继承——C++第二大特性
目录
一、概念及定义
1、概念
2、定义
(2)方式
(3)继承基类成员访问方式的变化
二、父类子类赋值转换
三、继承中的作用域
四、派生类的默认成员函数
六、继承与静态成员
七、复杂的菱形继承及菱形虚拟继承
八、归纳
一、概念及定义
1、概念
继承是类层次设计的复用
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
void Print()
{
cout << "name:" << _name << endl;
cout << "age:" << _age << endl;
}
protected:
string _name="sunlang";
int _age=21;
};
class Student :public Person
{
protected:
int _number;
};
class Teacher :public Person
{
protected:
int _teacher_number;
};
int main()
{
Student s;
Teacher t;
s.Print();
t.Print();
return 0;
} 继承父类Person之后,成员函数、成员变量都会成为子类的一部分。还是挺牛批的!
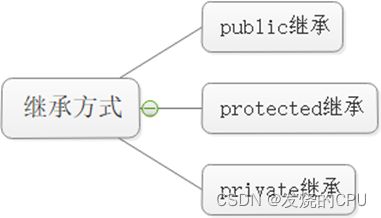
2、定义
(1)格式
(2)方式
(3)继承基类成员访问方式的变化
| 类成员/继承方式 |
public继承 |
protected继承 |
private继承 |
| 基类的public成员 |
派生类的public成员 |
派生类的protected 成员 |
派生类的private 成员 |
| 基类的protected 成员 |
派生类的protected 成员 |
派生类的protected 成员 |
派生类的private 成员 |
| 基类的private成员 |
在派生类中不可见 |
在派生类中不可见 |
在派生类中不可见 |
给我好好听课:
第一,基类的私有成员被继承到了派生类中,语法上限制派生类对象在类里类外都不能去访问它。
第二,protected说明基类成员不能在类外被访问,但能在派生类中访问。
第三,class默认继承方式是private,struct默认继承方式是public
第四,常用public继承,因为protetced/private继承下来的成员都只能在派生类的类里面使用,实际中扩展维护性不强。
class Person
{
public:
void Print()
{
cout << _name << endl;
cout << _age << endl;
}
protected:
string _name="sunlang";
private:
int _age=21;
};
class Student :private Person//错误
{
protected:
int _number=200700131;
};
int main()
{
Student s;
s.Print();
return 0;
}二、父类子类赋值转换
派生类对象可以赋值给基类的对象、基类的指针、基类的引用,俗称称甩刀手切割。
基类对象不能赋值给派生类对象噢,宝宝~
基类的指针或者引用可以通过强制类型转换赋值给派生类的指针或引用。
#include
using namespace std;
class Person
{
protected:
string _name;
string _sex;
int _age;
};
class Student :public Person
{
public:
int _No;
};
void Test()
{
Student sobj;
//派生类对象可以赋值给基类的对象、指针、引用
Person pobj = sobj;
Person* ppobj = &sobj;
Person& rpobj = sobj;
//基类对象不能赋值给派生类
//sobj = pobj;
//基类的指针可以通过强制类型转换赋值给派生类的指针
Student* ps1 = (Student*)(&pobj);
ps1->_No = 10;
} 三、继承中的作用域
1、子类成员将屏蔽父类对同名成员的直接访问,这种情况叫隐藏,也叫重定义,可以使用基类::基类成员显示访问
2、成员函数只需要函数名相同就构成隐藏
3、实际开发中不要定义同名成员,这是C++的缺陷啊,哥哥
class Person
{
protected:
string _name = "小李子";
int _num = 8848;
};
class Student :public Person
{
public:
void Print()
{
cout << _name << endl;
cout << Person::_num << endl;
cout << _num << endl;
}
protected:
int _num = 9999;
};
//B中的func和A中的func不构成重载,因为不在同一作用域
//B中的func和A中的func构成隐藏,成员函数满足函数名相同就构成隐藏
class A
{
public:
void func()
{
cout << "func()" << endl;
}
};
class B:public A
{
public:
void func(int i)
{
A::func();
cout << "func(int i)" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Student s;
s.Print();
cout << endl;
B b;
b.func(1);
return 0;
}四、派生类的默认成员函数
1、派生类的构造函数必须调用基类的构造函数初始化基类的那一部分成员。
2、派生类的拷贝构造函数必须调用基类的拷贝构造完成基类的那一部分拷贝初始化
3、派生类的operator=必须要调用基类的operator=完成基类的复制
4、派生类的析构函数会在被调用完成后自动调用基类的析构函数清理基类成员,保证派生类对象先清理派生类成员再清理基类成员
5、派生类对象初始化先调用基类构造再调用派生类构造
6、派生类对象清理先调用派生类析构再调用基类析构
7、父类析构函数不加virtual的情况下,子类析构函数和父类析构函数构成隐藏关系
总结:
子类构造函数原则:调用父类构造函数初始化继承父类成员
自己再初始化自己的成员,析构、拷贝构造、复制重载也类似
class Person
{
public:
Person(const char* name = "peter")
:_name(name)
{
cout << "Person()" << endl;
}
Person(const Person& p)
:_name(p._name)
{
cout << "Person(const Person& p)" << endl;
}
Person& operator=(const Person& p)
{
cout << "Person operator=(const Person& p)" << endl;
if (this != &p)
{
_name = p._name;
}
return* this;
}
~Person()
{
cout << "~Person()" << endl;
}
protected:
string _name;
};
class Student :public Person
{
public:
Student(const char* name, int num)
:Person(name)
, _num(num)
{
cout << "Student(const Student& s)" << endl;
}
Student(const Student& s)
:Person(s)
, _num(s._num)
{
cout << "Student(const Student&s)" << endl;
}
Student& operator=(const Student& s)
{
cout << "Student&operator=(const Student&s)" << endl;
if (this != &s)
{
Person::operator=(s);
_num = s._num;
}
return* this;
}
~Student()
{
cout << "~Student()" << endl;
}
protected:
int _num;
};
void Test()
{
Student s1("jack", 18);
Student s2(s1);
Student s3("rose", 17);
s1 = s3;
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}六、继承与静态成员
基类定义了static静态成员,只有一个static成员实例
class Person
{
public:
Person()
{
++_count;
}
protected:
string _name;
public:
static int _count;
};
int Person::_count = 0;
class Student :public Person
{
protected:
int _stuNum;
};
class Graduate :public Student
{
protected:
string _seminarCourse;
};
void TestPerson()
{
Student s1;
Student s2;
Student s3;
Graduate s4;
cout << " 人数 :" << Person::_count << endl;
Student::_count = 0;
cout << " 人数 :" << Person::_count << endl;
}
int main()
{
TestPerson();
return 0;
}七、复杂的菱形继承及菱形虚拟继承
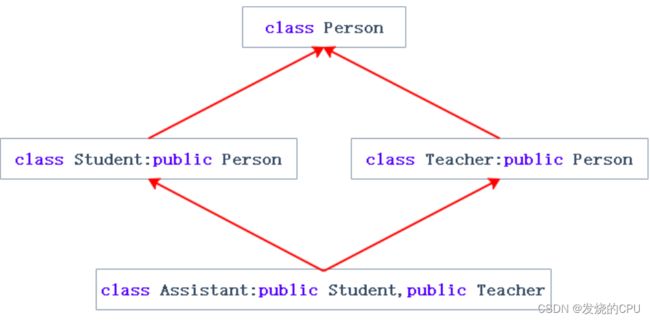
菱型继承是多继承的一种特殊情况
class Person
{
public:
string _name;
};
class Student :public Person
{
protected:
int _num;
};
class Teacher :public Person
{
protected:
int _id;
};
class Assistant :public Student, public Teacher
{
protected:
string _majorCourse;
};
void Test()
{
Assistant a;
a._name = "sunlang";
//显示指定访问哪个父类的成员可以解决二义性问题
a.Student::_name = "xxx";
a.Teacher::_name = "yyy";
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}虚拟继承可以解决菱形继承的二义性和数据冗余的问题
class Person
{
public:
string _name;
};
class Student :virtual public Person
{
protected:
int _num;
};
class Teacher :virtual public Person
{
protected:
int _id;
};
class Assistant :public Student, public Teacher
{
protected:
string _majorCourse;
};
void Test()
{
Assistant a;
a._name = "sunlang";
//显示指定访问哪个父类的成员可以解决二义性问题
a.Student::_name = "xxx";
a.Teacher::_name = "yyy";
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}虚拟继承的原理:
(234条消息) C++虚继承的概念_crystal_avast的博客-CSDN博客_c++的虚继承![]() https://blog.csdn.net/crystal_avast/article/details/7678704
https://blog.csdn.net/crystal_avast/article/details/7678704
八、归纳
1、一定不要设计菱形继承
2、多继承是缺陷
3、组合
public继承是is-a的关系,每个派生类对象都是一个基类对象
组合是has-a的关系,每个B对象中都有一个A对象
优先使用组合
白箱复用:耦合度高
黑箱复用:耦合度低
代码案例:
组合
class Tire
{
protected:
string _brand = "sun";
size_t _size = 89;
};
class Car
{
protected:
string _colour = "白色";
string _num = "赣B1234";
Tire _t;
};继承
class Car
{
protected:
string _colour = "白色";
string _num = "赣B1234";
};
class BMW :public Car
{
public:
void Drive()
{
cout << "好车" << endl;
}
};
class Bez:public Car
{
public:
void Drive()
{
cout << "快车" << endl;
}
};下次见……