Spring学习(全)
本文目录
- 1. Spring概述
- 2. IOC 控制反转
-
- 2.1 简单介绍
- 2.2 Spring的第一个程序
- 2.3 DI入门
-
- 2.3.1 XML之set注入
-
- 简单类型的set注入
- 引用类型的set注入
- 引用类型的自动注入autowire
- 2.3.2 XML之构造注入
- 2.3.3 包含关系的配置文件
- 2.3.4 注解
-
- 创建对象的几个注解
- 简单类型赋值
- 引用类型赋值
- 2.3.4 小结
- 3. AOP 面向切面编程
-
- 3.1 AOP简介
- 3.2 AOP的实现
-
- 3.2.1 aspectJ
- 3.2.2 前置通知
- 3.2.3 后置通知
- 3.2.4 环绕通知
- 3.2.5 管理切入点@Pointcut
- 3.3 小结
- 4. Spring与Mybatis的整合
- 5. Spring事务
-
- 5.1 中小型项目的事务处理方案----注解
- 5.2 大型项目事务处理方案----aspectJ配置文件
- 6.Web项目
-
- 6.1 简单案例---学生注册
- 6.2 配置监听器
1. Spring概述
Spring为简化企业级开发而生,使用Spring开发可以将Bean对象,Dao组件对象,Service组件对象等都交给Spring容器来管理,这样使得很多复杂的代码在Spring中开发却变得非常的优雅和简洁,有效的降低代码的耦合度,极大的方便项目的后期维护。
Spring的核心技术:IOC(控制反转) 和 AOP(面向切面编程)。
Spring可管理依赖 (类a中使用类b的属性或方法,叫做类a依赖类b。)
Spring优点
- 轻量:Spring框架使用的jar包都比较小,运行时占用的资源少
- 针对接口编程,解耦合
- AOP编程的支持
- 方便集成各种优秀框架
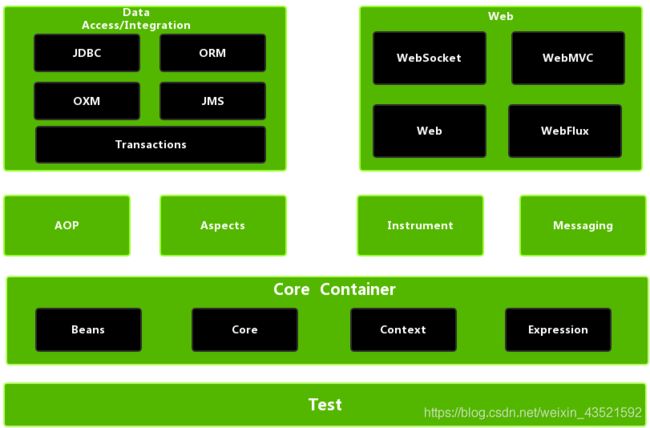
Spring框架至今已集成了20多个模块,这些模块分布在以下模块中:
- 数据访问/集成(Data Access/Integration)层
- Web层
- AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)模块
- 植入(Instrumentation)模块
- 核心容器(Core Container)
- 消息传输(Messaging)
- 测试(Test)模块
2. IOC 控制反转
2.1 简单介绍
IOC(Inversion of Control):控制反转,是一个概念、是一个思想。将对象的创建、复制和管理都交给代码外的容器(Spring)实现。
使用 IOC 的原因?
- 即使减少代码的改动也可以实现不同的功能。
- 实现解耦合。
专业名词解释:
“控制”:创建对象、对象属性的赋值,对象之间的关系管理。
“正转”:开发人员使用new主动创建对象。
“反转”:将创建对象的权限转移给代码之外的容器,由容器来创建对象。
“容器”:是指一个服务器软件,一个框架。比如Spring。
IOC既然是一个思想,那么肯定有落地的技术来实现它。
IOC的技术实现是DI(Dependency Injection 依赖注入),只需要在程序中提供要使用的对象名即可,其他都交给容器实现。比如Spring底层自动创建对象,其原理是利用了Java反射的机制。
IOC思想的体现:比如 Servlet 在浏览器中的创建。我们只需要在web.xml中使用Servlet ,然后Tomcat服务器会自动创建Servlet 对象。所以,Tomcat也可以叫做容器。
2.2 Spring的第一个程序
-
创建maven项目并在
pom.xml中加入spring的maven依赖<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version> </dependency> -
创建所需的类/接口
// 创建接口 package org.example.service; public interface Demo { void example(); }// 实现接口 package org.example.service.Impl; import org.example.service.Demo; public class DemoImpl implements Demo { @Override public void example() { System.out.println("执行了example方法"); } } -
在resources目录下创建spring的配置文件,在
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- spring的配置文件 beans是根标签,里面存储了java对象 spring-beans.xsd是约束文件,和mybatis中的dtd一样 --> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 声明bean,告诉spring要创建哪个类的对象(一个bean只能声明一个对象) id:对象的自定义名称(唯一) class:类的全限定名称,不能是接口。 --> <bean id="demo" class="org.example.service.Impl.DemoImpl"/> </beans>tips:spring把创建好的对象放入到map中,springMap.put(id, 对象);
例如:springMap.put("demo", new DemoImpl()); -
创建spring容器对象(在创建spring容器的时候会创建配置文件中所有的对象。默认调用类的无参构造方法。)
-
spring容器对象使用getBean获取到想要的对象
-
使用对象
@Test public void shouldAnswerWithTrue() { // 手动创建对象 // DemoImpl d = new DemoImpl(); // d.example(); // spring自动创建对象 // 1.指定spring配置文件的名称 String config = "beans.xml"; // 2.创建表示spring容器对象 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config); // 3.从容器中获取对象getBean(id) DemoImpl d = (DemoImpl) ac.getBean("demo"); // 4.使用对象 d.example(); }【注意】
2.3 DI入门
还记得吗,DI(依赖注入)表示创建对象、给属性赋值。
DI的实现方式有两种:
- 基于XML:在spring的配置文件中,使用标签和属性来实现。
- 基于注解:使用spring中的注解来完成属性赋值。(常用)
DI的语法分类:
- set注入:spring调用类的set方法来实现属性的赋值。
- 简单类型
- 引用类型
- 构造注入:spring调用类的有参构造函数完成属性的赋值。
【注意】set注入仅仅只是调用类的set方法
2.3.1 XML之set注入
简单类型的set注入
语法:
<bean id="对象名" class="类的全限定名">
<property name="属性名" value="属性值">
<property name="属性名" value="属性值">
</bean>
tips:一个property只能给一个属性赋值。
例子:
配置文件
<bean id="myStudent" class="org.example.Student">
<property name="name" value="codeKiang" />
<property name="age" value="18" />
</bean>
<!-- 非自定义类的属性赋值 -->
<bean id="myDate" class="java.util.Date">
<property name="time" value="2020082899" />
</bean>
测试文件
@Test
public void test01()
{
String config = "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
Student s = (Student)ac.getBean("myStudent");
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("=========以下为非自定义类的调用======");
Date date = (Date) ac.getBean("myDate");
System.out.println(date);
}
引用类型的set注入
语法:
<bean id="对象名" class="类的全限定名称">
<property name="属性名" ref="bean的id值(对象名称)" />
</bean>
例子
Student类:
package org.example.ba02;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
// 引用类型
private School school;
。。。省略setter/getter方法
}
School类:
package org.example.ba02;
public class School {
private String name;
private String address;
。。。省略setter/getter方法
}
配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myStudent" class="org.example.ba02.Student">
<property name="name" value="codeKiang" />
<property name="age" value="18" />
<!-- 引用类型 -->
<property name="school" ref="school" />
</bean>
<bean id="school" class="org.example.ba02.School">
<property name="name" value="清华" />
<property name="address" value="北京" />
</bean>
</beans>
引用类型的自动注入autowire
引用类型相对于简单类型的set注入有个好处,就是可以自动注入。即当一个类中有很多的引用类型时,你不需要写很多的
自动注入的两种方式:
-
byName(按名称注入):java类中引用类型的属性名要与bean标签的id值一致。语法:
<bean id="对象名" class="类的全限定名称" autowire="byName"> 简单类型的赋值 </bean>例子:
<bean id="myStudent" class="org.example.ba02.Student" autowire="byName"> <property name="name" value="byName" /> <property name="age" value="18" /> </bean> <!-- id名跟类中的属性名一致都是school --> <bean id="school" class="org.example.ba02.School"> <property name="name" value="清华" /> <property name="address" value="北京" /> </bean> -
byType(按类型注入):java类中引用类型的数据类型和bean的class属性是同源关系。同源就是一类的意思:
- java类中引用类型的数据类型和
bean的class值一样。 - java类中引用类型的数据类型和
bean的class值是父子关系。(引用类型的数据类型为父类) - java类中引用类型的数据类型和
bean的class值是接口与实现类关系。(引用类型的数据类型为接口类型)
语法:
<bean id="对象名" class="类的全限定名称" autowire="byType"> 简单类型的赋值 </bean>例子:
<bean id="myStudent" class="org.example.ba02.Student" autowire="byType"> <property name="name" value="byType" /> <property name="age" value="18" /> <!-- 因为属性school的类型是School,所以spring会自动找School类,或者其子类,或者其实现类 School school = new School(); --> </bean> <bean id="mySchool" class="org.example.ba02.School"> <property name="name" value="清华" /> <property name="address" value="北京" /> </bean> - java类中引用类型的数据类型和
思考:如果现在有两个`bean`,它们的关系为其中一个是父类,另一个为子类,也就是说引用类型是爷爷、父类bean是爸爸、子类bean是儿子,那么根据`byType`自动注入会是什么情况?
答:编辑器会报错。因为此时spring不知道该创建父类bean还是子类bean。
2.3.2 XML之构造注入
构造注入只是调用类的有参构造函数。
语法:(一个
当形参类型为引用类型时,需要把value 改成ref。
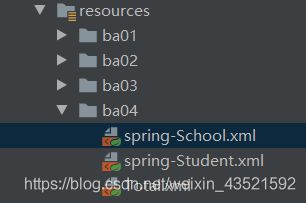
2.3.3 包含关系的配置文件
当入手一个大项目时,配置文件的内容自然会变多,修改起来不方便,而且大项目往往是团队合作,没道理所有人都对同一个配置文件进行修改,这时使用多个配置文件的思想就诞生了。
可以根据模块或功能的分类来对配置文件进行分配,问题是我们如何将这些文件关联在一起。
答案是 使用一个主配置文件的
spring-School.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- school模块的配置文件 -->
<bean id="school" class="org.example.ba04.School">
<property name="name" value="华南理工大学" />
<property name="address" value="大学城" />
</bean>
</beans>
spring-Student.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- student模块的配置文件 -->
<bean id="myStudent" class="org.example.ba04.Student" autowire="byName">
<property name="name" value="hang" />
<property name="age" value="22" />
</bean>
</beans>
Total.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 主配置文件:关联其他配置文件,一般不定义其他对象 -->
<import resource="classpath:ba04/spring-School.xml" />
<import resource="classpath:ba04/spring-Student.xml" />
</beans>
【注意】 classpath: 表示类路径。即告诉spring要去class文件下去找该文件。
通配符*:表示匹配任何字符。如Total.xml的第七八行的代码等价于
2.3.4 注解
spring还可以使用注解的方式来完成对象的创建,属性的赋值。需要注意的是,使用注解时需要使用到spring-aop的依赖。
注解的实现步骤
-
加入依赖(加入spring-context依赖的时候自动加入了spring-aop依赖)
-
创建类,在类中加入注解
@Component 语法:@Component(value = "对象名") 可以省略value,即 @Component("对象名") 默认名称:@Component, 默认就是首字母小写的类名 -
创建spring的配置文件
声明组件扫描器的标签,指明注解在项目中的位置。
<!-- 声明组件扫描器 base-package:指定注解在你项目中的包名 工作方式:spring会扫描遍历base-package指定的包中所有的类,找到类中的注解, 按照注解的功能创建对象/给属性赋值 --> <context:component-scan base-package="componentDemo" /> -
创建容器Application,使用对象。
组件扫描器扫描多个包的方式:
- 分隔符(
;或,): - 指定父包:
创建对象的几个注解
@Component
语法:@Component(value = “对象名”)
可以省略value,即 @Component(“对象名”)
默认名称:@Component , 默认就是首字母小写的类名
@Repository:表示创建dao对象(处于持久层类的上面)
@Service:创建service对象(处于业务层类的上面)
@Controller:创建控制器对象(处于控制器类的上面),相当于servlet
【最后三个注解是给项目的对象分层的,用法跟第一个一样】
简单类型赋值
@Value(value = "属性值") 简单类型赋值
属性:value是String类型,简单类型的属性值。(可省略)
位置:
- 在属性定义的上面,无需set方法。(推荐)
- 在set方法的上面
package ba02;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("myStudent")
public class Student {
@Value(value="codeKiang")
private String name;
private int age;
@Value("28")
public void setAge(int age) {
System.out.println("调用了setAge");
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
引用类型赋值
使用注解对引用类型的赋值有两种方法:@Autowired 和 @Resource
@Autowired:Spring提供的注解,使用的是自动注入原理。默认使用的是byType自动注入
属性:required 是一个boolean类型,默认为true 表示当引用类型赋值失败时,程序会报错,并终止执行。
位置:属性定义的上面或set方法的上面。
例子:
先创建school对象
package ba03;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class School {
@Value("华南理工大学")
private String name;
@Value("大学城")
private String address;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "School{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
再使用@Autowired给school属性赋值
package ba03;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("myStudent")
public class Student {
@Value("杭")
private String name;
@Value("22")
private int age;
@Autowired
private School school;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", school=" + school +
'}';
}
}
如果使用@Autowired的时候想要使用byName的方式给属性赋值呢?此时还需要用到另一个注解@Qualifier(value = "bean的id") ,同理value可以省略
例子:
创建school对象
package ba03;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component // 默认创建的对象名为school
public class School {
@Value("华南理工大学")
private String name;
@Value("大学城11")
private String address;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "School{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
使用byName的方式给属性赋值
package ba03;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("myStudent")
public class Student {
@Value("杭")
private String name;
@Value("22")
private int age;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("school") // 这两个注解无先后顺序
private School school;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", school=" + school +
'}';
}
}
注解对引用类型的赋值的第二种方式:@Resource
此注解是来自jdk的注解,并不是来自spring的。spring只是提供了对这个注解的支持,所以可以使用spring可以使用该注解对引用类型赋值。
此注解默认使用byName自动注入。如果byName的方式赋值失败,则会使用byType自动注入。
那如何让@Resource 只使用byName自动注入?答:@Resource(name="bean的id")
例子:
package ba04;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class School {
@Value("华南理工大学")
private String name;
@Value("大学城Resource")
private String address;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "School{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package ba04;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Component("myStudent")
public class Student {
@Value("杭")
private String name;
@Value("44")
private int age;
// @Resource(name = "school") 只使用byName自动注入
@Resource
private School school;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", school=" + school +
'}';
}
}
2.3.4 小结
IoC的解耦合是实现业务对象之间的解耦合,例如Service跟dao之间的解耦合。
xml配置文件和注解的对比
由于xml文件代码量多,比较繁琐,但是由于他与代码是分隔开的,所以它修改起代码来比较简单,因此我们可以在对经常需要改动的地方使用xml配置文件的方式使用依赖注入。
很明显,注解的方式很简单也很简洁,但是它与代码是嵌在一起的,修改起来不方便,因此我们可以在对不需要经常改动的地方使用注解的方式使用依赖注入。
3. AOP 面向切面编程
3.1 AOP简介
AOP面向切面编程是从动态角度考虑程序运行过程,其底层采用的是动态代理模式实现的。也可以说是动态代理的规范化,把动态代理实现的步骤和方式都定义好了,让我们程序员以统一的形式使用动态代理。为什么要统一?因为动态代理太灵活了,A人员可以用一种方式实现此功能,B人员可以使用另一种方式实现,C人员还有第三种方式,这对于开发来说肯定是不允许的。
常用的动态代理方式有两种:JDK的动态代理和CGLIB生成代理(常用于框架)。
-
JDK的动态代理是使用Proxy、Method、InvocatinHandler创建代理对象。
-
CGLIB代理的生成原理是生成目标类的子类,此子类对象就是代理对象。所以使用CGLIB生成动态代理,要求目标类必须能够继承即不是final修饰的类。
使用AOP的好处可以减少代码纠缠,即交叉业务与主业务逻辑可以分开。例如,转账,在真正转账业务逻辑前后,需要权限控制、日志记录、加载事务、结束事务等交叉业务逻辑,其代码量大且复杂,大大影响了主业务逻辑----转账。
专业术语解释:
Aspect:切面。给目标类所增加的功能就叫做切面,比如日志、事务。
JoinPoint:连接点,连接业务方法也切面的位置。即某类中的业务方法。
Pointcut:切入点,一个或多个连接点方法的集合。(可以学完本节再倒回来理解就容易了)
Advice:通知,表示切面功能执行的时间
如何理解面向切面编程?
- 要以切面为核心,分析项目中哪些功能可以用切面的形式去实现它
- 要合理的安排切面执行的时间Advice(在目标方法的前还是后)
- 要合理的安排切面执行的位置Pointcut(在哪个类哪个方法中)
什么时候考虑使用AOP?
- 当你不知道源码的情况下,要给一个系统中存在的类增加功能时。
- 给项目中多个类增加相同的功能时。
- 给业务方法增加事务、日志输出等。
3.2 AOP的实现
AOP的技术实现框架有两种:
- spring:其内部实现了AOP规范,可以做AOP的工作。但因为spring的AOP比较笨重,所以一般不用这种方式。
- aspectJ:一个专门做AOP的框架,轻量高效,所以开发中一般都用此方式。spring框架中集合了aspectJ框架,所以spring可以使用aspectJ的功能。
3.2.1 aspectJ
aspectJ实现AOP有两种方式:xml配置文件跟注解。本文中主要介绍注解的方式。
切入点表达式
语法:execution(访问权限? 返回值类型 包名.类名.?方法名(参数类型) 抛出异常类型?)
tips:?结尾的都是可选参数。也就是说 返回值类型 、方法名(参数类型) 是必不可少的。
切入表达式还可以使用通配符:
| 符号 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| * | 任意个字符 |
| … | 用在方法参数中,表示任意个参数 用在包名后,表示当前包及其子包路径 |
| + | 用在类名后,表示当前类及其子类 用在接口后,表示当前接口及其实现类 |
- 练习
execution(public * * (..)) 指定切入点为 任意公共的方法,即返回类型任意 方法名任意 参数任意
execution(* set*(..)) 指定切入点为:任何一个以“set”开始的方法
execution(* com.service..*.*(..)) 指定com.service包或子包下的任意方法都是切入点。【第二个*代表任意类名,第三个*代表任意方法名】
切面的执行时间advice的五个注解:
- @Before
- @AfterReturning
- @Around
- @AfterThrowing:异常后执行的切面方法,相当于catch里面的代码。
- @After:无论如何都会执行的切面方法,相当于finally里面的代码。
【注意】 下面不进行介绍第四第五注解。
3.2.2 前置通知
使用aspectJ的步骤:
- 新建maven项目,加入spring和aspectJ依赖
- 创建目标类:接口和其实现类
- 创建切面类
在类的上面加入@Aspect注解
在类中定义方法,即切面要执行的代码。
在切面方法上加入通知注解,例如@Before
通知注解的value属性中指定切入点表达式execution(),例如@Before(value = “execution(* *(…))”) - 使用DI创建对象
声明目标对象和切面类对象
声明aspectJ中的自动代理生成器标签,可以完成代理对象的自动创建。
第一步:在pom.xml中加入依赖
<!-- spring的maven依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- aspectJ的maven依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
第二步:
创建接口
package org.example.ba01;
public interface SomeService {
void doSome();
}
创建其实现类
package org.example.ba01;
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public void doSome() {
System.out.println("喝奶茶了!");
}
}
第三步:编写切面类
package org.example.ba01;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import java.util.Date;
// 声明当前类为切面类
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
// 前置通知
@Before(value = "execution(public void doSome(..))")
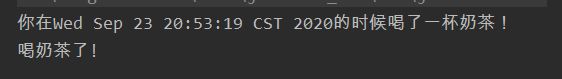
public void myBefore(){
System.out.println("你在"+ new Date() + "的时候喝了一杯奶茶!");
}
}
第四步:创建对象
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 声明目标对象 -->
<bean id="someService" class="org.example.ba01.SomeServiceImpl" />
<!-- 声明切面类对象 -->
<bean id="myAspect" class="org.example.ba01.MyAspect" />
<!-- 声明自动代理生成器:创建代理对象是在内存中完成的,创建代理对象实际是修改目标对象在内存中的结构。
即最后的目标对象实际是修改结构后的代理对象。
-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
</beans>
tips: 前置通知所修饰的切面方法即public void myBefore(),必须用public void修饰。方法参数可有可无。
方法参数可有可无,那切面方法的参数是什么呢?是JoinPoint 。
JoinPoint可以获取到原方法的一些信息,比如方法名称、方法的参数等。
【注意】这个JoinPoint 参数实际是每个通知注解修饰的切面方法都有的一个参数,其他切面如果要使用它的话就要把它放在第一个位置。
3.2.3 后置通知
后置通知@AfterReturning
- 属性:
value 切入点表达式
returning 接收目标方法的返回值 - 特点:
可以获取到目标方法的返回值,开发人员可以根据返回值来做不同的事情
可以修改返回值
被后置通知修饰的切面方法特点:
- public void修饰
- 有参数,参数为目标方法的返回值,类型推荐写
Object。参数名要与returning的属性值一致
创建接口
package org.example.ba02;
public interface SomeService {
String doSubmit();
}
接口的实现类
package org.example.ba02;
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public String doSubmit() {
System.out.println("事务提交成功!");
return "submit";
}
}
切面类
package org.example.ba02;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import java.util.Date;
// 声明当前类为切面类
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
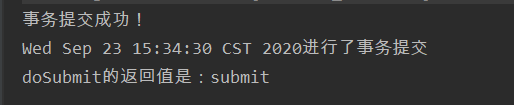
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* *..ba02.*.do*(..))", returning = "res")
public void myAfterReturning(Object res){
System.out.println(new Date() + "进行了事务提交");
System.out.println("doSubmit的返回值是:"+res);
}
}
【注意】
- returning的属性值与方法的形参名一致都是res。
* *..ba02.*.do*(..)表示任意返回类型 任意包下的 ba02包下的 任意类下的 以do开头的 方法
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 声明目标对象 -->
<bean id="someService" class="org.example.ba02.SomeServiceImpl" />
<!-- 声明切面类对象 -->
<bean id="myAspect" class="org.example.ba02.MyAspect" />
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
</beans>
后置通知修改返回值:
实现类
@Override
public Student doSubmit2() {
System.out.println("事务提交成功!");
Student stu = new Student("codekiang", "201810089");
return stu;
}
切面类
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* *..ba02.*.doSubmit2(..))", returning = "res")
public void myAfterReturning2(Student res){
System.out.println(new Date() + "进行了事务提交");
res.setId("20202323");
res.setName("hang");
System.out.println("myAfterReturning2中的返回值是:"+res);
}
可以看到修改是成功的。其实这个道理就跟方法传参一样,当你传递的是不可变参数时,则无论你在切面类如何进行改动都不会改变其返回值。当你传递的是引用类型的参数时,你只有在不改变指针指向的情况下才可以修改返回值。
3.2.4 环绕通知
后置通知@Around
-
属性:
value 切入点表达式 -
特点:
是功能最强的通知。可以在目标方法前后增强功能。经常用于事务操作。可控制目标方法是否调用
修改目标方法的执行结果,影响最后的调用结果
等同于jdk动态代理的InnovationHandler接口
被环绕通知修饰的切面方法特点:
-
public void修饰
-
固定参数:
ProceedingJoinPoint作用:等同于jdk动态代理的Method
-
返回值:目标方法的执行结果,可以被修改
接口
package org.example.ba03;
public interface SomeService {
void doAround();
}
实现类
package org.example.ba03;
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public void doAround() {
System.out.println("执行了doAround方法");
}
}
切面类
package org.example.ba03;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import java.util.Date;
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
@Around(value = "execution(* *..ba03.*.doAround(..))")
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
System.out.println("在执行doAround前打印时间:"+new Date());
// 执行目标方法
pjp.proceed(); // 等价于Method.invoke();
System.out.println("在执行doAround后提交事务");
// 有返回值的切面方法都要return
return result;
}
}
运行结果:

pjp.proceed(); 为执行目标方法,等价于Method.invoke();。

好像ProceedingJoinPoint有点不简单,看看它的源码发现它是继承JoinPoint,也就是说JoinPoint有的它都有。
正是因为它可以根据参数来决定目标方法执不执行或者其他灵活的操作,所以它的功能很强大。
3.2.5 管理切入点@Pointcut
如果你的项目有多个切入点表达式是重复的,那么你可以使用@Pointcut来减少重复代码。
@Pointcut属性: value 切入点表达式
特点:当使用@Pointcut定义在一个方法的上面,此时此方法的名称就是切入点表达式的别名。在其他通知的value属性中可以直接使用别名()代替切入点表达式。
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
@Around(value = "mypt()") // 一定要加上括号!!
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
System.out.println("在执行doAround前打印时间:"+new Date());
// 执行目标方法
pjp.proceed(); // 等价于Method.invoke();
System.out.println("在执行doAround后提交事务");
// 有返回值的切面方法都要return
return result;
}
@Around(value = "mypt()") // 一定要加上括号!!
public Object myAround2(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("测试类");
return null;
}
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* *..ba03.*.doAround(..))")
private void mypt(){
// 作为别名的函数,不需要代码,修饰符为private
}
}
3.3 小结
AOP是面向切面编程,是动态代理的规范化,开发项目时要注意三个点:切入面功能、切入时间和切入位置。
通知注解有5个,其中有三个是最常用的:@Before、@AfterReturning、@Around。
通知注解的value是切入点表达式execution,可以搭配通配符使用。
目标类有接口的,使用的是jdk动态代理。目标类没有接口的,spring会自动使用cglib代理。如果你期望目标类有接口时依旧使用cglib代理,则需要在配置文件的自动代理生成器标签加上一点东西:
4. Spring与Mybatis的整合
Mybatis的学习日记在我的另一篇博客:Mybatis学习日记(全)
在这里简单回顾下Mybatis的使用步骤:
-
读取主配置文件,创建SqlSessionFactory对象
最基本的配置文件应该有数据库信息、mapper文件的位置。
-
使用openSession()方法获取SqlSession对象
-
使用getMapper()方法获取到dao对象
-
使用dao对象
整合思路:我们手动创建基本所需的类与配置文件,创建对象(SqlSessionFactory,dao)的活都交给spring来实现,另外数据库连接池的部分也交由spring,然后使用service对象调用dao完成数据访问。
实现步骤:
-
创建项目,加入maven依赖
spring依赖、mybatis依赖、mysql驱动依赖、spring事务的依赖。
mybatis与spring继承的依赖:用来在项目中创建mybatis的SqlSessionFactory、dao对象的。
-
创建实体类
-
创建dao接口和mapper文件
-
创建mybatis主配置文件
-
创建service接口和实现类,属性是dao
-
创建spring主配置文件:声明mybatis的对象交给spring创建
数据源、SqlSessionFactory、dao对象、声明自定义的Service
-
创建测试类,通过Service对象调用dao完成数据访问
案例
第一步:在pom.xml中加入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- spring的maven依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring事务依赖1 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring事务依赖2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring和mybatis的集成依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql驱动依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.17</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 阿里的数据库连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory> <!--所在的目录-->
<includes> <!-- 包括目录下的.properties跟.xml文件都会进行编译 -->
<include>**/*.properties
**/ *.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>false</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
第二步:创建实体Student类
package org.example.entity;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private String email;
private int age;
public Student(){}
public Student(int id, String name, String email, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
第三步:dao接口和mapper文件
StudentDao
package org.example.dao;
import org.example.entity.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentDao {
List<Student> QueryAllStudent();
int InsertStudent(Student stu);
}
StudentDao.xml
<mapper namespace="org.example.dao.StudentDao">
<select id="QueryAllStudent" resultType="Student">
select * from student;
select>
<insert id="InsertStudent" >
insert into student values(#{id}, #{name}, #{email}, #{age});
insert>
mapper>
第四步:创建mybatis主配置文件
mybatis.xml
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
settings>
<typeAliases>
<package name="org.example.entity"/>
typeAliases>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/example/dao/StudentDao.xml"/>
mappers>
configuration>
第五步:创建service接口和实现类,属性是dao
StudentService
package org.example.service;
import org.example.entity.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentService {
List<Student> QueryAllStudent();
int InsertStudent(Student stu);
}
StudentServiceImpl
package org.example.service.impl;
import org.example.dao.StudentDao;
import org.example.entity.Student;
import org.example.service.StudentService;
import java.util.List;
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
private StudentDao studentDao;
@Override
public List<Student> QueryAllStudent() {
return studentDao.QueryAllStudent();
}
@Override
public int InsertStudent(Student stu) {
return studentDao.InsertStudent(stu);
}
public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao) {
this.studentDao = studentDao;
}
}
第六步:创建spring主配置文件
spring-config.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="密码" />
<property name="maxActive" value="20" />
bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource" />
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis.xml" />
bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer" >
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory" />
<property name="basePackage" value="org.example.dao" />
bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="org.example.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl" >
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao" />
bean>
beans>
测试:
@Test
public void test01()
{
String config = "spring-config.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
// 获取到service对象
StudentService std = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
List<Student> students = std.QueryAllStudent();
students.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x));
}
在实际开发中,我们一般是把数据库信息单独放在一个以.properties为后缀名的文件里,然后在spring的主配置文件中使用,这样方便管理。
如:
创建jdbc.properties文件
# 注意在文件中的&可以不用转义
jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
jdbc.username = root
jdbc.pwd = 5642818
jdbc.max = 20
数据库连接部分变成
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties" />
<bean id="myDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.pwd}" />
<property name="maxActive" value="${jdbc.max}" />
bean>
5. Spring事务
什么是事务?事务就是一组sql语句,这组语句要么全部执行成功,要么全部执行失败。
在java代码中写程序时,我们一般把事务放在service类的业务方法上。
那使用Spring事务有什么好处呢?spring提供了统一处理事务的模型,能统一使用事务的方式来完成不同数据库访问技术的事务处理。
spring处理事务的模型
-
使用事务管理器对象进行事务提交和回滚事务
事务管理器是一个接口和它的众多实现类
接口:PlatformTransactionManager,定义了commit、rollback方法
实现类:
mybatis对应的实现类为DataSourceTransactionManager
hibernate对应的实现类为HibernateTransactionManager
使用:
-
声明使用什么样的事务、事务的类型
-
指定事务的隔离级别
DEFAULT:使用DB默认的事务隔离级别。Mysql的默认级别是
REPEATABLE_READ;Oracle默认为READ_COMMITTED.READ_UNCOMMITTED:读未提交
READ_COMMITTED:读已提交
REPEATABLE_READ:可重复读
SERIALIZABLE:串行化
-
指定事务的超时时间:一个方法最长的执行时间。若该方法超过了时间,事务就回滚。单位是秒。默认值是-1,代表无限时间。(一般使用默认值)
-
指定事务的传播行为:控制业务是否有事务,是怎样的事务。
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED:指定的方法必须在事务内执行。若当前存在事务,则加入到当前事务中;否则创建一个新事物。(spring默认的传播行为)
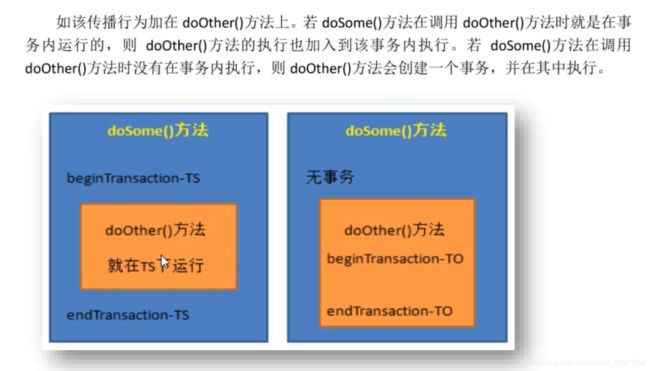
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED_NEW:总是创建一个事务。若当前存在事务,则将当前事务挂起,重新创建一个新事务,新事务执行完毕才将原事务唤醒。
如上述的doSome()跟doOther();若doSome()的执行有事务,则doOther()会创建一个新事务并将doSome()的事务挂起,直至新事务执行完毕。
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:指定的方法支持当前事务,但若当前没有事务,则以非事务的方式执行。
如doSome()的执行有事务,则doOther()会加入到当前事务;若doSome()的执行没有事务,则doOther()就以非事务的方式执行。
PROPAGATION_MANDATORY
PROPAGATION_NESTED
PROPAGATION_NEVER
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED
tips:掌握标黑体的
-
提交事务,回滚事务的机制
当业务方法执行成功,没有运行时异常,则spring在方法执行完之后提交事务。
当业务方法抛出运行时异常或ERROR,spring会执行回滚。
-
5.1 中小型项目的事务处理方案----注解
spring使用aop方式给业务方法增加事务的功能。使用@Transactional注解给当前方法增加事务,需放在public方法的上面;可以给@Transactional注解的属性进行赋值,如具体的隔离级别,传播行为,异常信息等。
使用@Transactional的步骤
- 主配置文件中声明事务管理器对象。如
- 使用**
@Transactional**创建代理对象,给方法增加事务功能
案例:
第一步:
在entity包中创建实体类
package org.example.entity;
public class Goods {
private int id;
private String name;
private int amount;
private float price;
public Goods(){}
public Goods(int id, int amount) {
this.id = id;
this.amount = amount;
}
// 省略了getter跟setter
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Goods{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", amount=" + amount +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
package org.example.entity;
public class Sale {
private int id;
private int gid;
private int nums;
public Sale(){}
public Sale(int gid, int nums) {
this.gid = gid;
this.nums = nums;
}
// 省略了getter跟setter
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Sale{" +
"id=" + id +
", gid=" + gid +
", nums=" + nums +
'}';
}
}
第二步:在dao包中创建dao类
package org.example.dao;
import org.example.entity.Goods;
public interface GoodsDao {
int updateGoods(Goods goods);
Goods selectGoods(int gid);
}
<mapper namespace="org.example.dao.GoodsDao">
<update id="updateGoods">
update goods set amount = amount - #{amount} where id=${id};
update>
<select id="selectGoods" resultType="org.example.entity.Goods">
select * from goods where id=#{gid};
select>
mapper>
package org.example.dao;
import org.example.entity.Sale;
public interface SaleDao {
int insertSale(Sale sale);
}
<mapper namespace="org.example.dao.SaleDao">
<insert id="insertSale">
insert into sale(gid,nums) value(#{gid}, #{nums});
insert>
mapper>
第三步:编写mybatis主配置文件
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
settings>
<typeAliases>
<package name="org.example.entity"/>
typeAliases>
<mappers>
<package name="org.example.dao"/>
mappers>
configuration>
第四步:自定义运行时异常类
package org.example.exceptions;
// 自定义运行时异常
public class NotEnoughException extends RuntimeException{
public NotEnoughException() {
super();
}
public NotEnoughException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
第五步:编写service层业务
package org.example.service;
public interface BuyGoodsService {
void buy(int gid, int nums);
}
实现类
package org.example.service.impl;
import org.example.dao.GoodsDao;
import org.example.dao.SaleDao;
import org.example.entity.Goods;
import org.example.entity.Sale;
import org.example.exceptions.NotEnoughException;
import org.example.service.BuyGoodsService;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
public class BuyGoodsServiceImpl implements BuyGoodsService {
private SaleDao saleDao;
private GoodsDao goodsDao;
// 事务注解【注意】
@Transactional
@Override
public void buy(int gid, int nums) {
// 记录销售信息
Sale sale = new Sale(gid, nums);
saleDao.insertSale(sale);
Goods s_goods = goodsDao.selectGoods(gid);
// 判断商品是否存在或库存是否足够
if(s_goods == null) throw new NullPointerException(gid+"商品不存在");
else if(s_goods.getAmount() < nums) throw new NotEnoughException(gid+"商品库存不足");
// 更新库存
Goods goods = new Goods(gid, nums);
goodsDao.updateGoods(goods);
}
public void setSaleDao(SaleDao saleDao) {
this.saleDao = saleDao;
}
public void setGoodsDao(GoodsDao goodsDao) {
this.goodsDao = goodsDao;
}
}
第六步:编写spring主配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties" />
<bean id="myDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.pwd}" />
<property name="maxActive" value="${jdbc.max}" />
bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource" />
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis.xml" />
bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer" >
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory" />
<property name="basePackage" value="org.example.dao" />
bean>
<bean id="goodsService" class="org.example.service.impl.BuyGoodsServiceImpl" >
<property name="goodsDao" ref="goodsDao" />
<property name="saleDao" ref="saleDao" />
bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource" />
bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
beans>
@Transactional等价于
@Transactional(
propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,
isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT,
readOnly = false,
rollbackFor = {}
)
rollbackFor表示发生指定的异常一定回滚。
- spring框架会首先检查方法抛出异常是不是处于rollbackFor的属性中。若在则不管是什么类型的异常都进行回滚。
- 如果抛出的异常不在rollbackFor的属性中,spring就会判断该异常是否为运行时异常;如果是,就回滚。
测试:
@Test
public void shouldAnswerWithTrue()
{
String config = "spring-config.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
BuyGoodsService service = (BuyGoodsService)ac.getBean("goodsService");
service.buy(1002, 10);
}
5.2 大型项目事务处理方案----aspectJ配置文件
在大型项目中事务处理使用aspectj框架功能,在spring配置文件中声明类、方法所需要的事务;使事务配置与业务方法完全分离。
实现步骤:
-
加入依赖,使用aspectJ框架
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId> <artifactId>spring-aspectsartifactId> <version>5.2.8.RELEASEversion> dependency> -
声明事务管理器对象
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource" /> bean> -
声明对应方法需要的事务类型
<tx:advice id="myAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="buy" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="DEFAULT"/> <tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRES_NEW"/> <tx:method name="*" read-only="true"/> tx:attributes> tx:advice> -
配置aop,指定哪些类要创建代理
<aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="service" expression="execution(* *..service..*.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="myAdvice" pointcut-ref="service" /> aop:config>
6.Web项目
6.1 简单案例—学生注册
在web项目中,大致流程如下:
- 创建maven,web项目
- 在之前的依赖基础上再加入jsp跟servlet依赖
- 创建需要是实体类,service、controller、dao。
- 使用ioc在控制层创建service对象,使用service对象调用dao层对象进行数据库访问
- 配置tomcat服务器,启动项目
第二步:在之前的依赖基础上加上jsp跟servlet依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId>
<version>3.1.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jspgroupId>
<artifactId>jsp-apiartifactId>
<version>2.2.1-b03version>
dependency>
第三步:拷贝之前项目的dao、entity、service以及resources包
第四步:创建一个jsp发送请求
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8" %>
<html>
<body>
<h2>学生注册</h2>
<form action="reg" method="post">
<tr>
<td>id:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="id"></td>
</tr><br>
<tr>
<td>姓名:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="name"></td>
</tr><br>
<tr>
<td>年龄:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="age"></td>
</tr><br>
<tr>
<td>邮箱:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="email"></td>
</tr><br>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" value="提交"></td>
</tr><br>
</form>
</body>
</html>
第五步:创建controller
package org.example.controller;
import org.example.entity.Student;
import org.example.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(name = "RegisterServlet")
public class RegisterServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
int id = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("id"));
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String email = request.getParameter("email");
int age = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("age"));
// 创建spring的容器对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
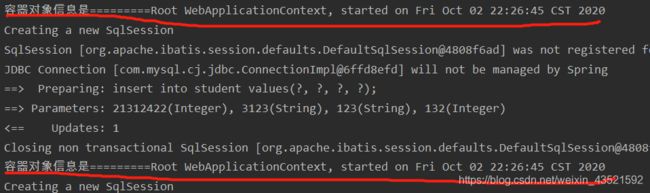
System.out.println("容器对象信息是========="+ac);
// 获取service
StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
Student stu = new Student(id, name, email, age);
studentService.InsertStudent(stu);
//页面跳转
request.getRequestDispatcher("/show.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
}
第六步:配置web.xml文件(因为项目自带的版本太低了,所以要删掉)
-
右键删掉web.xml
-
配置servlet
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>RegisterServletservlet-name> <servlet-class>org.example.controller.RegisterServletservlet-class> servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>RegisterServletservlet-name> <url-pattern>/regurl-pattern> servlet-mapping> web-app>
第七步:创建显示注册成功的jsp
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>注册成功title>
head>
<body>
<h2>恭喜你,小宝贝h2>
body>
html>
最后一步:配置tomcat服务器
6.2 配置监听器
到此为止,完成了一个web项目的搭建。但是你会发现,如果你有多个请求,你的容器就会被创建多次,这样很浪费资源,我们只需要一个容器对象就够了。那我们要如何避免这种情况呢?
思路:使用监听器,当全局作用域对象被创建时,创建容器对象并存入到ServletContext
在spring框架中有封装好的工具类ContextLoaderListener,可以直接获取到ServletContext。
第一步:加入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webartifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
第二步:在web.xml中注册监听器
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-config.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
第三步:使用框架提供的工具类获取监听器对象
// 手工创建spring的容器对象的方式
// ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
// 使用框架提供的工具类创建容器对象
ServletContext sc = getServletContext();
WebApplicationContext ac = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(sc);
System.out.println("容器对象信息是========="+ac);
运行项目,多次注册学生信息,发现每次的容器对象都是同一个。
tips:
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(sc); 内部的执行过程如下:
- 创建容器对象,执行
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); - 把容器对象放入到ServletContext中。
setAttribute的方式。