muduo库net源码分析一(网络编程本质)
TCP网络编程最本质的是处理三个半事件
1、连接建立:服务器accept(被动)接受连接,客户端connect(主动)发起连接。
2、连接断开:主动断开(close、shutdown),被动断开(read返回0)。
3、消息到达:文件描述符可读。
4、消息发送完毕:这算半个。对于低流量的服务,可不必关心这个事件,这里的发送完毕是指数据写入操作系统缓冲区,将由TCP协议栈负责数据的发送与重传,不代表对方已经接收到数据。对于高流量的程序,应用要在发送完毕后再发送,以免数据丢包。
一个套接字有两个缓冲区,一个接收缓冲区一个发送缓冲区,当一个套接字到来的时候先被内核缓冲区接收
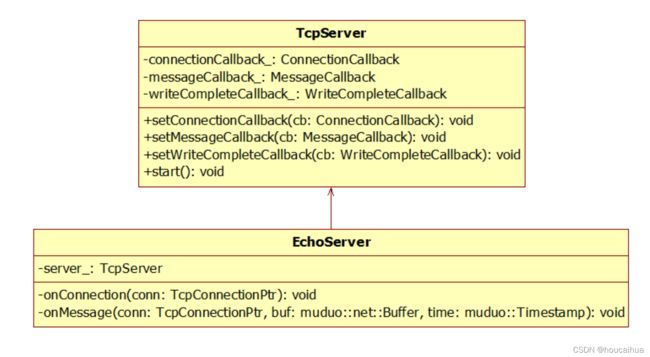
接下来看muduo 对这三个半事件的封装
通过TcpServer 提供了三个成员函数来注册三个回调函数,连接成功和断开用了一个回调函数。
Echo 服务示例:
#include "examples/simple/echo/echo.h"
#include "muduo/base/Logging.h"
#include "muduo/net/EventLoop.h"
#include
// using namespace muduo;
// using namespace muduo::net;
int main()
{
LOG_INFO << "pid = " << getpid();
muduo::net::EventLoop loop;
muduo::net::InetAddress listenAddr(2007);
EchoServer server(&loop, listenAddr);
server.start();
loop.loop();
}
#ifndef MUDUO_EXAMPLES_SIMPLE_ECHO_ECHO_H
#define MUDUO_EXAMPLES_SIMPLE_ECHO_ECHO_H
#include "muduo/net/TcpServer.h"
// RFC 862
class EchoServer
{
public:
EchoServer(muduo::net::EventLoop* loop,
const muduo::net::InetAddress& listenAddr);
void start(); // calls server_.start();
private:
void onConnection(const muduo::net::TcpConnectionPtr& conn);
void onMessage(const muduo::net::TcpConnectionPtr& conn,
muduo::net::Buffer* buf,
muduo::Timestamp time);
muduo::net::TcpServer server_;
};
#endif // MUDUO_EXAMPLES_SIMPLE_ECHO_ECHO_H
#include "examples/simple/echo/echo.h"
#include "muduo/base/Logging.h"
using std::placeholders::_1;
using std::placeholders::_2;
using std::placeholders::_3;
// using namespace muduo;
// using namespace muduo::net;
EchoServer::EchoServer(muduo::net::EventLoop* loop,
const muduo::net::InetAddress& listenAddr)
: server_(loop, listenAddr, "EchoServer")
{
server_.setConnectionCallback(
std::bind(&EchoServer::onConnection, this, _1));
server_.setMessageCallback(
std::bind(&EchoServer::onMessage, this, _1, _2, _3));
}
void EchoServer::start()
{
server_.start();
}
void EchoServer::onConnection(const muduo::net::TcpConnectionPtr& conn)
{
LOG_INFO << "EchoServer - " << conn->peerAddress().toIpPort() << " -> "
<< conn->localAddress().toIpPort() << " is "
<< (conn->connected() ? "UP" : "DOWN");
}
void EchoServer::onMessage(const muduo::net::TcpConnectionPtr& conn,
muduo::net::Buffer* buf,
muduo::Timestamp time)
{
muduo::string msg(buf->retrieveAllAsString());
LOG_INFO << conn->name() << " echo " << msg.size() << " bytes, "
<< "data received at " << time.toString();
conn->send(msg);
}
EventLoop的封装
one loop per thread意思是说每个线程最多只能有一个EventLoop对象。
EventLoop对象构造的时候,会检查当前线程是否已经创建了其他EventLoop对象,如果已创建,终止程序(LOG_FATAL)
EventLoop构造函数会记住本对象所属线程(threadId_)。
创建了EventLoop对象的线程称为IO线程,其功能是运行事件循环(EventLoop::loop)
#ifndef MUDUO_NET_EVENTLOOP_H
#define MUDUO_NET_EVENTLOOP_H
#include
#include
#include
namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{
///
/// Reactor, at most one per thread.
///
/// This is an interface class, so don't expose too much details.
class EventLoop : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
EventLoop();
~EventLoop(); // force out-line dtor, for scoped_ptr members.
///
/// Loops forever.
///
/// Must be called in the same thread as creation of the object.
///
void loop();
void assertInLoopThread()
{
if (!isInLoopThread())
{
abortNotInLoopThread();
}
}
bool isInLoopThread() const { return threadId_ == CurrentThread::tid(); }
static EventLoop* getEventLoopOfCurrentThread();
private:
void abortNotInLoopThread();
bool looping_; /* atomic */
const pid_t threadId_; // 当前对象所属线程ID
};
}
}
#endif // MUDUO_NET_EVENTLOOP_H #include
#include
#include
using namespace muduo;
using namespace muduo::net;
namespace
{
// 当前线程EventLoop对象指针
// 线程局部存储
__thread EventLoop* t_loopInThisThread = 0;
}
EventLoop* EventLoop::getEventLoopOfCurrentThread()
{
return t_loopInThisThread;
}
EventLoop::EventLoop()
: looping_(false),
threadId_(CurrentThread::tid())
{
LOG_TRACE << "EventLoop created " << this << " in thread " << threadId_;
// 如果当前线程已经创建了EventLoop对象,终止(LOG_FATAL)
if (t_loopInThisThread)
{
LOG_FATAL << "Another EventLoop " << t_loopInThisThread
<< " exists in this thread " << threadId_;
}
else
{
t_loopInThisThread = this;
}
}
EventLoop::~EventLoop()
{
t_loopInThisThread = NULL;
}
// 事件循环,该函数不能跨线程调用
// 只能在创建该对象的线程中调用
void EventLoop::loop()
{
assert(!looping_);
// 断言当前处于创建该对象的线程中
assertInLoopThread();
looping_ = true;
LOG_TRACE << "EventLoop " << this << " start looping";
::poll(NULL, 0, 5*1000);
LOG_TRACE << "EventLoop " << this << " stop looping";
looping_ = false;
}
void EventLoop::abortNotInLoopThread()
{
LOG_FATAL << "EventLoop::abortNotInLoopThread - EventLoop " << this
<< " was created in threadId_ = " << threadId_
<< ", current thread id = " << CurrentThread::tid();
}