springMvc 拦截器源码解析
统一请求处理
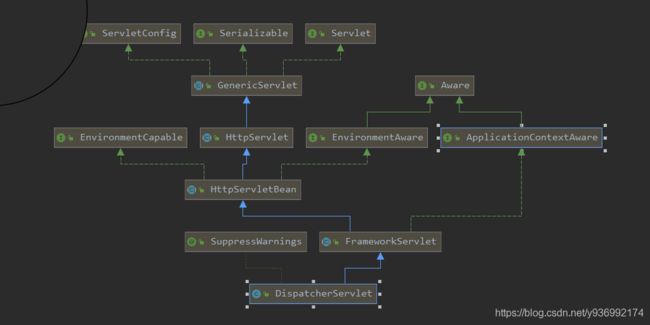
dispatcherServlet 类图结构
// FrameWorkServlet
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) { //<1>
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {//<2>
super.service(request, response);
}
}
无论是<1>还是<2> 都会进入FrameWorkServlet.processRequest方法
// FrameWorkServlet
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response);//进入DispatcherServlet的doservice方法
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
再进入DispatcherServlet的doservice方法
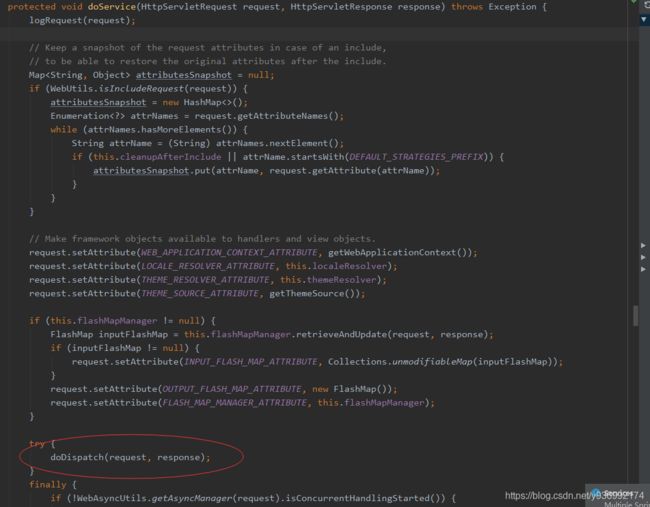
再进入DispatcherServlet 的 doDispatch方法
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
// 获得处理器
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 拦截器前置处理
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 调用请求方法
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 拦截器后置处理
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
先通过getHandler 获得 HandlerExecutionChain,调用 HandlerExecutionChain 的 applyPreHandle执行前置处理,调用 applyPostHandle 执行后置处理,至此可以看到拦截器的处理请求,拦截器处理前置请求方法如下:
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
return false;
}
this.interceptorIndex = i;
}
}
return true;
}
可以看到拦截器们实际上设置在HandlerExecutionChain .interceptors属性中,那么HandlerExecutionChain .interceptors是在哪里设置的呢?往下看
// AbstractHandlerMapping
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
// AbstractHandlerMapping
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
// 如果是 MappedInterceptor 类型的拦截器
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
// 只有路径匹配的请求,才添加到拦截器链中
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}// 不是 MappedInterceptor 类型的拦截器,直接添加到拦截器链中
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
回到AbstractHandlerMapping 的 getHandler方法,通过getHandlerExecutionChain创建 HandlerExecutionChain对象,HandlerExecutionChain 中 的 拦截器就是通过AbstractHandlerMapping 的 adaptedInterceptors 过滤得到。而AbstractHandlerMapping.adaptedInterceptors是在哪里初始化的呢,看下面:
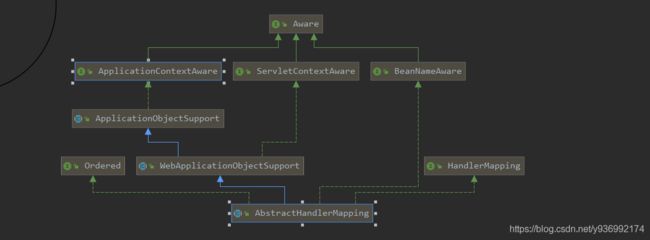
AbstractHandlerMapping 实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口,而 spring 中实现 Aware 接口的类一般在它创建完成后的初始化方法中会进行设置属性,此过程大致如下:
AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean
->AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean
->AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean
->AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
->ApplicationContextAwareProcessor.invokeAwareInterfaces
->ApplicationObjectSupport.setApplicationContext
->WebApplicationObjectSupport.initApplicationContext
->ApplicationObjectSupport.initApplicationContext
->AbstractHandlerMapping.initApplicationContext
->AbstractHandlerMapping.detectMappedInterceptors
protected void detectMappedInterceptors(List mappedInterceptors) {
// 获取 spring 容器中 所有类型为 MappedInterceptor 的对象
mappedInterceptors.addAll(
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
obtainApplicationContext(), MappedInterceptor.class, true, false).values());
}
至此,也知道AbstractHandlerMapping 的 adaptedInterceptors是怎么初始化的了。
整个流程大概就是spring容器初始化的时候,把所有拦截器填充到了AbstractHandlerMapping.adaptedInterceptors属性中缓存起来,等请求来了的时候通过getHandlerExecutionChain将符合条件的拦截器存到HandlerExecutionChain对象里,然后调用拦截器的前置以及后置处理方法