Spring Security 安全框架
Spring Security
一、 Spring Security 简介
1 概括
Spring Security 是一个高度自定义的安全框架。利用 Spring IoC/DI和 AOP 功能,为系统提供了声明式安全访问控制功能,减少了为系统安全而编写大量重复代码的工作。
使用Spring Secruity 的原因有很多,但大部分都是发现了javaEE的Servlet 规范或 EJB 规范中的安全功能缺乏典型企业应用场景。同时认识到他们在 WAR 或 EAR 级别无法移植。因此如果你更换服务器环境,还有大量工作去重新配置你的应用程序。使用 Spring Security解决了这些问题,也为你提供许多其他有用的、可定制的安全功能。
正如你可能知道的两个应用程序的两个主要区域是“认证”和“授权”(或者访问控制)。这两点也是 Spring Security 重要核心功能。“认证”,是建立一个他声明的主体的过程(一个“主体”一般是指用户,设备或一些可以在你的应用程序中执行动作的其他系统),通俗点说就是系统认为用户是否能登录。“授权”指确定一个主体是否允许在你的应用程序执行一个动作的过程。通俗点讲就是系统判断用户是否有权限去做某些事情。
2 历史
Spring Security 以“The Acegi Secutity System for Spring” 的名字始于 2003 年年底。其前身为 acegi 项目。起因是 Spring开发者邮件列表中一个问题,有人提问是否考虑提供一个基于 Spring 的安全实现。限制于时间问题,开发出了一个简单的安全实现,但是并没有深入研究。几周后,Spring 社区中其他成员同样询问了安全问题,代码提供给了这些人。2004 年 1 月份已经有 20 人左右使用这个项目。随着更多人的加入,在 2004 年 3 月左右在 sourceforge 中建立了一个项目。在最开始并没有认证模块,所有的认证功能都是依赖容器完成的,而 acegi 则注重授权。但是随着更多人的使用,基于容器的认证就显现出了不足。acegi 中也加入了认证功能。大约 1 年后 acegi 成为 Spring子项目。
在 2006 年 5 月发布了 acegi 1.0.0 版本。2007 年底 acegi 更名为Spring Security。
二、 第一个 Spring Security 项目
1 导入依赖
Spring Security 已经被 Spring boot 进行集成,使用时直接引入启动器即可。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId>
dependency>
2 访问页面
导入 spring-boot-starter-security 启动器后,Spring Security 已经生效,默认拦截全部请求,如果用户没有登录,跳转到内置登录页面。
在项目中新建 login.html 页面后
在浏览器输入:http://localhost:8080/login.html 后会显示下面页面

默认的 username 为 user,password 打印在控制台中。当然了,你们显示的肯定和我的不一样。
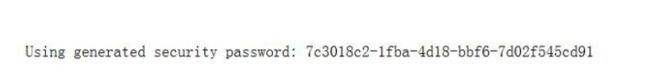
在浏览器中输入账号和密码后会显示 login.html 页面内容。
三、 UserDetailsService 详解
当什么也没有配置的时候,账号和密码是由 Spring Security 定义生成的。而在实际项目中账号和密码都是从数据库中查询出来的。所以我们要通过自定义逻辑控制认证逻辑。
如果需要自定义逻辑时,只需要实现UserDetailsService 接口即可。接口定义如下:

1 返回值
返回值 UserDetails 是一个接口,定义如下

要想返回 UserDetails 的实例就只能返回接口的实现类。Spring Security 中提供了如下的实例。对于我们只需要使用里面的 User 类即可。注意 User 的全限定路径是:
org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User
此处经常和系统中自己开发的 User 类弄混。

在 User 类中提供了很多方法和属性。

其中构造方法有两个,调用其中任何一个都可以实例化 UserDetails 实现类 User 类的实例。而三个参数的构造方法实际上也是调用 7 个参数的构造方法。
username:用户名
password:密码
authorities:用户具有的权限。此处不允许为 null

此处的用户名应该是客户端传递过来的用户名。而密码应该是从数据库中查询出来的密码。Spring Security 会根据 User 中的 password 和客户端传递过来的 password 进行比较。如果相同则表示认证通过,如果不相同表示认证失败。
authorities 里面的权限对于后面学习授权是很有必要的,包含的所有内容为此用户具有的权限,如有里面没有包含某个权限,而在做某个事情时必须包含某个权限则会出现 403。通常都是通过AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList(“”) 来 创 建authorities 集合对象的。参数时一个字符串,多个权限使用逗号分隔。
2 方法参数
方法参数表示用户名。此值是客户端表单传递过来的数据。默认情况下必须叫 username,否则无法接收。
3 异常
UsernameNotFoundException 用 户 名 没 有 发 现 异 常 。 在 loadUserByUsername 中是需要通过自己的逻辑从数据库中取值的。如果 通 过 用 户 名 没 有 查 询 到 对 应 的 数 据 , 应 该 抛 出
UsernameNotFoundException,系统就知道用户名没有查询到。
四、 PasswordEncoder 密码解析器详解
Spring Security 要求容器中必须有 PasswordEncoder 实例。所以当自定义登录逻辑时要求必须给容器注入 PaswordEncoder 的 bean 对象
1 接口介绍
encode():把参数按照特定的解析规则进行解析。
matches()验证从存储中获取的编码密码与编码后提交的原始密码是否匹配。如果密码匹配,则返回 true;如果不匹配,则返回 false。
第一个参数表示需要被解析的密码。第二个参数表示存储的密码。
upgradeEncoding():如果解析的密码能够再次进行解析且达到更安全的结果则返回 true,否则返回 false。默认返回 false。

2 内置解析器介绍
3 BCryptPasswordEncoder 简介
BCryptPasswordEncoder 是 Spring Security 官方推荐的密码解析器,平时多使用这个解析器。
BCryptPasswordEncoder 是对 bcrypt 强散列方法的具体实现。是基于 Hash 算法实现的单向加密。可以通过 strength 控制加密强度,默认 10。
4 代码演示
在 项 目 src/test/java 下 新 建 com.bjsxt.MyTest 测 试BCryptPasswordEncoder 用法。
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test(){
//创建解析器
PasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
//对密码进行加密
String password = encoder.encode("123");
System.out.println("------------"+password);
//判断原字符加密后和内容是否匹配
boolean result = encoder.matches("123",password);
System.out.println("============="+result);
}
}
五、 自定义登录逻辑
当 进 行 自 定 义 登 录 逻 辑 时 需 要 用 到 之 前 讲 解 的UserDetailsService 和PasswordEncoder。但是 Spring Security 要求:当进行自定义登录逻辑时容器内必须有 PasswordEncoder 实例。所以不能直接 new 对象。
1 编写配置类
新建类 com.bjsxt.config.SecurityConfig 编写下面内容
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder getPwdEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
2 自定义逻辑
在 Spring Security 中实现 UserDetailService 就表示为用户详情服务。在这个类中编写用户认证逻辑。
@Service
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder encoder;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws
UsernameNotFoundException {
//1. 查询数据库判断用户名是否存在,如果不存在抛出UsernameNotFoundException
if(!username.equals("admin")){
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户名不存在");
}
//把查询出来的密码进行解析,或直接把 password 放到构造方法中。
//理解:password 就是数据库中查询出来的密码,查询出来的内容不是 123
String password = encoder.encode("123");
return new User(username,password,AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin"));
}
}
3 查看效果
重启项目后,在浏览器中输入账号:admin,密码:123。后可以正确进入到 login.html 页面。
六、 自定义登录页面
虽然 Spring Security 给我们提供了登录页面,但是对于实际项目中,大多喜欢使用自己的登录页面。所以 Spring Security 中不仅仅提供了登录页面,还支持用户自定义登录页面。实现过程也比较简单,只需要修改配置类即可。
1 编写登录页面
别写登录页面,登录页面中的 action 不编写对应控制器也可以。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>内容</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/login" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username"/>
<input type="password" name="password"/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
2 修改配置类
修改配置类中主要是设置哪个页面是登录页面。配置类需要继承 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapte,并重写 configure 方法。
successForwardUrl()登录成功后跳转地址
loginPage() 登录页面
loginProcessingUrl 登录页面表单提交地址,此地址可以不真实存在。
antMatchers():匹配内容
permitAll():允许
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// 表单认证
http.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") //当发现/login 时认为是登录,需要执行 UserDetailsServiceImpl
.successForwardUrl("/toMain") //此处是 post 请求
.loginPage("/login.html");
// url 拦截
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login.html").permitAll() //login.html 不需要被认证
.anyRequest().authenticated();//所有的请求都必须被认证。必须登录后才能访问。
//关闭 csrf 防护
http.csrf().disable();
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder getPe(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
3 编写控制器
编写控制器,当用户登录成功后跳转 toMain 控制器。编写完成控制器后编写 main.html。页面中随意写上一句话表示 main.html 页面内容即可。而之前的/login 控制器方法是不执行的,所以可以删除了。
@Controller
public class LoginController {
// 该方法不会被执行
// @RequestMapping("/login")
// public String login(){
// System.out.println("执行了 login 方法");
// return "redirect:main.html";
// }
@PostMapping("/toMain")
public String toMain(){
return "redirect:/main.html";
}
}
七、 认证过程其他常用配置
1 失败跳转
表单处理中成功会跳转到一个地址,失败也可以跳转到一个地址中。
1.1编写页面
在 src/main/resources/static 下新建 fail.html 并编写如下内容
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
操作失败,请重新登录. <a href="/login.html">跳转</a>
</body>
</html>
1.2修改表单配置
在配置方法中表单认证部分添加 failureForwardUrl()方法,表示登录失败跳转的 url。此处依然是POST 请求,所以跳转到可以接收 POST请求的控制器/fail 中。
// 表单认证
http.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") //当发现/login 时认为是登录,需要执行
UserDetailsServiceImpl
.successForwardUrl("/toMain") //此处是 post 请求
.failureForwardUrl("/fail") //登录失败跳转地址
.loginPage("/login.html");
1.3添加控制器方法
在控制器类中添加控制器方法,方法映射路径/fail。此处要注意:由于是 POST 请求访问/fail。所以如果返回值直接转发到 fail.html 中,
即使有效果,控制台也会报警告,提示 fail.html 不支持 POST 访问方式。
@PostMapping("/fail")
public String fail(){
return "redirect:/fail.html";
}
1.4设置 fail.html 不需要认证
认证失败跳转到 fail.html 页面中,所以必须配置 fail.html 不需要被认证。需要修改配置类中内容
// url 拦截
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login.html").permitAll() //login.html 不需要被认证
.antMatchers("/fail.html").permitAll() //fail.html 不需要被认证
.anyRequest().authenticated();//所有的请求都必须被认证。必须登录后才能访问。
2 设置请求账户和密码的参数名
2.1源码简介
当进行登录时会执行UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 过滤器。
usernamePasrameter:账户参数名
passwordParameter:密码参数名
postOnly=true:默认情况下只允许 POST 请求
2.2修改配置
// 表单认证
http.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") //当发现/login 时认为是登录,需要执行
UserDetailsServiceImpl
.successForwardUrl("/toMain") //此处是 post 请求
.failureForwardUrl("/fail") //登录失败跳转地址
.loginPage("/login.html")
.usernameParameter("myusername")
.passwordParameter("mypassword");
2.3修改页面
修改 login.html
<form action = "/login" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="myusername"/><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="mypassword"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/>
</form>
3 自定义登录成功处理器
3.1源码分析
使用 successForwardUrl()时表示成功后转发请求到地址。内部是通过 successHandler()方法进行控制成功后交给哪个类进行处理

ForwardAuthenticationSuccessHandler 内部就是最简单的请求转发。由于是请求转发,当遇到需要跳转到站外或在前后端分离的项目中就无法使用了。

当需要控制登录成功后去做一些事情时,可以进行自定义认证成功控制器。
3.2代码实现
3.2.1 自定义类
新建类com.bjsxt.handler.MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler 编写如下:
public class MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements
AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
//Principal 主体,存放了登录用户的信息
User user = (User)authentication.getPrincipal();
System.out.println(user.getUsername());
System.out.println(user.getPassword());//密码输出为 null
System.out.println(user.getAuthorities());
//重定向到百度。这只是一个示例,具体需要看项目业务需求
httpServletResponse.sendRedirect("http://www.baidu.com");
}
}
3.2.2 修改配置项
使用 successHandler()方法设置成功后交给哪个对象进行处理
// 表单认证
http.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") //当发现/login 时认为是登录,需要执行
UserDetailsServiceImpl
.successHandler(new MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler())
//.successForwardUrl("/toMain") //此处是 post 请求
.failureForwardUrl("/fail") //登录失败跳转地址
.loginPage("/login.html");
4 自定义登录失败处理器
4.1源码分析
failureForwardUrl()内部调用的是 failureHandler()方法

ForwardAuthenticationFailureHandler 中也是一个请求转发,并在request 作用域中设置 SPRING_SECURITY_LAST_EXCEPTION 的 key,内容为异常对象。
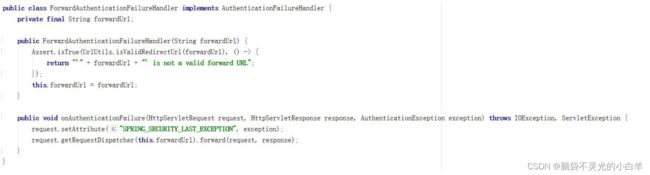
4.2代码实现
4.2.1 新建控制器
新建com.bjsxt.handler.MyForwardAuthenticationFailureHandler 实现 AuthenticationFailureHandler。在方法中添加重定向语句
public class MyForwardAuthenticationFailureHandler implements
AuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest,
HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, AuthenticationException e) throws
IOException, ServletException {
httpServletResponse.sendRedirect("/fail.html");
}
}
4.2.2 修改配置类
修改配置类中表单登录部分。设置失败时交给失败处理器进行操作。failureForwardUrl 和 failureHandler 不可共存。
// 表单认证
http.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") //当发现/login 时认为是登录,需
要执行 UserDetailsServiceImpl
.successHandler(new MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler())
//.successForwardUrl("/toMain") //此处是 post 请求
.failureHandler(new MyForwardAuthenticationFailureHandler())
// .failureForwardUrl("/fail") //登录失败跳转地址
.loginPage("/login.html");
八、 访问控制 url 匹配
在前面讲解了认证中所有常用配置,主要是对 http.formLogin()进行操作。而在配置类中 http.authorizeRequests()主要是对 url 进行控
制,也就是我们所说的授权(访问控制)。http.authorizeRequests()也支持连缀写法,总体公式为:
url 匹配规则.权限控制方法
通过上面的公式可以有很多 url 匹配规则和很多权限控制方法。这些内容进行各种组合就形成了 Spring Security 中的授权。
在所有匹配规则中取所有规则的交集。配置顺序影响了之后授权效果,越是具体的应该放在前面,越是笼统的应该放到后面。
1 anyRequest()
在之前认证过程中我们就已经使用过anyRequest(),表示匹配所有的请求。一般情况下此方法都会使用,设置全部内容都需要进行认证。
代码示例:
anyRequest().authenticated();
2 antMatcher()
方法定义如下:
public C antMatchers(String... antPatterns)
参数是不定向参数,每个参数是一个 ant 表达式,用于匹配URL规则。
规则如下:
? 匹配一个字符
* 匹配 0 个或多个字符
** 匹配 0 个或多个目录
在实际项目中经常需要放行所有静态资源,下面演示放行 js 文件夹下所有脚本文件。
.antMatchers("/js/**").permitAll()
还有一种配置方式是只要是.js 文件都放行
antMatchers("/**/*.js").permitAll()
3 regexMatchers()
3.1介绍
使用正则表达式进行匹配。和 antMatchers()主要的区别就是参数,antMatchers()参数是 ant 表达式,regexMatchers()参数是正则表达式。
演示所有以.js 结尾的文件都被放行。
.regexMatchers(".+[.]js").permitAll()
3.2两个参数时使用方式
无论是 antMatchers()还是 regexMatchers()都具有两个参数的方法,其中第一个参数都是HttpMethod,表示请求方式,当设置了HttpMethod 后表示只有设定的特定的请求方式才执行对应的权限设置。
枚举类型 HttpMethod 内置属性如下 :

4 mvcMatchers()
mvcMatchers()适用于配置了 servletPath 的情况。
servletPath 就是所有的 URL 的统一前缀。在 SpringBoot 整合SpringMVC 的项目中可以在 application.properties 中添加下面内容设置 ServletPath
spring.mvc.servlet.path= /bjsx
在 Spring Security 的配置类中配置.servletPath()是 mvcMatchers()返回值特有的方法,antMatchers()和 regexMatchers()没有这个方法。
在 servletPath()中配置了 servletPath 后,mvcMatchers()直接写 Spring MVC 中@RequestMapping()中设置的路径即可。
.mvcMatchers("demo").servletPath("/bjsxt").permitAll()
如果不习惯使用 mvcMatchers()也可以使用 antMatchers(),下面代码和上面代码是等效的
antMatchers("/bjsxt/demo").permitAll()
九、 内置访问控制方法介绍
Spring Security 匹配了 URL 后调用了 permitAll()表示不需要认证,随意访问。在 Spring Security 中提供了多种内置控制。
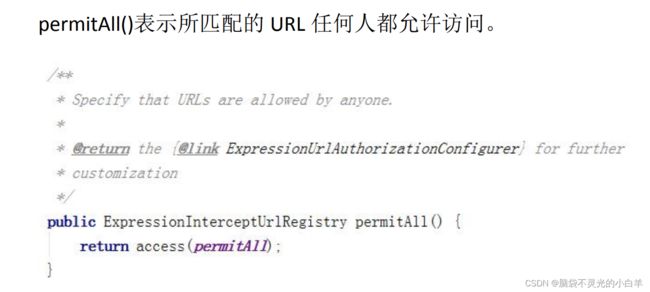
1 permitAll()
permitAll()表示所匹配的 URL 任何人都允许访问。
2 authenticated()
authenticated()表示所匹配的 URL 都需要被认证才能访问。

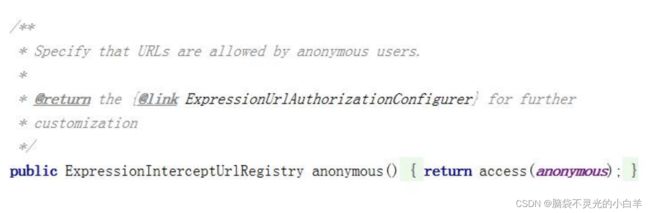
3 anonymous()
anonymous()表示可以匿名访问匹配的 URL。和 permitAll()效果类似,只是设置为 anonymous()的 url 会执行 filter 链中官方源码定义如下:
4 denyAll()
5 rememberMe()
6 fullyAuthenticated()
十、 角色权限判断
除了之前讲解的内置权限控制。Spring Security 中还支持很多其他权限控制。这些方法一般都用于用户已经被认证后,判断用户是否具有特定的要求。
1 hasAuthority(String)
判断用户是否具有特定的权限,用户的权限是在自定义登录逻辑中创建 User 对象时指定的。
下图中 admin 就是用户的权限。admin 严格区分大小写。

在配置类中通过 hasAuthority(“admin”)设置具有 admin 权限时才能访问。
.antMatchers("/main1.html").hasAuthority("admin")
2 hasAnyAuthority(String …)
如果用户具备给定权限中某一个,就允许访问。
下面代码中由于大小写和用户的权限不相同,所以用户无权访问 /main1.html
.antMatchers("/main1.html").hasAnyAuthority("adMin","admiN")
3 hasRole(String)
如果用户具备给定角色就允许访问。否则出现 403。
参数取值来源于自定义登录逻 UserDetailsService 实现类中创建 User 对象时给 User 赋予的授权。
在给用户赋予角色时角色需要以:ROLE_ 开头,后面添加角色名称。例如:ROLE_abc 其中 abc 是角色名,ROLE_是固定的字符开头。使用 hasRole()时参数也只写 abc 即可。否则启动报错。
给用户赋予角色:

在配置类中直接写 abc 即可。
![]()
4 hasAnyRole(String …)
如果用户具备给定角色的任意一个,就允许被访问
5 hasIpAddress(String)
如果请求是指定的 IP 就运行访问。
可以通过 request.getRemoteAddr()获取 ip 地址。
需要注意的是在本机进行测试时 localhost 和 127.0.0.1 输出的 ip 地址是不一样的。
当浏览器中通过 localhost 进行访问时控制台打印的内容:
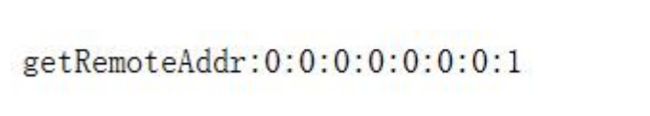
当浏览器中通过 127.0.0.1 访问时控制台打印的内容:

当浏览器中通过具体 ip 进行访问时控制台打印内容:

十一、 自定义 403 处理方案
使用 Spring Security 时经常会看见 403(无权限),默认情况下显示的效果如下:

而在实际项目中可能都是一个异步请求,显示上述效果对于用户就不是特别友好了。Spring Security 支持自定义权限受限。
1 新建类
新建类实现 AccessDeniedHand
@Component
public class MyAccessDeniedHandler implements AccessDeniedHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse
httpServletResponse, AccessDeniedException e) throws IOException,ServletException {
httpServletResponse.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_FORBIDDEN);
httpServletResponse.setHeader("Content-Type","application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = httpServletResponse.getWriter();
out.write("{\"status\":\"error\",\"msg\":\"权限不足,请联系管理员!\"}");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
2 修改配置类
配置类中重点添加异常处理器。设置访问受限后交给哪个对象进行处理。
myAccessDeniedHandler 是在配置类中进行自动注入的。
//异常处理
http.exceptionHandling()
.accessDeniedHandler(myAccessDeniedHandler);
十二、 基于表达式的访问控制
1 access()方法使用
之前学习的登录用户权限判断实际上底层实现都是调用 access(表达式)
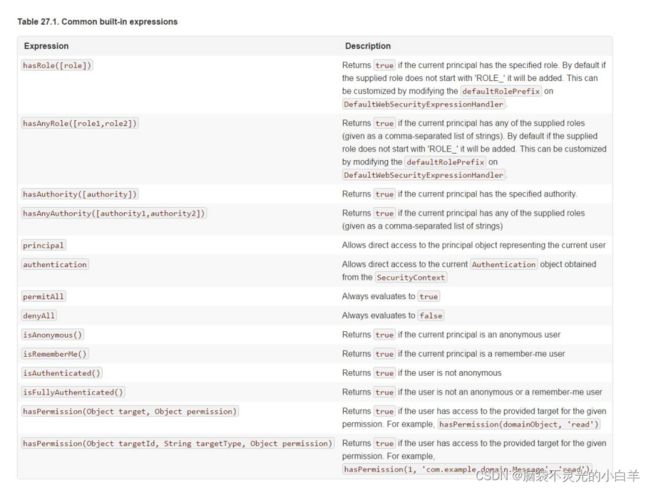
可以通过 access()实现和之前学习的权限控制完成相同的功能。
1.1以 hasRole 和 permitAll 举例
下面代码和直接使用 permitAll()和 hasRole()是等效的。

2 使用自定义方法
虽然这里面已经包含了很多的表达式(方法)但是在实际项目中很有可能出现需要自己自定义逻辑的情况。
判断登录用户是否具有访问当前 URL 权限。
2.1新建接口及实现类
新建接口 com.bjsxt.service.MyService 后新建实现类。
public interface MyService {
boolean hasPermission(HttpServletRequest request, Authentication
authentication);
}
@Component
public class MyServiceImpl implements MyService {
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(HttpServletRequest request, Authentication
authentication) {
Object obj = authentication.getPrincipal();
if(obj instanceof UserDetails){
UserDetails user = (UserDetails) obj;
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities =
user.getAuthorities();
return authorities.contains(new
SimpleGrantedAuthority(request.getRequestURI()));
}
return false;
}
}
2.2修改配置类
在 access 中通过@bean 的 id 名.方法(参数)的形式进行调用配置类中修改如下:
// url 拦截 (授权)
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login.html").access("permitAll")
.antMatchers("/fail.html").permitAll()
.anyRequest().access("@myServiceImpl.hasPermission(request,authentication)");
十三、 基于注解的访问控制
在 Spring Security 中提供了一些访问控制的注解。这些注解都是默认是都不可用的,需要通过@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 进行开启后使用。
如果设置的条件允许,程序正常执行。如果不允许会报 500.

这些注解可以写到 Service 接口或方法上上也可以写到 Controller 或 Controller 的方法上。通常情况下都是写在控制器方法上的,控制接口 URL 是否允许被访问。
1 @Secured
@Secured 是专门用于判断是否具有角色的。能写在方法或类上。
参数要以 ROLE_开头。

1.1实现步骤
1.1.1 开启注解
在 启 动 类 ( 也 可 以 在 配 置 类 等 能 够 扫 描 的 类 上 ) 上 添 加
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
public class MyApp {
public static void main(String [] args){
SpringApplication.run(MyApp.class,args);
}
}
1.1.2 在控制器方法上添加@Secured 注解
在 LoginController 中方法上添加注解
@Secured("abc")
@RequestMapping("/toMain")
public String toMain(){
return "redirect:/main.html";
}
1.1.3 配置类
配置类中方法配置保留最基本的配置即可。
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// 表单认证
http.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") //当发现/login 时认为是登录,需要执行 UserDetailsServiceImpl
.successForwardUrl("/toMain") //此处是 post 请求
.loginPage("/login.html");
// url 拦截
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login.html").permitAll() //login.html 不需要被认证
.anyRequest().authenticated();//所有的请求都必须被认证。必须登录后才能访问。
//关闭 csrf 防护
http.csrf().disable();
}
2 @PreAuthorize/@PostAuthorize
@PreAuthorize 和@PostAuthorize 都是方法或类级别注解。

@PreAuthorize 表示访问方法或类在执行之前先判断权限,大多情况下都是使用这个注解,注解的参数和 access()方法参数取值相同,都是权限表达式。
@PostAuthorize 表示方法或类执行结束后判断权限,此注解很少被使用到。
2.1实现步骤
2.1.1 开启注解
在启动类中开启@PreAuthorize 注解。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class MyApp {
public static void main(String [] args){
SpringApplication.run(MyApp.class,args);
}
}
2.1.2 添加@PreAuthorize
在控制器方法上添加@PreAuthorize,参数可以是任何 access()支持的表达式
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('abc')")
@RequestMapping("/toMain")
public String toMain(){
return "redirect:/main.html";
}
十四、 Remember Me 功能实现
Spring Security 中 Remember Me 为“记住我”功能,用户只需要在登录时添加 remember-me 复选框,取值为 true。Spring Security 会自动把用户信息存储到数据源中,以后就可以不登录进行访问。
1 添加依赖
Spring Security 实 现 Remember Me 功 能 时 底 层 实 现 依 赖 Spring-JDBC,所以需要导入 Spring-JDBC。以后多使用 MyBatis 框架而
很少直接导入 spring-jdbc,所以此处导入 mybatis 启动器同时还需要添加 MySQL 驱动
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.1.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.47version>
dependency>
2 配置数据源
在 application.properties 中配置数据源。请确保数据库中已经存在 security 数据库
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/security
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
3 编写配置
新建 com.bjsxt.config.RememberMeConfig 类,并创建 Bean 对象
@Configuration
public class RememberMeConfig {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Bean
public PersistentTokenRepository getPersistentTokenRepository() {
JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl jdbcTokenRepositoryImpl=new
JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl();
jdbcTokenRepositoryImpl.setDataSource(dataSource);
//自动建表,第一次启动时需要,第二次启动时注释掉
// jdbcTokenRepositoryImpl.setCreateTableOnStartup(true);
return jdbcTokenRepositoryImpl;
}
}
4 修改 SecurityConfig
在 SecurityConfig 中添加 RememberMeConfig 和 UserDetailsService实现类对象,并自动注入。
在 configure 中添加下面配置内容:
http.rememberMe()
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService) //登录逻辑交给哪个对象
.tokenRepository(repository); //持久层对象
5 在客户端页面中添加复选框
在客户端登录页面中添加 remember-me 的复选框,只要用户勾选了复选框下次就不需要进行登录了。
<form action = "/login" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
密码:<input type="text" name="password"/><br/>
<input type="checkbox" name="remember-me" value="true"/> <br/>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/>
</form>
6 有效时间
默认情况下重启项目后登录状态失效了。但是可以通过设置状态有效时间,即使项目重新启动下次也可以正常登录。
//remember Me
http.rememberMe()
.tokenValiditySeconds(120)//单位:秒
.tokenRepository(repository)
.userDetailsService(userDetailsServiceImpl);
十五、 Thymeleaf 中 Spring Security 的使用
Spring Security 可以在一些视图技术中进行控制显示效果。例如:JSP 或 Thymeleaf。在非前后端分离且使用 Spring Boot 的项目中多使用 Thymeleaf 作为视图展示技术。
Thymeleaf 对 Spring Security 的 支 持 都 放 在
thymeleaf-extras-springsecurityX 中,目前最新版本为 5。所以需要在项目中添加此 jar 包的依赖和 thymeleaf 的依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extrasgroupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5artifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
在 html 页面中引入 thymeleaf 命名空间和 security 命名空间
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5">
1 获取属性
可 以 在 html 页 面 中 通 过 sec:authentication="" 获 取UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 中所有 getXXX 的内容,包含父类中的 getXXX 的内容。
根据源码得出下面属性:
name:登录账号名称
principal:登录主体,在自定义登录逻辑中是 UserDetails
credentials:凭证
authorities:权限和角色
details:实际上是 WebAuthenticationDetails 的实例。可以获取
remoteAddress(客户端 ip)和 sessionId(当前 sessionId)
1.1实现步骤:
1.1.1 新建 demo.html
在项目 resources 中新建 templates 文件夹,在 templates 中新建 demo.html 页面
1.1.2 编写 demo.html
在 demo.html 中编写下面内容,测试获取到的值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
登录账号:<span sec:authentication="name">123</span><br/>
登录账号:<span sec:authentication="principal.username">456</span><br/>
凭证:<span sec:authentication="credentials">456</span><br/>
权限和角色:<span sec:authentication="authorities">456</span><br/>
客户端地址:<span sec:authentication="details.remoteAddress">456</span><br/>
sessionId:<span sec:authentication="details.sessionId">456</span><br/>
</body>
</html>
1.1.3 编写控制器
thymeleaf 页面需要控制转发,在控制器类中编写下面方法
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public String demo(){
return "demo";
}
2 权限判断
在 html 页面中可以使用 sec:authorize=”表达式”进行权限控制,判断是否显示某些内容。表达式的内容和 access(表达式)的用法相同。
如果用户具有指定的权限,则显示对应的内容;如果表达式不成立,则不显示对应的元素。
2.1不同权限的用户显示不同的按钮
2.1.1 设置用户角色和权限
设定用户具有 admin,/insert,/delete 权限ROLE_abc 角色
return new User(username,password,
AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin,ROLE_abc,/insert,/de
lete"));
2.1.2 控制页面显示效果
在页面中根据用户权限和角色判断页面中显示的内容
通过权限判断:
<button sec:authorize="hasAuthority('/insert')">新增</button>
<button sec:authorize="hasAuthority('/delete')">删除</button>
<button sec:authorize="hasAuthority('/update')">修改</button>
<button sec:authorize="hasAuthority('/select')">查看</button>
<br/>
通过角色判断:
<button sec:authorize="hasRole('abc')">新增</button>
<button sec:authorize="hasRole('abc')">删除</button>
<button sec:authorize="hasRole('abc')">修改</button>
<button sec:authorize="hasRole('abc')">查看</button>
十六、 退出登录
用户只需要向 Spring Security 项目中发送/logout 退出请求即可。
1 退出实现
实现退出非常简单,只要在页面中添加/logout 的超链接即可。
<a href="/logout">退出登录</a>
为了实现更好的效果,通常添加退出的配置。默认的退出 url 为/logout,退出成功后跳转到/login?logout

如果不希望使用默认值,可以通过下面的方法进行修改。
http.logout()
.logoutUrl("/logout")
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login.html");
2 logout 其他常用配置源码解读
2.1addLogoutHandler(LogoutHandler)
默认是 contextLogoutHandle

默认实例内容

2.2clearAuthentication(boolean)
2.3invalidateHttpSession(boolean)
2.4logoutSuccessHandler(LogoutSuccessHandler)
退出成功处理器。

也 可 以 自 己 进 行 定 义 退 出 成 功 处 理 器 。 只 要 实 现 了 LogoutSuccessHandler 接口。与之前讲解的登录成功处理器和登录失败处理器极其类似。
十七、 Spring Security 中 CSRF
从刚开始学习 Spring Security 时,在配置类中一直存在这样一行代码:http.csrf().disable();如果没有这行代码导致用户无法被认证。这行代码的含义是:关闭 csrf 防护。
1 什么是 CSRF
CSRF(Cross-site request forgery)跨站请求伪造,也被称为“One Click Attack” 或者 Session Riding。通过伪造用户请求访问受信任站点
的非法请求访问。
跨域:只要网络协议,ip 地址,端口中任何一个不相同就是跨域请求。
客户端与服务进行交互时,由于 http 协议本身是无状态协议,所以引入了 cookie 进行记录客户端身份。在 cookie 中会存放 session id用来识别客户端身份的。在跨域的情况下,session id 可能被第三方恶意劫持,通过这个 session id 向服务端发起请求时,服务端会认为这个请求是合法的,可能发生很多意想不到的事情。
2 Spring Security 中 CSRF
从 Spring Security4 开始 CSRF 防护默认开启。默认会拦截请求。进行 CSRF 处理。CSRF 为了保证不是其他第三方网站访问,要求访问时携带参数名为_csrf 值为 token(token 在服务端产生)的内容,如果token 和服务端的 token 匹配成功,则正常访问。
2.1实现步骤
2.1.1 编写控制器方法
编写控制器方法,跳转到 templates 中 login.html 页面。
@GetMapping("/showLogin")
public String showLogin() {
return "login"
}
2.1.2 新建 login.html
在项目 resources 下新建 templates 文件夹,并在文件夹中新建 login.html 页面。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action = "/login" method="post">
<input type="hidden" th:value="${_csrf.token}" name="_csrf"
th:if="${_csrf}"/>
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
2.1.3 修改配置类
在配置类中注释掉 CSRF 防护失效
//关闭 csrf 防护
http.csrf().disable();
练习源码:https://gitee.com/cutelili/Spring-Security
Vue框架和前后端开发
Spring Cloud






