6.10 自动清理(AUTOVACUUM)
- 6.11 客户端连接默认值(CLIENT CONNECTION DEFAULTS)
-
- 6.11.1 声明行为(Statement Behavior)
- 6.11.2 语言环境和格式(Locale and Formatting)
- 6.11.3 共享库预加载(Shared Library Preloading)
- 6.12 其他默认值(Other Defaults )
- 6.13 锁管理(LOCK MANAGEMENT)
- 6.14 版本和平台兼容性(VERSION AND PLATFORM COMPATIBILITY)
-
- 6.14.1 以前的PostgreSQL版本(Previous PostgreSQL Versions)
- 6.14.2 其他平台和客户(Other Platforms and Client)
- 6.15 错误处理(ERROR HANDLING)
- 6.16 配置文件包括(CONFIG FILE INCLUDES)
- 6.17 自定义选项
-
一、概述
本文讲解PG的三个主要的配置文件:
postgresql.conf
pg_hba.conf
pg_ident.conf
二、pg_setting视图
该视图用于访问服务器用到的一些参数,是show和set 命令的代替接口,有些show命令查看不了的也可以用该视图来查看。
官方关于该视图的解释
通过pg_setting ,我们可以看到postgresql主要有下面三个配置文件
select name, setting,source from pg_settings where category='File Locations' ;
sql查询结果:
name | setting | source
-----------------+-------------------------------------+----------
config_file | /data/pgsql/12/data/postgresql.conf | override
data_directory | /data/pgsql/12/data | override
external_pid_file | | default
hba_file | /data/pgsql/12/data/pg_hba.conf | override
ident_file | /data/pgsql/12/data/pg_ident.conf | override
三、数据库相关配置 postgresql.conf
该文件包含内存分配、日志文件未知、监听端口、监听地址、数据库数据目录等一些数据库通用配置
通过pg_setting查看参数的值
select name, context, unit, setting, boot_val, reset_val from pg_settings where name in ('listen_address','max_connetctons','shared_buffers','effective_cache_size','work_mem','maintenance_work_mem') order by context, name;
SQL结果
name | context | unit | setting | boot_val | reset_val
----------------------+------------+------+----------+----------+-----------
shared_buffers | postmaster | 8kB | 12582912 | 1024 | 12582912
effective_cache_size | user | 8kB | 524288 | 524288 | 524288
maintenance_work_mem | user | kB | 33554432 | 65536 | 33554432
work_mem | user | kB | 4096 | 4096 | 4096
● 字段说明:
a. context: 设置为postmaster,更改此形参后需要重启PostgreSQL服务才能生效;设置为user,那么只需要执行一次重新加载即可全局生效。重启数据库服务会终止活动连接,但重新加载不会。
b. unit : 字段表示这些设置的单位;
c. setting:是指当前设置;
d. boot_val:是指默认设置;
e. reset_val:是指重新启动服务器或重新加载设置之后的新设置;
在postgresql.conf中修改了设置后,一定记得查看一下setting和reset_val并确保二者是一致,否则说明设置并未生效,需要重新启动服务器或者重新加载设置
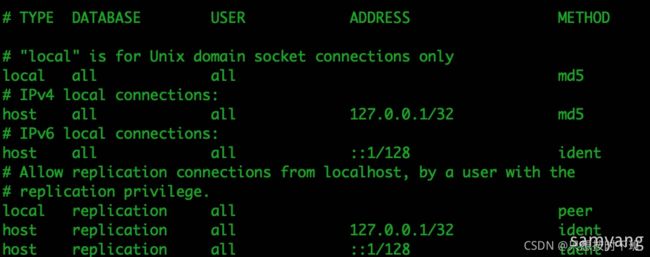
四、客户端认证配置文件 pg_hba.conf
该配置文件有五个参数,分别为:
● TYPE(主机类型)
● DATABASE(数据库名)
● USER(用户名)
● ADDRESS(IP地址和掩码)
● METHOD(加密方法)
local:使用Unix-domainsocket
host:使用TCP/IP连接,可以是SSL的,也可以不是
hostssl:必须是SSL的
hostnossl:必须是非SSL的
DATABASE(数据库名):
数据库名,可以是"all", "sameuser", "samerole", "replication"。all表示所有,但不包括replication。多个数据库用“,”隔开。
USER(用户名):
用户名,可以为"all",表示所有,也可以具体指定一个用户。多个用户用“,”隔开。和DATABASE一样,也可以将配置放到文件中,文件名加上前缀@
ADDRESS(IP地址和掩码):
可以是为一个主机名,或者由IP地址和CIDR掩码组成。掩码可以为0-32(IPv4)或者0-128(IPv6)间的一个整数,32表示子网掩码为255.255.255.255,24表示子网掩码为255.255.255.0。主机名以“.”开头。samehost可以匹配所有主机、samenet可以匹配同一个掩码内的所有主机。
例:192.168.10.122/32表示单一主机,192.168.10.0/24表示192.168.0.1~192.168.0.255网段内所有主机,0.0.0.0/0表示所有主机。
METHOD(加密方法):
密码加密策略,password表示以明文方式发送密码,md5和scram-sha-256会以对应的方式加密再发送密码。
下面试配置文件中自带的说明,很详细:
# PostgreSQL Client Authentication Configuration File
# ===================================================
#
# Refer to the "Client Authentication" section in the PostgreSQL
# documentation for a complete description of this file. A short
# synopsis follows.
#
# This file controls: which hosts are allowed to connect, how clients
# are authenticated, which PostgreSQL user names they can use, which
# databases they can access. Records take one of these forms:
#
# local DATABASE USER METHOD [OPTIONS]
# host DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD [OPTIONS]
# hostssl DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD [OPTIONS]
# hostnossl DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD [OPTIONS]
#
# (The uppercase items must be replaced by actual values.)
#
# The first field is the connection type: "local" is a Unix-domain
# socket, "host" is either a plain or SSL-encrypted TCP/IP socket,
# "hostssl" is an SSL-encrypted TCP/IP socket, and "hostnossl" is a
# plain TCP/IP socket.
#
# DATABASE can be "all", "sameuser", "samerole", "replication", a
# database name, or a comma-separated list thereof. The "all"
# keyword does not match "replication". Access to replication
# must be enabled in a separate record (see example below).
#
# USER can be "all", a user name, a group name prefixed with "+", or a
# comma-separated list thereof. In both the DATABASE and USER fields
# you can also write a file name prefixed with "@" to include names
# from a separate file.
#
# ADDRESS specifies the set of hosts the record matches. It can be a
# host name, or it is made up of an IP address and a CIDR mask that is
# an integer (between 0 and 32 (IPv4) or 128 (IPv6) inclusive) that
# specifies the number of significant bits in the mask. A host name
# that starts with a dot (.) matches a suffix of the actual host name.
# Alternatively, you can write an IP address and netmask in separate
# columns to specify the set of hosts. Instead of a CIDR-address, you
# can write "samehost" to match any of the server's own IP addresses,
# or "samenet" to match any address in any subnet that the server is
# directly connected to.
#
# METHOD can be "trust", "reject", "md5", "password", "scram-sha-256",
# "gss", "sspi", "ident", "peer", "pam", "ldap", "radius" or "cert".
# Note that "password" sends passwords in clear text; "md5" or
# "scram-sha-256" are preferred since they send encrypted passwords.
#
# OPTIONS are a set of options for the authentication in the format
# NAME=VALUE. The available options depend on the different
# authentication methods -- refer to the "Client Authentication"
# section in the documentation for a list of which options are
# available for which authentication methods.
#
# Database and user names containing spaces, commas, quotes and other
# special characters must be quoted. Quoting one of the keywords
# "all", "sameuser", "samerole" or "replication" makes the name lose
# its special character, and just match a database or username with
# that name.
#
# This file is read on server startup and when the server receives a
# SIGHUP signal. If you edit the file on a running system, you have to
# SIGHUP the server for the changes to take effect, run "pg_ctl reload",
# or execute "SELECT pg_reload_conf()".
#
# Put your actual configuration here
# ----------------------------------
#
# If you want to allow non-local connections, you need to add more
# "host" records. In that case you will also need to make PostgreSQL
# listen on a non-local interface via the listen_addresses
# configuration parameter, or via the -i or -h command line switches.
五、ident认证配置文件pg_ident.conf
在pg_hba.conf里面讲到ident认证方式,需要建立映射用户或具备同名用户,就是在pg_ident.conf中配置。
同名用户比较方便,新建一个同名的操作系统用户和数据库用户,两个用户密码不必相同,但名字必须相同。用该用户登录到操作系统或su到该用户后,即可用psql登录。
如果不想新建同名用户,也可以配置pg_ident.conf文件.
pg_ident.conf用来配置哪些操作系统用户可以映射为数据库用户。
pg_ident.conf的格式如下:
MAPNAME SYSTEM-USERNAME PG-USERNAME
usermap username dbuser
usermap为映射名,要在pg_hba.conf中用到,多个映射可以共用同一个映射名,username为操作系统用户名,dbuser为映射到的数据库用户。
比如,服务器上有名为user1的操作系统用户,同时数据库上也有同名的数据库用户,user1登录操作系统后可以直接输入psql,以user1数据库用户身份登录数据库且不需密码。
很多初学者都会遇到psql -U username登录数据库却出现“username ident 认证失败”的错误,明明数据库用户已经createuser。
原因就在于此,使用了ident认证方式,却没有同名的操作系统用户或没有相应的映射用户。
解决方案:
1)、在pg_ident.conf中添加映射用户;
2)、改变认证方式。
CentOS7安装了PostgreSQL12和pgadmin4后,pgadmin4始终登陆数据库提示用户认证失败,
就是因为Linux下PostgreSQL默认的local认证方式是ident,而pg_ident.conf用户映射文件里并没有任何映射用户,所以可以修改认证方式为md5,即可使用密码成功登陆了.
六、详解postgresql.conf
# 此文件由以下几行组成:
#
# name = value
# ("="是可选的.)可以使用空格.注释是在一行的任何地方用"#"开头.参数名和允许值的完整列表可以在PostgreSQL文档中找到.
# 该文件中显示的注释化设置表示默认值.重新注释设置不足以将其还原为默认值;您需要重新加载服务器.
#
# 此文件在服务器启动时以及服务器接收到SIGHUP信号时读取.如果您在一个正在运行的系统上编辑文件,您必须检查服务器以使
# 更改生效,运行"pg_ctl reload",或者执行"SELECT pg_reload_conf()".下面标记的一些参数需要服务器关闭并重新启动才能
# 生效.
#
# 任何参数也可以作为服务器的命令行选项,例如,"postgres -c log_connections=on".有些参数可以在运行时使用"SET"SQL命令
# 进行更改.
#
# Memory units(内存单元): kB = kilobytes Time units(时间单元): ms = milliseconds
# MB = megabytes(兆字节) s = seconds(秒)
# GB = gigabytes(千兆字节) min = minutes(分钟)
# TB = terabytes(兆兆字节) h = hours{时}
# d = days(天)
备注:
· 配置文件中注释使用"#".
· 配置项参数名大小写不敏感.
· 参数值有5中类型:
(1)布尔值:布尔值大小写无关. 可以是true、false、1、0
(2)整数值:整数值可以指定单位,如1h,1GB
(3)浮点数
(4)字符串
(5)枚举
6.1 文件位置(FILE LOCATION)
# 这些变量的默认值由-D命令行选项或PGDATA环境变量驱动,这里表示为ConfigDir.
#data_directory = 'ConfigDir' # 使用其他目录中的数据(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
#hba_file = 'ConfigDir/pg_hba.conf' # 基于主机的认证文件(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
#ident_file = 'ConfigDir/pg_ident.conf' # 标识配置文件(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
# 如果未显式设置外部PID文件,则不会写入额外的PID文件.
#external_pid_file = '' # 写一个额外的PID文件(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
查看参数配置
show data_directory
select name,setting from pg_setting where name='data_directory'
6.2 连接和验证(CONNECTIONS AND AUTHENTICATION)
6.2.1 连接设置(Connection Settings)
#默认情况下,只允许登录了数据库的用户执行本地连接. 若想要任何远程的安装程序进行连接.则需要修改listen_addresses配置参数. 修改为='*',表示允许并接受任何地方传入的连接请求.
listen_addresses = '*' # 监听哪个IP地址;以逗号分隔的地址列表.默认监听"localhost",(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
port = 5678 # PG服务监听端口号-默认端口5432.(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
#每个客户端连接都会占用很小一部分的"共享内存",系统有限的共享内存默认是不允许过多的连接的. 该参数不能设置得过大,会浪费"共享内存".
max_connections = 100 # 最大连接数(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
#superuser_reserved_connections = 3 #(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
#unix_socket_directories = '/tmp' #逗号分隔的目录列表(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
#unix_socket_group = '' # (更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
#unix_socket_permissions = 0777 # 从0开始使用八进制记数法(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
#bonjour = off # 通过Bonjour发布服务器(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
#bonjour_name = '' # 默认为计算机名(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
# - TCP Keepalives -
# see "man 7 tcp" for details
#tcp_keepalives_idle = 0 # TCP_KEEPIDLE, in seconds(秒); 0-选择系统默认值
#tcp_keepalives_interval= 0 # TCP_KEEPINTVL, in seconds(秒);0-选择系统默认值
#tcp_keepalives_count = 0 # TCP_KEEPCNT;0-选择系统默认值
6.2.2 认证(Authentication)
#authentication_timeout = 1min # 1s-600s
#password_encryption = md5 # md5 or scram-sha-256
#db_user_namespace = off
# GSSAPI using Kerberos(使用kerberos的gssapi)
#krb_server_keyfile = ''
#krb_caseins_users = off
6.2.3 SSL
#ssl = off
#ssl_ca_file = ''
#ssl_cert_file = 'server.crt'
#ssl_crl_file = ''
#ssl_key_file = 'server.key'
#ssl_ciphers = 'HIGH:MEDIUM:+3DES:!aNULL' # allowed SSL ciphers
#ssl_prefer_server_ciphers = on
#ssl_ecdh_curve = 'prime256v1'
#ssl_dh_params_file = ''
#ssl_passphrase_command = ''
#ssl_passphrase_command_supports_reload = off
6.3 资源使用(RESOURCE USAGE (except WAL))
6.3.1 内存(Memory)
# 共享内存,服务器使用共享内存的主要部分是分配给缓存块的大型块.用于读取或是写入数据库.
# 预估共享内存大小请参考:https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/kernel-resources.html
shared_buffers = 128MB # 最小128kB(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
#huge_pages = try # on, off, or try(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
#temp_buffers = 8MB # 最小800kB
#max_prepared_transactions= 0 # 0-表示禁用该功能(更改需要重新启动PG数据库);注意:不建议将max_prepared_transactions设置为非零, 除非你打算用已经准备好的事务
#work_mem = 4MB # 最小64kB.可以限制用于排序内存的大小,该值在客户端连接之后可以增加,该类型分配使用的是"非共享内存"
#maintenance_work_mem = 64MB # 最小1MB
#autovacuum_work_mem = -1 # 最小1MB, or -1 to use maintenance_work_mem
#max_stack_depth = 2MB # 最小100kB
dynamic_shared_memory_type = posix #默认值是操作系统支持的第一个选项:posix,sysv,windows,mmap;使用none禁用动态共享内存
6.3.2 磁盘(Disk)
#temp_file_limit = -1 # 每个进程的临时文件空间限制(以KB为单位).如果没有限制,则为-1
6.3.3 内核资源(Kernel Resources)
#max_files_per_process = 1000 # 最小25(更改需要重新启动PG数据库)
6.3.4 基于成本的真空延迟( Cost-Based Vacuum Delay)
#vacuum_cost_delay = 0 # 0-100 milliseconds
#vacuum_cost_page_hit = 1 # 0-10000 credits
#vacuum_cost_page_miss = 10 # 0-10000 credits
#vacuum_cost_page_dirty = 20 # 0-10000 credits
#vacuum_cost_limit = 200 # 1-10000 credits
6.3.5 后台写入(Background Writer)
#bgwriter_delay = 200ms # 10-10000ms between rounds
#bgwriter_lru_maxpages = 100 # max buffers written/round, 0 disables
#bgwriter_lru_multiplier = 2.0 # 0-10.0 multiplier on buffers scanned/round
#bgwriter_flush_after = 512kB # 以页计算,0-禁用
6.3.6 异步行为(Asynchronous Behavior)
#effective_io_concurrency = 1 # 1-1000; 0-禁用预取
#max_worker_processes = 8 # (更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#max_parallel_maintenance_workers = 2 # 取自max_parallel_workers
#max_parallel_workers_per_gather = 2 # 取自max_parallel_workers
#parallel_leader_participation = on
#max_parallel_workers = 8 # 可以在并行操作中使用的max_worker_processes的最大数量
#old_snapshot_threshold = -1 # 1min-60d; -1:禁用 0:立刻(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#backend_flush_after = 0 # 以页为单位测量,0-禁用
6.4 预写日志(WRITE-AHEAD LOG)
6.4.1 设置(Settings)
#wal_level = replica # 最小、副本或逻辑(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#fsync = on # 将数据刷新到磁盘以确保崩溃安全(关闭此功能可能导致不可恢复的数据损坏)
#synchronous_commit = on # 同步等级: off, local, remote_write, remote_apply, or on
#wal_sync_method = fsync # 默认是操作系统支持的第一个选项:open_datasync, fdatasync (Linux默认),fsync,fsync_writethrough,
open_sync
#full_page_writes = on # 从部分页面写恢复
#wal_compression = off # 启用整页写的压缩
#wal_log_hints = off # 也做整个页写的非关键的更新(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#用于控制缓存预写式日志数据的内存大小
#wal_buffers = -1 # 最小32kB, -1:基于shared_buffers的设置(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#wal_writer_delay = 200ms # 1-10000 milliseconds
#wal_writer_flush_after = 1MB # 以页计算, 0-禁用
#commit_delay = 0 # range 0-100000, 以微妙为单位
#commit_siblings = 5 # range 1-1000
6.4.2 检查点(Checkpoints)
/*
*若用户的系统速度赶不上写数据的速度,则可以适当提高该值.默认为5分钟。
*/
#checkpoint_timeout = 5min # range 30s-1d
max_wal_size = 1GB
min_wal_size = 80MB
#checkpoint_completion_target = 0.5 # 检查点目标持续时间, 0.0 - 1.0
#checkpoint_flush_after = 256kB # 以页计算, 0-禁用
#checkpoint_warning = 30s # 0-禁用
6.4.3 存档(Archiving)
#archive_mode = off # 启用存档-enables;关闭-off,打开-on 或始终-always (更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#archive_command = '' # 用于存档日志文件段占位符的命令:%p =文件路径到存档;%f =文件名.e.g. 'test ! -f /mnt/server/archivedir/%f && cp %p /mnt/server/archivedir/%f'
#archive_timeout = 0 # 在此秒数后强制执行日志文件段切换;0-禁用
6.5 复制(REPLICATION)
6.5.1 发送服务器(Sending Servers)
# 将它们设置在主服务器和任何将发送复制数据的备用服务器上.
#max_wal_senders = 10 # 最大walsender进程数.(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#wal_keep_segments = 0 # 在日志文件段中;0-禁用
#wal_sender_timeout = 60s # 以毫秒为单位;0-禁用
#max_replication_slots = 10 # 复制槽的最大数目(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#track_commit_timestamp = off # 收集事务提交的时间戳(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
6.5.2 主服务器(Master Server)
# 这些设置在备用服务器上被忽略.
#synchronous_standby_names = '' # 提供sync rep方法的备用服务器,用于选择同步备用服务器,
#同步备用服务器的数量和备用服务器中的application_name的逗号分隔列表;‘*’=all
#vacuum_defer_cleanup_age = 0 # 延迟清理的xact数
6.5.3 备用服务器(Standby Servers)
# 在主服务器上忽略这些设置.
#hot_standby = on # "off"不允许在恢复期间进行查询(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#max_standby_archive_delay = 30s # 从存档读取wal时取消查询之前的最大延迟;-1允许无限延迟
#max_standby_streaming_delay = 30s # 读取流wal时取消查询之前的最大延迟;-1允许无限延迟
#wal_receiver_status_interval = 10s # 至少要经常回复 0-禁用
#hot_standby_feedback = off # 从备用服务器发送信息以防止查询冲突
#wal_receiver_timeout = 60s # 接收方等待主方通信的时间(毫秒);0-禁用
#wal_retrieve_retry_interval = 5s # 在尝试失败后重新尝试检索WAL之前,需要等待的时间
6.5.4 订阅者(Subscribers)
# 在发布服务器上这些设置将被忽略
#max_logical_replication_workers = 4 # 取自max_worker_processes(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#max_sync_workers_per_subscription = 2 # 取自max_logical_replication_workers
6.6 查询调优(QUERY TUNING)
6.6.1 计划方法配置(Planner Method Configuration)
#enable_bitmapscan = on
#enable_hashagg = on
#enable_hashjoin = on
#enable_indexscan = on
#enable_indexonlyscan = on
#enable_material = on
#enable_mergejoin = on
#enable_nestloop = on
#enable_parallel_append = on
#enable_seqscan = on
#enable_sort = on
#enable_tidscan = on
#enable_partitionwise_join = off
#enable_partitionwise_aggregate = off
#enable_parallel_hash = on
#enable_partition_pruning = on
6.6.2 计划成本常量(Planner Cost Constants)
#seq_page_cost = 1.0 # 在任意比例上测量
#random_page_cost = 4.0 # 同上量表
#cpu_tuple_cost = 0.01 # 同上量表
#cpu_index_tuple_cost = 0.005 # 同上量表
#cpu_operator_cost = 0.0025 # 同上量表
#parallel_tuple_cost = 0.1 # 同上量表
#parallel_setup_cost = 1000.0 # 同上量表
#jit_above_cost = 100000 #如果可用,执行JIT编译并查询比这更昂贵的开销.-1:禁用
#jit_inline_above_cost = 500000 # 如果查询的开销大于此值,则内联小函数.-1:将禁用
#jit_optimize_above_cost = 500000 # 如果查询的开销大于此值,则使用昂贵的JIT优化;-1将禁用
#min_parallel_table_scan_size = 8MB
#min_parallel_index_scan_size = 512kB
#effective_cache_size = 4GB
6.6.3 查询优化器(Genetic Query Optimizer)
#geqo = on
#geqo_threshold = 12
#geqo_effort = 5 # range 1-10
#geqo_pool_size = 0 # selects default based on effort
#geqo_generations = 0 # selects default based on effort
#geqo_selection_bias = 2.0 # range 1.5-2.0
#geqo_seed = 0.0 # range 0.0-1.0
6.6.4 其他计划选项(Other Planner Options)
/* 备注:为了注释的属性简洁,这里的注释用了C/C++中的注释语法,若是postgresql.conf文件中,则应该用"#"号
* PostgreSQL根据数据库中每个表的统计情况来决定如何执行查询.这些信息通过“ANALYZE”或是“autovacuum”等
* 步骤来获得,任一情况下,在分析任务期间所获得的信息量由default_statistics_target设置. 加大该值会延长
* 分析时间.
*/
#default_statistics_target = 100 # range 1-10000
#constraint_exclusion = partition # on, off, or partition
#cursor_tuple_fraction = 0.1 # range 0.0-1.0
#from_collapse_limit = 8
#join_collapse_limit = 8 # 1:禁用显式联接子句的折叠
#force_parallel_mode = off
#jit = off
6.7 报告和记录(REPORTING AND LOGGING)
6.7.1 记录位置(Where to Log)
#log_destination = 'stderr' # 1有效值是stderr、csvlog、syslog和eventlog的组合,具体取决于平台.
#csvlog要求日志采集器处于打开状态.
# 这在登录到stderr时使用
#logging_collector = off # 启用将stderr和csvlog捕获到日志文件中.CSVLogs需要打开(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
# 这些仅在logging_collector为on状态时候使用.
#log_directory = 'log' # 写入日志文件的目录,可以是绝对的,也可以是相对于PGDATA的
#log_filename = 'postgresql-%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S.log' # 日志文件名模式,可以包含strftime()转义
#log_file_mode = 0600 # 日志文件的创建模式,从0开始使用八进制表示法
#log_truncate_on_rotation = off # 如果ON,与新日志文件具有相同名称的现有日志文件将被截断而不是附加到.但这种截断只发生在时间驱动的旋转上,
#而不是在重新启动或大小驱动的旋转上.默认为"关闭",意味着在所有情况下都追加到现有文件.
#log_rotation_age = 1d # 日志文件的自动循环将在该时间之后发生.0-禁用.
#log_rotation_size = 10MB # 日志文件的自动循环将在日志输出这么多之后发生.0-禁用
# These are relevant when logging to syslog:(登录到syslog时,这些都是相关的)
#syslog_facility = 'LOCAL0'
#syslog_ident = 'postgres'
#syslog_sequence_numbers = on
#syslog_split_messages = on
#:这仅在登录到eventlog(win32)时才相关(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#event_source = 'PostgreSQL'
6.7.2 何时记录(When to Log)
#log_min_messages = warning # 按细节降序排列的值:
# debug5
# debug4
# debug3
# debug2
# debug1
# info
# notice
# warning
# error
# log
# fatal
# panic
#log_min_error_statement = error # 按细节降序排列的值:
# debug5
# debug4
# debug3
# debug2
# debug1
# info
# notice
# warning
# error
# log
# fatal
# panic (effectively off)
#log_min_duration_statement = -1 # -1被禁用,0记录所有语句及其持续时间,>0只记录至少运行此毫秒数的语句
6.7.3 记录什么(What to Log)
#debug_print_parse = off
#debug_print_rewritten = off
#debug_print_plan = off
#debug_pretty_print = on
#log_checkpoints = off
#log_connections = off
#log_disconnections = off
#log_duration = off
#log_error_verbosity = default # terse, default, or verbose messages(简洁、默认或详细的消息)
#log_hostname = off
#log_line_prefix = '%m [%p] ' # 特素值:
# %a = application name-应用程序名称
# %u = user name-用户名
# %d = database name-数据库名称
# %r = remote host and port-远程主机和端口
# %h = remote host-远程主机
# %p = process ID-进程ID
# %t = timestamp without milliseconds-不带毫秒的时间戳
# %m = timestamp with milliseconds-毫秒时间戳
# %n = timestamp with milliseconds (as a Unix epoch)-时间戳(以毫秒计)(作为Unix纪元)
# %i = command tag-命令标记
# %e = SQL state-SQL状态
# %c = session ID-会话ID
# %l = session line number-会话行号
# %s = session start timestamp-会话开始时间戳
# %v = virtual transaction ID-虚拟事务ID
# %x = transaction ID (0 if none)-事务ID(如果没有,则为0)
# %q = stop here in non-session-processes -在非会话进程中此处停止
# %% = '%'
# e.g. '<%u%%%d> '
#log_lock_waits = off # 日志锁等待 >= deadlock_timeout
# log_statement可选值范围:none(不记录任何语句级的日志信息), ddl(只记录数据定义语言语句,如:CREATE,DROP),
# mod(记录修改了值的语句), all(记录每一条语句,不要轻易使用该选项,日志的写操作会对系统带来巨大的开销)
#log_statement = 'none' # none, ddl, mod, all
#log_replication_commands = off
#log_temp_files = -1 # 日志临时文件等于或大于指定的大小(以千字节为单位);-1禁用,0记录所有临时文件
log_timezone = 'PRC'
6.8 流程标题(PROCESS TITLE)
#cluster_name = '' # 如果非空,则添加到进程标题(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#update_process_title = on
6.9 统计数据(STATISTICS)
6.9.1 查询和索引统计信息收集器(Query and Index Statistics Collector)
#track_activities = on
#track_counts = on
#track_io_timing = off
#track_functions = none # none, pl, all
#track_activity_query_size = 1024 # (change requires restart)
#stats_temp_directory = 'pg_stat_tmp'
6.9.2 监控(Monitoring)
#log_parser_stats = off
#log_planner_stats = off
#log_executor_stats = off
#log_statement_stats = off
6.10 自动清理(AUTOVACUUM)
//从PostgreSQL 8.1开始,便提供了autovacuum守护进程,在后台执行日志的自动清理功能.
#autovacuum = on #
#log_autovacuum_min_duration = -1 # -1 disables, 0 logs all actions and
# their durations, > 0 logs only
# actions running at least this number
# of milliseconds.
#autovacuum_max_workers = 3 # 自动清理的最大子进程数量(更改需重启PG数据库生效)
#autovacuum_naptime = 1min # time between autovacuum runs
#autovacuum_vacuum_threshold = 50 # 清理前的最小行更新数量
#autovacuum_analyze_threshold = 50 # 分析前的最小行更新数
#autovacuum_vacuum_scale_factor = 0.2 # fraction of table size before vacuum
#autovacuum_analyze_scale_factor = 0.1 # fraction of table size before analyze
#autovacuum_freeze_max_age = 200000000 # maximum XID age before forced vacuum
# (change requires restart)
#autovacuum_multixact_freeze_max_age = 400000000 # maximum multixact age
# before forced vacuum
# (change requires restart)
#autovacuum_vacuum_cost_delay = 20ms # default vacuum cost delay for
# autovacuum, in milliseconds;
# -1 means use vacuum_cost_delay
#autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit = -1 # default vacuum cost limit for
# autovacuum, -1 means use
# vacuum_cost_limit
6.11 客户端连接默认值(CLIENT CONNECTION DEFAULTS)
6.11.1 声明行为(Statement Behavior)
#client_min_messages = notice # 按细节降序排列的值:
# debug5
# debug4
# debug3
# debug2
# debug1
# log
# notice
# warning
# error
#search_path = '"$user", public' # schema names
#row_security = on
#default_tablespace = '' # a tablespace name, '' uses the default
#temp_tablespaces = '' # a list of tablespace names, '' uses
# only default tablespace
#check_function_bodies = on
#default_transaction_isolation = 'read committed'
#default_transaction_read_only = off
#default_transaction_deferrable = off
#session_replication_role = 'origin'
#statement_timeout = 0 # in milliseconds, 0 is disabled
#lock_timeout = 0 # in milliseconds, 0 is disabled
#idle_in_transaction_session_timeout = 0 # in milliseconds, 0 is disabled
#vacuum_freeze_min_age = 50000000
#vacuum_freeze_table_age = 150000000
#vacuum_multixact_freeze_min_age = 5000000
#vacuum_multixact_freeze_table_age = 150000000
#vacuum_cleanup_index_scale_factor = 0.1 # fraction of total number of tuples
# before index cleanup, 0 always performs
# index cleanup
#bytea_output = 'hex' # hex, escape
#xmlbinary = 'base64'
#xmloption = 'content'
#gin_fuzzy_search_limit = 0
#gin_pending_list_limit = 4MB
6.11.2 语言环境和格式(Locale and Formatting)
datestyle = 'iso, ymd'
#intervalstyle = 'postgres'
timezone = 'PRC'
#timezone_abbreviations = 'Default' # Select the set of available time zone
# abbreviations. Currently, there are
# Default
# Australia (historical usage)
# India
# You can create your own file in
# share/timezonesets/.
#extra_float_digits = 0 # min -15, max 3
#client_encoding = sql_ascii # actually, defaults to database
# encoding
# These settings are initialized by initdb, but they can be changed.
lc_messages = 'zh_CN.UTF-8' # locale for system error message
# strings
lc_monetary = 'zh_CN.UTF-8' # locale for monetary formatting
lc_numeric = 'zh_CN.UTF-8' # locale for number formatting
lc_time = 'zh_CN.UTF-8' # locale for time formatting
# default configuration for text search
default_text_search_config = 'pg_catalog.simple'
6.11.3 共享库预加载(Shared Library Preloading)
#shared_preload_libraries = '' # (change requires restart)
#local_preload_libraries = ''
#session_preload_libraries = ''
#jit_provider = 'llvmjit' # JIT library to use
6.12 其他默认值(Other Defaults )
#dynamic_library_path = '$libdir'
6.13 锁管理(LOCK MANAGEMENT)
#deadlock_timeout = 1s
#max_locks_per_transaction = 64 # min 10(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#max_pred_locks_per_transaction = 64 # min 10(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
#max_pred_locks_per_relation = -2 # 负值平均值(max_pred_locks_per_transaction / -max_pred_locks_per_relation) - 1
#max_pred_locks_per_page = 2 # min 0
6.14 版本和平台兼容性(VERSION AND PLATFORM COMPATIBILITY)
6.14.1 以前的PostgreSQL版本(Previous PostgreSQL Versions)
#array_nulls = on
#backslash_quote = safe_encoding # on, off, or safe_encoding
#default_with_oids = off
#escape_string_warning = on
#lo_compat_privileges = off
#operator_precedence_warning = off
#quote_all_identifiers = off
#standard_conforming_strings = on
#synchronize_seqscans = on
6.14.2 其他平台和客户(Other Platforms and Client)
#transform_null_equals = off
6.15 错误处理(ERROR HANDLING)
#exit_on_error = off # 出现任何错误时终止会话?
#restart_after_crash = on # 后端崩溃后重新初始化?
#data_sync_retry = off # fsync数据失败时重试或死机?(更改需要重新启动PG数据库生效)
6.16 配置文件包括(CONFIG FILE INCLUDES)
# 这些选项允许从默认postgresql.conf以外的文件加载设置.
#include_dir = '' # 包括目录中以".conf"结尾的文件,例如"conf.d"
#include_if_exists = '' # 仅在存在时才包含文件
#include = '' # 包含文件
6.17 自定义选项
# Add settings for extensions here(在此处添加扩展设置)