Spring @Transactional 注解初探
AOP 事务代理(针对 proxy 模式)
Spring 中事务相关的介绍,详情可以参考官网的介绍。之前我有写过一个简单的Spring 事务控制的博客。不知道,会不会有小伙伴遇到事务配置了,但是没有干活。关于这个官网有这样一句话:
@EnableTransactionManagementandonly looks for@Transactionalon beans in the same application context they are defined in. This means that, if you put annotation driven configuration in a WebApplicationContext for a DispatcherServlet, it only checks for@Transactionalbeans in your controllers, and not your services.
测试代码
@Test
public void dbTest() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring-jdbc.xml");
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
User user = new User("" + System.currentTimeMillis() % 1000, "" + System.currentTimeMillis() % 1431);
userService.save(user);
List list = userService.queryAllUser();
for (User u : list) {
System.out.println(u);
}
}
- 关注: ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, 类图如下:

Spring 是面向接口编程的。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext在这个儿就是一个叶子节点,父节点上父节点上会有调用到子节点的方法,这个图还是勉强重要吧。
<bean id="userService" class="com.yhj.chapter17.jdbc.service.impl.UserServiceI">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
refresh 函数
这个行数几乎包含了 `ApplicationContext` 所有的功能,在这儿只是简单的提一下。 Service 也是一个普通的 bean,只是在加载过程中,Spring 通过动态代理生成子类通过 AOP 实现事务的控制。 bean 加载,首先定位到 `org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()` 这个方法。 获取 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
- 代码:
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory()。
获取一个
DefaultListableBeanFactory实例并调用loadBeanDefinitions()方法解析 xml 中有关 bean 的定义。 registerBeanPostProcessors()方法,注册拦截器。这里主要InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的注册。
解析自定义标签
主要关注
标签的解析:org.springframework.transaction.config.TxNamespaceHandler#init()方法,里面注册了标签的解析类org.springframework.transaction.config.AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser,这个类的parse()方法会在类加载的时候被调用。定义了标签的解析和相关类的注册,会在解析自定义标签的时候调用。
- 解析标签
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate#parseCustomElement(org.w3c.dom.Element, org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition)
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBd) {
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
// 调用
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}在代理模式下主要是:
org.springframework.transaction.config.AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser.AopAutoProxyConfigurer#configureAutoProxyCreator() 方法。
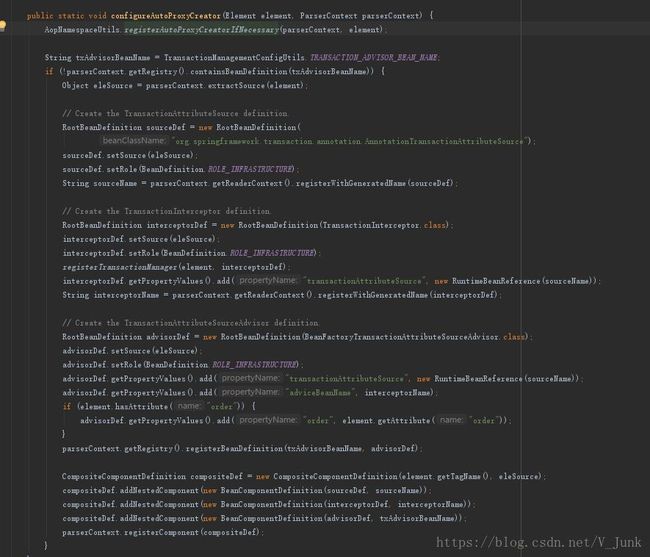
这里面主要涉及一下几个类的注册:
AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource:
- beanName:
org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource#0
- beanName:
TransactionInterceptor
- beanName:
org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor#0
- beanName:
- BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
- beanName:
org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor - 实现了
Advisor接口
- beanName:
这里把TransactionInterceptor 和 AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource 都注入到BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 中。
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element) 这行简单且关键的代码:
public static BeanDefinition registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}注册了:InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator(key 为 org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator), 且间接实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口所以在 bean 的创建过程(getBean 时)中会被调用,具体的方法实现在 org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization 中。
事务标签的解析
在 bean 的加载过程中会调用实例化后置处理器 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization, 这里就会调用到之注册的 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 内的后置处理器方法:
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
protected List findEligibleAdvisors(Class beanClass, String beanName) {
List candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
List eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
findCandidateAdvisors()总是返回可用增强器列表,这里主要是BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisorfindAdvisorsThatCanApply()对于当前的 bean 返回可用的增强器,相关源码如下:
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set> classes = new LinkedHashSet>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
classes.add(targetClass);
for (Class clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null &&
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) ||
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} canApply() 方法,通过判断当前 bean 的实现类或其接口的方法上上是否有 @Transactional(@transactional 注解有 @Inherited 表示故可以被继承)。相关源码如下:
org.springframework.transaction.annotation.SpringTransactionAnnotationParser#parseTransactionAnnotation(java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement)@Override public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement ae) { AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotationAttributes(ae, Transactional.class); if (attributes != null) { return parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes); } else { return null; } }这里把最后处理的代码贴出来了,过程中有一个比较重要的方法
org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource#computeTransactionAttribute()中对于@Transactional注解检索的顺序是 目标类的方法 > 目标类 > 接口,这也就是为什么方法中的@Transactional注解会覆盖类和接口的注解 (个人觉得是这样)。至此已经完成了关于事务标签的解析。创建代理
现在我们还是回到 org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary() 这个方法。相关源码如下:
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
找到合适的增强器之后就调用
createProxy()方法创建代理,关于创建代理的内容会在后续的博客补全。