高数题型总结
高数题型总结
- 一、 函数、极限与连续
-
- (一)函数有界性、单调性、周期性及奇偶性的判定
-
- 1. 单调性
- 2. 奇偶性
- 3. 周期性
- 4. 有界性
- (二) 复合函数
- (三) 极限的概念与性质
-
- 1. 极限的概念
-
-
- 1) 数列极限
- 2) 函数极限
-
- 2. 极限的性质
-
- 1) 一般性质
-
- (1) 有界性
- (2) 保号性
- (3)与无穷小的关系
- 2) 存在准则
-
- (1) 夹逼准则
- (2) 单调有界准则
- 3. 极限运算法则
-
- (1) 有理运算法则
- (2) 注意
- (3) 常见结论
- 4. 无穷小
- 5. 无穷大
- (四) 左右极限
- (五) 求极限
-
- 1. n项和\积求极限
- 2. 不定型求极限
-
- (1) 0 0 \frac{0}{0} 00
- (2) ∞ ∞ \frac{\infty}{\infty} ∞∞
- (3) 1 ∞ 1^{\infty} 1∞
- (4) ∞ 0 \infty^0 ∞0、 0 ∞ 0^\infty 0∞
- (5) 0 × ∞ 0\times\infty 0×∞
- (6) ∞ − ∞ \infty-\infty ∞−∞
- 3. 中值定理
- (六) 判断连续性及连续函数的性质
-
- 1. 判断连续性
- 2. 连续函数的性质
- (七) 间断点的种类
一、 函数、极限与连续
(一)函数有界性、单调性、周期性及奇偶性的判定
1. 单调性
2. 奇偶性
常见的奇函数: s i n x , t a n x , a r c s i n x , a r c t a n x , l n 1 − x 1 + x , l n ( x + 1 + x 2 ) , e x − 1 e x + 1 , f ( x ) − f ( − x ) sinx,tanx,arcsinx,arctanx,ln\frac{1-x}{1+x},ln(x+\sqrt{1+x^2}),\frac{e^x-1}{e^x+1},f(x)-f(-x) sinx,tanx,arcsinx,arctanx,ln1+x1−x,ln(x+1+x2),ex+1ex−1,f(x)−f(−x)
常见的偶函数: x 2 , ∣ x ∣ , c o s x , f ( x ) + f ( − x ) x^2,|x|,cosx,f(x)+f(-x) x2,∣x∣,cosx,f(x)+f(−x)
3. 周期性
! 若 f ( x ) 以 T 为 周 期 , 则 f ( a x + b ) 以 T ∣ a ∣ 为 周 期 若f(x)以T为周期,则f(ax+b)以\frac{T}{|a|}为周期 若f(x)以T为周期,则f(ax+b)以∣a∣T为周期
4. 有界性
∣ s i n x ∣ ≤ 1 , ∣ c o s x ∣ ≤ 1 , ∣ a r c s i n x ∣ ≤ π 2 , ∣ a r c c o s x ∣ ≤ π |sinx| \leq1,|cosx| \leq1,|arcsinx| \leq\frac{\pi}{2},|arccosx| \leq\pi ∣sinx∣≤1,∣cosx∣≤1,∣arcsinx∣≤2π,∣arccosx∣≤π
补充:常见函数
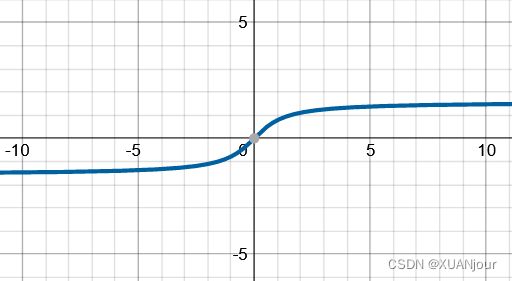
1) y = arctan x y=\arctan x y=arctanx
2) y = arcsin x y=\arcsin x y=arcsinx

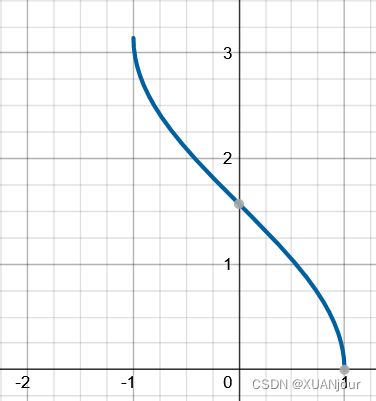
3) y = arccos x y=\arccos x y=arccosx
4) 符号函数:
y = sgnx= { − 1 , x < 0 0 , x = 0 1 , x > 0 \begin{cases} -1, x<0\\ 0, x=0\\ 1,x>0\\ \end{cases} ⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧−1,x<00,x=01,x>0
5) 取整函数: y = [ x ] y = [x] y=[x]
x − 1 < [ x ] ≤ x x-1<[x]\leq x x−1<[x]≤x
(二) 复合函数
只有外函数的定义域与内函数的值域的交不为空时,则可进行复合。
(三) 极限的概念与性质
1. 极限的概念
1) 数列极限
∀ ϵ > 0 , ∃ N > 0 , 当 n > N 时 , 恒 有 ∣ x n − a ∣ < ϵ , 则 称 lim x → ∞ x n = a \forall \epsilon>0,\exists N>0,当n>N时,恒有|x_n-a|< \epsilon,则称\displaystyle\lim_{x\to\infty}x_n=a ∀ϵ>0,∃N>0,当n>N时,恒有∣xn−a∣<ϵ,则称x→∞limxn=a
! b < a , ∃ N , 当 n > N 时 , x n > b b
! c > a , ∃ N , 当 n > N 时 , x n < c c>a,\exists N,当n>N时,x_n
! 数 列 极 限 { x } 的 极 限 与 前 有 限 项 无 关 数列极限\{x\}的极限与前有限项无关 数列极限{x}的极限与前有限项无关
! 整 体 极 限 ∃ ⇒ 部 分 极 限 ∃ 整体极限\exists\Rightarrow部分极限\exists 整体极限∃⇒部分极限∃
! 全 部 部 分 极 限 ∃ ⇒ 整 体 极 限 ∃ 全部部分极限\exists\Rightarrow整体极限\exists 全部部分极限∃⇒整体极限∃
2) 函数极限
(1) 自变量趋于无穷大时:
lim x → + ∞ \lim_{x\to+\infty} limx→+∞
∀ ϵ > 0 , ∃ X > 0 , 当 x > X 时 , 恒 有 ∣ f ( x ) − A ∣ < ϵ , 则 称 lim x → + ∞ f ( x ) = a \forall \epsilon>0,\exists X>0,当x>X时,恒有|f(x)-A|< \epsilon,则称\displaystyle\lim_{x\to+\infty}f(x)=a ∀ϵ>0,∃X>0,当x>X时,恒有∣f(x)−A∣<ϵ,则称x→+∞limf(x)=a
lim x → − ∞ \lim_{x\to-\infty} limx→−∞
∀ ϵ > 0 , ∃ X > 0 , 当 x < − X 时 , 恒 有 ∣ f ( x ) − A ∣ < ϵ , 则 称 lim x → − ∞ f ( x ) = a \forall \epsilon>0,\exists X>0,当x<-X时,恒有|f(x)-A|< \epsilon,则称\displaystyle\lim_{x\to-\infty}f(x)=a ∀ϵ>0,∃X>0,当x<−X时,恒有∣f(x)−A∣<ϵ,则称x→−∞limf(x)=a
lim x → ∞ \lim_{x\to\infty} limx→∞
∀ ϵ > 0 , ∃ X > 0 , 当 ∣ x ∣ > X 时 , 恒 有 ∣ f ( x ) − A ∣ < ϵ , 则 称 lim x → ∞ f ( x ) = a \forall \epsilon>0,\exists X>0,当|x|>X时,恒有|f(x)-A|< \epsilon,则称\displaystyle\lim_{x\to\infty}f(x)=a ∀ϵ>0,∃X>0,当∣x∣>X时,恒有∣f(x)−A∣<ϵ,则称x→∞limf(x)=a
(2)自变量趋于有限值:
∀ ϵ > 0 , ∃ δ > 0 , 当 0 < ∣ x − x 0 ∣ > δ 时 , 恒 有 ∣ f ( x ) − A ∣ < ϵ , 则 称 lim x → ∞ f ( x ) = A \forall \epsilon>0,\exists \delta>0,当0<|x-x_0|>\delta时,恒有|f(x)-A|< \epsilon,则称\displaystyle\lim_{x\to\infty}f(x)=A ∀ϵ>0,∃δ>0,当0<∣x−x0∣>δ时,恒有∣f(x)−A∣<ϵ,则称x→∞limf(x)=A
! x → x o , 但 x ≠ x o 【 即 lim x → ∞ f ( x ) 与 f ( x ) 是 否 存 在 无 关 】 x\to x_o,但x\neq x_o【即\displaystyle\lim_{x\to\infty}f(x)与f(x)是否存在无关】 x→xo,但x=xo【即x→∞limf(x)与f(x)是否存在无关】
2. 极限的性质
1) 一般性质
(1) 有界性
收敛 → \to →有界,反之不然
(2) 保号性
(3)与无穷小的关系
lim f ( x ) = A ↔ f ( x ) = A + α ( x ) , 【 其 中 lim α ( x ) = 0 】 \lim f(x) = A\leftrightarrow f(x) = A + \alpha(x),【其中\lim\alpha(x) = 0】 limf(x)=A↔f(x)=A+α(x),【其中limα(x)=0】
2) 存在准则
(1) 夹逼准则
(2) 单调有界准则
3. 极限运算法则
(1) 有理运算法则
若 l i m f ( x ) = A , l i m g ( x ) = B limf(x) = A,limg(x) = B limf(x)=A,limg(x)=B,那么
- l i m ( f ( x ) ± g ( x ) ) = l i m f ( x ) ± g ( x ) lim(f(x)\pm g(x)) = limf(x) \pm g(x) lim(f(x)±g(x))=limf(x)±g(x)
- l i m ( f ( x ) × g ( x ) ) = f ( x ) × g ( x ) lim(f(x)\times g(x)) = f(x)\times g(x) lim(f(x)×g(x))=f(x)×g(x)
- l i m f ( x ) g ( x ) = l i m f ( x ) l i m g ( x ) , ( B ≠ 0 ) lim\frac{f(x)}{g(x)} = \frac{limf(x)}{limg(x)},(B \neq 0) limg(x)f(x)=limg(x)limf(x),(B=0)
(2) 注意
- 存在 ± \pm ± 不存在 = = = 不存在
- 不存在 ± \pm ± 不存在 = = = 不一定
- 存在 × ÷ \times\div ×÷ 不存在 = = = 不一定
- 不存在 × ÷ \times\div ×÷ 不存在 = = = 不一定
(3) 常见结论
-
l i m f ( x ) = A ≠ 0 → l i m f ( x ) g ( x ) = A l i m g ( x ) limf(x) = A \neq 0 \rightarrow limf(x)g(x) = Alimg(x) limf(x)=A=0→limf(x)g(x)=Alimg(x)
即:极限非零的因子的极限可先求出来 -
l i m f ( x ) g ( x ) lim\frac{f(x)}{g(x)} limg(x)f(x)存在, l i m g ( x ) = 0 → l i m f ( x ) = 0 limg(x) = 0 \rightarrow limf(x) = 0 limg(x)=0→limf(x)=0
-
l i m f ( x ) g ( x ) = A lim\frac{f(x)}{g(x)} = A limg(x)f(x)=A, l i m f ( x ) = 0 → l i m g ( x ) = 0 limf(x) = 0 \rightarrow limg (x) = 0 limf(x)=0→limg(x)=0
4. 无穷小
1) 无穷小量阶:高阶、k阶、同阶、等价
2) 无穷小性质
- 有限个无穷小的和/积仍是无穷小
- 无穷小与有界量的积仍是无穷小
5. 无穷大
1) 常见无穷大的比较:
当x → + ∞ \to+\infty →+∞时, l n α x ≪ x β ≪ a x ln^\alpha x \ll x^\beta\ll a^x lnαx≪xβ≪ax
当n → ∞ \to\infty →∞时, l n α n ≪ n β ≪ a n ≪ n ! ≪ n n ln^\alpha n\ll n^\beta \ll a^n\ll n! \ll n^n lnαn≪nβ≪an≪n!≪nn
2) 无穷大的性质:
- 两个无穷大的积仍为无穷大
- 无穷大与有界变量之和仍为无穷大量
3) 无穷大与无界变量的关系:
- 无穷大量 → \to →无界变量,反之则不然【 ( − 1 ) n (-1)^n (−1)n】
4) 无穷大与无穷小的关系:
- f ( x ) f(x) f(x)是无穷小,且 f ( x ) ≠ 0 f(x)\neq 0 f(x)=0,则 1 f ( x ) \frac{1}{f(x)} f(x)1为 ∞ \infty ∞
! 如果 f ( x ) ≠ 0 f(x)\neq 0 f(x)=0,则 1 f ( x ) \frac{1}{f(x)} f(x)1无意义
(四) 左右极限
- 分段函数在分界点处的极限
- e ∞ e^\infty e∞型极限
- a r c t a n ∞ arctan\infty arctan∞型极限
(五) 求极限
1. n项和\积求极限
1)先求和公式,后求极限
2) 夹逼定理:n项求和失败,且分子分母次数有一不齐
3) 定积分定义:分子、分母次数分别齐,且分母比分子次数多一
2. 不定型求极限
(1) 0 0 \frac{0}{0} 00
0 0 \frac{0}{0} 00: { 等 价 无 穷 小 洛 必 达 法 则 : 0 0 或 ∞ ∞ 泰 勒 公 式 \begin{cases} 等价无穷小\\ 洛必达法则:\frac{0}{0}或\frac{\infty}{\infty}\\ 泰勒公式\\ \end{cases} ⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧等价无穷小洛必达法则:00或∞∞泰勒公式
补充:等价无穷小
- s i n x , t a n x , a r c s i n x , a r c t a n x , l n ( 1 + x ) , e x − 1 ∼ x sinx,tanx,arcsinx,arctanx,ln(1+x),e^x-1 \sim x sinx,tanx,arcsinx,arctanx,ln(1+x),ex−1∼x
- a x − 1 x ∼ l n a \frac{a^x-1}{x}\sim lna xax−1∼lna
- ( 1 + x ) α − 1 ∼ α x (1+x)^\alpha-1\sim \alpha x (1+x)α−1∼αx
- ( 1 + α ( x ) β ( x ) ) − 1 ∼ α ( x ) β ( x ) ( α ( x ) → 0 , α ( x ) β ( x ) → 0 ) (1+\alpha(x)^{\beta(x)} )-1\sim \alpha (x)\beta(x) (\alpha(x)\rightarrow0,\alpha(x)\beta(x)\rightarrow0) (1+α(x)β(x))−1∼α(x)β(x)(α(x)→0,α(x)β(x)→0)
- 1 − c o s x ∼ 1 2 x 2 1-cosx \sim \frac{1}{2}x^2 1−cosx∼21x2
- x − l n ( 1 + x ) ∼ 1 2 x 2 x-ln(1+x)\sim \frac{1}{2}x^2 x−ln(1+x)∼21x2
- x − s i n x ∼ 1 6 x 3 x-sinx\sim \frac{1}{6}x^3 x−sinx∼61x3
- a r c s i n x − x ∼ 1 6 x 3 arcsinx-x\sim \frac{1}{6}x^3 arcsinx−x∼61x3
- t a n x − x ∼ 1 3 x 3 tanx-x\sim \frac{1}{3}x^3 tanx−x∼31x3
- x − a r c t a n x ∼ 1 3 x 3 x-arctanx\sim \frac{1}{3}x^3 x−arctanx∼31x3
补充:替换公式
- u ( x ) v ( x ) → e v ( x ) l n u ( x ) u(x)^{v(x)}\to e^{v(x)lnu(x)} u(x)v(x)→ev(x)lnu(x)
- l n ( … … ) → l n ( 1 + △ ) ∼ △ ln(……)\to ln(1+\triangle)\sim \triangle ln(……)→ln(1+△)∼△
- ( … … ) − 1 → { e △ − 1 ∼ △ ( 1 + △ ) a − 1 ∼ a △ (……)-1\to \begin{cases} e^\triangle-1\sim\triangle\\ (1+\triangle)^a-1\sim a\triangle \end{cases} (……)−1→{e△−1∼△(1+△)a−1∼a△
(2) ∞ ∞ \frac{\infty}{\infty} ∞∞
∞ ∞ \frac{\infty}{\infty} ∞∞: { 0 0 洛 必 达 法 则 : 0 0 或 ∞ ∞ lim x → + ∞ a m x m + … … + a 1 x + a 0 b n x n + … … + b 1 x + b 0 = { 0 , m < n ∞ , m > n a m b n , m = n \begin{cases} \frac{0}{0}\\ 洛必达法则:\frac{0}{0}或\frac{\infty}{\infty}\\ \displaystyle\lim_{x\to+\infty}\frac{a_mx^m+……+a_1x+a_0}{b_nx^n+……+b_1x+b_0}=\begin{cases} 0,m
补充:无穷大
-
当x → + ∞ \to+\infty →+∞时, l n α x ≪ x β ≪ a x ln^\alpha x \ll x^\beta\ll a^x lnαx≪xβ≪ax
-
当n → ∞ \to\infty →∞时, l n α n ≪ n β ≪ a n ≪ n ! ≪ n n ln^\alpha n\ll n^\beta \ll a^n\ll n! \ll n^n lnαn≪nβ≪an≪n!≪nn
-
无穷大量 → \to →无界变量,反之则不然【 ( − 1 ) n (-1)^n (−1)n】
(3) 1 ∞ 1^{\infty} 1∞
1 ∞ 1^{\infty} 1∞:恒等变形,凑 ( 1 + △ ) 1 △ ∼ e (1+\triangle)^{\frac{1}{\triangle}}\sim e (1+△)△1∼e
(4) ∞ 0 \infty^0 ∞0、 0 ∞ 0^\infty 0∞
{ ∞ 0 0 ∞ → u ( x ) v ( x ) → e v ( x ) l n u ( x ) \begin{cases} \infty^0\\ 0^\infty\\ \end{cases}\to u(x)^{v(x)}\to e^{v(x)lnu(x)} {∞00∞→u(x)v(x)→ev(x)lnu(x)
(5) 0 × ∞ 0\times\infty 0×∞
0 × ∞ 0\times\infty 0×∞: { 0 1 ∞ → 0 0 ∞ 1 0 → ∞ ∞ \begin{cases} \frac{0}{\frac{1}{\infty}}\to\frac{0}{0}\\ \\ \frac{\infty}{\frac{1}{0}}\to\frac{\infty}{\infty}\\ \end{cases} ⎩⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎧∞10→0001∞→∞∞
(6) ∞ − ∞ \infty-\infty ∞−∞
∞ − ∞ : → 0 × ∞ \infty-\infty:\to 0\times\infty ∞−∞:→0×∞ 同上
补充:代换原则
- 该值为函数区间连续点【 lim x → x 0 f ( x ) = f ( x 0 ) \displaystyle\lim_{x\to x_0}f(x) = f(x_0) x→x0limf(x)=f(x0)】
- 部分因子极限 ∃ \exists ∃即可拆分【 ∃ lim x → x 0 f ( x ) = A , lim x → x 0 [ f ( x ) ± g ( x ) ] = A + lim x → x 0 g ( x ) \exists\displaystyle\lim_{x\to x_0}f(x) = A,\displaystyle\lim_{x\to x_0}[f(x)\pm g(x)] = A + \displaystyle\lim_{x\to x_0}g(x) ∃x→x0limf(x)=A,x→x0lim[f(x)±g(x)]=A+x→x0limg(x)(含未知数题中,应先拆出极限 ∃ \exists ∃)
- 加减关系在一定条件下可换
【 α ∼ α 1 , β ∼ β 1 , 且 { lim = α 1 β 1 = A ≠ 1 , 则 α − β ∼ α 1 − β 1 lim = α 1 β 1 = A ≠ − 1 , 则 α + β ∼ α 1 + β 1 \alpha \sim \alpha_1,\beta \sim \beta_1,且\begin{cases}\lim = \frac{\alpha_1}{\beta_1} = A \neq 1 , 则 \alpha - \beta \sim \alpha_1 - \beta_1\\ \lim = \frac{\alpha_1}{\beta_1} = A \neq -1 , 则 \alpha + \beta \sim \alpha_1 + \beta_1\\ \end{cases} α∼α1,β∼β1,且{lim=β1α1=A=1,则α−β∼α1−β1lim=β1α1=A=−1,则α+β∼α1+β1】
3. 中值定理
(六) 判断连续性及连续函数的性质
1. 判断连续性
1) 定义
设 y = f ( x ) y=f(x) y=f(x)在点 x 0 x_0 x0某去心邻域内有定义,则 { lim △ x → 0 △ y = lim △ x → 0 [ f ( x 0 + △ x ) − f ( x 0 ) ] lim △ x → 0 f ( x ) = f ( x 0 ) \begin{cases} \displaystyle\lim_{\triangle x\to 0}\triangle y = \displaystyle\lim_{\triangle x\to 0}[f(x_0+\triangle x)-f(x_0)]\\ \displaystyle\lim_{\triangle x\to 0}f(x) = f(x_0)\\ \end{cases} ⎩⎨⎧△x→0lim△y=△x→0lim[f(x0+△x)−f(x0)]△x→0limf(x)=f(x0)
2) 定理
① f ( x ) 和 g ( x ) f(x)和g(x) f(x)和g(x)在点 x 0 x_0 x0处连续,则 f ( x ) ± g ( x ) , f ( x ) g ( x ) , f ( x ) g ( x ) ( g ( x ) ≠ 0 ) f(x)\pm g(x),f(x)g(x),\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}(g(x)\neq 0) f(x)±g(x),f(x)g(x),g(x)f(x)(g(x)=0)在点处连续
②设函数 u = ϕ ( x ) u = \phi (x) u=ϕ(x)在点 x 0 x_0 x0处连续,且 ϕ ( x 0 ) = u 0 \phi (x_0) = u_0 ϕ(x0)=u0,函数 y = f ( u ) y = f(u) y=f(u)在点 u 0 u_0 u0处连续,则 y = f [ ϕ ( x ) ] y = f[\phi(x)] y=f[ϕ(x)]在 x = x 0 x = x_0 x=x0处连续
③基本初等函数在其定义域内连续
④初等函数在其定义区间内连续
2. 连续函数的性质
设 f ( x ) ∈ C [ a , b ] f(x)\in C[a,b] f(x)∈C[a,b]
1) (m,M) f ( x ) f(x) f(x)在[a,b]上有min,MAX
2)(有界) ∃ k > 0 , 使 ∣ f ( x ) ∣ ≤ k \exists k>0,使|f(x)|\leq k ∃k>0,使∣f(x)∣≤k
3)(零点) 且 f ( a ) f ( b ) < 0 , ∃ c ∈ [ a , b ] , 使 f ( c ) = 0 且f(a)f(b)<0,\exists c\in [a,b],使f(c)=0 且f(a)f(b)<0,∃c∈[a,b],使f(c)=0
4)(介值) ∀ η ∈ [ m , M ] , 则 ∃ ξ ∈ [ a , b ] , 使 f ( ξ ) = η \forall\eta\in[m,M],则\exists\xi\in[a,b],使f(\xi)=\eta ∀η∈[m,M],则∃ξ∈[a,b],使f(ξ)=η
(七) 间断点的种类
第一类: f ( a − 0 ) = f ( a + 0 ) f(a-0)=f(a+0) f(a−0)=f(a+0)均有值
{ 可 去 间 断 点 : f ( a − 0 ) = f ( a + 0 ) ≠ f ( a ) 跳 跃 间 断 点 : f ( a − 0 ) ≠ f ( a + 0 ) \begin{cases} 可去间断点:f(a-0)=f(a+0)\neq f(a)\\ 跳跃间断点:f(a-0)\neq f(a+0)\\ \end{cases} {可去间断点:f(a−0)=f(a+0)=f(a)跳跃间断点:f(a−0)=f(a+0)
第二类: f ( a − 0 ) 、 f ( a + 0 ) f(a-0)、f(a+0) f(a−0)、f(a+0)至少一个不存在
判断间断点前(即求极限前),能变形则变形,不着急代入