C#语言入门详解13-19
文章目录
- 十三、十四、十五、十六、表达式,语句详解
-
- 框架
- 表达式的定义
- 各类表达式的概览
- 语句的定义
- 语句详解
-
- 声明语句
- 表达式语句
- 块语句
- 选择(判断、分支)语句
- try语句
- 迭代语句
- 跳转语句
- 十七、字段,属性,索引器,常量
-
- 字段
- 属性
- 索引器
- 常量
- 十八传值/输出/引用/数组/具名/可选参数,扩展方法
-
- 值参数,也叫传值参数
- 引用参数
- 输出参数
- 数组参数
- 具名参数
- 可选参数
- 扩展方法(this参数)
- 总结
- 十九、委托详解--难度300!
-
- 什么是委托
- 委托的声明(自定义委托)
- 委托的使用
-
- 多播委托:指的是一个委托内部封装这不止一个方法。实例:
- 隐式异步调用
- 适时使用接口取代委托的使用()
十三、十四、十五、十六、表达式,语句详解
框架
- 表达式的定义
- 各类表达式的概览
- 语句的定义
- 语句详解
表达式的定义
什么是表达式?
- 未来想要成为专家,并设计一门语言的时候,可参考这本书
- 表达式、命令、声明是任何一门编程语言的基本组件,表达式是其中之一。表达式是任何一门编程语言的核心组件。
- 表达式是一种语法实体(比如方法(数据加工厂,通过参数把数据原料传进加工厂,加工厂加工完数据通过返回值讲加工的结果交还给你)、变量(存储一个值)),表达式语法实体的功能就是求值,结果只可能有两个,要么成功要么失败,成功会产生一个产出值,失败会得到一个终值。
- 表达式是最小的算法元素。
C#语言是如何定义表达式的:
C#语言的表达式是由一个或多个操作数与0个或多个操作符组成的一个序列
int x = 10;//这里int是操作符,x是操作数,最后返回value,也就是x变量的值
Form fo = new Form();//这里返回的是object
Action myAction = new Action[Console.WriteLine];//这里是委托,返回一个方法,模仿的C、C++的函数指针功能
System.Windows.Forms.Form myForm = new Form();//这里System.Windows就是一个名称空间表达式,.为操作符,返回一个namespace
C#语言中表达式有可能长什么样子:C#语言表达式有可能是由字面值组成的,也有可能是方法调用组成的,也有可能是由操作符和操作数组成的,或者就是一个简单的名字(变量或类型的成员,也有可能是方法的参数,也有可能是名称空间或类型名)
//由字面值参与构成表达式
int x;
x = 100;//100是字面值
string name;
name = "Mr.Okey"//"Mr.Okey"就是一个字面值
//函数调用参与构成表达式
double x = Math.Pow(2,3);//这里Math.Pow(2,3)就是函数调用表达式
//由操作符和操作数构成表达式
int x = 2 + 3;//这里2+3就是,2,3为操作数,+为操作符
//由变量名构成的表达式
int x = 100;
int y;
y = x;//这一句就是由变量名构成的表达式
//由类型名构成的表达式
Type myType = typeof(Int64);//这里typeof是操作符,Int64是操作数,是个类型的名字,Int64本身就是一个表达式
Console.WriteLine(myType.FullName);
各类表达式的概览

凡是能够通过运算得到值的都是表达式,通常把表达式能得到的值的数据类型叫做表达式的数据类型
3<5就是一个bool类型的表达式。
- 成员访问表达式,它的数据类型是不一定的,根据你所访问的这个成员的数据类型决定。
- 由方法调用操作符组成的表达式类型也不一定,取决于这个方法的返回值类型
由元素访问操作符组成的表达式取决于这个集合元素的类型
x++和x–表达式的数据类型和操作数的数据类型是一致的,注意表达式的值和操作数的值的区别,相对于++x和–x
new表达式的数据类型就是创建的实例的数据类型
typrof操作符返回值类型是固定的,就是type类型
default就是你操作的数据类型
cheaked和unchecked与操作数的类型一致
delegate、sizeof、->、&x、*x研究这几个操作符的返回值意义不大
+、-、~与操作数数据类型一致
!返回值为bool类型
(T)x数据类型就是你要转换去的那个数据类型
await异步再讲
&、^、|与操作数数据类型一致
var x = 5 > 3 ? 2 : 3.0;
Console.WriteLine(x);//x=2
Consolw.WriteLine(x.GetType().FullName);//这里2是double类型
赋值操作符的返回值类型就是赋值符号左边这个变量所拿到的值
int x = 100;
int y;
Console.WriteLine(y=x);//100
Console.WriteLine((y=x).GteType().FullName);//System.Int32
Console.WriteLine(“Hello,World!”);这一条语句里面有几个表达式呢?
有两个,第一个是Console.WriteLine,他拿到的是一个方法组,(“Hello,World!”)在这个方法组里利用重载决策出一个最合适的方法进行调用
Action a = delegate(){Console.WriteLine("Hello,World!")};
a();
这里delegate(){Console.WriteLine("Hello,World!")}就是一个匿名方法表达式,其返回值是一个委托
myForm.Text = "Hello";//这里执行顺序为先执行myForm.Text得到属性,在执行赋值
myForm.ShowDialog();
An event access:访问某个对象的事件,这也是一个表达式
namespace ConsoleApp14
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Form myForm = new Form();
myForm.Text = "Hello";
//这里myForm.Load是访问事件,访问事件也是一个表达式
myForm.Load += MyForm_Load;//如果Load事件发生,则刷新Tite
myForm.ShowDialog();
}
private static void MyForm_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Form form = sender as Form;//用柔和的方法讲object的sender转化为Form类型
if (form == null)
{
return;
}
form.Text = "New Title";
}
}
}
语句的定义
广义的定义:
在计算机编程学科范畴里,语句是命令式编程语言(大部分是高级语言如C、C++、C#)中最小的独立元素,语句也是一种语法实体,任何一种语法实体都有自己的功能,语句的功能为表达一些将被执行的动作,一个action对应着语句中的一个表达式的动作。编程就是使用语句编写程序,语句还有自己的内部组件(表达式)
- 指令对应着CPU可以直接执行的动作
- 贴近人类思维的是高级语言,借助编辑器将高级语言编译成低级语言,这样CPU就能读懂了。贴近机器思维的是低级语言

下面演示C语言代码如何查看编译的汇编语言代码: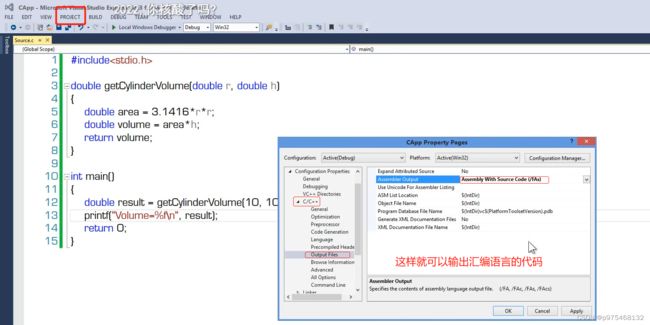

这里就是c语言经过汇编后生成的汇编语言的代码。
下面是C#语言项目查看生成的汇编语言代码:

搜索Developer Command Prompt应用

il是中间语言,dasm叫反编译
这个工具就是用来帮助我们查看C#语言编译好了之后的低级语言代码的。
C#语言中的定义

程序当中语句所执行的顺序叫做控制流或执行流,程序编完语句不在变,但是控制流是可能变的;
在C#语言中,语句只可能出现在函数体里面,字段声明在类体里,不是语句。
namespace ConsoleApp15
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string input = Console.ReadLine();
try
{
double score = double.Parse(input);
if (score > 60)
{
Console.WriteLine("Pass!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed!");
}
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("Not a number.");
}
}
}
}
并不是所有以分号结尾的都是语句
using 名称空间;不是语句,叫做using指令。类的字段声明也不是语句。
语句详解
语句分三类:标签语句、声明语句、嵌入式语句。

横线以上的语句是要求初学者熟练掌握的。

这种嵌套在其他语句里面的语句叫做嵌入式语句
声明语句
局部变量声明、局部常量声明
int x = 100;//在声明变量的同时追加了初始化器
和
int x;
x = 100;//这种叫做赋值操作
不是一回事 ,
数组初始化器:int[] myArray = {1,2,3};//{}叫做数组初始化器。
表达式语句
有些表达式是可以作为语句使用的
下列表达式可以作为语句:
Console.WriteLine("Hello!");//方法调用表达式
new Form();//对象创建表达式
int x;
x = 100;//赋值语句
x++;
x--;
++x;
--x;
在编写方法时,要注意专一性:一件方法只做一件事情
块语句
如何判断一对花括号是不是语句?
块语句是语句,而语句只能出现在方法体里面,在方法体里看到花括号就是块语句
这里演示一下标签语句:
所谓标签语句,就是一句语句前面加上一个标签,标签就是一个标识符,标签的命名规范和变量的一样,只是前面不用加数据类型
namespace ConsoleApp16
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
{
hello: Console.WriteLine("Hello!");
goto hello;//会陷入循环
}//编译器永远把块语句当作一条语句看待,无论块语句里面容纳了多少子语句
}
}
}
**小技巧:**有时候在程序之间呢,开始花括号和结束花括号没有在同一个屏幕里,我们需要上下的去跳动,如果我想在两个花括号之间跳转的话,可以按快捷键”Ctrl+},这样光标会在两个花括号之间跳动。
选择(判断、分支)语句

代码的逻辑优化叫做代码的重构。
else if语句其实就是对if-else语句的整理(嵌入式语句部分如果只有一条语句的话可以省略{})
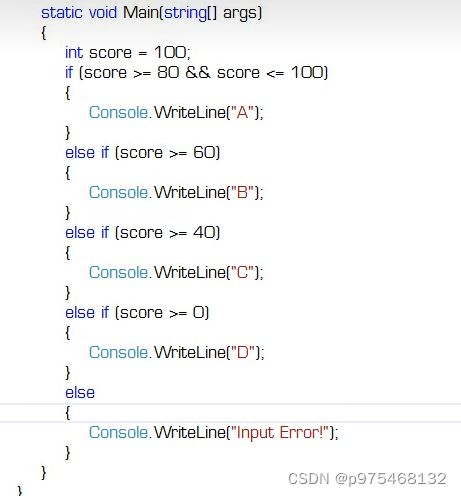
switch里面表达式为整数类型/bool类型/字符类型/字符串类型/枚举类型/可空类型,没有浮点类型,不过现在可以了,连类都可以使用,会调用静态方法Equals(),进行深度比较

case后面必须跟一个常量值
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//需求:80-100->A;60-79->B;40-59->C;0-39->D;其它->Error.
double score = 100;
switch (score/10)
{
case 10:
if (score == 100)
{
goto case 8;
}
else
{
goto default;
}
case 9:
case 8:
Console.WriteLine("A");
break;
case 7:
case 6:
Console.WriteLine("B");
break;
case 5:
case 4:
Console.WriteLine("C");
break;
case 3:
case 2:
case 1:
case 0:
Console.WriteLine("D");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Error!");
break;
}
}
}
}
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Level myLevel = Level.High;
switch (myLevel)
{
case Level.High:
break;
case Level.Mid:
break;
case Level.Low:
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
enum Level
{
High,
Mid,
Low
}
}
sw+Tab+Tab+my+Enter+Enter
try语句
机制为:尝试执行一个语句块,如果在这个语句块中发生了异常,那么try语句就会使用他的catch子句抓住这个异常,然后对捕捉到的异常分门别类进行处理,try语句还可以带有一个finally子句,它的作用是不论在try执行这个语句块时是否发生异常,这个finally子句最终都会执行。

当有多个catch子句,只能执行其中一个

catch子句有两种类型:一种是通用类型,捕捉所有异常;另一类是捕捉特定异常。

捕捉通用异常:
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator ca = new Calculator();
int result = ca.Add("99999999999999", "200");
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
}
class Calculator
{
public int Add(string str1, string str2)
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
try
{
a = int.Parse(str1);
b = int.Parse(str2);
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("Your argument(s) have error.");
}
int result = a + b;
return result;
}
}
}
捕捉特定异常:
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator ca = new Calculator();
int result = ca.Add("abc" , "200");
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
}
class Calculator
{
public int Add(string str1, string str2)
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
bool hasError = false;
try
{
a = int.Parse(str1);
b = int.Parse(str2);
}
/*
catch (ArgumentNullException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Your argument(s) are null.");
}
*/
//如果想打印处异常所包含的信息:
catch (ArgumentNullException ane)
{
Console.WriteLine(ane.Message);
hasError = true;
}
catch (FormatException anb)
{
// Console.WriteLine("Your argument(s) are not int the correct format");
Console.WriteLine(anb.Message);
hasError = true;
}
catch (OverflowException)
{
Console.WriteLine("less than MinValue or greater than MaxValue.");
hasError = true;
}
finally //中写释放资源的语句,写程序的执行记录
{
if (hasError)
{
Console.WriteLine("Execution has error!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Done!");
}
}
int result = a + b;
return result;
}
}
}
throw关键字:把异常throw出去,谁调用这个方法,你去抓住这个异常,然后进行处理。在编写程序时,应该在会出现异常的地方用try语句捕捉异常。
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator ca = new Calculator();
int result = 0;
try
{
result = ca.Add("99999999999", "200");
}
catch (OverflowException oe)
{
Console.WriteLine(oe.Message);
}
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
}
class Calculator
{
public int Add(string str1, string str2)
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
bool hasError = false;
try
{
a = int.Parse(str1);
b = int.Parse(str2);
}
/*
catch (ArgumentNullException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Your argument(s) are null.");
}
*/
//如果想打印处异常所包含的信息:
catch (ArgumentNullException ane)
{
Console.WriteLine(ane.Message);
hasError = true;
}
catch (FormatException anb)
{
// Console.WriteLine("Your argument(s) are not int the correct format");
Console.WriteLine(anb.Message);
hasError = true;
}
catch (OverflowException anc)
{
//throw的语法比较灵活
throw anc;//这里省略掉anc,编译器也知道你想把抓住的这个异常抛出去
}
finally //中写释放资源的语句,写程序的执行记录
{
if (hasError)
{
Console.WriteLine("Execution has error!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Done!");
}
}
int result = a + b;
return result;
}
}
}
迭代语句
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int score = 0;
bool canContinue = true;
while (canContinue)
{
Console.WriteLine("Please input first number:");
string str1 = Console.ReadLine();
int x = int.Parse(str1);
Console.WriteLine("Please input second number:");
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
int y = int.Parse(str2);
int sum = x + y;
if (sum == 100)
{
score++;
Console.WriteLine("Correct!{0}+{1}={2}", x, y, sum);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Error!{0}+{1}={2}",x,y,sum);
canContinue = false;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Your score is {0}",score);
Console.WriteLine("GAME OVER!");
}
}
}
do语句
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int score = 0;
bool canContinue = true;
do
{
Console.WriteLine("Please input first number:");
string str1 = Console.ReadLine();
if (str1.ToLower()=="end")
{
break;
}
int x = 0;
try
{
x = int.Parse(str1);
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("First number has problem!Restart.");
continue;
}
Console.WriteLine("Please input second number:");
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
if (str2.ToLower() == "end")
{
break;
}
int y = 0;
try
{
y = int.Parse(str2);
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("Second number has problem!Restart.");
continue;
}
int sum = x + y;
if (sum == 100)
{
score++;
Console.WriteLine("Correct!{0}+{1}={2}", x, y, sum);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Error!{0}+{1}={2}", x, y, sum);
canContinue = false;
}
} while (canContinue);
Console.WriteLine("Your score is {0}",score);
Console.WriteLine("GAME OVER!");
}
}
}
break和continue只会影响到包含他的那一层循环,不会影响外层循环
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)//打印99乘法表
{
for (int a = 1; a <= 9; a++)
{
for (int b = 1; b <=a; b++)
{
Console.Write("{0}+{1}={2}\t",a,b,a*b);//\t是制表位
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
foreach语句:本质上是对集合遍历的一种简记法。用于枚举一个集合的元素,并对该集合中的每个元素执行一次相关的嵌入语句。其最佳应用场合就是对集合进行遍历。
什么样的集合可以被遍历:
C#语言中所有实现了IEnumerable(I大写开头的都是接口)这个接口的类,就是可以被遍历的集合

class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] intArray = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
Console.WriteLine(intArray.GetType().FullName);
Console.WriteLine(intArray is Array);
List<int> intList = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
}
}
迭代器:是一种检查容器内元素并遍历元素的数据类型。C#中所有能够被迭代的集合,他都能够获得自己的迭代器。
下面看一下泛型的List
他们各自的数据结构共同实现了这个接口的GetEnumerator方法
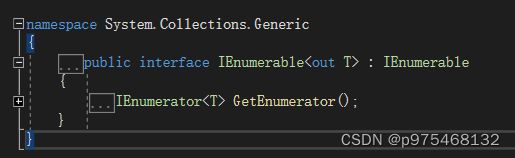
集合遍历的底层原理和迭代器
下面演示有迭代器迭代集合的方法:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] intArray = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
//以接口作为类型声明一个变量
IEnumerator enumerator = intArray.GetEnumerator();//因为Array类实现了IEnumerable这个接口,所以Array类也有GetEnumerator()这个方法,而我们的整数类型数组又是Array类的子类,所以也有这个方法
while (enumerator.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(enumerator.Current);
}
enumerator.Reset();
while (enumerator.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(enumerator.Current);
}
// List intList = new List() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] intArray = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
//以接口作为类型声明一个变量
List<int> intList = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,6 };
IEnumerator enumerator = intList.GetEnumerator();//因为Array类实现了IEnumerable这个接口,所以Array类也有GetEnumerator()这个方法,而我们的整数类型数组又是Array类的子类,所以也有这个方法
while (enumerator.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(enumerator.Current);
}
enumerator.Reset();
while (enumerator.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(enumerator.Current);
}
}
下面接着将foreach语句,本质为对集合遍历的一种简记法:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] intArray = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
List<int> intList = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,6 };
foreach (var current in intList)//此处可以保留var
{
Console.WriteLine(current);
}
}
跳转语句
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Greeting("Mr.Okey!");
}
static void Greeting(string name)//返回值为void的方法,不用写return,,方法执行到最后也就return了
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(name))
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello,{0}",name);
}
}
}
}
尽早return原则,下面这样写可以让都这段代码的人立刻就鉴别出来name这个参数在什么情况下是有问题的,而且可以避免整个方法写起来头重脚轻
static void Greeting(string name)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(name))
{
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Hello,{0}", name);
}
如果你的返回值不是void,并且在方法体里用了选择语句,那么要保证每个分支里都有return
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var result = WhoIsWho("Mr.Okey");
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
static string WhoIsWho(string alias)
{
if (alias == "Mr.Okey")
{
return "Tim";
}
else
{
return "I don't know.";
}
}
}
}
十七、字段,属性,索引器,常量
字段
这四种成员都是用来表达数据的
提到C#的类型指的就是类或者结构体,他们可能具有这样的成员:
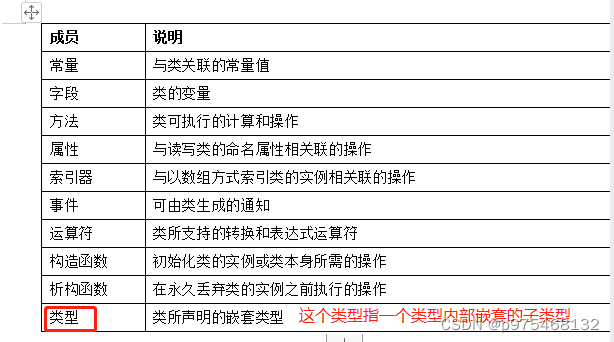
补充:为什么字段的英文单词时filed,filed在英文中表示空间、田地,在编程里指数据存放空间。
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.Age = 40;
stu1.Score = 90;
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.Age = 24;
stu2.Score = 60;
Student.ReportAmount();
}
class Student
{
public int Age;//实例字段
public int Score;
public static int AverageAge;//静态字段
public static int AverageScore;
public static int Amount;
public Student()
{
Amount++;
}
public static void ReportAmount()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.Amount);
}
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<Student> stuList = new List<Student>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.Age = 24;
stu.Score = i;
stuList.Add(stu);
}
int totalAge = 0;
int totalScore = 0;
foreach (var stu in stuList)
{
totalAge += stu.Age;
totalScore += stu.Score;
}
Student.AverageAge = totalAge / Student.Amount;
Student.AverageScore = totalScore / Student.Amount;
Student.ReportAmount();
Student.ReportAverageAge();
Student.ReportAverageScore();
}
class Student
{
public int Age;
public int Score;
public static int AverageAge;
public static int AverageScore;
public static int Amount;
public Student()
{
Amount++;
}
public static void ReportAmount()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.Amount);
}
public static void ReportAverageAge()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.AverageAge);
}
public static void ReportAverageScore()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.AverageScore);
}
}
}
}

静态构造器会在数据类型被加载的时候执行,并且只执行一次,但是一般在声明字段的时候初始化。
对于只读实例字段而言,它只有一个机会给它赋值,那就在构造器里:

还有只读静态字段:
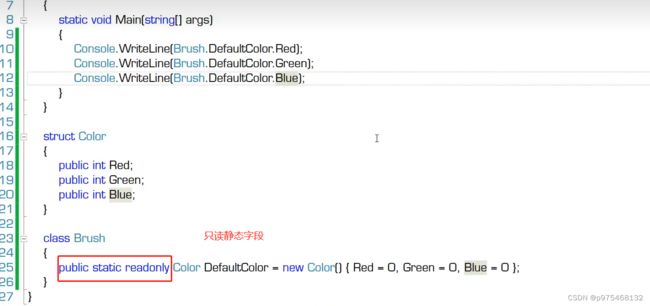

注意,const和readonly的区别:const在编译阶段就已经确定,必须用常量给他赋值,readonly的值是在runtime决定的,可以用变量赋值。
属性
- 属性是由Get/Set方法对进化而来的:
现在C++中仍然用的这种Set/Get的方法来保护字段,因为C++中没有属性的概念。
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.SetAge(20);
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.SetAge(20);
Student stu3 = new Student();
stu3.SetAge(200);
int aveAge = (stu1.GetAge() + stu2.GetAge() + stu3.GetAge()) / 3;
Console.WriteLine(aveAge);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
class Student
{
private int Age;
public int GetAge()
{
return this.Age;
}
public void SetAge(int value)
{
if (value > 0 && value < 120)
{
this.Age = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Age value has error!");//否则抛出异常
}
}
}
}
}
采用语法糖(foreach索引器也是语法糖)-属性编写:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.Age = 20;
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.Age = 20;
Student stu3 = new Student();
stu3.Age = 200;
int aveAge = (stu1.Age + stu2.Age + stu3.Age) / 3;
Console.WriteLine(aveAge);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;//驼峰命名法
public int Age//帕斯卡命名法
{
get
{
return this.age;
}
set
{
if (value >= 0 && value <= 120)//没有看到value这个变量的声明,是因为微软准备了一个默认的变量,就叫value,叫做上下文关键字,就是说这个单词在某个特定的代码上下文中是关键字。代表由用户传进来的设置的值
{
this.age = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Age value has error");
}
}
}
}
}
}

编译器会自动生成这两个方法。这就是语法糖背后的秘密。
属性声明有两种:一种是完整的,一种是简略的(二者区别在于你怎么去写geter和seter)

完整声明:
输入propfull再按两下Tab,即可生成完整声明模板
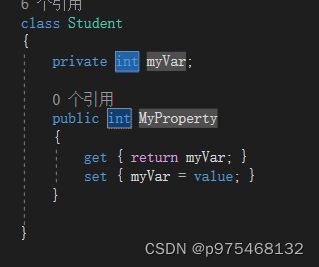

再补充get和set的逻辑,这就是完整写法。
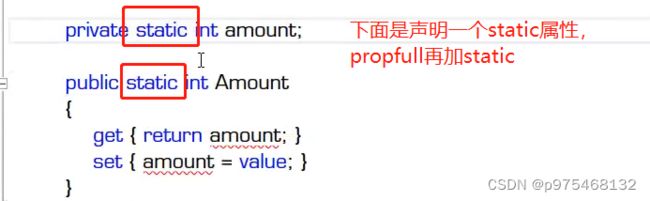
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Student.Amount = 100;
Console.WriteLine(Student.Amount);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age
{
get { return age; }
set { age = value; }
}
private static int amount;
public static int Amount
{
get { return amount; }
set {
if (value > 0)
{
Student.amount = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Amount must greater than 0.");
}
}
}
}
}
通过简略声明声明出来的属性,其功能上和一个共有的字段是完全一样的,也就是说这个值是不受保护的,你可能把错误的值赋给这个属性,带有这种属性的类一般就是传递数据用的。
简略声明:输入prop,再按tab
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.Age = 10100;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int Age { get; set; }
}
}
简要声明也是语法糖
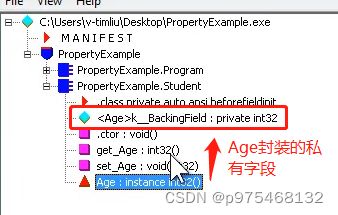
很多时候,我们的类是先有字段,但实际上我们需要的是属性
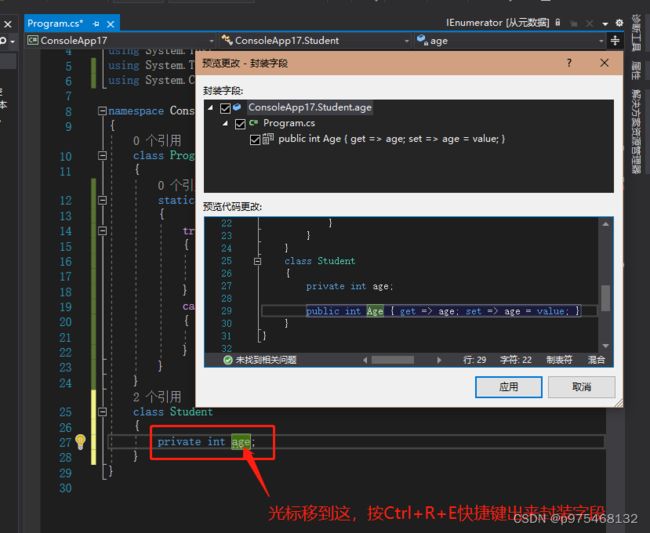
高级版,对着age右键也行。
只读属性只需要删掉set,还有一种属性,它具有set,但是是private的,这样的属性不能叫做只读属性,只是说他的set不能从外界访问。
动态计算值的属性:
第一种被动的计算
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.Age = 12;
Console.WriteLine(stu.CanWork);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age
{
get { return age; }
set { age = value; }
}
public bool CanWork//并没有封装字段,而从外界访问它的时候,他的值是实时动态更新的
{
get
{
if (this.age>=16)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
}
}
第二种,主动的计算,接口没变,只是内部的实现逻辑变了,可以根据具体应情况选择合适的逻辑
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.Age = 12;
Console.WriteLine(stu.CanWork);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age
{
get { return age; }
set { age = value;
this.CalculateCanWork();//主动计算,适用于对CanWork这个值访问的频繁的情况
}
}
private bool canWork;
public bool CanWork
{
get { return canWork; }
}
private void CalculateCanWork()
{
if (this.age >= 16)
{
this.canWork = true;
}
else
{
this.canWork = false;
}
}
}
}
索引器
索引器是用来检索一个集合的,拥有索引器这种成员的类一般是集合类型,有是也有例外
用非集合形式讲解,为了让学生方便的用索引器检索自己的成绩
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu["Math"] = 90;
var mathScore = stu["Math"];
Console.WriteLine(mathScore.HasValue);
}
}
class Student
{
private Dictionary<string, int> scoreDictionary = new Dictionary<string, int>();
//下面声明索引器,也是使用代码提示,输入index+Tab+Tab
public int? this[string subject]//返回值为可空int类型
{
get
{
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
return this.scoreDictionary[subject];
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
set
{
if (value.HasValue==false)
{
throw new Exception("Score can't be null.");
}
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
this.scoreDictionary[subject] = value.Value;//可空类型.value才是它真正的值,那么如果value是null,就该出异常了,所以要加一个保护措施
}
else
{
this.scoreDictionary.Add(subject, value.Value);
}
}
}
}
}
常量
常量值指的是编译器在编译这段代码的时候,就会拿这个值把常量的标识符替换掉,这样就可以提高程序运行的效率。
Math.PI就是一个常量,int.MaxValue
常量隶属于类型而不是对象
const后面不能跟类或自定义结构体,只能跟int double

namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(WASPEC.WebsiteURL);
}
}
class WASPEC
{
public const string WebsiteURL = "http://www.waspec.org";
}
}
十八传值/输出/引用/数组/具名/可选参数,扩展方法
本节将学习各种参数,参数也是方法的一部分,所以这节课是对方法的进一步学习

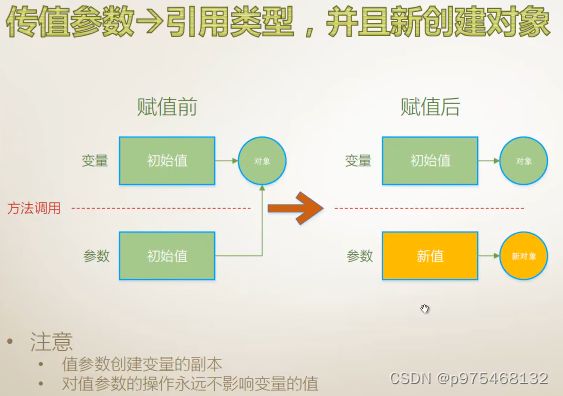
值参数,也叫传值参数


现在讲的值参数,也叫传值参数,讲的是参数的种类,而参数作为变量,是有数据类型的,现在讲的是数据类型为值类型的传值参数。
实例演示:
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student();
int y = 100;
stu.AddOne(y);//101
Console.WriteLine(y);//100
}
}
class Student
{
public void AddOne(int x)//这里是值参数,int为结构体,所以未值类型的值参数
{
x = x + 1;
Console.WriteLine(x);
}
}
}
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student() { Name = "Tim"};
SomeMethod(stu);//Tom
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);//Tim
}
static void SomeMethod(Student stu)
{
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);//Tim
stu = new Student() { Name = "Tom" };
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
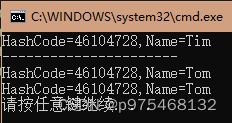
如果两个stu都是Tim,那么该如何区分呢?这里介绍一个方法:GetHashCode()方法,他可以认为是获取实例对象的某个编号,是唯一的,每个实例的编号都不一样。
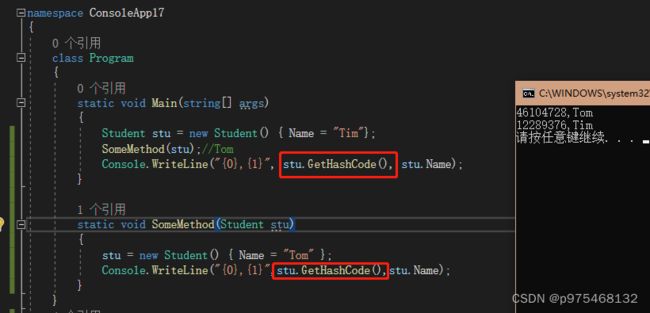

vs2019中Ctrl+。不能用,可以点小灯泡。vs2019为Alt+Enter+。

namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student() { Name = "Tim"};
UpdateObjict(stu);//Tom
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
}
static void UpdateObjict(Student stu)
{
stu.Name = "Tom";
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
一般情况下,把这种修改参数所引用的对象的值的操作叫做某个方法的副作用(side-effect),编程时要尽量避免
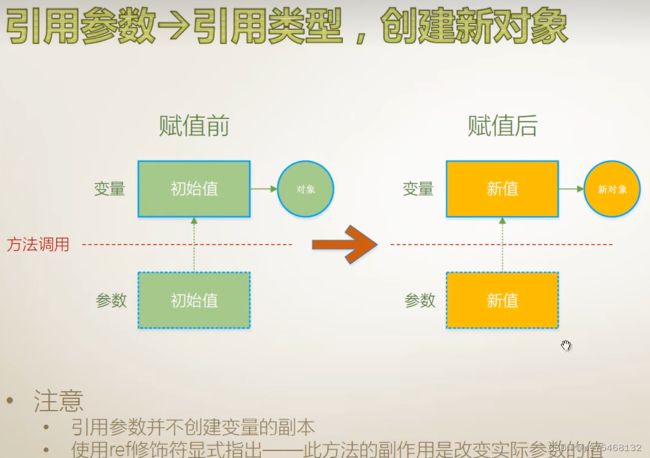
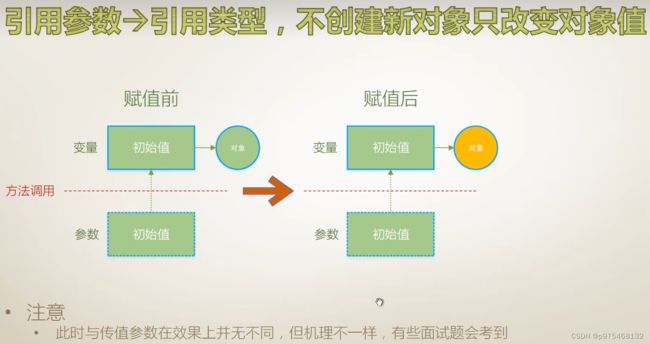
引用参数
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int y = 1;
IWantSideEffect(ref y);
Console.WriteLine(y);//101
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref int x)
{
x = x + 100;
}
}
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student outterStu = new Student() { Name = "Tim" };
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}", outterStu.GetHashCode(), outterStu.Name);
IWantSideEffect(ref outterStu);
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}", outterStu.GetHashCode(), outterStu.Name);
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref Student stu)
{
stu = new Student() { Name = "Tom"};
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
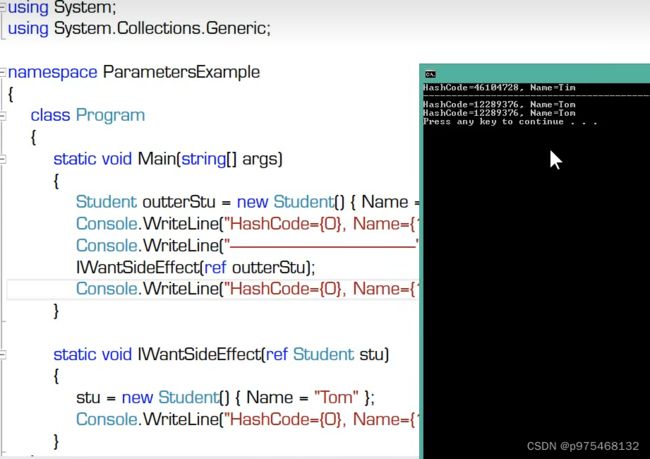
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student outterStu = new Student() { Name = "Tim" };
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}", outterStu.GetHashCode(), outterStu.Name);
Console.WriteLine("----------------------");
IWantSideEffect(ref outterStu);
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}", outterStu.GetHashCode(), outterStu.Name);
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref Student stu)
{
stu.Name = "Tom";
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
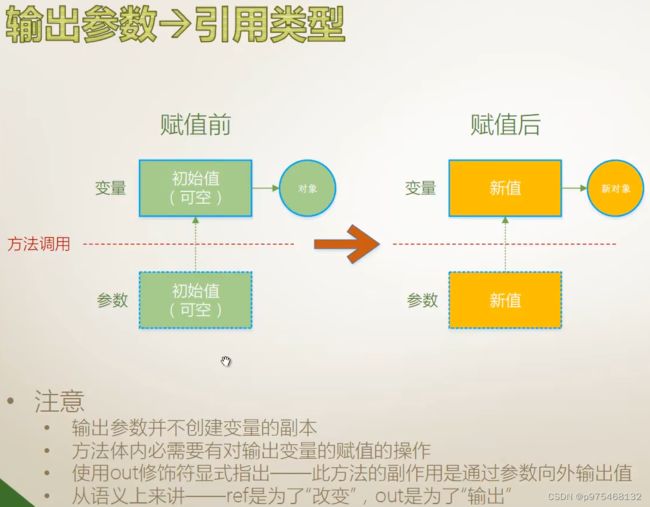
输出参数
利用输出形参来获得除返回值之外的额外的输出
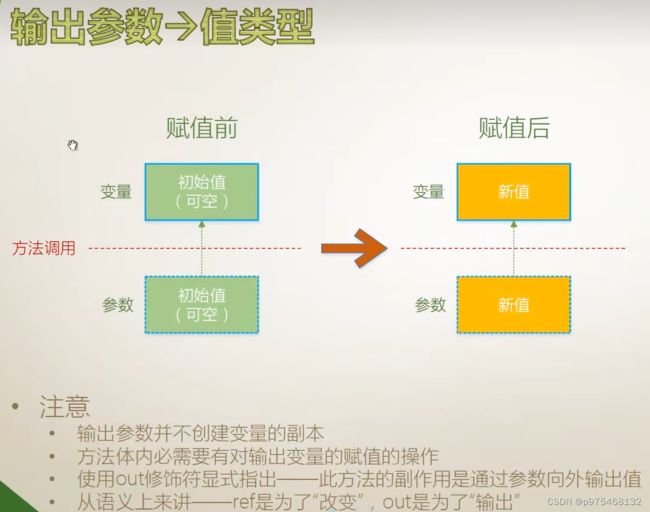
为什么没有声明带有输出参数的方法,就去调用它呢?
因为类库当中有些类型他就具有带输出参数的方法,比如int、double类型

TryParse方法(将string类型转化为double类型),返回值为bool类型,用来表示是否解析成功,转换的结果就是通过输出参数输出。
实例:
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Please input the first number: ");
string str1 = Console.ReadLine();
double x = 0;
bool b1 = double.TryParse(str1, out x);
if (b1==false)
{
Console.WriteLine("Input error!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Please input the second number: ");
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
double y = 0;
bool b2 = double.TryParse(str2, out y);
if (b2==false)
{
Console.WriteLine("Input error!");
return;
}
double z = x+y;
Console.WriteLine("{0}+{1}={2}",x,y,z);
}
}
}
编写TryParse:
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x = 0;
bool b = DoubleParse.TryParse("789", out x);
if (b==true)
{
Console.WriteLine(x+1);//790
}
}
}
class DoubleParse
{
public static bool TryParse(string str, out double b1)
{
try
{
b1 = double.Parse(str);
return true;
}
catch (Exception)
{
b1 = 0;
return false;
}
}
}
}
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = null;
bool b = StudentFactory.Create(34, "Tim", out stu);
if (b==true)
{
Console.WriteLine("Student:{0},age is {1}.",stu.Name,stu.Age);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
class StudentFactory
{
public static bool Create(int age, string name, out Student stu)
{
stu = null;
if (age<=20||age>=80)
{
return false;
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(name))
{
return false;
}
stu = new Student() { Age = age, Name = name };
return true;
}
}
}
数组参数
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] myArray = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 };
int sum = CalculateSum(myArray);
Console.WriteLine(sum);
}
static int CalculateSum(int[] myArray)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (var x in myArray)
{
sum += x;
}
return sum;
}
}
}
可以用params参数:
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int sum = CalculateSum(1,2,3);//会自动创建数组,传递给myArray
Console.WriteLine(sum);
}
static int CalculateSum(params int[] myArray)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (var x in myArray)
{
sum += x;
}
return sum;
}
}
}
![]()
他会先声明一个object的数组,再把xyz放进这个数组,然后再传进WriteLine方法
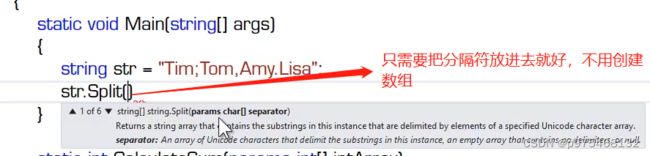
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str = "Tim;Tom,Amy.Lisa";
string[] result = str.Split(';', ',', '.');//其返回值是字符串数组类型,就是将一个字符串分割出来的结果
foreach (var name in result)
{
Console.WriteLine(name);
}
}
static int CalculateSum(params int[] myArray)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (var x in myArray)
{
sum += x;
}
return sum;
}
}
}
具名参数
具名参数两个优点:
1.提高代码的可读性
2.不再受参数顺序的约束
可选参数
扩展方法(this参数)

double里面没有Round这个方法,那么我想用她该怎么办呢,当我们无法对一个类型的源码进行修改的时候,可以使用扩展方法为这种目标数据类型来追加方法

什么是LinQ?语言集成查询,他就是扩展方法
实例:写一个方法,这个方法可以接受一个集合类型的参数,然后判断一下这个集合当中的值是不是都大于10
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Collections;
using System.Linq;//使用LinQ要引用这个名称空间
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> myList = new List<int>() { 11, 12, 3, 14, 15 };
//bool result = AllGreaterThanTen(myList);
bool result = myList.All(i => i > 10);//All()是扩展方法
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
static bool AllGreaterThanTen(List<int> intList)
{
foreach (var item in intList)
{
if (item<=10)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
}
总结
十九、委托详解–难度300!
什么是委托
#include 下面演示为什么说委托是函数指针的升级版:
提包里装着一些方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Collections;
using System.Linq;//使用LinQ要引用这个名称空间
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
//函数指针需要新建,而委托有许多现成的可以使用
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
//下面看Action这个委托
Action action = new Action(calculator.Report);//封装一个方法,该方法没有参数,没有返回值,不加圆括号
calculator.Report();//直接调用
action.Invoke();//间接调用
action();//间接调用的简便写法
//Func委托是泛型委托
Func<int, int, int> func1 = new Func<int, int, int>(calculator.Add);
Func<int, int, int> func2 = new Func<int, int, int>(calculator.Sub);
int x = 100;
int y = 200;
int z = 0;
//间接调用
z = func1.Invoke(x, y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
z = func1(x, y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
z = func2.Invoke(x, y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
}
}
class Calculator
{
public void Report()
{
Console.WriteLine("I have three methods.");
}
public int Add(int a, int b)
{
int result = a + b;
return result;
}
public int Sub(int a, int b)
{
int result = a - b;
return result;
}
}
}
委托的声明(自定义委托)
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type t = typeof(Action);
Console.WriteLine(t.IsClass);//True
}
}
}
实例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Collections;
using System.Linq;//使用LinQ要引用这个名称空间
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
//委托也是类,所以要把它声明在名称空间里,与其它类并列
//public表示谁都可以访问,delegate表示要声明一个委托,第一个double为目标返回值的类型,圆括号里写目标方法的参数列表
public delegate double Cake(double x, double y);//自定义委托类型
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
Cake calc1 = new Cake(calculator.Add);
Cake calc2 = new Cake(calculator.Sub);
Cake calc3 = new Cake(calculator.Mul);
Cake calc4 = new Cake(calculator.Div);
double a = 100;
double b = 200;
double c = 0;
c = calc1.Invoke(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = calc2.Invoke(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = calc3(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = calc4(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
}
}
class Calculator
{
public double Add(double x, double y)
{
return x + y;
}
public double Sub(double x, double y)
{
return x - y;
}
public double Mul(double x, double y)
{
return x * y;
}
public double Div(double x, double y)
{
return x / y;
}
}
}
委托的使用
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Collections;
using System.Linq;//使用LinQ要引用这个名称空间
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);
Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToyCar);
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
class Product//产品
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
class Box//包装箱
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
class WrapFactory//包装工厂,把产品包上盒子,交给用户
{
//模板方法,接受一个委托类型的参数,选择Func委托
public Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct)//Box包装方法,传入产品生产的方法,返回box
{
Box box = new Box();
Product product = getProduct();
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
class ProductFactory//产品生产工厂
{
public Product MakePizza()//生产Pizza的方法
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
return product;
}
public Product MakeToyCar()//生产ToyCar的方法
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "ToyCar";
return product;
}
}
}
这样写的好处是:
在进行继续开发是只需要扩展产品生产类里面的方法就行,其他的都不用动

回调方法实例:
回调方法是通过委托类型的参数传递进主调方法的被调用方法,主调方法可以根据自己的逻辑决定是否调用这个方法,也叫做好莱坞方法(演员去导演那面试,留下自己的联系方式,导演说我如果用你会通知你,你不要给我打电话)。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Collections;
using System.Linq;//使用LinQ要引用这个名称空间
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);
Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToyCar);
Logger logger = new Logger();
Action<Product> log = new Action<Product>(logger.Log);
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1,log);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2,log);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
class Logger//这个类用来记录程序的运行状态,用来找程序那个地方出了问题,软件系统都有这一部分
{
public void Log(Product product)//然后把这个Log方法以回调方法的形式传进模板方法里
{
Console.WriteLine("Product'{0}'created at {1}.Price is {2}",product.Name,DateTime.UtcNow,product.Price);//UtcNow不带时区
}
}
class Product//产品
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Price{ get; set; }
}
class Box//包装箱
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
class WrapFactory//包装工厂,把产品包上盒子,交给用户
{
//模板方法,接受一个委托类型的参数,选择Func委托
public Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct,Action<Product> logCallback)//Box包装方法,传入产品生产的方法,返回box,对于没有参数只有返回值的方法,用Func委托对于没有返回值的方法,使用Action委托
{
Box box = new Box();
Product product = getProduct();
//下面添加逻辑决定是否调用这个方法:
if (product.Price>50)
{
logCallback(product);
}
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
class ProductFactory//产品生产工厂
{
public Product MakePizza()//生产Pizza的方法
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
product.Price = 12;
return product;
}
public Product MakeToyCar()//生产ToyCar的方法
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "ToyCar";
product.Price = 100;
return product;
}
}
}
多播委托:指的是一个委托内部封装这不止一个方法。实例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Collections;
using System.Linq;//使用LinQ要引用这个名称空间
using System.Threading;
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID=1,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow};
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID=2,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green};
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID=3,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red};
Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);
Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);
//单播委托
/*
action1.Invoke();
action2.Invoke();
action3.Invoke();*/
//多播委托
action1 += action2;
action1 += action3;
action1.Invoke();
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomework()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hours.",this.ID,i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);//你在哪个线程调用这个,哪个线程就睡上1s
}
}
}
}
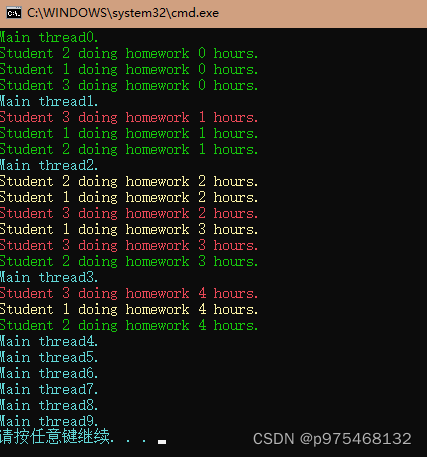
隐式异步调用
第一个运行起来的线程叫做主线程,主线程之外的线程叫做分支线程,知道什么是进程和线程之后,再来看看方法的调用:
当我们在同一个线程内去调用方法的时候,方法的执行是前一个执行完了后一个再执行,像这种在同一个线程内依次执行的方法调用,叫做同步调用

红色为主线程,CPU执行指针执行到方法的时候,进入方法。
异步调用指的是在不同的线程当中去调用方法,每个线程与另外一个线程都不相干,你执行你的,我执行我的,一个线程的开始和结束并不会像影响到另一个线程的开始和结束,而且线程的开始和结束的实际又有可能构成不同的组合,这就是对方法的异步调用,也叫做多线程调用。换句话说,异步调用的底层机理就是多线程。


同步调用有三种形式:
1.直接同步调用(直接调用就使用方法的名字调用),实例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Collections;
using System.Linq;//使用LinQ要引用这个名称空间
using System.Threading;
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//主线程
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID=1,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow};
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID=2,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green};
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID=3,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red};
stu1.DoHomework();//调用方法
stu2.DoHomework();//调用方法
stu3.DoHomework();//调用方法
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("Main thread{0}."i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomework()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hours.",this.ID,i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);//你在哪个线程调用这个,哪个线程就睡上1s
}
}
}
}
2.间接同步调用,实例:
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//主线程
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID=1,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow};
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID=2,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green};
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID=3,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red};
Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);
Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);
action1.Invoke();
action2.Invoke();
action3.Invoke();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("Main thread{0}."i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomework()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hours.",this.ID,i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);//你在哪个线程调用这个,哪个线程就睡上1s
}
}
}
}
3.多播同步调用
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//主线程
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID=1,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow};
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID=2,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green};
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID=3,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red};
Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);
Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);
action1 += action2;
action1 += action3;
action1.Invoke();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("Main thread{0}.",i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomework()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hours.",this.ID,i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);//你在哪个线程调用这个,哪个线程就睡上1s
}
}
}
}
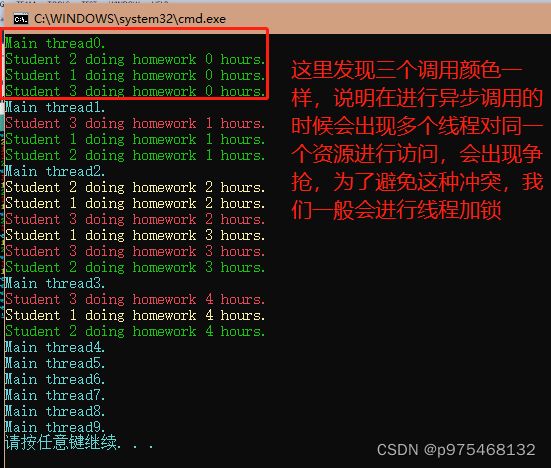
异步调用:
使用委托进行隐式异步调用,使用Invode方法是同步调用,使用BeginInvoke方法就是隐式异步调用,它会自动为我们生成一个分支线程,然后在分支线程里去调用封装的方法
显式异步调用:自己声明多线程。有两种方式,第一种比较古老,使用Thread
也会发生资源争抢。
C#准备的另一种更高级的方式——使用Task
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
using System.Linq;//使用LinQ要引用这个名称空间
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//主线程
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID=1,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow};
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID=2,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green};
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID=3,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red};
Task task1 = new Task(new Action(stu1.DoHomework));//Alt+Enter,引入名称空间
Task task2 = new Task(new Action(stu2.DoHomework));//Alt+Enter,引入名称空间
Task task3 = new Task(new Action(stu3.DoHomework));//Alt+Enter,引入名称空间
task1.Start();
task2.Start();
task3.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("Main thread{0}.",i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomework()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hours.",this.ID,i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);//你在哪个线程调用这个,哪个线程就睡上1s
}
}
}
}
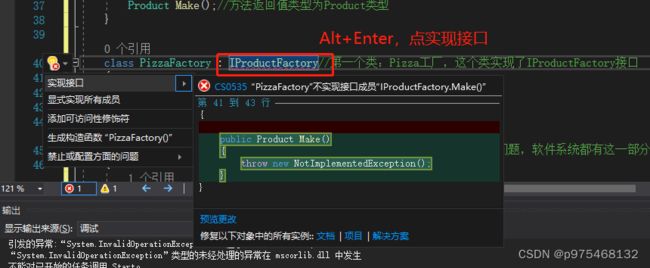
适时使用接口取代委托的使用()
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
using System.Linq;//使用LinQ要引用这个名称空间
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IProductFactory pizzaFactory = new PizzaFactory();
IProductFactory toycarFactory = new ToyCarFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(pizzaFactory);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(toycarFactory);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
interface IProductFactory//声明接口
{
Product Make();//方法返回值类型为Product类型
}
class PizzaFactory : IProductFactory//第一个类:Pizza工厂,这个类实现了IProductFactory接口
{
public Product Make()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
return product;
}
}
class ToyCarFactory : IProductFactory
{
public Product Make()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "ToyCar";
return product;
}
}
class Logger//这个类用来记录程序的运行状态,用来找程序那个地方出了问题,软件系统都有这一部分
{
public void Log(Product product)//然后把这个Log方法以回调方法的形式传进模板方法里
{
Console.WriteLine("Product'{0}'created at {1}.Price is {2}", product.Name, DateTime.UtcNow, product.Price);//UtcNow不带时区
}
}
class Product//产品
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
}
class Box//包装箱
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
class WrapFactory//包装工厂,把产品包上盒子,交给用户
{
//模板方法
public Box WrapProduct(IProductFactory productFactory)//参数为工厂类型的参数
{
Box box = new Box();
Product product =productFactory.Make();
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
}