【STL七】序列容器——effective STL
【STL七】序列容器——effective STL
- 一、优先采用emplace系列函数
- 二、调用empty而不是检查size()是否为0?
-
- 1、网上的说法
- 2、验证(以vector为例,其实list也一样)
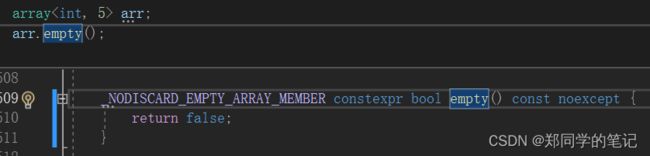
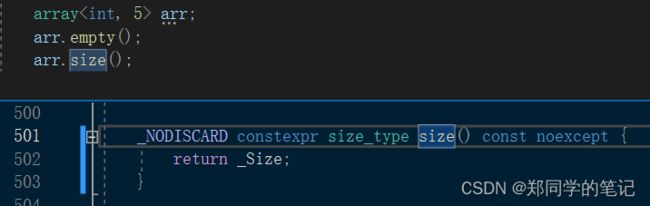
- 3、array的empty和size的实现
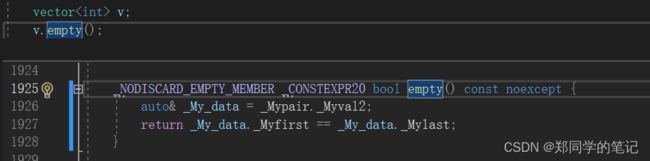
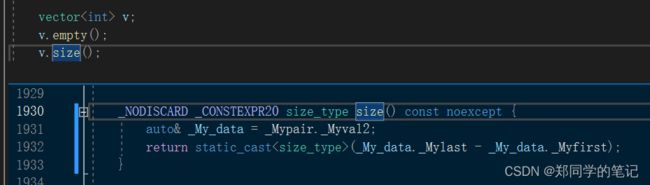
- 4、vector的empty和size的实现
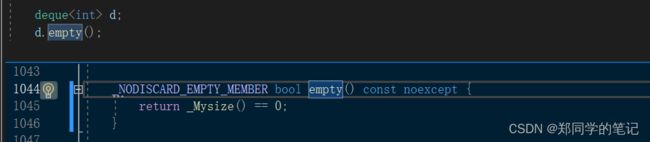
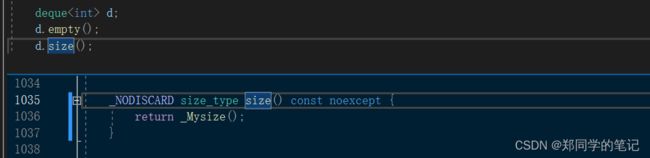
- 5、deque的empty和size的实现
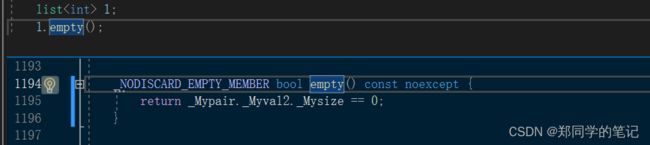
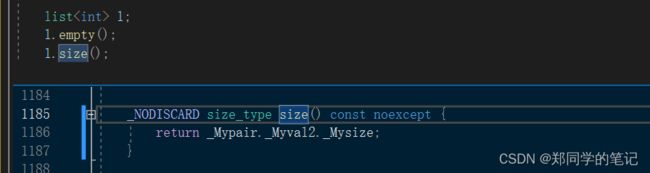
- 6、list的empty和size的实现
- 7、个人意见
- 三、C++ vector容量(capacity)和大小(size)的区别
- 四、使用reserve来避免不必要的重新分配
- 五、reserve和resize的区别
- 六、remove和erase有什么不同?
-
- 1、list容器成员函数remove
- 2、stl算法std::remove
- 七、容器operator[]和at()的差异
- 八、容器中包含了通过new操作创建的指针,切记在容器对象析构前将指针delete掉
- 九、遍历删除?
-
- 适用于vector、deque、list
- 十、vector容器的clear与swap
一、优先采用emplace系列函数
| 函数 | 函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| push_back | emplace_back | 在容器尾部生成一个元素。和 push_front() 的区别是,该函数直接在容器头部构造元素,省去了复制移动元素的过程。 |
| push_front | emplace_front | 在容器头部生成一个元素。和 push_front() 的区别是,该函数直接在容器头部构造元素,省去了复制移动元素的过程。 |
| insert | emplace | 都是容器中插入新元素。插入类对象,insert需要调用类的构造函数和移动构造函数(或拷贝构造函数);而通过 emplace() 函数实现同样的功能,只需要调用构造函数即可。 |
见【STL四】序列容器——vector容器
二、调用empty而不是检查size()是否为0?
1、网上的说法
因为empty对所有标准容器都是常数时间O(1),常被实现为内联函数(inline function)。而对于一些list实现,size需要遍历链表,耗费线性时间O(n)。
list<int> lst;
if (lst.size() == 0) { ... } // 不推荐使用
if (lst.empty()) { ... } // 推荐使用
2、验证(以vector为例,其实list也一样)
- 我们分别在vector为空时empty的耗时
- 我们分别在vector为空时size的耗时
- 我们分别在vector为10000个时size的耗时
#include(end1 - start1);
cout << (double)l.count();*/
cout << "vector 含有0个对象时的size" << endl;
auto start2 = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
v.size();
auto end2 = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
cout << start2.time_since_epoch().count() << endl;
cout << end2.time_since_epoch().count() << endl<<endl;
/*auto l2 = std::chrono::duration_cast(end2 - start2);
cout << (double)l2.count();*/
cout << "vector 含有10000个对象时的size" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; ++i)
v.push_back(i); //像普通数组一样使用数组容器
auto start3 = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
v.size();
auto end3 = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
cout << start3.time_since_epoch().count() << endl;
cout << end3.time_since_epoch().count() << endl;
/*auto l3 = std::chrono::duration_cast(end3 - start3);
cout << (double)l3.count();*/
return 0;
}
输出
vector 含有0个对象时的empty
109725992888000
109725992888100
vector 含有0个对象时的size
109725994739300
109725994739500
vector 含有10000个对象时的size
109725995782100
109725995782100
虽然每次输出的时间的相差略有不同,但是并没有证据证明他们耗费线性时间。
3、array的empty和size的实现
4、vector的empty和size的实现
5、deque的empty和size的实现
6、list的empty和size的实现
7、个人意见
基于以上这些,个人并不支持网上的这个说法,个人认为他们的时间都是O(1);
三、C++ vector容量(capacity)和大小(size)的区别
- vector 容器的容量(用 capacity 表示),指的是在不分配更多内存的情况下,容器可以保存的最多元素个数;
- 而 vector 容器的大小(用 size 表示),指的是它实际所包含的元素个数。
//vector 容器。
#include 输出
v.size = 1 ; v.capacity = 1
v.size = 2 ; v.capacity = 2
v.size = 3 ; v.capacity = 3
v.size = 4 ; v.capacity = 4
v.size = 5 ; v.capacity = 6
v.size = 6 ; v.capacity = 6
v.size = 7 ; v.capacity = 9
v.size = 8 ; v.capacity = 9
v.size = 9 ; v.capacity = 9
v.size = 10 ; v.capacity = 13
v.size = 11 ; v.capacity = 13
v.size = 12 ; v.capacity = 13
v.size = 13 ; v.capacity = 13
v.size = 14 ; v.capacity = 19
v.size = 15 ; v.capacity = 19
v.size = 16 ; v.capacity = 19
v.size = 17 ; v.capacity = 19
v.size = 18 ; v.capacity = 19
v.size = 19 ; v.capacity = 19
v.size = 20 ; v.capacity = 28
- vector每次进行空间扩展时,windows是按照临界值的1.5倍左右进行,linux是按照2的倍数进行扩展。
四、使用reserve来避免不必要的重新分配
基于《三、C++ vector容量(capacity)和大小(size)的区别》我们可知,我们在知道大概容量的前提下,可以提前使用reserve来避免内存的浪费。
//vector 容器。
#include 输出
v.size = 1 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 2 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 3 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 4 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 5 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 6 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 7 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 8 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 9 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 10 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 11 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 12 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 13 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 14 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 15 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 16 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 17 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 18 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 19 ; v.capacity = 21
v.size = 20 ; v.capacity = 21
- 对比《三、C++ vector容量(capacity)和大小(size)的区别》,我们便节省了7(28-21)个int大小的内存。
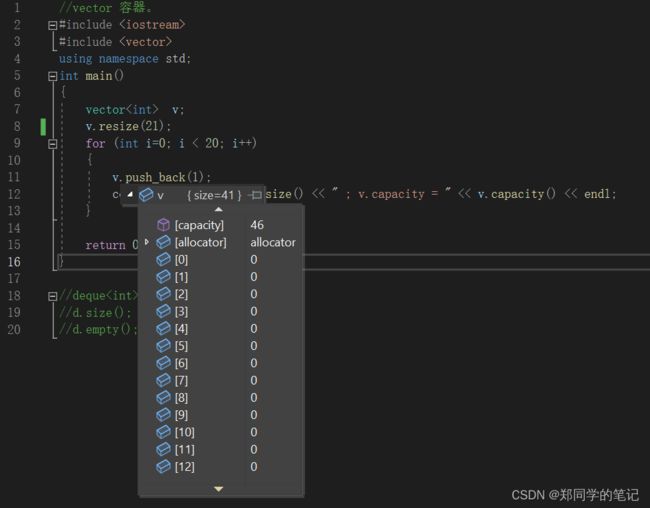
五、reserve和resize的区别
- reserve:申请内存,但内存还未被初始化,
可以和pushBack搭配使用
- resize:申请内存,并在这块内存上调用元素的构造函数进行初始化,
可以和operator[]配合使用
//vector 容器。
#include 输出
v.size = 22 ; v.capacity = 31
v.size = 23 ; v.capacity = 31
v.size = 24 ; v.capacity = 31
v.size = 25 ; v.capacity = 31
v.size = 26 ; v.capacity = 31
v.size = 27 ; v.capacity = 31
v.size = 28 ; v.capacity = 31
v.size = 29 ; v.capacity = 31
v.size = 30 ; v.capacity = 31
v.size = 31 ; v.capacity = 31
v.size = 32 ; v.capacity = 46
v.size = 33 ; v.capacity = 46
v.size = 34 ; v.capacity = 46
v.size = 35 ; v.capacity = 46
v.size = 36 ; v.capacity = 46
v.size = 37 ; v.capacity = 46
v.size = 38 ; v.capacity = 46
v.size = 39 ; v.capacity = 46
v.size = 40 ; v.capacity = 46
v.size = 41 ; v.capacity = 46
六、remove和erase有什么不同?
1、list容器成员函数remove
只有list容器才有成员函数remove,而array、vector和deque是没有remove成员函数的。
- remove:remove是以value相等为标准,也改变size的值。
- erase:erase是以迭代器为基本单位,清除元素,改变size的值;
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l{ 1,2,2,3,3,4,5 };
auto begin = l.cbegin();
auto end = l.cend();
l.remove(3);
while( begin != end)
{
cout << *begin << endl;
begin++;
}
cout << "l.size = " << l.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
1
3
3
4
5
l.size = 5
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l{ 1,2,2,3,3,4,5 };
auto first = l.begin();
first++;
auto last = l.end();
last--;
// l.erase(first,last);
l.erase(first);
for( auto begin = l.begin();begin != l.end();begin++)
{
cout << *begin << endl;
}
cout << "l.size = " << l.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
1
2
3
3
4
5
l.size = 6
2、stl算法std::remove
- std::remove() 可以从它的前两个正向迭代器参数指定的序列中移除和第三个参数相等的对象
- 我们可以从下面的demo看到,stl算法提供的remove并没有真正的删除,只是把迭代器向前移动了下,所以如果想要真正的删除,还是要调用erase;
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l{ 1,2,2,3,3,4,5 };
std::remove(l.begin(), l.end(), 2);//除了list,其他容器也可以使用,array,vector,deque)
for( auto begin = l.begin();begin != l.end();begin++)
{
cout << *begin << endl;
}
cout << "l.size = " << l.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
1
3
3
4
5
4
5
l.size = 7
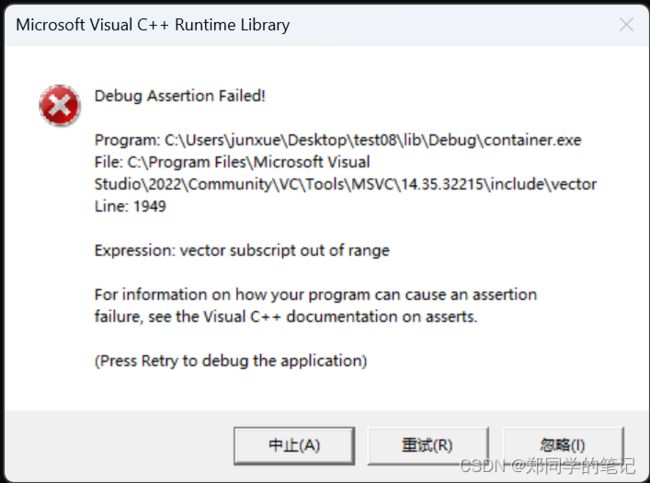
七、容器operator[]和at()的差异
- at()
#include 输出
invalid vector subscript
exit process!
- operator[]
#include 八、容器中包含了通过new操作创建的指针,切记在容器对象析构前将指针delete掉
#include 九、遍历删除?
适用于vector、deque、list
#include 十、vector容器的clear与swap
- vec.clear():清空内容,但是不释放内存。
#include 输出
v.capacity = 8
- .swap():清空内容,且释放内存,想得到一个全新的vector。
- shrink_to_fit():清空未使用的内存,请求移除未使用的容量。
#include 尽管clear()会主动调用vector中元素的析构函数,但是并不会释放掉元素所占用的内存。所以vector所占的内存并不会随着元素的释放而释放。
如果你想在vector生命周期结束之前及时释放掉vector的内存,
方案一:swap()用一个匿名的vector对象来和已有的vector对象v来swap。
方案二:调用成员函数shrink_to_fit
参考:
1、C++ STL 容器库 中文文档
2、STL教程:C++ STL快速入门
3、https://www.apiref.com/cpp-zh/cpp/header.html
4、https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container
5、STL 使用要点总结20条——王凡