@Transactional源码分析二:事务传播属性
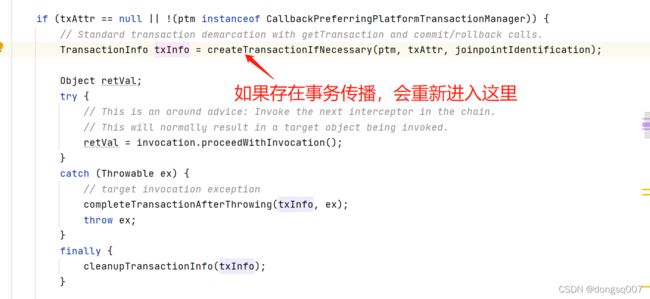
当事务存在传播机制,又会重新进入以下代码:
@Override
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
TransactionDefinition def = (definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults());
//因为第一次进来的时候,没有值,获取到之后存入了threadLocal当中,所以第二次进来
//进来的时候threadLocal当中就有值了
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
//第一次进来connectionHolder为空的,所以不存在事务
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
//如果不是第一次进来,则会走这个逻辑
return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
.....
}
@Override
protected boolean isExistingTransaction(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
//如果事务对象中有连接且是active的,则说明之前存在事务
return (txObject.hasConnectionHolder() && txObject.getConnectionHolder().isTransactionActive());
}
第一次之后,再次进来transaction中connectionHolder就不为空了,connectionHolder可以理解为连接对象的包装,同一个事务的前提必须是同一个连接对象,所以接下来会进入handleExistingTransaction方法。
private TransactionStatus handleExistingTransaction(
TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction, boolean debugEnabled)
throws TransactionException {
//不允许有事务,直接异常
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never'");
}
//以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction");
}
//挂起当前事务
Object suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
//修改事务状态信息,把事务的一些信息存储到当前线程中,ThreadLocal中
return prepareTransactionStatus(
definition, null, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction, creating new transaction with name [" +
definition.getName() + "]");
}
//挂起
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
try {
return startTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error beginEx) {
resumeAfterBeginException(transaction, suspendedResources, beginEx);
throw beginEx;
}
}
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed()) {
throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException(
"Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " +
"specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'");
}
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]");
}
//默认是可以嵌套事务的
if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction()) {
//这里的newTransaction 为 false
DefaultTransactionStatus status =
prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null);
//创建回滚点
status.createAndHoldSavepoint();
return status;
}
else {
return startTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
// Assumably PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS or PROPAGATION_REQUIRED.
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Participating in existing transaction");
}
if (isValidateExistingTransaction()) {
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT) {
Integer currentIsolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
if (currentIsolationLevel == null || currentIsolationLevel != definition.getIsolationLevel()) {
Constants isoConstants = DefaultTransactionDefinition.constants;
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] specifies isolation level which is incompatible with existing transaction: " +
(currentIsolationLevel != null ?
isoConstants.toCode(currentIsolationLevel, DefaultTransactionDefinition.PREFIX_ISOLATION) :
"(unknown)"));
}
}
if (!definition.isReadOnly()) {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] is not marked as read-only but existing transaction is");
}
}
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
//如果第二次进来还是PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,走这里,newTransaction为false
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
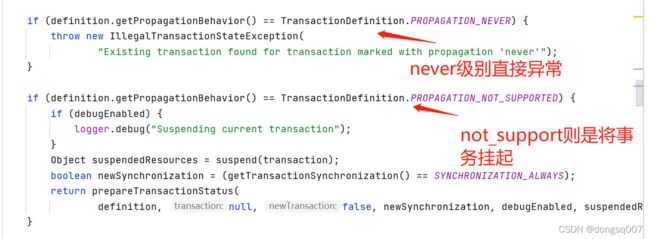
遇到传播属性为never则直接抛异常,遇到不支持事务的not_support属性则是先将事务挂起,看挂起的代码:
@Override
protected Object doSuspend(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null);
return TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(obtainDataSource());
}
public static Object unbindResource(Object key) throws IllegalStateException {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Object value = doUnbindResource(actualKey);
if (value == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No value for key [" + actualKey + "] bound to thread [" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
return value;
}
@Nullable
private static Object doUnbindResource(Object actualKey) {
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
if (map == null) {
return null;
}
Object value = map.remove(actualKey);
// Remove entire ThreadLocal if empty...
if (map.isEmpty()) {
resources.remove();
}
// Transparently suppress a ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (value instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) value).isVoid()) {
value = null;
}
if (value != null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Removed value [" + value + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] from thread [" +
Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
return value;
}
解绑操作是将数据源对象和connectionHolder进行解绑,并将connectionHolder对象返回,作为标识解绑的 suspendedResources(其实就是connectionHolder,只不过spring用这个suspendedResources作为解绑的标识,事务恢复绑定就是拿数据源对象和suspendedResources重新绑定)

require_new 这个传播属性会先挂起当前的事务,再重新开启一个新的事务(newTransaction为true),单独提交和回滚新的事务,然后再重新绑定之前挂起的事务。
接下来看嵌套事务的开启:
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed()) {
throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException(
"Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " +
"specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'");
}
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]");
}
//默认是可以嵌套事务的
if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction()) {
//这里的newTransaction 为 false
DefaultTransactionStatus status =
prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null);
//创建回滚点
status.createAndHoldSavepoint();
return status;
}
else {
return startTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
嵌套事务的回滚:

嵌套事务的回滚操作包括事务回滚和释放回滚点。
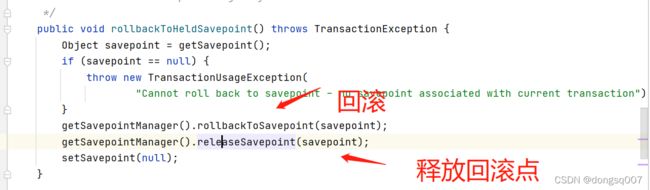
回滚的时候会重置连接对象ConnectionHolder的属性rollbackOnly属性为false,这个属性可以控制最外围的事务是否回滚,当嵌套事务出现异常时,会回滚本事务,同时将ConnectionHolder的属性rollbackOnly设置为false(如果rollbackOnly为true,最终会全部进行回滚,因为这个rollbackOnly属于连接对象的属性,而多个事务切面是同一个连接对象),这样就保证了最外层的事务在一定情况下可以进行commit操作(前提是嵌套事务捕获了异常,如果没有捕获,异常会往上抛,最终最外层的事务也会进行回滚操作)。