Socket网络编程--简单Web服务器(1)
这一次的Socket系列准备讲Web服务器。就是编写一个简单的Web服务器,具体怎么做呢?我也不是很清楚流程,所以我找来了一个开源的小的Web服务器--tinyhttpd。这个服务器才500多行的代码,使用C语言。这一小节就不讲别的内容了。就对这个程序进行一些注释和讲解了。
主函数:
1 int main(void) 2 { 3 int server_sock = -1; 4 u_short port = 0; 5 int client_sock = -1; 6 struct sockaddr_in client_name; 7 int client_name_len = sizeof(client_name); 8 pthread_t newthread; 9 10 server_sock = startup(&port);//Web服务器打开指定端口 11 printf("httpd running on port %d\n", port); 12 13 while (1) 14 { 15 client_sock = accept(server_sock,(struct sockaddr *)&client_name,&client_name_len); 16 if (client_sock == -1) 17 error_die("accept"); 18 if (pthread_create(&newthread , NULL, accept_request, client_sock) != 0) 19 perror("pthread_create"); 20 } 21 close(server_sock); 22 return(0); 23 }
从主函数我们可以知道,这个服务器是对于每一个客户端的连接都采用一个线程对其处理。上面对应的startup函数是对指定的端口进行socket的创建,绑定,监听。
startup函数:
1 int startup(u_short *port) 2 { 3 int httpd = 0; 4 struct sockaddr_in name; 5 6 httpd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); 7 if (httpd == -1) 8 error_die("socket"); 9 memset(&name, 0, sizeof(name)); 10 name.sin_family = AF_INET; 11 name.sin_port = htons(*port); 12 name.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); 13 if (bind(httpd, (struct sockaddr *)&name, sizeof(name)) < 0) 14 error_die("bind"); 15 if (*port == 0) /* if dynamically allocating a port */ 16 { 17 int namelen = sizeof(name); 18 if (getsockname(httpd, (struct sockaddr *)&name, &namelen) == -1) 19 error_die("getsockname"); 20 *port = ntohs(name.sin_port); 21 } 22 if (listen(httpd, 5) < 0) 23 error_die("listen"); 24 return(httpd); 25 }
对于上面的getsockname函数是,如果传进来的port为0,那么就前面的bind就会失败,所以要使用getsockname函数来获取一个当前可用的可连接的Socket套接字的名字。此时返回的端口就是随机的。
接下来就是一个对每个客户端连接的处理函数
accept_request函数
1 void accept_request(int client) 2 { 3 char buf[1024]; 4 int numchars; 5 char method[255]; 6 char url[255]; 7 char path[512]; 8 size_t i, j; 9 struct stat st; 10 int cgi = 0; /* becomes true if server decides this is a CGI 11 * program */ 12 char *query_string = NULL; 13 14 numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));//获取第一行客户端的请求 GET / HTTP/1.1 类似这样的 15 i = 0; j = 0; 16 while (!ISspace(buf[j]) && (i < sizeof(method) - 1))//获取第一个单词,一般为GET或POST 两种请求方法 17 { 18 method[i] = buf[j]; 19 i++; j++; 20 } 21 method[i] = '\0'; 22 23 if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") && strcasecmp(method, "POST"))//如果不是GET或POST方法的,那么就回复一个不支持的请求方法页面。话说如果自己写服务器可以加自己的请求方法。不过有个问题就是浏览器是没有的?怎么办,看来还要自己弄个小的浏览器 24 { 25 unimplemented(client); 26 return; 27 } 28 29 if (strcasecmp(method, "POST") == 0)//如果是使用POST方法,那么就一定是cgi程序 30 cgi = 1; 31 32 i = 0; 33 while (ISspace(buf[j]) && (j < sizeof(buf)))//取出空格 34 j++; 35 // GET / HTTP/1.1 接下来是取第二个字符串,第二个串是此次请求的页面地址 36 while (!ISspace(buf[j]) && (i < sizeof(url) - 1) && (j < sizeof(buf))) 37 { 38 url[i] = buf[j]; 39 i++; j++; 40 } 41 url[i] = '\0'; 42 43 if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") == 0)//如果是GET方法,GET方法和POST方法是有点区别的,GET方法是通过URL请求来传递用户的数据,将表单等各个字段名称与内容,以成对的字符串进行连接来传递参数的。 44 //例如 http://www.baidu.com/s?wd=cnblogs 这个URL就是使用百度搜索cnblogs的URL地址,baidu搜索怎么知道我在输入框中输入的是什么数据?就是通过这样的一个参数来告诉它的。一般参数都是在?(问号)后面的。 45 { 46 query_string = url; 47 while ((*query_string != '?') && (*query_string != '\0'))//一直读,直到遇到问号 48 query_string++; 49 if (*query_string == '?')//如果有问号,就表示可能要调用cgi程序了,不是简单的静态HTML页面的。 50 { 51 cgi = 1; 52 *query_string = '\0'; 53 query_string++; 54 } 55 } 56 57 sprintf(path, "htdocs%s", url);//这个是web服务器的主目录 58 if (path[strlen(path) - 1] == '/') 59 strcat(path, "index.html");//如果输入的网址没有指定网页,那么默认使用index.html这个页面 60 if (stat(path, &st) == -1) {//根据文件名,获取该文件的文件信息,如果为-1,表示获取该文件的文件信息失败,可能的问题是没有该文件,或是权限什么的问题,具体失败的原因可以查看errno 61 while ((numchars > 0) && strcmp("\n", buf)) /* read & discard headers */ 62 numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf)); 63 not_found(client);//返回一个not found 404的页面了 64 } 65 else 66 { 67 if ((st.st_mode & S_IFMT) == S_IFDIR)//如果该文件名对应的是一个目录,那么就访问该目录下的默认主页index.html,这里如果是jsp,就是index.jsp什么的。 68 strcat(path, "/index.html"); 69 if ((st.st_mode & S_IXUSR) || (st.st_mode & S_IXGRP) || (st.st_mode & S_IXOTH))//判断该文件的执行权限问题 70 cgi = 1; 71 if (!cgi)//如果不是cgi程序,而是一个简单的静态页面 72 serve_file(client, path); 73 else//一个cgi程序 74 execute_cgi(client, path, method, query_string); 75 } 76 77 close(client); 78 }
关于GET和POST的区别,可以参考别的博客,这里就不详解了。指说一个我们处理是要注意的问题,那就是GET方法的参数是在URL地址中。而Post 方法通过 HTTP post 机制,将表单内各字段名称与其内容放置在 HTML 表头(header)内一起传送给服务器端交由 action 属性能所指的程序处理,该程序会通过标准输入(stdin)方式,将表单的数据读出并加以处理。说的有点抽象,还是上几张图片比较容易看吧。
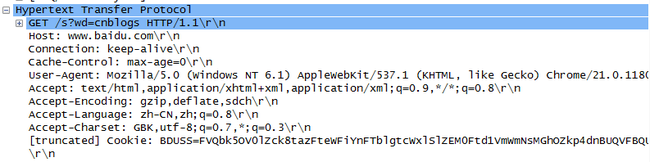
这一张是get方法的(使用百度搜索功能,搜索的关键字是使用get方法提交)
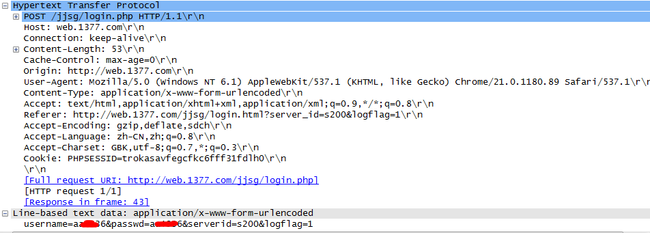
这一张是post方法的(使用一个游戏的登录界面,该登录界面的帐号和密码的提交方式是使用POST方式)
可以看到,在Hypertext Transfer Protocol后面有个Line-based text data。可以看到有个这样的字符串,username=...&passwd=...&serverid=...居然明文传输,这个游戏太不厚道了,伐开心了,我一直不知道。我们可以看到上面的Content-Length:53 就表示在\r\n\r\n后面会有接着的53个字符要接收。这个看起来是不是跟应答信息很像啊。
提示:通过get方法提交数据,可能会带来安全性的问题。比如一个登陆页面。当通过get方法提交数据时,用户名和密码将出现在URL上。
1.登陆页面可以被浏览器缓存;
2.其他人可以访问客户的这台机器。
那么,别人即可以从浏览器的历史记录中,读取到此客户的账号和密码。所以,在某些情况下,get方法会带来严重的安全性问题。所以建议在Form中,建议使用post方法。
好,我们继续讲解其他的函数了。
serve_file函数,就是对一个简单的HTML静态页面进行返回
1 void serve_file(int client, const char *filename) 2 { 3 FILE *resource = NULL; 4 int numchars = 1; 5 char buf[1024]; 6 7 buf[0] = 'A'; buf[1] = '\0'; 8 while ((numchars > 0) && strcmp("\n", buf)) /* read & discard headers */ 9 numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));//从上面的图我们可以看到还有一些请求信息如Connection,Cache-Control,User-Agent,Accept等等的信息,这些在这个简单Web服务器中就忽略了。如果要增加功能,就可以使用这些信息。如最简单的判断使用的浏览器类型,操作系统等。 10 11 resource = fopen(filename, "r");//根据GET 后面的文件名,将文件打开。 12 if (resource == NULL) 13 not_found(client); 14 else 15 { 16 headers(client, filename);//发送一个应答头信息 17 cat(client, resource);//逐字符发送 18 } 19 fclose(resource); 20 }
cat函数,这个就不用讲了。就是一个发送send
1 void cat(int client, FILE *resource) 2 { 3 char buf[1024]; 4 5 fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), resource); 6 while (!feof(resource)) 7 { 8 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 9 fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), resource); 10 } 11 }
还有一个关键的函数,execute_cgi这个函数,用来执行cgi程序的。
1 void execute_cgi(int client, const char *path, const char *method, const char *query_string) 2 { 3 char buf[1024]; 4 int cgi_output[2]; 5 int cgi_input[2]; 6 pid_t pid; 7 int status; 8 int i; 9 char c; 10 int numchars = 1; 11 int content_length = -1; 12 13 buf[0] = 'A'; buf[1] = '\0'; 14 if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") == 0)//同什么的serve_file函数,对那些请求头进行忽略 15 { 16 while ((numchars > 0) && strcmp("\n", buf)) /* read & discard headers */ 17 numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf)); 18 } 19 else /* POST方法 */ 20 { 21 numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf)); 22 while ((numchars > 0) && strcmp("\n", buf))//这里同样是忽略请求头 23 { 24 buf[15] = '\0'; 25 if (strcasecmp(buf, "Content-Length:") == 0)//但是考虑到在请求头后面还有信息要读,而信息的大小就在这里。这个Content-Length后面,也就是上面截图是所说的。看了这个代码是不是对刚才说的有了更深的理解了 26 content_length = atoi(&(buf[16]));//获取后面字符的个数 27 numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf)); 28 } 29 //注意到了这里后Post请求头后面的附带信息还没有读出来,要在下面才读取。 30 if (content_length == -1) { 31 bad_request(client); 32 return; 33 } 34 } 35 36 sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n"); 37 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 38 39 if (pipe(cgi_output) < 0) {//创建管道,方便程序或进程之间的数据通信 40 cannot_execute(client); 41 return; 42 } 43 if (pipe(cgi_input) < 0) { 44 cannot_execute(client); 45 return; 46 } 47 //子进程中,用刚才初始化的管道替换掉标准输入标准输出,将请求参数加到环境变量中,调用execl执行cgi程序获得输出。 48 if ( (pid = fork()) < 0 ) { 49 cannot_execute(client); 50 return; 51 } 52 if (pid == 0) /* child: CGI script */ 53 { 54 char meth_env[255]; 55 char query_env[255]; 56 char length_env[255]; 57 58 dup2(cgi_output[1], 1);//将文件描述符为1(stdout)的句柄复制到output中 59 dup2(cgi_input[0], 0);//将文件描述符为0(stdin)的句柄复制到input中 60 close(cgi_output[0]);//关闭output的读端 61 close(cgi_input[1]);//关闭input的写端 62 sprintf(meth_env, "REQUEST_METHOD=%s", method); 63 putenv(meth_env);//putenv保存到环境变量中 64 if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") == 0) { 65 sprintf(query_env, "QUERY_STRING=%s", query_string); 66 putenv(query_env); 67 } 68 else { /* POST */ 69 sprintf(length_env, "CONTENT_LENGTH=%d", content_length); 70 putenv(length_env); 71 } 72 execl(path, path, NULL);//保存在环境变量中的数据,还有parent进行的write到cgi_input[1]中的数据,都是存在的,可以在cgi程序本身中进行判断。看起来有点复杂,我到时候实现就实现个简单的吧。 73 exit(0); 74 } else { /* parent */ 75 close(cgi_output[1]);//关闭output的写端 76 close(cgi_input[0]);//关闭input的读端 77 if (strcasecmp(method, "POST") == 0)//Post方式,读取后面还没有读的附带信息 78 for (i = 0; i < content_length; i++) { 79 recv(client, &c, 1, 0); 80 write(cgi_input[1], &c, 1);//读取到的信息一个一个字符写到input的写端 81 } 82 while (read(cgi_output[0], &c, 1) > 0)//循环读取output的读端,然后发送个客户端,注意这里接收的是cgi程序的输出(也就是打印在stdin上的数据) 83 send(client, &c, 1, 0); 84 85 close(cgi_output[0]); 86 close(cgi_input[1]); 87 waitpid(pid, &status, 0);//等待子进程结束 88 } 89 }
上面第72行处,原来的代码就是那样,但据说好像是错的。应该是:execl(path,参数列表,NULL);而参数列表对于get方法就是query_string,而对于post方法就没有参数,它的参数是在父进程中第80行处通过stdin进行输入,所以cgi程序要手动从控制台stdin读取数据。现在重要的函数都基本完了,接下来就是几个应答信息头。
400 Bad Request
1 void bad_request(int client) 2 { 3 char buf[1024]; 4 5 sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 400 BAD REQUEST\r\n"); 6 send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0); 7 sprintf(buf, "Content-type: text/html\r\n"); 8 send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0); 9 sprintf(buf, "\r\n"); 10 send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0); 11 sprintf(buf, "<P>Your browser sent a bad request, "); 12 send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0); 13 sprintf(buf, "such as a POST without a Content-Length.\r\n"); 14 send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0); 15 }
500 Internal Server Error
1 void cannot_execute(int client) 2 { 3 char buf[1024]; 4 5 sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 500 Internal Server Error\r\n"); 6 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 7 sprintf(buf, "Content-type: text/html\r\n"); 8 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 9 sprintf(buf, "\r\n"); 10 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 11 sprintf(buf, "<P>Error prohibited CGI execution.\r\n"); 12 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 13 }
200 OK
1 void headers(int client, const char *filename) 2 { 3 char buf[1024]; 4 (void)filename; /* could use filename to determine file type */ 5 6 strcpy(buf, "HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n"); 7 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 8 strcpy(buf, SERVER_STRING); 9 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 10 sprintf(buf, "Content-Type: text/html\r\n"); 11 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 12 strcpy(buf, "\r\n"); 13 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 14 }
404 Not Found
1 void not_found(int client) 2 { 3 char buf[1024]; 4 5 sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 404 NOT FOUND\r\n"); 6 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 7 sprintf(buf, SERVER_STRING); 8 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 9 sprintf(buf, "Content-Type: text/html\r\n"); 10 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 11 sprintf(buf, "\r\n"); 12 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 13 sprintf(buf, "<HTML><TITLE>Not Found</TITLE>\r\n"); 14 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 15 sprintf(buf, "<BODY><P>The server could not fulfill\r\n"); 16 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 17 sprintf(buf, "your request because the resource specified\r\n"); 18 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 19 sprintf(buf, "is unavailable or nonexistent.\r\n"); 20 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 21 sprintf(buf, "</BODY></HTML>\r\n"); 22 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 23 }
501 Method Not Implemented
1 void unimplemented(int client) 2 { 3 char buf[1024]; 4 5 sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 501 Method Not Implemented\r\n"); 6 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 7 sprintf(buf, SERVER_STRING); 8 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 9 sprintf(buf, "Content-Type: text/html\r\n"); 10 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 11 sprintf(buf, "\r\n"); 12 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 13 sprintf(buf, "<HTML><HEAD><TITLE>Method Not Implemented\r\n"); 14 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 15 sprintf(buf, "</TITLE></HEAD>\r\n"); 16 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 17 sprintf(buf, "<BODY><P>HTTP request method not supported.\r\n"); 18 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 19 sprintf(buf, "</BODY></HTML>\r\n"); 20 send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 21 }
这个简单的服务器目前应该是不支持图片声音等非文本信息(到我自己写时,不知道能不能实现)。总的来说,这次对整个HTTP协议的处理过程,还有Web服务器的内部实现简单的进行了解。接下来的几个小节,我就自己参考这个程序,自己写一个。当然代码肯定没有这个程序那么简练。不过如果可以实现,还是不错的。到时候对我开发web服务器是遇到的问题再进行讲解。
参考资料:
GET,POST的区别 http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_50e4caf701009eys.html
什么是CGI http://www.doc88.com/p-173100939493.html