Android R WindowManagerService 添加window过程分析 (一)
有一段时间没有在这边发博客了,之前的笔记都写在有道云笔记上. 使用有道随记还是不错的,但是通常缺乏体系. 后面会将之前的笔记整理总结出来.希望可以坚持下去吧, 加油.
WIndowManagerService的内容相对来说比较庞杂, 需要花费很大气力才能真正理解它. 本篇是从添加window 的角度去分析它, 将它拆分为多个部分,进而层层分析.
WindowManager#addView
通常,我们都是通过WindowManager#addView方法来添加窗口. WindowManager的具体实现类是 WindowManagerImpl , 它的addView方法如下
// @frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/WindowManagerImpl.java
private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance(); // 单例
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
android.util.SeempLog.record_vg_layout(383,params);
applyDefaultToken(params);
// 直接通过mGlobal来处理, 它是WindowManagerGlobal对象
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplayNoVerify(), mParentWindow,
mContext.getUserId());
}
WindowManagerImpl#addView方法直接调用了WindowManagerGlobal#addView方法, WindowManagerGlobal实例是进程单例的.
WindowManagerImpl#addView
此方法的主要逻辑
-
参数检查
-
有parentWindow 时调整子窗口参数, 否则根据配置判断是否启动硬件加速
-
系统属性加载与监听
-
处理view重复添加情况
-
处理 panel window 情况
-
创建ViewRootImpl , 并调用其 setView方法
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params, Display display, Window parentWindow, int userId) { // 参数检查 if (view == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null"); } if (display == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("display must not be null"); } if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams"); } final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params; if (parentWindow != null) {// 处理子窗口参数 parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams); } else { // 根据配置判断是否启动硬件加速 // If there's no parent, then hardware acceleration for this view is // set from the application's hardware acceleration setting. final Context context = view.getContext(); if (context != null && (context.getApplicationInfo().flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0) { wparams.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED; } } ViewRootImpl root; View panelParentView = null; synchronized (mLock) { // Start watching for system property changes. if (mSystemPropertyUpdater == null) { mSystemPropertyUpdater = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { synchronized (mLock) { for (int i = mRoots.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) { mRoots.get(i).loadSystemProperties(); } } } }; SystemProperties.addChangeCallback(mSystemPropertyUpdater); } int index = findViewLocked(view, false); if (index >= 0) { // 已经存在 if (mDyingViews.contains(view)) { // 如果在dying队列,则立即doDie 移除 // Don't wait for MSG_DIE to make it's way through root's queue. mRoots.get(index).doDie(); } else { // 否则重复添加, 跑出异常 throw new IllegalStateException("View " + view + " has already been added to the window manager."); } // The previous removeView() had not completed executing. Now it has. } // If this is a panel window, then find the window it is being // attached to for future reference. if (wparams.type >= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FIRST_SUB_WINDOW && wparams.type <= WindowManager.LayoutParams.LAST_SUB_WINDOW) { final int count = mViews.size(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { if (mRoots.get(i).mWindow.asBinder() == wparams.token) { // sub window使用的是其parent的token panelParentView = mViews.get(i); // 根据token找到其parent view } } } // 创建ViewRootImpl root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display); view.setLayoutParams(wparams); // 将 view, ViewRootImpl , params 存储在 WindowManagerGlobal的相关集合予以保存 mViews.add(view); // ArrayListmViews mRoots.add(root); // ArrayList mParams.add(wparams); // ArrayList mParams // do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things try { root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView, userId); // 开启 ViewRootImpl的工作 } catch (RuntimeException e) { // BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up. if (index >= 0) { removeViewLocked(index, true); } throw e; } } }
ViewRootImpl
ViewRootImpl 类的定义如下, 按注释描述,它是View层次结构的顶部, 实现了View和WindowManager之间所需的协议, 完成了WindowManagerGlobal 的绝大部分内部实现细节.
通过注释知道,它实现了View和WindowManager之间所需的协议, 更确切的说是View与WindowManagerService之间所需的协议.
ViewRootImpl的功能比较庞杂,包括单不限于:
-
Window的添加与删除等(WindowSession#addToDisplay, WindowSession#remove等)
-
处理WMS派发过来的一些Window变化(如 (resized, moved, windowFocusChanged, 在W类实现 IWindow.Stub )
-
View的绘制刷新(包括measure,layout,draw等)
-
input事件处理(keyevent, motion event等)
-
关键信息的管理(如View.AttachInfo, Surface, ViewConfiguration)
-
一些 回调处理 WindowCallbacks, View.AttachInfo.Callbacks
/** * The top of a view hierarchy, implementing the needed protocol between View * and the WindowManager. This is for the most part an internal implementation * detail of {@link WindowManagerGlobal}. * * {@hide} */ @SuppressWarnings({"EmptyCatchBlock", "PointlessBooleanExpression"}) public final class ViewRootImpl implements ViewParent, View.AttachInfo.Callbacks, ThreadedRenderer.DrawCallbacks {
ViewRootImpl#setView
通过WindowManager添加的View, 都对应这个一个ViewRootImpl对象. ViewRootImpl只能持有一个根View(即mView),也是它的parent,都继承自ViewParent. setView大致做了如下工作:
-
一些成员初始化,如 mView , mAttachInfo , params
-
requestLayout, 提前请求一次layout. 在下次VSync信号到来时执行
-
根据attrs判断是否需要InputChannel, 此时创建的InputChannel还是空壳子
-
向WMS addToDisplay添加此窗口,
-
添加窗口的结果处理
-
WindowInputEventReceiver 的创建, 用于接收input事件
-
各种 InputStage的创建等
// @frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java /** * We have one child */ public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView, int userId) { synchronized (this) { if (mView == null) { mView = view; // 根view ... mAttachInfo.mRootView = view; mAttachInfo.mScalingRequired = mTranslator != null; mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale = mTranslator == null ? 1.0f : mTranslator.applicationScale; if (panelParentView != null) { mAttachInfo.mPanelParentWindowToken = panelParentView.getApplicationWindowToken(); } mAdded = true; int res; /* = WindowManagerImpl.ADD_OKAY; */ // Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window // manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving // any other events from the system. requestLayout(); // 在 addToDisplay 之前请求一次layout InputChannel inputChannel = null; if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures & WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) { // 创建input channel inputChannel = new InputChannel(); } mForceDecorViewVisibility = (mWindowAttributes.privateFlags & PRIVATE_FLAG_FORCE_DECOR_VIEW_VISIBILITY) != 0; try { mOrigWindowType = mWindowAttributes.type; mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = true; collectViewAttributes(); adjustLayoutParamsForCompatibility(mWindowAttributes); // mWindowSession 即IWindowSession对象, 在构造方法赋值, 通过WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession()获取 // 添加到WMS, 重点关注参数 mWindow , inputChannel等 res = mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes, getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), userId, mTmpFrame, mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets, mAttachInfo.mDisplayCutout, inputChannel, mTempInsets, mTempControls); setFrame(mTmpFrame); } catch (RemoteException e) {...} ... if (inputChannel != null) { if (mInputQueueCallback != null) { mInputQueue = new InputQueue(); mInputQueueCallback.onInputQueueCreated(mInputQueue); } // 通过inputChannel创建WindowInputEventReceiver, 用于接收input事件 // 具体实现细节都掩藏在类的native方法 mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(inputChannel, Looper.myLooper()); } view.assignParent(this); // 创建InputStage , 并建立各InputStage的连接 // Set up the input pipeline. CharSequence counterSuffix = attrs.getTitle(); mSyntheticInputStage = new SyntheticInputStage(); InputStage viewPostImeStage = new ViewPostImeInputStage(mSyntheticInputStage); InputStage nativePostImeStage = new NativePostImeInputStage(viewPostImeStage, "aq:native-post-ime:" + counterSuffix); InputStage earlyPostImeStage = new EarlyPostImeInputStage(nativePostImeStage); InputStage imeStage = new ImeInputStage(earlyPostImeStage, "aq:ime:" + counterSuffix); InputStage viewPreImeStage = new ViewPreImeInputStage(imeStage); InputStage nativePreImeStage = new NativePreImeInputStage(viewPreImeStage, "aq:native-pre-ime:" + counterSuffix); mFirstInputStage = nativePreImeStage; mFirstPostImeInputStage = earlyPostImeStage; mPendingInputEventQueueLengthCounterName = "aq:pending:" + counterSuffix; /// ... }
mWindowSession 即 IWindowSession 对象, 它通过WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession(). 通过代码可知, 一个进程只会开启一个WindowSession:
// @frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/WindowManagerGlobal.java
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public static IWindowSession getWindowSession() {
synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {
if (sWindowSession == null) {
try {
// Emulate the legacy behavior. The global instance of InputMethodManager was instantiated here.
// TODO(b/116157766): Remove this hack after cleaning up @UnsupportedAppUsage
InputMethodManager.ensureDefaultInstanceForDefaultDisplayIfNecessary();
IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService();
sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession( // 通过WMS 创建一个IWindowSession ,为client端
new IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() {
@Override
public void onAnimatorScaleChanged(float scale) {
ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(scale);
}
});
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
return sWindowSession;
}
}
WMS的openSession方法如下, 创建并返回一个 Session 对象
// @frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
@Override
public IWindowSession openSession(IWindowSessionCallback callback) {
return new Session(this, callback);
}
// @frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Session.java
// session 类是wms端的IWindowSession 实现. 通过注释也可以知道,一个进程对应一个Session对象
/**
* This class represents an active client session. There is generally one
* Session object per process that is interacting with the window manager.
*/
class Session extends IWindowSession.Stub implements IBinder.DeathRecipient {...}
本文主要分析window添加过程,接下来看IWindowSession#addToDisplayAsUser 方法.
Session#addToDisplayAsUser
通过WindowManagerGlobal返回的sWindowSession实际上是WMS创建的Session对象的bp端, 而bn端正是Session对象. 因此在ViewRootImpl通过mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser实际上调用到了Session的addToDisplayAsUser方法, 这通常是一个IPC调用,binder很好的封装了这一切. addToDisplayAsUser 方法相对addToDisplay方法仅仅多了一个 userId 参数, 它们都调用了WMS的addWindow 方法
// @frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Session.java
@Override
public int addToDisplayAsUser(IWindow window, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int viewVisibility, int displayId, int userId, Rect outFrame,
Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets,
DisplayCutout.ParcelableWrapper outDisplayCutout, InputChannel outInputChannel,
InsetsState outInsetsState, InsetsSourceControl[] outActiveControls) {
// mService 是构造传入的WIndowManagerService对象
return mService.addWindow(this, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId, outFrame,
outContentInsets, outStableInsets, outDisplayCutout, outInputChannel,
outInsetsState, outActiveControls, userId);
}
接下来进入WMS#addWindow 方法
WindowManagerService#addWindow
addWindow方法代码较长, 将加锁的部分添加操作折叠后, 结构还是比较清晰:
-
使用mPolicy ( PhoneWindowManager )对象先检查添加权限
-
记录 callingUid/Pid , window类型, 清除调用者身份
-
加锁mGlobalLock , 执行真正的添加过程
-
恢复调用者身份, 返回添加结果
public int addWindow(Session session, IWindow client, int seq, LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility, int displayId, Rect outFrame, Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets, DisplayCutout.ParcelableWrapper outDisplayCutout, InputChannel outInputChannel, InsetsState outInsetsState, InsetsSourceControl[] outActiveControls, int requestUserId) { Arrays.fill(outActiveControls, null); int[] appOp = new int[1]; final boolean isRoundedCornerOverlay = (attrs.privateFlags & PRIVATE_FLAG_IS_ROUNDED_CORNERS_OVERLAY) != 0; // mPolicy 即 PhoneWindowManager 对象, 先检查添加权限 int res = mPolicy.checkAddPermission(attrs.type, isRoundedCornerOverlay, attrs.packageName, appOp); // 注意后面有一个appOp参数 if (res != WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_OKAY) { return res; } WindowState parentWindow = null; final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid(); final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid(); final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); // 清除调用者身份 final int type = attrs.type; // 添加的Window类型 synchronized (mGlobalLock) {...} // 加锁的操作 // 恢复调用者身份 Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId); return res; }
PhoneWindowManager#checkAddPermission
这部分主要是预检查权限:
-
检查type为PRIVATE_FLAG_IS_ROUNDED_CORNERS_OVERLAY的权限
-
检查type是否满足预设范围
- APPLICATION_WINDOW 1 ~ 99
- SUB_WINDOW 1000 ~ 1999
- SYSTEM_WINDOW 2000 ~ 2999
-
对于非Systm Window的, wms 自行处理
-
处理一些非 alert window type的系统窗口
-
处理 alert window
-
在方法中对不同的type给 outAppOp[0] 赋值
@Override public int checkAddPermission(int type, boolean isRoundedCornerOverlay, String packageName, int[] outAppOp) { // 检查设置 PRIVATE_FLAG_IS_ROUNDED_CORNERS_OVERLAY 是否有权限 INTERNAL_SYSTEM_WINDOW if (isRoundedCornerOverlay && mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(INTERNAL_SYSTEM_WINDOW) != PERMISSION_GRANTED) { return ADD_PERMISSION_DENIED; } outAppOp[0] = AppOpsManager.OP_NONE; // type的返回是否满足预设的 // APPLICATION_WINDOW 1 ~ 99 // SUB_WINDOW 1000 ~ 1999 // SYSTEM_WINDOW 2000 ~ 2999 if (!((type >= FIRST_APPLICATION_WINDOW && type <= LAST_APPLICATION_WINDOW) || (type >= FIRST_SUB_WINDOW && type <= LAST_SUB_WINDOW) || (type >= FIRST_SYSTEM_WINDOW && type <= LAST_SYSTEM_WINDOW))) { return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_INVALID_TYPE; } // 非Systm Window的, wms 自行处理 if (type < FIRST_SYSTEM_WINDOW || type > LAST_SYSTEM_WINDOW) { // Window manager will make sure these are okay. return ADD_OKAY; } // 接下来处理一些系统type if (!isSystemAlertWindowType(type)) { // 处理一些非 alert window 的type switch (type) { case TYPE_TOAST: // Only apps that target older than O SDK can add window without a token, after // that we require a token so apps cannot add toasts directly as the token is // added by the notification system. // Window manager does the checking for this. outAppOp[0] = OP_TOAST_WINDOW; return ADD_OKAY; case TYPE_INPUT_METHOD: case TYPE_WALLPAPER: case TYPE_PRESENTATION: case TYPE_PRIVATE_PRESENTATION: case TYPE_VOICE_INTERACTION: case TYPE_ACCESSIBILITY_OVERLAY: case TYPE_QS_DIALOG: case TYPE_NAVIGATION_BAR_PANEL: // The window manager will check these. return ADD_OKAY; } // 其他情况需检查权限 return (mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(INTERNAL_SYSTEM_WINDOW) == PERMISSION_GRANTED) ? ADD_OKAY : ADD_PERMISSION_DENIED; } // 下面处理 alert windows // Things get a little more interesting for alert windows... outAppOp[0] = OP_SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW; final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid(); // system processes will be automatically granted privilege to draw if (UserHandle.getAppId(callingUid) == Process.SYSTEM_UID) { // 系统应用直接拥有权限 return ADD_OKAY; } ApplicationInfo appInfo; try { // 获取 ApplicationInfo appInfo = mPackageManager.getApplicationInfoAsUser( packageName, 0 /* flags */, UserHandle.getUserId(callingUid)); } catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) { appInfo = null; } // 不是 TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY if (appInfo == null || (type != TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY && appInfo.targetSdkVersion >= O)) { // 通过注释可知在 > 8 , 需要持有 INTERNAL_SYSTEM_WINDOW 权限来添加非TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY的alert window /** * Apps targeting >= {@link Build.VERSION_CODES#O} are required to hold * {@link android.Manifest.permission#INTERNAL_SYSTEM_WINDOW} (system signature apps) * permission to add alert windows that aren't * {@link android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams#TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY}. */ return (mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(INTERNAL_SYSTEM_WINDOW) == PERMISSION_GRANTED) ? ADD_OKAY : ADD_PERMISSION_DENIED; } // check if user has enabled this operation. SecurityException will be thrown if this app // has not been allowed by the user. The reason to use "noteOp" (instead of checkOp) is to // make sure the usage is logged. final int mode = mAppOpsManager.noteOpNoThrow(outAppOp[0], callingUid, packageName, null /* featureId */, "check-add"); switch (mode) { case AppOpsManager.MODE_ALLOWED: case AppOpsManager.MODE_IGNORED: // although we return ADD_OKAY for MODE_IGNORED, the added window will // actually be hidden in WindowManagerService return ADD_OKAY; case AppOpsManager.MODE_ERRORED: // Don't crash legacy apps if (appInfo.targetSdkVersion < M) { return ADD_OKAY; } return ADD_PERMISSION_DENIED; default: // in the default mode, we will make a decision here based on // checkCallingPermission() return (mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW) == PERMISSION_GRANTED) ? ADD_OKAY : ADD_PERMISSION_DENIED; }}
alert window 的type 包含如下
/**
* Return true if the window type is an alert window.
*
* @param type The window type.
* @return If the window type is an alert window.
* @hide
*/
public static boolean isSystemAlertWindowType(@WindowType int type) {
switch (type) {
case TYPE_PHONE:
case TYPE_PRIORITY_PHONE:
case TYPE_SYSTEM_ALERT:
case TYPE_SYSTEM_ERROR:
case TYPE_SYSTEM_OVERLAY:
case TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY:
return true;
}
return false;
}
接下来分段来分析addWindow 加锁部分的过程
WindowManagerService#addWindow part1
这部分主要处理一些预检查,如Display, type:
synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
if (!mDisplayReady) { // Display 还没有ready
throw new IllegalStateException("Display has not been initialialized");
}
// 通过displayId 获取一个 DisplayContent. 通常一个Display会对应一个 DisplayContent
final DisplayContent displayContent = getDisplayContentOrCreate(displayId, attrs.token);
if (displayContent == null) {
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add window to a display that does "
+ "not exist: %d. Aborting.", displayId);
return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_INVALID_DISPLAY;
}
if (!displayContent.hasAccess(session.mUid)) { // displayContent访问权限判断
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR,
"Attempted to add window to a display for which the application "
+ "does not have access: %d. Aborting.", displayId);
return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_INVALID_DISPLAY;
}
if (mWindowMap.containsKey(client.asBinder())) { // 判断是否重复添加
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Window %s is already added", client);
return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_DUPLICATE_ADD;
}
if (type >= FIRST_SUB_WINDOW && type <= LAST_SUB_WINDOW) { // 处理子窗口
// 子窗口使用了父窗口的token , 通过此token查找父窗口
parentWindow = windowForClientLocked(null, attrs.token, false);
if (parentWindow == null) { // 子窗口的父窗口不存在
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add window with token that is not a window: "
+ "%s. Aborting.", attrs.token);
return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_SUBWINDOW_TOKEN;
}
if (parentWindow.mAttrs.type >= FIRST_SUB_WINDOW
&& parentWindow.mAttrs.type <= LAST_SUB_WINDOW) { // 子窗口的父窗口不能是子窗口.
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add window with token that is a sub-window: "
+ "%s. Aborting.", attrs.token);
return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_SUBWINDOW_TOKEN;
}
}
if (type == TYPE_PRIVATE_PRESENTATION && !displayContent.isPrivate()) { // 向非private的Display添加TYPE_PRIVATE_PRESENTATION
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR,
"Attempted to add private presentation window to a non-private display. "
+ "Aborting.");
return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
if (type == TYPE_PRESENTATION && !displayContent.getDisplay().isPublicPresentation()) { // 向非suitable 的Display添加TYPE_PRESENTATION
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR,
"Attempted to add presentation window to a non-suitable display. "
+ "Aborting.");
return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_INVALID_DISPLAY;
}
int userId = UserHandle.getUserId(session.mUid);
if (requestUserId != userId) { // userId检查过
try {
mAmInternal.handleIncomingUser(callingPid, callingUid, requestUserId,
false /*allowAll*/, ALLOW_NON_FULL, null, null);
} catch (Exception exp) {
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Trying to add window with invalid user=%d",
requestUserId);
return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_INVALID_USER;
}
// It's fine to use this userId
userId = requestUserId;
}
...
}
子窗口使用了父窗口的token , 通过此token查找父窗口 . 可以发现token是Binder对象
final WindowState windowForClientLocked(Session session, IBinder client, boolean throwOnError) {
WindowState win = mWindowMap.get(client); // 通过token取出 mWindowMap 中的 WindowState
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG_WM, "Looking up client " + client + ": " + win);
if (win == null) {
if (throwOnError) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Requested window " + client + " does not exist");
}
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Failed looking up window session=%s callers=%s", session,
Debug.getCallers(3));
return null;
}
if (session != null && win.mSession != session) {
if (throwOnError) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Requested window " + client + " is in session "
+ win.mSession + ", not " + session);
}
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Failed looking up window session=%s callers=%s", session,
Debug.getCallers(3));
return null;
}
return win;
}
WindowManagerService#addWindow part2
这一部分主要处理token相关的, 总结一下:
-
DisplayContent管理着一个Display上所有的WindowToken, 存储在mTokenMap , 以客户端的token (IBinder对象) 为键, WindowToken对象为值
-
客户端的token对应着WMS内部的WindowToken. 对于应用窗口而言,它的token是在ActivityRecord中创建的IApplicationToken.Stub对象, 而对应一些没有token的则直接使用IWindow的bp对象
-
Sub Window 通常共用其parent window的token, 通过此token可以获取一个对应的WindowToken
-
创建应用类型的窗口一定需要WindowToken
-
创建某些系统窗口, 如果WindowToken为null, 系统会自动创建一个WindowToken. 例如 TYPE_SYSTEM_ALERT
-
对于应用类型的窗口,它的WindowToken实际上是ActivityRecord(它是WindowToken的子类), 可以通过token.asActivityRecord()来获取此ActivityRecord
-
检查添加的一些系统窗口的type与WindowToken对应的type的一致性
synchronized (mGlobalLock) { .../ 一些检查 ActivityRecord activity = null; final boolean hasParent = parentWindow != null; // Use existing parent window token for child windows since they go in the same token // as there parent window so we can apply the same policy on them. WindowToken token = displayContent.getWindowToken( // 有parent使用parent的,否则使用自身token来获取WindowToken hasParent ? parentWindow.mAttrs.token : attrs.token); // If this is a child window, we want to apply the same type checking rules as the // parent window type. 有parent使用parent的 type 为 rootType final int rootType = hasParent ? parentWindow.mAttrs.type : type; boolean addToastWindowRequiresToken = false; // toast是否需要权限 if (token == null) { // 没有token // 非privileged应用是否可以创建token if (!unprivilegedAppCanCreateTokenWith(parentWindow, callingUid, type, rootType, attrs.token, attrs.packageName)) { return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_APP_TOKEN; } final IBinder binder = attrs.token != null ? attrs.token : client.asBinder(); token = new WindowToken(this, binder, type, false, displayContent, session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow, isRoundedCornerOverlay); } else if (rootType >= FIRST_APPLICATION_WINDOW && rootType <= LAST_APPLICATION_WINDOW) { // 应用类型 activity = token.asActivityRecord(); // 返回 ActivityRecord if (activity == null) { // 返回null, 说明不是应用类型的token ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add window with non-application token " + ".%s Aborting.", token); return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_NOT_APP_TOKEN; } else if (activity.getParent() == null) { // 对于app token, 此处的parent 是 Task ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add window with exiting application token " + ".%s Aborting.", token); return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_APP_EXITING; } else if (type == TYPE_APPLICATION_STARTING && activity.startingWindow != null) { // 是starting window ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add starting window to token with already existing" + " starting window"); return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_DUPLICATE_ADD; } } else if (rootType == TYPE_INPUT_METHOD) { if (token.windowType != TYPE_INPUT_METHOD) { // type不一致 ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add input method window with bad token " + "%s. Aborting.", attrs.token); return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_APP_TOKEN; } } else if (rootType == TYPE_VOICE_INTERACTION) { if (token.windowType != TYPE_VOICE_INTERACTION) { ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add voice interaction window with bad token " + "%s. Aborting.", attrs.token); return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_APP_TOKEN; } } else if (rootType == TYPE_WALLPAPER) { if (token.windowType != TYPE_WALLPAPER) { ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add wallpaper window with bad token " + "%s. Aborting.", attrs.token); return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_APP_TOKEN; } } else if (rootType == TYPE_ACCESSIBILITY_OVERLAY) { if (token.windowType != TYPE_ACCESSIBILITY_OVERLAY) { ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add Accessibility overlay window with bad token " + "%s. Aborting.", attrs.token); return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_APP_TOKEN; } } else if (type == TYPE_TOAST) { // 处理 toast , 检查添加toast是否需要 token // Apps targeting SDK above N MR1 cannot arbitrary add toast windows. addToastWindowRequiresToken = doesAddToastWindowRequireToken(attrs.packageName, callingUid, parentWindow); if (addToastWindowRequiresToken && token.windowType != TYPE_TOAST) { ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add a toast window with bad token " + "%s. Aborting.", attrs.token); return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_APP_TOKEN; } } else if (type == TYPE_QS_DIALOG) { if (token.windowType != TYPE_QS_DIALOG) { ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add QS dialog window with bad token " + "%s. Aborting.", attrs.token); return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_BAD_APP_TOKEN; } } else if (token.asActivityRecord() != null) { // 不能在其他系统type上使用app token ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Non-null activity for system window of rootType=%d", rootType); // It is not valid to use an app token with other system types; we will // instead make a new token for it (as if null had been passed in for the token). attrs.token = null; token = new WindowToken(this, client.asBinder(), type, false, displayContent, session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow); } /// ... }
unprivilegedAppCanCreateTokenWith
这个方法检查非特权应用是否可以创建WindowToken
private boolean unprivilegedAppCanCreateTokenWith(WindowState parentWindow,
int callingUid, int type, int rootType, IBinder tokenForLog, String packageName) {
if (rootType >= FIRST_APPLICATION_WINDOW && rootType <= LAST_APPLICATION_WINDOW) { // 创建应用类型的窗口一定需要WindowToken
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add application window with unknown token "
+ "%s. Aborting.", tokenForLog);
return false;
}
if (rootType == TYPE_INPUT_METHOD) {
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add input method window with unknown token "
+ "%s. Aborting.", tokenForLog);
return false;
}
if (rootType == TYPE_VOICE_INTERACTION) {
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR,
"Attempted to add voice interaction window with unknown token "
+ "%s. Aborting.", tokenForLog);
return false;
}
if (rootType == TYPE_WALLPAPER) {
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add wallpaper window with unknown token "
+ "%s. Aborting.", tokenForLog);
return false;
}
if (rootType == TYPE_QS_DIALOG) {
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add QS dialog window with unknown token "
+ "%s. Aborting.", tokenForLog);
return false;
}
if (rootType == TYPE_ACCESSIBILITY_OVERLAY) {
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR,
"Attempted to add Accessibility overlay window with unknown token "
+ "%s. Aborting.", tokenForLog);
return false;
}
if (type == TYPE_TOAST) { // 这里处理 Toast是否需要token问题,
// Apps targeting SDK above N MR1 cannot arbitrary add toast windows.
if (doesAddToastWindowRequireToken(packageName, callingUid, parentWindow)) {
ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Attempted to add a toast window with unknown token "
+ "%s. Aborting.", tokenForLog);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
doesAddToastWindowRequireToken
这个方法检查添加toast是否需要WindowToken
private boolean doesAddToastWindowRequireToken(String packageName, int callingUid,
WindowState attachedWindow) {
// Try using the target SDK of the root window
if (attachedWindow != null) { // 有父窗口且是应用窗口, 并且sdk >= O
return attachedWindow.mActivityRecord != null
&& attachedWindow.mActivityRecord.mTargetSdk >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O;
} else {
// Otherwise, look at the package
try {
ApplicationInfo appInfo = mContext.getPackageManager()
.getApplicationInfoAsUser(packageName, 0,
UserHandle.getUserId(callingUid));
if (appInfo.uid != callingUid) { // 检查uid的一致性
throw new SecurityException("Package " + packageName + " not in UID "
+ callingUid);
}
if (appInfo.targetSdkVersion >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) { // 大于O ,需要
return true;
}
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
/* ignore */
}
}
return false;
}
WindowManagerService#addWindow part3
下面一部分主要是涉及WindowState的一部分, 在WMS内部使用WindowState来表示一个窗口,存储了Window相关的信息, 而实际上用来绘制使用的是Surface.
这部分的主要工作有:
-
创建 WindowState 对象, 用于管理窗口的各种信息
-
displayPolicy调整客户端传过来的params参数, -使用策略执行诸如确保特定类型的窗口无法获得输入焦点之类的操作
-
displayPolicy 检查窗口是否能被添加到系统. 如对于某一个Display,只能添加一个StatusBar
-
判断是否要创建 InputChannel , 这个跟window的input事件息息相关
-
win.attach() 回调 session的 windowAddedLocked , 创建SurfaceSession,这个跟创建Surface相关
-
win保存到mWindowMap 及处理 app op 状态 等
synchronized (mGlobalLock) { ... // ① 根据以上的信息创建WindowState. client是IWindow的bp对象, token是WindowToken对象 final WindowState win = new WindowState(this, session, client, token, parentWindow, appOp[0], seq, attrs, viewVisibility, session.mUid, userId, session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow); if (win.mDeathRecipient == null) { // win注册死亡监听失败时mDeathRecipient为null, 说明客户端已经挂了 // Client has apparently died, so there is no reason to // continue. ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Adding window client %s" + " that is dead, aborting.", client.asBinder()); return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_APP_EXITING; } if (win.getDisplayContent() == null) { // 此处内部通过WindowToken 来获取dc ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Adding window to Display that has been removed."); return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_INVALID_DISPLAY; } // 获取 dc 中创建的 DisplayPolicy final DisplayPolicy displayPolicy = displayContent.getDisplayPolicy(); // ② 清理来自客户端的布局参数。 使用策略执行诸如确保特定类型的窗口无法获得输入焦点之类的操作。 displayPolicy.adjustWindowParamsLw(win, win.mAttrs, callingPid, callingUid); // 检查窗口是否能被添加到系统. 如对于某一个Display,只能添加一个StatusBar res = displayPolicy.validateAddingWindowLw(attrs, callingPid, callingUid); if (res != WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_OKAY) { return res; } // ③ 判断是否要创建 InputChannel final boolean openInputChannels = (outInputChannel != null && (attrs.inputFeatures & INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0); if (openInputChannels) { // 开启用于接收input事件 win.openInputChannel(outInputChannel); } // If adding a toast requires a token for this app we always schedule hiding // toast windows to make sure they don't stick around longer then necessary. // We hide instead of remove such windows as apps aren't prepared to handle // windows being removed under them. // // If the app is older it can add toasts without a token and hence overlay // other apps. To be maximally compatible with these apps we will hide the // window after the toast timeout only if the focused window is from another // UID, otherwise we allow unlimited duration. When a UID looses focus we // schedule hiding all of its toast windows. if (type == TYPE_TOAST) { if (!displayContent.canAddToastWindowForUid(callingUid)) { // 根据uid判断是否能够添加toast ProtoLog.w(WM_ERROR, "Adding more than one toast window for UID at a time."); return WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_DUPLICATE_ADD; } // Make sure this happens before we moved focus as one can make the // toast focusable to force it not being hidden after the timeout. // Focusable toasts are always timed out to prevent a focused app to // show a focusable toasts while it has focus which will be kept on // the screen after the activity goes away. if (addToastWindowRequiresToken || (attrs.flags & LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE) == 0 || displayContent.mCurrentFocus == null || displayContent.mCurrentFocus.mOwnerUid != callingUid) { // 添加toast超时 mH.sendMessageDelayed( mH.obtainMessage(H.WINDOW_HIDE_TIMEOUT, win), win.mAttrs.hideTimeoutMilliseconds); } } // From now on, no exceptions or errors allowed! res = WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_OKAY; if (mUseBLAST) { // Whether the system should use BLAST for ViewRootImpl res |= WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_FLAG_USE_BLAST; } if (sEnableTripleBuffering) { // 根据属性 ro.sf.disable_triple_buffer 获取 res |= WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_FLAG_USE_TRIPLE_BUFFERING; } if (displayContent.mCurrentFocus == null) { // dc的focus窗口为null, 将当前win添加到mWinAddedSinceNullFocus displayContent.mWinAddedSinceNullFocus.add(win); } if (excludeWindowTypeFromTapOutTask(type)) { // 将一些特殊type的win添加到mTapExcludedWindows displayContent.mTapExcludedWindows.add(win); } win.attach(); // ④ 回调 session的 windowAddedLocked mWindowMap.put(client.asBinder(), win); // 以IWindow的bp端为key, 将win 保存到mWindowMap win.initAppOpsState(); // ⑤ 处理 app op 状态 final boolean suspended = mPmInternal.isPackageSuspended(win.getOwningPackage(), UserHandle.getUserId(win.getOwningUid())); win.setHiddenWhileSuspended(suspended); final boolean hideSystemAlertWindows = !mHidingNonSystemOverlayWindows.isEmpty(); win.setForceHideNonSystemOverlayWindowIfNeeded(hideSystemAlertWindows); final ActivityRecord tokenActivity = token.asActivityRecord(); if (type == TYPE_APPLICATION_STARTING && tokenActivity != null) { // 处理 startingWindow tokenActivity.startingWindow = win; ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_STARTING_WINDOW, "addWindow: %s startingWindow=%s", activity, win); } }
WindowManagerService#addWindow part4
这部分是最后的收尾的一部分, 主要工作如下
-
将此WindowState存储到WindowToken , 与此token相关的窗口可以很好的管理起来
-
焦点窗口的更新 与 input window的更新, 使input事件可以正确的分发到目标窗口
-
处理IME相关的变化及计算新的IME window
-
子窗口层级更新 , 准备窗口动画
-
DisplayContent orientation 改变处理
addWindow(... ) {... synchronized (mGlobalLock) { ...// 接上 boolean imMayMove = true; win.mToken.addWindow(win); // ① 将win存储到WindowToken中 displayPolicy.addWindowLw(win, attrs); // 使用displayPolicy处理一些window的inset if (type == TYPE_INPUT_METHOD) { // 输入法窗口 displayContent.setInputMethodWindowLocked(win); imMayMove = false; } else if (type == TYPE_INPUT_METHOD_DIALOG) { displayContent.computeImeTarget(true /* updateImeTarget */); imMayMove = false; } else { if (type == TYPE_WALLPAPER) { // 处理 wallpaper displayContent.mWallpaperController.clearLastWallpaperTimeoutTime(); displayContent.pendingLayoutChanges |= FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_WALLPAPER; } else if ((attrs.flags & FLAG_SHOW_WALLPAPER) != 0) { displayContent.pendingLayoutChanges |= FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_WALLPAPER; } else if (displayContent.mWallpaperController.isBelowWallpaperTarget(win)) { // If there is currently a wallpaper being shown, and // the base layer of the new window is below the current // layer of the target window, then adjust the wallpaper. // This is to avoid a new window being placed between the // wallpaper and its target. displayContent.pendingLayoutChanges |= FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_WALLPAPER; } } final WindowStateAnimator winAnimator = win.mWinAnimator; winAnimator.mEnterAnimationPending = true; winAnimator.mEnteringAnimation = true; // 准备开启动画 // Check if we need to prepare a transition for replacing window first. if (activity != null && activity.isVisible() && !prepareWindowReplacementTransition(activity)) { // 处理 replacing window // If not, check if need to set up a dummy transition during display freeze // so that the unfreeze wait for the apps to draw. This might be needed if // the app is relaunching. prepareNoneTransitionForRelaunching(activity); // 处理activity relaunching } if (displayPolicy.getLayoutHint(win.mAttrs, token, outFrame, outContentInsets, outStableInsets, outDisplayCutout)) { res |= WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_FLAG_ALWAYS_CONSUME_SYSTEM_BARS; } outInsetsState.set(win.getInsetsState(), win.isClientLocal()); if (mInTouchMode) { res |= WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_FLAG_IN_TOUCH_MODE; } if (win.mActivityRecord == null || win.mActivityRecord.isClientVisible()) { res |= WindowManagerGlobal.ADD_FLAG_APP_VISIBLE; } displayContent.getInputMonitor().setUpdateInputWindowsNeededLw(); // mUpdateInputWindowsNeeded = true boolean focusChanged = false; if (win.canReceiveKeys()) { // 如果可以接收key事件 // 更新focus window , 注意mode是UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_ASSIGN_LAYERS, updateInputWindows 为false focusChanged = updateFocusedWindowLocked(UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_ASSIGN_LAYERS, false /*updateInputWindows*/); if (focusChanged) { imMayMove = false; } } if (imMayMove) { // 重新计算 ime window displayContent.computeImeTarget(true /* updateImeTarget */); } // Don't do layout here, the window must call // relayout to be displayed, so we'll do it there. win.getParent().assignChildLayers(); // if (focusChanged) { // 焦点改变, 设置当前input 焦点 displayContent.getInputMonitor().setInputFocusLw(displayContent.mCurrentFocus, false /*updateInputWindows*/); } displayContent.getInputMonitor().updateInputWindowsLw(false /*force*/); // 更新 input window 信息 ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ADD_REMOVE, "addWindow: New client %s" + ": window=%s Callers=%s", client.asBinder(), win, Debug.getCallers(5)); if (win.isVisibleOrAdding() && displayContent.updateOrientation()) { // 处理 orientation变化 displayContent.sendNewConfiguration(); } getInsetsSourceControls(win, outActiveControls); } Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId); return res; }
对于part3与part4 细节较多, 在后面另外开篇分析.
总结
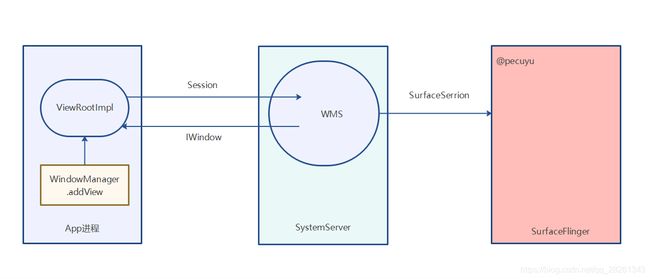
本篇大致分析了客户端添加窗口的过程, 从WindowManager的addView 到Session的addToDisplay, 再到WMS的addWindow 整个脉络. 这个过程通常涉及两个进程, 客户端和SystemServer进程. 客户端通过系统提供的WindowManager API请求相关服务, 在addWinow过程中, 客服端向SystemServer进程的WMS传递了一个IWindow参数, 它是一个Binder对象,可以看成是向WMS注册了一个回调,这个回调是具有跨进程的能力的. 因此, 当客户端的窗口有改变的时候, WMS则可以通过此IWindow对象回调改变(如window focus改变).
添加窗口涉及的细节比较多, 诸如建立客户端与SystemServer的input channel , 使得客户端能够收到相关input事件. 还有窗口的焦点以及窗口的层级问题, 窗口动画等,这些设涉及到更细节的部分, 留待后续分析
后记:
前人栽树后人乘凉. 有许多前辈之前已经深入分析了WMS, 我们应该吸取他们书籍的精髓,站在更高的层次去理解WMS. 以下著作值得拜读,感谢相关作者的付出:
深入理解Android 卷三
Android内核剖析
深入理解Android内核设计思想
后续将文章都托管到gitee上的仓库 Android Notes