ACM模式下输入输出总结(Java)
1、使用 java.util.Scanner包
-
nextInt():直至读取到空格或回车之后结束本次的int值; -
next():直至读取到空格或回车之后结束本次的String值,不可读取回车; -
nextLine():直至读取到换行符(回车)之后结束本次读取的String,可读取回车(空值)
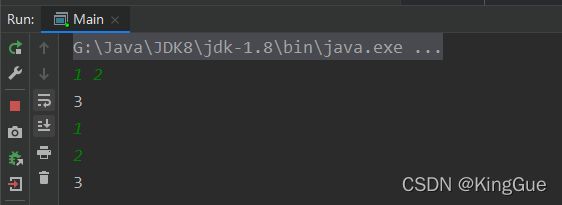
1.1 读取连续整数(两个整数a和b)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
while(in.hasNext()){
int a=in.nextInt();
int b=in.nextInt();
System.out.println(a+b);
}
}
}
1.2 读取有限整数
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=in.nextInt();
while(n-->0){
int a=in.nextInt();
int b=in.nextInt();
System.out.println(a+b);
}
}
}
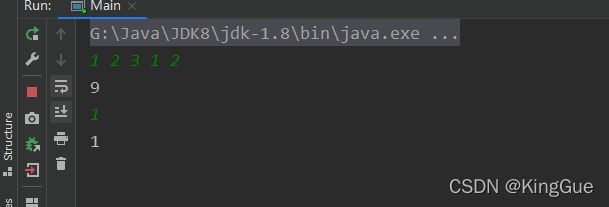
1.3 每行读取空格隔开的整数
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.String;
import java.lang.Integer;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
while(in.hasNext()){
String[] temp=in.nextLine().split(" ");
int sum=0;
for(String s:temp)
sum+=Integer.valueOf(s);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
}
2 使用 BufferedReader和InputStreamReader
2.1 整体函数框架
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
......
}
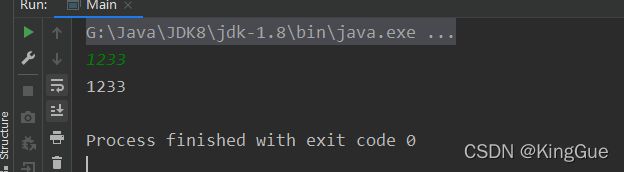
}2.2.1 输入为一个字符串时
abcd
// 创建一个BufferedReader对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// 读取字符串
String line = br.readLine();
// 测试输入是否正确
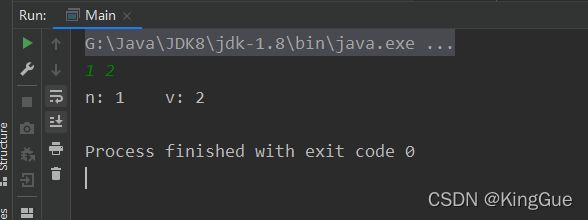
System.out.println(line);2.2.2 输入为多个数字
1 2
// 创建一个BufferedReader对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// 读取第一行数据
String line = br.readLine();
// 将字符串根据空格进行分隔
String[] strings = line.trim().split(" ");
// 分别将其中的每个数值读出
int n = Integer.parseInt(strings[0]);
int v = Integer.parseInt(strings[1]);
// 测试输入是否正确
System.out.println("n: " + n + "\tv: " + v);2.2.3 输入中有一个数组,且有数组的长度
7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
// 创建一个BufferedReader对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// 读取第一行数据
String line = br.readLine();
// 将字符串根据空格进行分隔
String[] strings = line.trim().split(" ");
// 分别将其中的每个数值读出
int n = Integer.parseInt(strings[0]);
int v = Integer.parseInt(strings[1]);
// 读取第二行数据
line = br.readLine();
strings = line.trim().split(" ");
// 创建一个int型的数组用来储存第二行的多个数字
int[] nums = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
nums[i] = Integer.parseInt(strings[i]);
}
// 测试输入是否正确
for (int num: nums) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}3 各类输入输出构造(题目示例)
3.1 多行输入(分隔符为空格)
题目描述:
- 小v今年有n门课,每门都有考试,为了拿到奖学金,小v必须让自己的平均成绩至少为avg。
- 每门课由平时成绩和考试成绩组成,满分为 r。
- 在他知道每门课的平时成绩为ai ,若想让这门课的考试成绩多拿一分的话,小v要花bi 的时间复习,不复习的话当然就是0分。
- 同时我们显然可以发现复习得再多也不会拿到超过满分的分数。为了拿到奖学金,小v至少要花多少时间复习。
输入描述:
- 第一行三个整数 n , r , avg (n大于等于1小于等于1e5,r 大于等于1小于等于1e9,avg大于等于1小于等于1e6),接下来n行,每行两个整数 ai 和 bi,均小于等于1e6大于等于1
输入
- 5 10 9
- 0 5
- 9 1
- 8 1
- 0 1
- 9 100
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Scanner类默认的分隔符就是空格
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext()){
int n=sc.nextInt();
int full=sc.nextInt();
int avg=sc.nextInt();
int[][] nums=new int[n][2];
for(int i=0;i o1[1] - o2[1]); //按复习代价从小到大排序
long sum=0;
for(int[] a:nums) {
sum+=a[0];
}
long limit=avg*n;
int index=0;
long time=0;
while(sum 3.2 数组输入(分隔符为空格)
题目描述:
-
一条长l的笔直的街道上有n个路灯,若这条街的起点为0,终点为l,第i个路灯坐标为 ai,每盏灯可以覆盖到的最远距离为d,为了照明需求,所有灯的灯光必须覆盖整条街,但是为了省电,要使这个d最小,请找到这个最小的 d。
-
输入描述:每组数据第一行两个整数n和l(n大于0小于等于1000,l小于等于1000000000大于0)。 第二行有n个整数(均大于等于0小于等于l),为每盏灯的坐标,多个路灯可以在同一点。 输入: 7 15 15 5 3 7 9 14 0
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext()){
int n=sc.nextInt();
long l=sc.nextLong();
long[] nums=new long[n];
for(int i=0;i3.3 输入为一个链表
反转链表题目描述:
-
对于一个链表 L: L0→L1→…→Ln-1→Ln , 将其翻转成 L0→Ln→L1→Ln-1→L2→Ln-2→…
输入描述:
- 输入是一串数字,用逗号分隔(1,2,3,4,5),请将其转换成单链表格式之后,再进行操作。
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
static class LinkNode {
int val;
LinkNode next;
public LinkNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//以字符串形式作为输入
String str = scanner.next().toString();
//通过分隔符将其转为字符串数组
String[] arr = str.split(",");
//初始化一个整数数组
int[] ints = new int[arr.length];
//给整数数组赋值
for(int j = 0; j stack = new Stack<>();
LinkNode head = new LinkNode(0);
LinkNode p = head;
//链表初始化并放入stack中
for(int i = 0; i < ints.length; i++){
p.next = new LinkNode(ints[i]);
p = p.next;
stack.add(p);
}
head = head.next;
//开始链表转换
p = head;
LinkNode q = stack.peek();
while ((!p.equals(q)) && (!p.next.equals(q))) {
q = stack.pop();
q.next = p.next;
p.next = q;
p = p.next.next;
q = stack.peek();
}
q.next = null;
//输出
//1,5,2,4,3
//打印
while (head != null) {
if(head.next == null){
System.out.print(head.val);
}else{
System.out.print(head.val + ",");
}
head = head.next;
}
}
} 3.4 输入是一棵树(主要是构建树的过程)
-
题目描述 给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。 假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征: 节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。 例如: 输入: 5 / \ 1 3 / \ 4 6 输出: false -
输入描述: 第一行两个数 n,root,分别表示二叉树有n个节点,第root个节点是二叉树的根,接下来共n行,第i行三个数val_i,left_i,right_i,分别表示第i个节点的值val是val_i,左儿子left是第left_i个节点,右儿子right是第right_i个节点。节点0表示空。1<=n<=100000,保证是合法的二叉树。 输入 5 1 5 2 3 1 0 0 3 4 5 4 0 0 6 0 0
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Stack;
//构造树需要的结点类
class TreeNode {
TreeNode left, right;
int val;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] s = reader.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int root = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
TreeNode[] tree = new TreeNode[n + 1];
int[][] leaf = new int[n + 1][2];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
String[] ss = reader.readLine().split(" ");
int val_i = Integer.parseInt(ss[0]);
int left_i = Integer.parseInt(ss[1]);
int right_i = Integer.parseInt(ss[2]);
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val_i);
leaf[i][0] = left_i;
leaf[i][1] = right_i;
tree[i] = node;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int left = leaf[i][0];
if (left != 0) {
tree[i].left = tree[left];
} else {
tree[i].left = null;
}
int right = leaf[i][1];
if (right != 0) {
tree[i].right = tree[right];
} else {
tree[i].right = null;
}
}
TreeNode head = tree[root];
boolean flag = isBinarySearchTree(head);
System.out.println(flag);
}
private static boolean isBinarySearchTree(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null){
return true;
}
int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Stack s = new Stack<>();
while(!s.isEmpty() || node != null){
while(node != null){
s.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = s.pop();
if(node == null){
break;
}
if(pre > node.val){
return false;
}
pre = node.val;
node = node.right;
}
return true;
}
}