Gin 文档学习
1.自定义模板渲染器
// 自定义html模板渲染器,要指定所有的html路径,不推荐
html := template.Must(template.ParseFiles(
"templates/login.html",
"templates/users/index.html",
"templates/center/index.html",
))
//应用这些模板
router.SetHTMLTemplate(html)
router.GET("/users/index", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.HTML(http.StatusOK, "users/index.html", gin.H{
"title": "users/index.html",
})
})
2.自定义模板功能
func formatAsDate(t time.Time) string {
year, month, day := t.Date()
return fmt.Sprintf("%d/%02d/%02d", year, month, day)
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
//用于代替模板里的 {{ }}(调用后端变量)的用法
router.Delims("<{", "}>")
//自定义模板函数 注意要把这个函数放在加载模板前
router.SetFuncMap(template.FuncMap{
"formatAsDate": formatAsDate,
})
//加载指定的模板文件
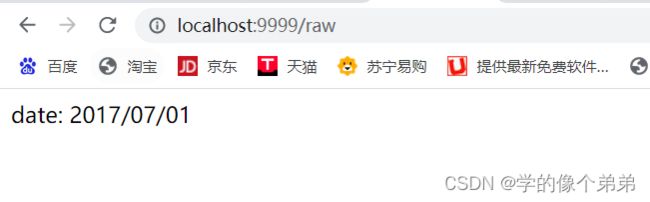
router.LoadHTMLFiles("./templates/raw.html")
router.GET("/raw", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "raw.html", map[string]interface{}{
"now": time.Date(2017, 07, 01, 0, 0, 0, 0, time.UTC),
})
})
router.Run(":9999")
}
raw.html
<body>
date: <{.now | formatAsDate}>
body>
3.Multipart/Urlencoded 绑定
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
type LoginForm struct {
User string `form:"user" binding:"required"`
Password string `form:"password" binding:"required"`
}
func main() {**加粗样式**
router := gin.Default()
router.POST("/login", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 你可以使用显式绑定声明绑定 multipart form:
//c.ShouldBindWith(&form, binding.Form)
// 或者简单地使用 ShouldBind 方法自动绑定:
var form LoginForm
// 在这种情况下,将自动选择合适的绑定
if c.ShouldBind(&form) == nil {
if form.User == "Winnie-OCEAN" && form.Password == "789" {
c.JSON(200, gin.H{"status": "you are logged in",
"user": form.User,
"password": form.Password,
})
} else {
c.JSON(401, gin.H{"status": "unauthorized"})
}
}
})
router.Run()
}
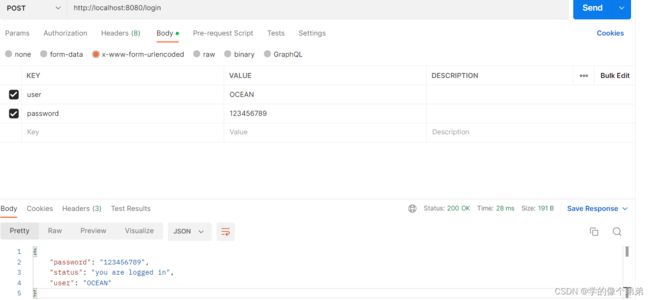
router.POST("/login", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 或者简单地使用 ShouldBind 方法自动绑定:
//c.ShouldBind(&form)
var form LoginForm
// 你可以使用显式绑定声明绑定 multipart form:
if c.ShouldBindWith(&form, binding.Form) == nil {
if form.User == "OCEAN" && form.Password == "123456789" {
c.JSON(200, gin.H{"status": "you are logged in",
"user": form.User,
"password": form.Password,
})
} else {
c.JSON(401, gin.H{"status": "unauthorized"})
}
}
})
4.Multipart/Urlencoded 表单
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
engine.POST("/post_form", func(context *gin.Context) {
//获取post过来的名为user的值
user := context.PostForm("user")
//获取post过来的名为password的值,第二个参数为默认值
password := context.DefaultPostForm("password", "123456")
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"success": "login in",
"username": user,
"password": password,
})
})
engine.Run()
}
5.PureJSON
JSON 使用 unicode 替换特殊 HTML 字符,例如 < 变为 \ u003c。如果要按字面对这些字符进行编码,则可以使用 PureJSON。
package main
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
//结果为 {"html":"\u003cb\u003eHello, world!\u003c/b\u003e"}
// 提供 unicode 实体
r.GET("/json", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(200, gin.H{
"html": "Hello, world!",
})
})
//输出结果{"html":"Hello, world!"}
// 提供字面字符
r.GET("/purejson", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.PureJSON(200, gin.H{
"html": "Hello, world!",
})
})
// 监听并在 0.0.0.0:8080 上启动服务
r.Run(":8080")
}
6.提取url参数同时获取post或来的数据 Query 和 post form
package main
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
engine.POST("/post_query", func(context *gin.Context) {
username := context.Query("username")
password := context.DefaultQuery("password", "123")
age := context.PostForm("age")
page := context.PostForm("page")
context.JSON(200, gin.H{
"username": username,
"password": password,
"age": age,
"page": page,
})
})
engine.Run(":9999")
}
7.SecureJSON 防止 json 劫持
JSON劫持,其实就是恶意网站,通过