C#高级--委托详解
C#高级–委托详解
零、文章目录
一、委托是什么
1、委托是什么
委托和类一样是一种用户自定义类型,它存储的就是一系列具有相同签名和返回类型的方法的地址,调用委托的时候,它所包含的所有方法都会被执行。
2、委托声明
(1)委托可以声明在类外部,也可以在类内部
(2)跟方法有点类似,有参数,返回值,访问修饰符,比方法声明多一个关键字delegate
namespace MyDelegate
{
///
/// 1.无参数无返回值委托
///
public delegate void NoReturnNoParaOutClass();
public class CustomDelegate
{
///
/// 2.无参数无返回值委托
///
public delegate void NoReturnNoPara();
///
/// 3.有参数无返回值委托
///
///
///
public delegate void NoReturnWithPara(int x, int y);
///
/// 4.无参数有返回值的委托
///
///
/// 5.带参数带返回值的委托
///
///
///
/// 3、委托的本质
反编译程序看委托NoReturnNoParaOutClass的IL代码
.class public auto ansi sealed NoReturnNoParaOutClass
extends [System.Runtime]System.MulticastDelegate
{
.method public hidebysig specialname rtspecialname instance void .ctor(object 'object', native int 'method') runtime managed
{
}
.method public hidebysig newslot virtual instance class [System.Runtime]System.IAsyncResult BeginInvoke(class [System.Runtime]System.AsyncCallback callback, object 'object') runtime managed
{
}
.method public hidebysig newslot virtual instance void EndInvoke(class [System.Runtime]System.IAsyncResult result) runtime managed
{
}
.method public hidebysig newslot virtual instance void Invoke() runtime managed
{
}
}
(1)委托是一个类,继承自MulticastDelegate
MulticastDelegate这个类我们自己定义的类是无法继承的
(2)委托的构造函数,需要传递一个方法作为参数
(3)委托的内部有三个方法Invoke,BeginInvoke,EndInvoke
二、委托实例化和执行
1、委托实例化
(1)通过New来实例化
(2)直接=一个方法,这个是编译器提供的语法糖
(3)直接=一个匿名委托
(4)直接=一个Lambda
2、委托执行
(1)Inovke执行委托
如果委托定义没有参数,则Inovke也没有参数;委托没有返回值,则Inovke也没有返回值
(2)BeginInvoke开启一个新线程执行委托
NetCore不支持,NetFamework支持 NetCore有更好的多线程功能来支持实现类似功能
(3)EndInvoke等待BeginInvoke执行完成后再执行
using System;
namespace MyDelegate
{
public class CustomDelegateShow
{
public static void Show()
{
//1、委托实例化
//(1)通过New来实例化,要求传递一个和这个委托的参数和返回值完全匹配的方法
NoReturnNoParaOutClass noReturnNoParaOutClass = new NoReturnNoParaOutClass(NoReturnNoParaMehtod);
//(2)直接=一个方法,要求方法和这个委托的参数和返回值完全匹配,这个是编译器提供的语法糖
NoReturnNoParaOutClass noReturnNoParaOutClass2 = NoReturnNoParaMehtod;
//(3)直接=一个匿名委托,要求和这个委托的参数和返回值完全匹配
NoReturnNoParaOutClass noReturnNoParaOutClass3 = delegate () { Console.WriteLine("这是一个无参数无返回值的方法。。。"); };
//(4)直接=一个Lambda,要求和这个委托的参数和返回值完全匹配
NoReturnNoParaOutClass noReturnNoParaOutClass4 = ()=> { Console.WriteLine("这是一个无参数无返回值的方法。。。"); };
//无参无返回值委托实例化
CustomDelegate.NoReturnNoPara noReturnNoPara = NoReturnNoParaMehtod;
//带参数无返回值委托实例化
CustomDelegate.NoReturnWithPara noReturnWithPara = NoReturnWithParaMehtod;
//无参数带返回值委托实例化
CustomDelegate.WithReturnNoPara withReturnNoPara = WithReturnNoParaMehtod;
//带参数带返回值委托实例化
CustomDelegate.WithReturnWithPara withReturnWithPara = WithReturnWithParaMehtod;
//2、委托执行
//(1)Inovke执行方法,如果委托定义没有参数,则Inovke也没有参数;委托没有返回值,则Inovke也没有返回值
noReturnNoParaOutClass.Invoke();
//(2)BeginInvoke开启一个新的线程去执行委托
//NetCore不支持,NetFamework支持 NetCore有更好的多线程功能来支持实现类似功能
//noReturnNoParaOutClass.BeginInvoke((a) => Console.WriteLine("方法调用结束。。。"), null);
//(3)EndInvoke等待BeginInvoke方法执行完成后再执行EndInvoke后面的代码
//NetCore不支持,NetFamework支持 NetCore有更好的多线程功能来支持实现类似功能
//noReturnNoParaOutClass.EndInvoke(null);
//无参无返回值委托执行
noReturnNoPara.Invoke();
//带参数无返回值委托执行
noReturnWithPara.Invoke(1,2);
//无参数带返回值委托执行
int result=withReturnNoPara.Invoke();
//带参数带返回值委托执行
int x = 1;
int y = 1;
int result2 = withReturnWithPara.Invoke(out x, ref y);
}
private static void NoReturnNoParaMehtod()
{
Console.WriteLine("这是一个无参数无返回值的方法。。。");
}
private static void NoReturnWithParaMehtod(int x, int y)
{
Console.WriteLine($"这是一个带参数无返回值的方法。。。");
}
private static int WithReturnNoParaMehtod()
{
Console.WriteLine($"这是一个无参数带返回值的方法。。。");
return default(int);
}
private static int WithReturnWithParaMehtod(out int x, ref int y)
{
Console.WriteLine($"这是一个带参数带返回值的方法。。。");
x = 1;
return default(int);
}
}
}
三、委托作用和意义
1、需求:不同的学生实现不同打招呼方式
定义一个类
using System;
namespace MyDelegate
{
///
/// 学生类
///
public class Student
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public UserType ClassId { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
///
/// 问好
///
public void SayHi()
{
Console.WriteLine("招手。。。");
switch (ClassId)
{
case UserType.Wuhan:
Console.WriteLine("吃了么?过早了吗?");
break;
case UserType.Shanghai:
Console.WriteLine("侬好!");
break;
case UserType.GuangDong:
Console.WriteLine("雷猴!");
break;
default:
throw new Exception("NO UserType");
}
}
public void SayHiWuhHan()
{
Console.WriteLine("吃了么?过早了吗?");
}
public void SayHiShangHai()
{
Console.WriteLine("侬好!");
}
public void SayHiGuangDong()
{
Console.WriteLine("雷猴!");
}
public void SayHiBeijing()
{
Console.WriteLine("早上好!");
}
///
/// 既没有重复代码
/// 也相对稳定
///
public void SayHiPerfect(SayHiDalegate sayHiDalegate)
{
Console.WriteLine("招手。。。");
sayHiDalegate.Invoke();
}
}
}
定义一个枚举
public enum UserType
{
Wuhan = 1,
Shanghai = 2,
GuangDong = 3,
BeiJing = 4
}
定义一个委托
public delegate void SayHiDalegate();
方案1:定义枚举,不同枚举值调用不同代码
Student student = new Student()
{
Id = 1234,
Name = "张三",
Age = 25,
ClassId = UserType.Shanghai
};
student.SayHi();
方案2:根据不同的类型的人,调用不同方法
student.SayHiWuhHan();
student.SayHiShangHai();
student.SayHiGuangDong();
方案3:使用委托将方法传递进去执行
student.SayHiPerfect(student.SayHiWuhHan);
student.SayHiPerfect(student.SayHiShangHai);
student.SayHiPerfect(student.SayHiGuangDong);
2、需求变更:如果增加一个类型的人
- 方案1:SayHi里面增加一个分支,SayHi不稳定。
- 方案2:每个方法都式独立的,只需要增加一个方法。
- 方案3:也只需要增加一个方法,然后传进去执行。
3、需求再变更:每个人打招呼之前先招手
- 方案1:SayHi在所有逻辑之前加招手逻辑。
- 方案2:每个方法都式独立的,每个方法都需要增加招手逻辑,要修改所有方法。
- 方案3:SayHiPerfect里面委托执行前加招手逻辑。
4、方案比较下来,方案3既没有重复代码,也相对稳定
委托既然是一个类型,可以赋值和执行,使得委托可以将方法当作另一个方法的参数来进行传递,这种将方法动态地赋给参数的做法,使得程序具有更好的可扩展性。
5、什么情况下,可以考虑使用委托?
- 方法内部业务逻辑耦合严重
- 如果多个方法,有很多重复代码,逻辑重用
四、委托实现嵌套中间件
1、委托朴素嵌套实现
(1)声明一个委托
public delegate void ShowDelegate();
(2)定义一个普通类
///
/// 普通类
///
public class CustomClass
{
public void Method()
{
Console.WriteLine("朴素嵌套业务核心");
}
}
(3)委托嵌套实现
ShowDelegate showMthod1 = new ShowDelegate(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("showMthod1执行前");
new CustomClass().Method();
Console.WriteLine("showMthod1执行后");
});
ShowDelegate showMthod2 = new ShowDelegate(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("showMthod2执行前");
showMthod1.Invoke();
Console.WriteLine("showMthod2执行后");
});
ShowDelegate showMthod3 = new ShowDelegate(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("showMthod3执行前");
showMthod2.Invoke();
Console.WriteLine("showMthod3执行后");
});
showMthod3.Invoke();
(4)运行结果
showMthod3执行前
showMthod2执行前
showMthod1执行前
朴素嵌套业务核心
showMthod1执行后
showMthod2执行后
showMthod3执行后
2、委托花式嵌套实现
(1)定义一个委托
public delegate void ShowDelegate();
(2)定义几个特性
using System;
namespace MyDelegate
{
///
/// 定义一个抽象特性
///
public abstract class AbstractMethodAttribute : Attribute
{
///
/// 在xxx 执行之前执行的点业务落
///
public abstract ShowDelegate Do(ShowDelegate action);
}
///
/// Log
///
public class DelegateLogAttribute : AbstractMethodAttribute
{
///
/// 前后业务
///
public override ShowDelegate Do(ShowDelegate action)
{
ShowDelegate actionResult = new ShowDelegate(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("在执行之前LOG");
action.Invoke();
Console.WriteLine("在执行之后LOG");
});
return actionResult;
}
}
///
/// Error
///
public class DelegateErrorAttribute : AbstractMethodAttribute
{
///
/// 前后业务
///
public override ShowDelegate Do(ShowDelegate action)
{
ShowDelegate actionResult = new ShowDelegate(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("在执行之前ERROR");
action.Invoke();
Console.WriteLine("在执行之后ERROR");
});
return actionResult;
}
}
///
/// Auth
///
public class DelegateAuthAttribute : AbstractMethodAttribute
{
///
/// 前后业务
///
public override ShowDelegate Do(ShowDelegate action)
{
ShowDelegate actionResult = new ShowDelegate(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("在执行之前AUTH");
action.Invoke();
Console.WriteLine("在执行之后AUTH");
});
return actionResult;
}
}
}
(3)定义一个类,方法标记特性
///
/// 普通类 方法标记特性
///
public class CustomClass2
{
[DelegateLog]
[DelegateError]
[DelegateAuth]
public void Method()
{
Console.WriteLine("花式嵌套业务核心");
}
}
(4)委托嵌套实现
//反射获取类的方法信息
CustomClass2 invokerAction = new CustomClass2();
Type type = invokerAction.GetType();
MethodInfo methodInfo = type.GetMethod("Method");
//给委托赋值,初始委托方法
ShowDelegate showMethod = new ShowDelegate(() =>
{
invokerAction.Method();
});
//判断是否定义特性对每个特性进行执行
//继承自父类的特性都算
if (methodInfo.IsDefined(typeof(AbstractMethodAttribute), true))
{
//Reverse越靠近方法越先执行
foreach (AbstractMethodAttribute attribute in methodInfo.GetCustomAttributes().Reverse())
{
//把初始方法传入,返回封装好的委托再作为下一个参数传入
showMethod = attribute.Do(showMethod);
}
}
//执行委托
showMethod.Invoke();
(5)运行结果
在执行之前LOG
在执行之前ERROR
在执行之前AUTH
花式嵌套业务核心
在执行之后AUTH
在执行之后ERROR
在执行之后LOG
五、框架内置委托
Action/Func是.NET Framework3.0时代的产物
1、Action
(1)Action是来自于System.RunTime的一个声明好的可以带有一个或者多个参数无返回值的委托
(2)最多支持16个入参,正常使用足够
Action action = new Action(NoreturnNopara);
Action action1 = new Action(DoNothingInt);
(3)想要支持更多的参数呢,可以自己定义
//参数不够自己定义
public delegate void Action(T1 arg1, T2 arg2, T3 arg3, T4 arg4, T5 arg5, T6 arg6, T7 arg7, T8 arg8, T9 arg9, T10 arg10, T11 arg11, T12 arg12, T13 arg13, T14 arg14, T15 arg15, T16 arg16, T17 arg17);
2、Func
(1)Func是来自于System.RunTime的一个声明好有返回值的委托,也可以有参数
(2)如果既然有参数也有返回值,前面是输入参数类型,最后面的作为返回值类型
(3)最多支持16个入参,正常足够使用
Func func = new Func(ReturnNopara);
Func func1 = new Func(ToInt);
Func func2 = new Func(DoNothingIntAndStringNew);
(4)想要支持更多的参数呢,可以自己定义
//参数不够自己定义
public delegate TResult Func(T1 arg1, T2 arg2, T3 arg3, T4 arg4, T5 arg5, T6 arg6, T7 arg7, T8 arg8, T9 arg9, T10 arg10, T11 arg11, T12 arg12, T13 arg13, T14 arg14, T15 arg15, T16 arg16, T17 arg17);
3、为什么要用框架内置委托
(1)委托的本质是类,定义多个委托,其实就是新增了多个类,定义好的两个委托参数和返回值都是一致的,但是因为是不同的类,没有继承不能通用
(2)既然是系统框架给我们定义好了这两个委托,自然是希望我们在以后的开发中,都去使用这两个委托,这样就可以把委托类型做到统一
(3)那之前定义好的委托是去不掉的,这被称之为历史包袱
六、多播委托
1、多播委托
(1)委托都是继承自MulticastDelegate(多播委托),定义的所有的委托都是多播委托
(2)可以通过+=把多个方法添加到这个委托中,形成一个方法的执行链,执行委托的时候,按照添加方法的顺序,依次去执行方法
(3)action.BeginInvoke();会开启一个新的线程 去执行委托,注册有多个方法的委托,不能使用BeginInvoke
(4)注册有多个方法的委托想要开启新线程去执行委托,可以通过action.GetInvocationList()获取到所有的委托,然后循环,每个方法执行的时候可以BeginInvoke
定义一个测试类
using System;
namespace MyDelegate
{
///
/// 多播委托
///
public class CustomMulticastDelegation
{
private void DoNothing()
{
Console.WriteLine("This is DoNothing");
}
private void DoNothing2()
{
Console.WriteLine("This is DoNothing2");
}
private static void DoNothingStatic()
{
Console.WriteLine("This is DoNothingStatic");
}
private static void DoNothingStatic2()
{
Console.WriteLine("This is DoNothingStatic2");
}
}
}
多播委托注册执行
//注册方法链
Action action = new Action(DoNothing);
action += DoNothingStatic;
action += DoNothing;//同一个方法注册两次会执行两次
action += () =>
{
Console.WriteLine("this is Lambda。。。");
};
//action.BeginInvoke();//开启一个新的线程去执行委托,如果注册有多个方法的委托,不能使用BeginInvoke
action.Invoke();
//注册有多个方法的委托想要开启新线程去执行委托,可以通过action.GetInvocationList()获取到所有的委托,然后循环,每个方法执行的时候可以BeginInvoke
//foreach (Action action1 in action.GetInvocationList())
//{
// action1.Invoke();
// //action1.BeginInvoke(null,null);
//}
运行结果
This is DoNothing
This is DoNothingStatic
This is DoNothing
this is Lambda。。。
(5)可以通过-=移除方法,是从后往前,逐个匹配,如果匹配不到,就不做任何操作,如果匹配到,就把当前这个移除,且停止去继续往后匹配
(6)在移除的方法的时候,必须是同一个实例的同一个方法才能移除,每个lambda表达式在底层会生成不同的方法名的,看起来一样实际不同
多播委托注册移除执行
//注册方法链
Action action = new Action(DoNothing);
action += DoNothingStatic;
action += new CustomMulticastDelegation().DoNothing2;
action += CustomMulticastDelegation.DoNothingStatic2;
action += DoNothing;
action += () =>
{
Console.WriteLine("this is Lambda。。。");
};
//移除方法链方法
action -= DoNothing;//是从后往前,逐个匹配,如果匹配不到,就不做任何操作,如果匹配到,就把当前这个移除,且停止去继续往后匹配
action -= new CustomMulticastDelegation().DoNothing2; //没有移除掉,因为不是同一个实例的方法,引用的地址是不同的
action -= CustomMulticastDelegation.DoNothingStatic2;//静态方法是同一个方法,可以移除掉
action -= () => //没有移除,因为不同同一个方法,每个lambda表达式在底层会生成不同的方法名的,看起来一样实际不同
{
Console.WriteLine("this is Lambda。。。");
};
action.Invoke();
运行结果
This is DoNothing
This is DoNothingStatic
This is DoNothing2
this is Lambda。。。
2、观察者模式
(1)需求:猫叫之后引发一系列的动作
方案1:封装一个方法,调用一系列动作
- 职责不单一,依赖于其他的类太多,代码不稳定,任何一个类的修改,都有可能会影响到这只猫
public void Miao()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} Miao", this.GetType().Name);
new Dog().Wang(); //狗叫了
new Mouse().Run();//老鼠跑了
new Baby().Cry(); // 小孩哭了
}
程序调用
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.Miao();
方案2:引发的动作注册到多播委托中去
- 职责单一,猫只是执行委托的方法链,方法链注册交个第三方,不在猫内部
- 使用委托的方式来实现观察者模式
public Action MiaoDelegateHandler = null;
public void MiaoDelegate()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} MiaoDelegate", this.GetType().Name);
MiaoDelegateHandler?.Invoke();//?. 如果不为null ,就执行后面的动作
}
程序调用
cat.MiaoDelegateHandler += new Dog().Wang; //狗叫了
cat.MiaoDelegateHandler += new Mouse().Run;//老鼠跑了
cat.MiaoDelegateHandler += new Baby().Cry; // 小孩哭了
cat.MiaoDelegate();//执行
方案3:引发的动作注册到方法列表中去
- 职责单一,猫只是执行方法列表,方法列表的注册交给第三方,不在猫的内部
- 完全使用面向对象的方式来实现观察者模式
public List observerlist = new List();
public void MiaoObsever()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} MiaoObsever", this.GetType().Name);
if (observerlist.Count>0)
{
foreach (var item in observerlist)
{
item.Invoke();
}
}
}
定义一个基类,其他类都实现基类
namespace MyDelegate.Event
{
public interface IObject
{
void Invoke();
}
}
using System;
namespace MyDelegate.Event
{
public class Baby : IObject
{
public void Invoke()
{
this.Cry();
}
public void Cry()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} Cry", this.GetType().Name);
}
}
}
using System;
namespace MyDelegate.Event
{
public class Dog : IObject
{
public void Invoke()
{
this.Wang();
}
public void Wang()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} Wang", this.GetType().Name);
}
}
}
using System;
namespace MyDelegate.Event
{
public class Mouse : IObject
{
public void Invoke()
{
this.Run();
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} Run", this.GetType().Name);
}
}
}
程序调用
cat.observerlist.Add(new Dog()); //狗叫了
cat.observerlist.Add(new Mouse());//老鼠跑了
cat.observerlist.Add(new Baby()); // 小孩哭了
cat.MiaoObsever();//执行
方案4:引发的动作注册到事件中去
复制方案2,加上关键字event
public event Action MiaoEventHandler = null;
public void MiaoEnvent()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} MiaoEnvent", this.GetType().Name);
MiaoEventHandler?.Invoke();//?. 如果不为null ,就执行后面的动作
}
程序调用
cat.MiaoEventHandler += new Mouse().Run;//老鼠跑了
cat.MiaoEventHandler += new Dog().Wang; //狗叫了
cat.MiaoEventHandler += new Baby().Cry; // 小孩哭了
cat.MiaoEnvent();
//cat.MiaoEventHanlder.Invoke();//类外部无法执行到类中的事件方法
子类调用
namespace MyDelegate.Event
{
public class CatChild:Cat
{
public void Show()
{
base.MiaoDelegateHandler.Invoke(); //子类中执行父类中多播委托
//base.MiaoEventHanlder.Invoke();//子类中无法访问到父类中的事件
}
}
}
(2)观察者模式几个要素
- 发布者
- 订阅者
- 订阅
- 触发事件
七、事件是什么
1、事件是什么
(1)事件是委托实例,增加一个关键字Event,是特殊的委托
(2)事件只能在当前类被访问,子类和类外部均不能执行类中的事件方法(安全)
(3)委托和事件从本质上来说没啥区别
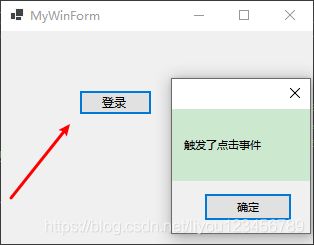
2、WinForm中按钮点击事件解析
页面上添加登录按钮双击生成了一个方法,运行起来,点击按钮,触发这个方法,这个过程是怎么完成的?
(1)按钮其实是一个Button类,继承Control类,Control有一个Click事件,( EventHandler(object? sender, EventArgs e))
(2)MyWinForm构造函数函数中有一个InitializeComponent方法,在InitializeComponent方法中初始化Button按钮实例,Button的实例中的Click事件+=一个动作btnLogin_Click方法
(3)点击按钮,触发事件,执行注册事件的方法,也就是btnLogin_Click方法
(4)更具体一些:程序运行,句柄被监听,监听鼠标的点击的动作,触发操作系统去找这个句柄是在哪个应用程序中,找到控件,执行这个控件中的事件,触发了方法
(5)在按钮点击触发方法的设计中,有很多相同的逻辑,就把不变的业务逻辑封装代码重用,可变的业务逻辑对外发布一个事件,由外部给事件注册动作;框架设计的时候,是非常需要这种设计的,ASP.NET MVC5管道处理模型就是通过19大事件来完成的;
Winform添加按钮,注册事件
namespace MyWinform
{
partial class MyWinForm
{
///
/// Required designer variable.
///
private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null;
///
/// Clean up any resources being used.
///
/// true if managed resources should be disposed; otherwise, false.
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing && (components != null))
{
components.Dispose();
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
#region Windows Form Designer generated code
///
/// Required method for Designer support - do not modify
/// the contents of this method with the code editor.
///
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.btnLogin = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.SuspendLayout();
//
// btnLogin
//
this.btnLogin.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(78, 59);
this.btnLogin.Margin = new System.Windows.Forms.Padding(2, 3, 2, 3);
this.btnLogin.Name = "btnLogin";
this.btnLogin.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(73, 25);
this.btnLogin.TabIndex = 0;
this.btnLogin.Text = "登录";
this.btnLogin.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true;
this.btnLogin.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.btnLogin_Click);
//
// MyWinForm
//
this.AutoScaleDimensions = new System.Drawing.SizeF(7F, 17F);
this.AutoScaleMode = System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode.Font;
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(312, 213);
this.Controls.Add(this.btnLogin);
this.Margin = new System.Windows.Forms.Padding(2, 3, 2, 3);
this.Name = "MyWinForm";
this.Text = "MyWinForm";
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
#endregion
private System.Windows.Forms.Button btnLogin;
}
}
添加执行逻辑
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MyWinform
{
public partial class MyWinForm : Form
{
public MyWinForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnLogin_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("触发了点击事件");
}
}
}
运行效果
3、标准事件的定义
(1)发布者发布事件
(2)订阅者订阅事件
(3)触发事件
定义发布者
///
/// 发布者:对外发布事件;触发事件;
///
public class Publisher
{
//发布事件
public event EventHandler Publish;
//发布者触发事件
public void EventAction()
{
Console.WriteLine("触发事件");
Publish?.Invoke(null,null);
}
}
定义订阅者
///
/// 订阅者:对发布者发布的事情关注
///
public class Observer1
{
///
/// 订阅者1的行为
///
///
///
public void Action1(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("订阅者1的行为");
}
}
///
/// 订阅者:对发布者发布的事情关注
///
public class Observer2
{
///
/// 订阅者2的行为
///
///
///
public void Action2(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("订阅者2的行为");
}
}
发布订阅触发事件
//初始化发布者
Publisher publisher = new Publisher();
//初始化订阅者1
Observer1 observer1 = new Observer1();
//初始化订阅者2
Observer2 observer2 = new Observer2();
//订阅者订阅事件
publisher.Publish += observer1.Action1;
publisher.Publish += observer2.Action2;
//触发事件
publisher.EventAction();
运行结果
触发事件
订阅者1的行为
订阅者2的行为