用于非线性时间序列预测的稀疏局部线性和邻域嵌入(Matlab代码实现)
个人主页: 研学社的博客
欢迎来到本博客 ❤️ ❤️
博主优势: 博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳ 座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
本文目录如下:
目录
1 概述
2 运行结果
3 参考文献
4 Matlab代码实现
1 概述
“本文提出了一种基于字典的L1范数稀疏编码,用于时间序列预测,不需要训练阶段,参数调整最少,适用于非平稳和在线预测应用。预测过程被表述为基础追求 L1 范数问题,其中为每个测试向量估计一组稀疏权重。尝试了约束稀疏编码公式,包括稀疏局部线性嵌入和稀疏最近邻嵌入。16个时间序列数据集用于测试离线时间序列预测方法,其中训练数据是固定的。所提出的方法还与Bagging树(BT),最小二乘支持向量回归(LSSVM)和正则化自回归模型进行了比较。所提出的稀疏编码预测显示出比使用10倍交叉验证的LSSVM更好的性能,并且比正则化AR和Bagging树的性能明显更好。平均而言,在LSSVM训练时可以完成几千个稀疏编码预测。
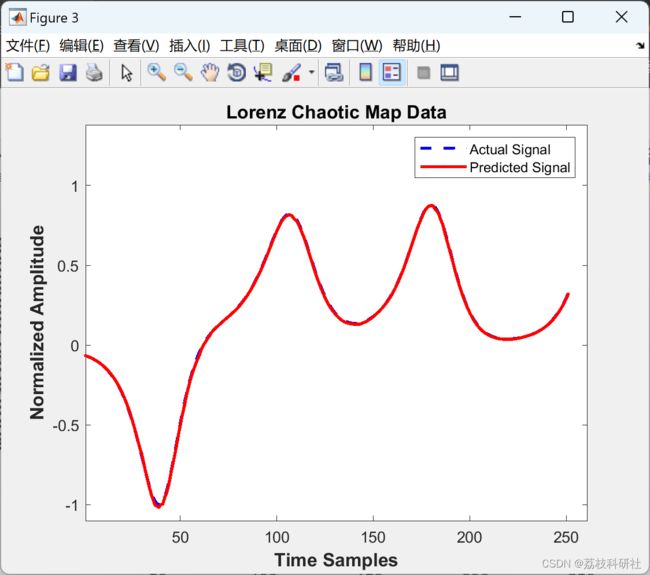
2 运行结果
部分代码:
clear all;
%Time series Prediction using Sparse coding with overcomplete dictionaries
%In each case, the test data prediction is plotted versus the real data
%and the sparsity of the solution is recorded.
%both L1-magic (if LASSO=0) and CVX libraries (if LASSO=1) must be included
% in the Matlab path
%if normalize=1 use sqrt(x*x'), normalize=2 use st.dev., normalize=3 use
%the L1 norm, or zero then no normalization.
normalize1=2;
normalize2=2;
eps=0.001; %the error constraint
thr=0.001; %the pruning threshold
NN=20000; %these are the max number of neighbors allowed
dthr=0.0; %the distance threshold used to filter the dictionary. If it
%is zero then no dictionary filtering is done
LASSO=1; %0 for BP and 1 for BPDN or LASSO using CVX
for kkk=1:16 %The 16 data sets used for evaluation
nnnn=kkk;
if(nnnn==1) %Mackey-Glass data
load MGData;
a = MGData;
time = a(:, 1);
x_t = a(:, 2);
trn_data = zeros(500, 5);
chk_data = zeros(500, 5);
time = 1:sz;
Train = x_t(1:100);
Test = x_t(101:190);
K=6;
eps=0.001;
C = 'USD-EURO Data'
elseif(nnnn==15)
load IkedaData1; %Z-normalized
if(nonorm==1)
for i=1:L1-K
dzz(i)=1;
end
end
end
%Now we normalize the targets of the training data
for i=1:L1-K
if(normalize1==5)
T(i) = (trg1(i)-dmm(i))/dvv(i);
else
T(i) = trg1(i)/dzz(i);
end
end
TR = T;
%%%%%%%%This is the dictionary filtering process (if we want to reduce the
%%%%%%%%number of similar atoms. It is controlled by the dthr value
%%%%%%%%specified by the user. I have not investigated this a lot
dictsize=size(DD);
nn=dictsize(1); %the large dimension
mm=dictsize(2); %the small dimension
RR=randn(nn,mm);
RR=orth(RR);
tooclose=0;
for io=1:nn %over all the atoms
xio = DD(io,1:mm);
cnt=0;
for jo= io+1 : nn
dddd(jo) = dist(xio,DD(jo,1:mm)');
if(dddd(jo) <= dthr) cnt=cnt+1; %one or more atoms are too close
end
end
if(io mindist(io) = min(dist(xio,DD(io+1:nn,1:mm)')); %the min distance for each atom with the next ones else mindist(io)=0; end if(cnt==0) %no atoms are too close FF(io,1:mm) = DD(io,1:mm); FT(io) = TR(io); else %some atoms are too close, so we remove this one and put a random atom FF(io,1:mm) = RR(io, 1:mm); FT(io) = 0; %the target for the random atoms is zero tooclose=tooclose+1; end end %So, now the new dictionary is FF and the new targets is FT %(if no filtering happened then FF is the same as DD) TooClose(kkk) = tooclose; %this will tell us how many atoms were replaced (removed) MinDist(kkk,1:nn)=mindist(1:nn); %here we construct the test data Test(1:(L2-K),1:K) = tst(1:(L2-K),1:K); TT = trg2(1:(L2-K)); M=L2-K; tic %to get the test time sprs=0; %to accumulate the sparsity over test vectors for i=1:M %loop over M vectors from the test data disp('**************'); disp(i); test(1:K) = Test(i,1:K); %here we normalize the test vector by its own dot product if(normalize2==1) normtest = sqrt(test*test'); elseif(normalize2==2) normtest = sqrt(var(test)); elseif(normalize2==3) normtest = norm(test,1); elseif(normalize2==0) normtest=1; end [1]Waleed Fakhr, "Sparse Locally Linear and Neighbor Embedding for Nonlinear Time Series Prediction", ICCES 2015, December 2015.3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
4 Matlab代码实现