超强二叉树解析(数组,链表实现,8种遍历方法,前,中,后序线索化二叉树及其遍历)---风之java
二叉树
- 链表实现
-
- 利用数组建立二叉树
-
- 整体代码实现
- 直接添加元素,建立二叉排序树
- 二叉树的搜索
- 二叉运算树
- 接下来实现二叉运算树
- 八种遍历方式
-
- 前序遍历递归实现
- 前序遍历非递归实现
-
- 解法一
- 解法二
- 中序遍历递归实现
- 中序遍历非递归实现
- 后序遍历递归实现
- 后序遍历非递归实现
- 层序遍历递归实现
- 层序遍历非递归实现
- 线索化二叉树
- 中序遍历线索化二叉树及其遍历
-
- 先定义一个结点类
- 实现中序线索化二叉树
- 从后继节点开始遍历
- 从前驱结点开始遍历
- 先定义一个节点类
- 前序线索化二叉树
-
- 遍历前序线索化二叉树
- 后序线索化二叉树
-
- 后序线索化二叉树的节点类
- 实现后序线索化二叉树
- 遍历后序线索化二叉树
- 数组实现
-
- 添加元素,利用数组建立二叉搜索树
- 遍历数组实现的二叉树
- 整体代码实现
- 归总
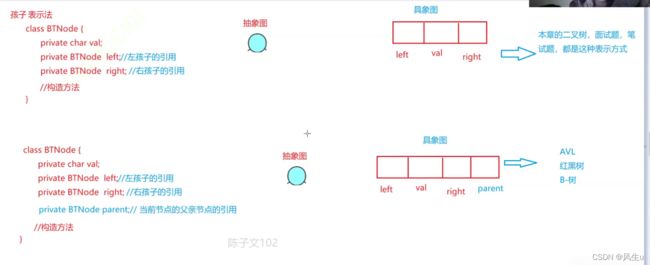
链表实现
先创建一个节点类
public class TreeNode {
int value;//数据
TreeNode left;//指向左子树
TreeNode right;//指向右子树
public TreeNode(){}
public TreeNode(int value){
this.value=value;
left=null;
right=null;
}
}
利用数组建立二叉树
利用递归一一将数组中的数全部存储到二叉树中建立二叉树
public TreeNode create(char[] arr,int index){
if(index>=arr.length){
return null;
}else{
TreeNode tmpNode=new TreeNode((int)(arr[index]));
tmpNode.left=create(arr,2*index);
tmpNode.right=create(arr,2*index+1);
return tmpNode;
}
}
整体代码实现
```java
public class BinaryTree {
public TreeNode root;
public TreeNode(){}
public BinaryTree(char[] ch,int index){
root=create(ch,index);
}
//将数组表示法转换为链表表示法
public TreeNode create(char[] arr,int index){
if(index>=arr.length){
return null;
}else{
TreeNode tmpNode=new TreeNode((int)(arr[index]));
tmpNode.left=create(arr,2*index);
tmpNode.right=create(arr,2*index+1);
return tmpNode;
}
}
直接添加元素,建立二叉排序树
public void add(int data){
TreeNode newNode=new TreeNode(data);
//建立树根
if(root==null){
root=newNode;
return;
}
TreeNode cur=root;
while(true){
if(newNode.value<cur.value){
if(cur.left==null){
cur.left=newNode;
return;
}else{
cur=cur.left;
}
}else{
if(cur.right==null){
cur.right=newNode;
return;
}else{
cur=cur.right;
}
}
}
}
二叉树的搜索
可以看到二叉树的搜索是建立在二叉排序树的基础上
//查找该二叉树上是否含有该元素
public boolean findTreeNode(TreeNode root,int value){
if(root==null){
return false;
}else{
if(root.value==value){
return true;
}else{
if(value<root.value){
count++;
return findTreeNode(root.left,value);
}else{
count++;
return findTreeNode(root.right,value);
}
}
}
}
二叉运算树
先创建一个节点类
public class TreeNode {
int value;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(){}
public TreeNode(int data){
this.value=data;
left=null;
right=null;
}
}
接下来实现二叉运算树
public class BinaryTree {
public TreeNode root;
public BinaryTree(char[] ch,int index){
root=create(ch,index);
}
//添加元素
public void add(int data){
TreeNode newNode=new TreeNode(data);
if(root==null){
root=newNode;
return;
}
TreeNode cur=root;
while(true){
if(newNode.value<cur.value){
if(cur.left==null){
cur.left=newNode;
return;
}else {
cur=cur.left;
}
}else{
if(cur.right==null){
cur.right=newNode;
return;
}else{
cur=cur.right;
}
}
}
}
//将数组表示法转换为链表表示法
public TreeNode create(char[] arr,int index){
if(index>=arr.length){
return null;
}else{
TreeNode tmpNode=new TreeNode((int)(arr[index]));
tmpNode.left=create(arr,2*index);
tmpNode.right=create(arr,2*index+1);
return tmpNode;
}
}
//判断表达式如何运算的方法声明
public int condition(char ch,int n1,int n2){
switch(ch){
case '+': return n1+n2;
case '-': return n1-n2;
case '*': return n1*n2;
case '/': return n1/n2;
case '%': return n1%n2;
default: return -1;
}
}
//计算二叉运算树的值
public int answer(TreeNode root){
int first=0;
int second=0;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
return Character.getNumericValue((char)root.value);
}else{
first=answer(root.left);
second=answer(root.right);
return condition((char)root.value,first,second);
}
}
//中序表示法
public void inOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root!=null){
inOrder(root.left);
System.out.print((char)root.value+" ");
inOrder(root.right);
}
}
//后序表示法
public void postOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root!=null){
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
System.out.print((char)root.value+" ");
}
}
//前序表示法
public void preOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root!=null){
System.out.print((char)root.value+" ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
}
}
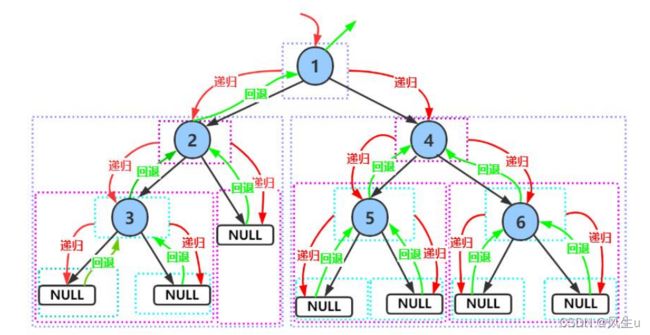
八种遍历方式
所谓遍历(Traversal)是指沿着某条搜索路线,依次对树中每个结点均做一次且仅做一次访问。访问结点所做的操作依赖于具体的应用问题(比如:打印节点内容、节点内容加1)。 遍历是二叉树上最重要的操作之一,是二叉树上进
行其它运算之基础。
在遍历二叉树时,如果没有进行某种约定,每个人都按照自己的方式遍历,得出的结果就比较混乱,如果按照某种规则进行约定,则每个人对于同一棵树的遍历结果肯定是相同的。如果N代表根节点,L代表根节点的左子树,R代表根节点的右子树,则根据遍历根节点的先后次序有以下遍历方式:
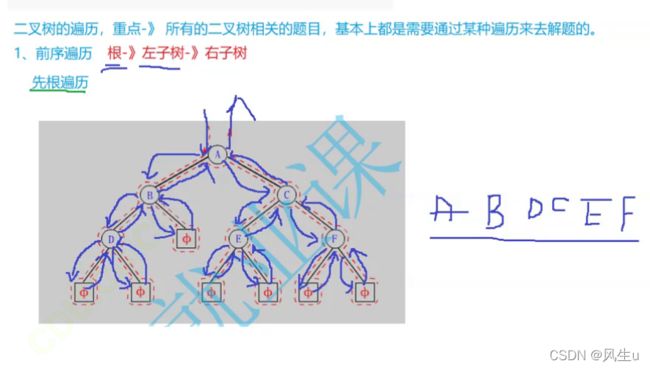
1. NLR:前序遍历(Preorder Traversal 亦称先序遍历)——访问根结点—>根的左子树—>根的右子树。
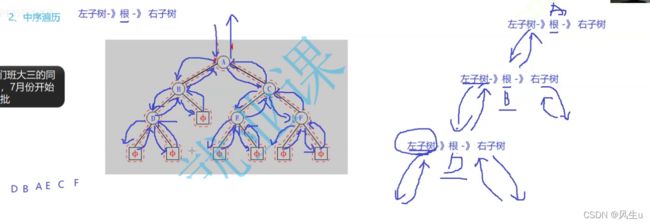
2. LNR:中序遍历(Inorder Traversal)——根的左子树—>根节点—>根的右子树。
3. LRN:后序遍历(Postorder Traversal)——根的左子树—>根的右子树—>根节点。
由于被访问的结点必是某子树的根,所以N(Node)、L(Left subtree)和R(Right subtree)又可解释为根、根
的左子树和根的右子树。NLR、LNR和LRN分别又称为先根遍历、中根遍历和后根遍历。
前序遍历递归实现
//前序遍历
public void preOrder1(TreeNode root){
if(root!=null){
System.out.print(root.value+" ");
preOrder1(root.left);//遍历左子树
preOrder1(root.right);//遍历右子树
}
}
前序遍历非递归实现
解法一
利用堆栈的性质
//前序遍历非递归1
public void preOrder2(TreeNode cur){
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
while(cur!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur!=null){
stack.add(cur);
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
cur=cur.left;
}
cur=stack.pop();
cur=cur.right;
}
}
解法二
将元素按照前序遍历的顺序压入栈中,再依次弹出即可
//前序遍历非递归2
public void preOrder3(TreeNode cur){
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
stack.add(cur);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
cur=stack.pop();
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
if(cur.right!=null)
stack.add(cur.right);
if(cur.left!=null)
stack.add(cur.left);
}
}
中序遍历递归实现
//中序遍历
public void inOrder1(TreeNode root){
if(root!=null){
inOrder1(root.left);//处理左子树
System.out.print(root.value+" ");
inOrder1(root.right);//处理右子树
}
}
中序遍历非递归实现
和前序遍历的非递归实现一样,只不过是交换了打印顺序。
//中序遍历非递归
public void inOrder2(TreeNode cur){
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
while(cur!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur!=null){
stack.add(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
cur=stack.pop();
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
cur=cur.right;
}
}
后序遍历递归实现
//后序遍历
public void postOrder1(TreeNode root){
if(root!=null){
postOrder1(root.left);//处理左子树
postOrder1(root.right);//处理右子树
System.out.print(root.value+" ");
}
}
后序遍历非递归实现
后序遍历较为复杂,需要用到栈的性质,且用 cur 来判断打印树叶,用 pre 来记录左或右节点来判断是否打印父节点
public void postOrder2(TreeNode cur){
if(cur==null)
return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre=null;
stack.add(cur);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
cur=stack.peek();
if((cur.left==null&&cur.right==null)||(pre!=null&&(pre==cur.left||pre==cur.right))){
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
stack.pop();
pre=cur;
}else{
if(cur.right!=null)
stack.add(cur.right);
if(cur.left!=null)
stack.add(cur.left);
}
}
}
层序遍历递归实现
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
helper(root, 0, result);
return result;
}
public void helper(TreeNode root, int level, List<List<Integer>> lists) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (lists.size() < level + 1) {
lists.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
lists.get(level).add(root.val);
helper(root.left, level + 1, lists);
helper(root.right, level + 1, lists);
}
}
层序遍历非递归实现
利用队列先进先出的性质即可。
//层序遍历非递归
public void levelOrder(TreeNode cur){
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(cur);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
cur=queue.pop();
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
if(cur.left!=null)
queue.add(cur.left);
if(cur.right!=null)
queue.add(cur.right);
}
}
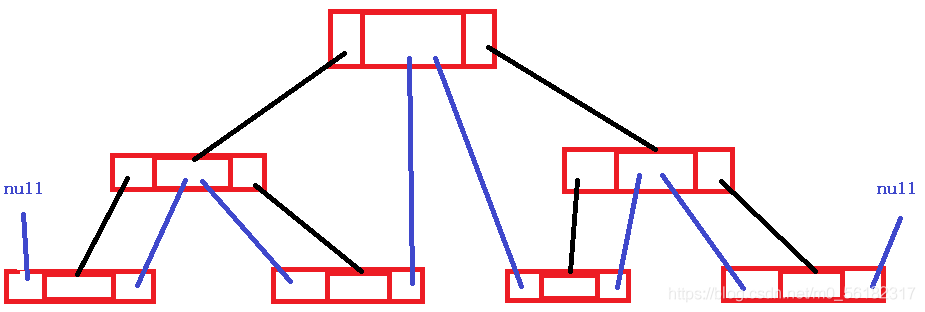
线索化二叉树
学过链表的读者肯定存在双向链表的,也就是节点相连两个节点之间相互指引,那么二叉树是否也可以通过特定的遍历方式变成特殊的“双向链表”呢?
答案是肯定的。
我们选定一种遍历方式时,遍历到节点A时,遍历A前一个节点叫做节点A的前驱节点,遍历节点A过后,所遍历到的下一个节点叫节点A的后继节点。
中序遍历线索化二叉树及其遍历
先定义一个结点类
public class TreeNode {
int value;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
boolean lef=false;
boolean rig=false;
public TreeNode(){}
public TreeNode(int data){
this.value=data;
left=null;
right=null;
}
}
实现中序线索化二叉树
//中序线索化二叉树
public void inThreadOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
//处理左子树
inThreadOrder(root.left);
if (root.left == null) {
root.left = pre;
root.lef = true;
}
//前一个节点的后继结点指向当前节点
if (pre != null && pre.right == null) {
pre.right = root;
pre.rig = true;
}
pre = root;
inThreadOrder(root.right);
}
从后继节点开始遍历
//中序遍历线索二叉树,按照后继方式遍历
public void inOrderBlack() {
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null && !cur.lef) {
cur = cur.left;
}
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
if (cur.rig) {
cur = cur.right;
} else {
cur = cur.right;
while (cur != null && !cur.lef)
cur = cur.left;
}
}
}
从前驱结点开始遍历
//中序遍历线索二叉树,按照前驱方式遍历
public void inOrderBefore() {
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur.right != null && !cur.rig)
cur = cur.right;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
if (cur.lef) {
cur = cur.left;
} else {
cur = cur.left;
while (cur.right != null && !cur.rig)
cur = cur.right;
}
}
}
先定义一个节点类
public class TreeNode {
int value;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
boolean lef=false;
boolean rig=false;
public TreeNode(){}
public TreeNode(int data){
this.value=data;
left=null;
right=null;
}
}
前序线索化二叉树
//前序遍历线索化二叉树
public void preOrderBinaryTrree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
//左指针为空,将左指针指向前驱节点
if (root.left == null) {
root.left = pre;
root.lef = true;
}
//将前一个节点的后继节点指向当前节点
if (pre != null && pre.right == null) {
pre.right = root;
root.rig = true;
}
pre = root;
if (!root.lef)
preOrderBinaryTrree(root.left);
if (!root.rig)
preOrderBinaryTrree(root.right);
}
遍历前序线索化二叉树
//前序遍历线索二叉树
public void preOrderblack() {
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
while (!cur.lef) {
System.out.println(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.left;
}
System.out.println(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.right;
}
}
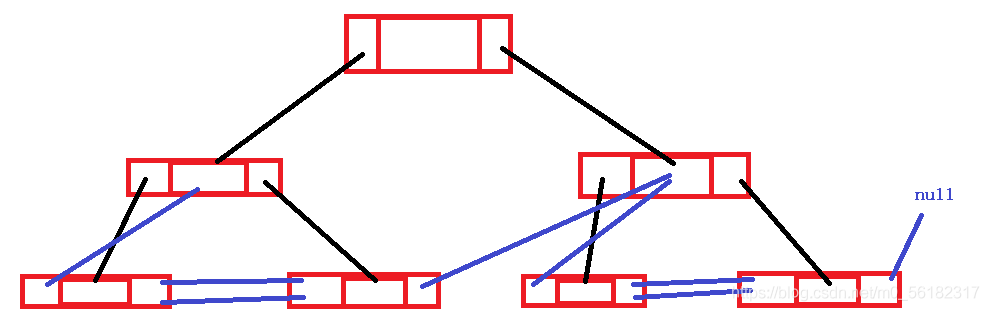
后序线索化二叉树
后序线索化二叉树的节点类
后序线索化二叉树创建的节点类,与前面有所不同,需要一个parent记录父节点
public class TreeNode {
int value;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode parent;
boolean lef=false;
boolean rig=false;
public TreeNode(){}
public TreeNode(int data){
this.value=data;
left=null;
right=null;
}
}
实现后序线索化二叉树
//后序遍历线索化二叉树
public void postThreadOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
//处理左子树
postThreadOrder(root.left);
//处理右子树
postThreadOrder(root.right);
if (root.left == null) {
root.left = pre;
root.lef = true;
}
if (pre != null && pre.right == null) {
pre.right = root;
pre.rig = true;
}
pre = root;
}
遍历后序线索化二叉树
//遍历后序遍历线索化的二叉树
public void postOrderBinaryTree() {
pre = null;
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null && !cur.lef)
cur = cur.left;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.lef) {
System.out.println(cur.value + " ");
pre = cur;
cur = cur.right;
} else {
if (cur.right == pre) {
System.out.println(cur.value + " ");
if(cur==root)
return;
pre=cur;
cur=cur.parent;
}else{
if(cur==root&&cur.right==null)
return;
cur=cur.right;
while(cur!=null&&!cur.lef)
cur=cur.left;
}
}
}
}
数组实现
添加元素,利用数组建立二叉搜索树
可以发现规律,左子树索引值为父节点索引值2+1
右子树索引值为父节点索引值2+2
故有:
//添加元素
public void add(){
int level=1;
for(int i=0;i<data.length;i++){
for(level=1;btree[level]!=0; ){
if(data[i]<btree[level])
level=level*2;
else
level=level*2+1;
}
btree[level]=data[i];
}
}
遍历数组实现的二叉树
因为数组是连续存储的,所以直接打印就行。
//遍历二叉树
public void ergodic(){
System.out.println("二叉树的内容");
for(int i=1;i<btree.length;i++)
System.out.print(btree[i]+" ");
System.out.println();
}
整体代码实现
public class BinaryTreeByArray {
int[] data;
int[] btree=new int[300];
public BinaryTreeByArray(int[] arr){
data=arr;
}
//添加元素
public void add(){
int level=1;
for(int i=0;i<data.length;i++){
for(level=1;btree[level]!=0; ){
if(data[i]<btree[level])
level=level*2;
else
level=level*2+1;
}
btree[level]=data[i];
}
}
//遍历二叉树
public void ergodic(){
System.out.println("二叉树的内容");
for(int i=1;i<btree.length;i++)
System.out.print(btree[i]+" ");
System.out.println();
}
}
归总
package 二叉树链表实现及遍历方法和基本方法;
import java.util.*;
public class BinaryTreeByLink {
public TreeNode root;
//添加节点
public void add(int data) {
TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(data);
//建立树根
if (root == null) {
root = newNode;
return;
}
TreeNode cur = root;
while (true) {
if (newNode.value < cur.value) {
if (cur.left == null) {
cur.left = newNode;
return;
} else {
cur = cur.left;
}
} else {
if (cur.right == null) {
cur.right = newNode;
return;
} else {
cur = cur.right;
}
}
}
}
//二叉树的遍历
//前序遍历
public void preOrder1(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.value + " ");
preOrder1(root.left);
preOrder1(root.right);
}
}
//前序遍历非递归1
public void preOrder2(TreeNode cur) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.add(cur);
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.left;
}
cur = stack.pop();
cur = cur.right;
}
}
//前序遍历非递归2
public void preOrder3(TreeNode cur) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.add(cur);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
cur = stack.pop();
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
if (cur.right != null)
stack.add(cur.right);
if (cur.left != null)
stack.add(cur.left);
}
}
//中序遍历
public void inOrder1(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
inOrder1(root.left);
System.out.print(root.value + " ");
inOrder1(root.right);
}
}
//中序遍历非递归
public void inOrder2(TreeNode cur) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.add(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
cur = stack.pop();
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.right;
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder1(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
postOrder1(root.left);
postOrder1(root.right);
System.out.print(root.value + " ");
}
}
//后序遍历非递归
public void postOrder2(TreeNode cur) {
if (cur == null)
return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre = null;
stack.add(cur);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
cur = stack.peek();
if ((cur.left == null && cur.right == null) || (pre != null && (pre == cur.left || pre == cur.right))) {
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
stack.pop();
pre = cur;
} else {
if (cur.right != null)
stack.add(cur.right);
if (cur.left != null)
stack.add(cur.left);
}
}
}
void postOrderNor(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode prev = null;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.peek();
//如果当前节点的右子树被打印过 或者 遍历过 直接弹出了
if (top.right == null || top.right == prev) {
stack.pop();
System.out.print(top.value+" ");
prev = top;//记录一下 最近一次打印的节点
} else {
cur = top.right;
}
}
}
//层序遍历递归
public void levelOrder1(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) return;
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
//层序遍历:分层打印
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder3(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return ret;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();//这个值代表 当前层有多少个节点
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (size != 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
//list.add(cur.val); 你在OJ写的时候 需要放开这个注释
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
size--;//1 0
}
ret.add(list);
}
return ret;
}
//层序遍历非递归
public void levelOrder2(TreeNode cur) {
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(cur);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
cur = queue.pop();
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
if (cur.left != null)
queue.add(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null)
queue.add(cur.right);
}
}
/**
*获取树中节点的个数
*/
/*
int count = 0;
int size1(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
count++;
size1(root.left);
size1(root.right);
return count;
}
*/
/**
* 子问题思路
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
int size(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return size(root.left) + size(root.right) + 1;
}
/**
* 获取叶子节点的个数
* 遍历思路:
*/
static int leafCount = 0;
/* void getLeafNodeCount(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {
leafCount ++;
}
getLeafNodeCount(root.left);
getLeafNodeCount(root.right);
}*/
/**
* 获取叶子节点的个数
* 子问题思路
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
void getLeafNodeCount(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
leafCount++;
}
getLeafNodeCount(root.left);
getLeafNodeCount(root.right);
}
/**
* 获取叶子节点的个数
* 子问题思路
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
int getLeafNodeCount2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
//当前的root是叶子节点
return 1;
}
return getLeafNodeCount2(root.left) + getLeafNodeCount2(root.right);
}
/**
* 获取第K层节点的个数
* 子问题思路:
*/
int getKLevelNodeCount(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root == null || k <= 0) {
return 0;
}
if (k == 1) {
return 1;
}
return getKLevelNodeCount(root.left, k - 1) + getKLevelNodeCount(root.right, k - 1);
}
/**
* 获取二叉树的高度
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* 空间复杂度:O()
*/
int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);
int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
//递归次数容易太多,超出时间限制
int getHeight2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return getHeight2(root.left) > getHeight2(root.right) ? getHeight2(root.left) + 1 : getHeight2(root.right) + 1;
}
/**
* 检测值为value的元素是否存在
*/
TreeNode find(TreeNode root, char val) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (root.value == val) return root;
TreeNode ret = find(root.left, val);
if (ret != null) {
return ret;
}
ret = find(root.right, val);
if (ret != null) {
return ret;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 是不是完全二叉树
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if (cur != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
queue.offer(cur.right);
} else {
break;
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = queue.peek();
if (top != null) {
return false;
}
queue.poll();
}
return true;
}
//判断两个二叉树是否完全相等
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q != null || p != null && q == null) {
return false;
}
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
}
if (p.value != q.value) {
return false;
}
//p != null && q!= null && p.val == q.val
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
//判断一个树是否是该树的子树
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if (root == null || subRoot == null) {
return false;
}
//等价于上面
// if(root == null && subRoot != null) {
// return false;
// }
// if(root != null && subRoot == null) {
// return false;
// }
// if(root == null && subRoot == null) {
// return true;
// }
//判断根节点是不是两棵相同的树
if (isSameTree(root, subRoot)) {
return true;
}
//subroot是不是root的左子树
if (isSubtree(root.left, subRoot)) {
return true;
}
//subroot是不是root的右子树
if (isSubtree(root.right, subRoot)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断是否是平衡二叉树
* 时间复杂度:O(N^2)
*/
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
int left = getHeight(root.left);
int right = getHeight(root.right);
return Math.abs(left - right) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
/**
* 判断是否是平衡二叉树
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
*/
public boolean isBalanced2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
return getHeight3(root) >= 0;
}
int getHeight3(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);
int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right);
if (leftHeight >= 0 && rightHeight >= 0 && Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) <= 1) {
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
//检查二叉树是否轴对称。
public boolean judge(TreeNode leftTree, TreeNode rightTree) {
if (leftTree != null && rightTree == null) return false;
if (leftTree == null && rightTree != null) return false;
if (leftTree == null && rightTree == null) return true;
if (leftTree.value != rightTree.value) return false;
return judge(leftTree.left, rightTree.right) && judge(leftTree.right, rightTree.left);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
} else {
return judge(root.left, root.right);
}
}
//求最小公共祖先 理解不了!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
// LCA 问题
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
if (root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if (left != null && right != null) {
return root;
} else if (left != null) {
return left;
} else if (right != null) {
return right;
}
return null;
}
// 求最小公共祖先 栈模拟链表实现
public boolean getPath(TreeNode root,TreeNode node,Stack<TreeNode> stack){
if(root==null||node==null) return false;
stack.push(root);
if(root==node) return true;
boolean flag=getPath(root.left,node,stack);
if(flag==true) return true;
flag=getPath(root.right,node,stack);
if(flag==true) return true;
stack.pop();
return false;
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor2(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack1=new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack2=new Stack<>();
getPath(root,p,stack1);
getPath(root,q,stack2);
Stack<TreeNode> stackmax=stack1.size()>stack2.size() ? stack1:stack2;
Stack<TreeNode> stackmin= stackmax==stack1 ? stack2 : stack1;
while(!stackmax.isEmpty() && !stackmin.isEmpty() && stackmax.size()!=stackmin.size()){
stackmax.pop();
}
while(!stackmax.isEmpty() && !stackmin.isEmpty()){
if(stackmax.peek()==stackmin.peek()){
return stackmax.peek();
}else{
stackmax.pop();
stackmin.pop();
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 二叉搜索树 转换为排序的双向链表
*/
TreeNode prev = null;
public void inorder(TreeNode pCur) {
if(pCur == null) return;
inorder(pCur.left);
//打印
pCur.left = prev;
if(prev != null) {
prev.right = pCur;
}
prev = pCur;
//System.out.print(pCur.val+" ");
inorder(pCur.right);
}
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree == null) return null;
inorder(pRootOfTree);
TreeNode head = pRootOfTree;
while(head.left != null) {
head = head.left;
}
return head;
}
/*
根据前中序遍历创建二叉树
*/
public int preIndex = 0;
public TreeNode createTreeByPandI(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend) {
if(inbegin > inend) {
//如果满足这个条件 说明 没有左树 或者 右树了
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preIndex]);
//找到根在中序遍历的位置
int rootIndex = findIndexOfI(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[preIndex]);
if(rootIndex == -1) {
return null;
}
preIndex++;
//分别创建 左子树 和 右子树
root.left = createTreeByPandI(preorder,inorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);
root.right = createTreeByPandI(preorder,inorder,rootIndex+1,inend);
return root;
}
private int findIndexOfI(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key) {
for(int i = inbegin; i <= inend;i++) {
if(inorder[i] == key) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder == null || inorder == null) return null;
return createTreeByPandI(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
/*
根据前中后遍历创建二叉树
public int postIndex = 0;
public TreeNode createTreeByPandI(int[] inorder, int[] postorder,int inbegin,int inend) {
if(inbegin > inend) {
//如果满足这个条件 说明 没有左树 或者 右树了
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postIndex]);
//找到根在中序遍历的位置
int rootIndex = findIndexOfI(inorder,inbegin,inend,postorder[postIndex]);
if(rootIndex == -1) {
return null;
}
postIndex--;
//分别创建右子树 和 左子树
root.right = createTreeByPandI(inorder,postorder,rootIndex+1,inend);
root.left = createTreeByPandI(inorder,postorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);
return root;
}
private int findIndexOfI(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key) {
for(int i = inbegin; i <= inend;i++) {
if(inorder[i] == key) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if(postorder == null || inorder == null) return null;
postIndex = postorder.length-1;
return createTreeByPandI(inorder,postorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}*/
}