Vue3 基础学习笔记
一、非脚手架搭建vue实例
- vue 3也可以直接下载 vue3 源码来创建vue实例,这里只是一个简单用例介绍一下,更具体的内容,可以参考我的 vue2 文章
- 建议 vue3 中使用 Composition API 而非 option API ,以下只是作为示例用
<div id="app">div>
<script type="text/x-template" id="my_pnc1">
<h2>{{ message }}</h2>
<p>{{ counter }}</p>
<button @click="addCounter">counter ++ </button>
<br>
<input type="text" v-model="text">
<p>{{ text }}</p>
<h2 v-bind:[attrName]="attrValue">绑定自定义属性</h2>
<p>sonMsg: {{ sonMsg }}</p>
<!-- 使用全局组件 -->
<global-com :parent-msg="message"/>
<!-- 使用局部组件 -->
<local-tmp @sendMsg="getMsg"/>
script>
<template id="global-tmp">
<div style="border:1px solid red;">
<h2>{{title}}h2>
<p>job:{{info.job}}p>
<p>parentMsg:{{ parentMsg }}p>
<button @click="setInfoJob">修改jobbutton>
div>
template>
<template id="local-tmp">
<div style="border:1px solid blue;">
<h2>{{title}}h2>
<button @click="sendParentMsg">向父组件传递数据button>
div>
template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next">script>
<script>
const localTmp = {
template: '#local-tmp',
data() {
return {
title: '局部组件'
}
},
methods: {
sendParentMsg() {
this.$emit('sendMsg', '子组件向父组件传递的信息')
}
}
}
const App = {
template: '#my_pnc1', //抽离模板
components: {
localTmp: localTmp
},
data() { //与 vue2 不同。vue3 全部都是 data函数
return {
message: 'Hello World',
counter: 100,
text: '',
attrName: 'data-id', // 支持大写
attrValue: 123,
sonMsg: ''
}
},
methods: {
addCounter() {
this.counter++
},
getMsg(msg) {
this.sonMsg = msg
}
}
}
//创建vue实例 并
const app = Vue.createApp(App)
//创建一个全局组件
app.component('global-com', {
template: '#global-tmp',
props: {
parentMsg: {
type: String,
default: ''
}
},
data() {
return {
title: '我是全局组件',
info: {
job: '搬砖的'
}
}
},
methods: {
setInfoJob() {
this.info.job = '拉砖的'
}
}
})
//将vue实例挂在到 id 为 app 的元素上,与vue2也不同
app.mount('#app')
script>
二、 搭建 vue3
1. 使用 webpack 搭建 vue3
- 安装或者升级 vue-cli, 需要使用管理员权限
# 全局安装 vue npm install @vue/cli -g # 升级vue npm update @vue/cli -g - 查看 vue-cli ,保证 vue cli 版本在 4.5.0 以上
vue --version - 创建项目
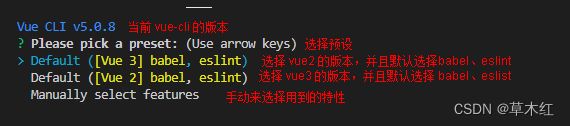
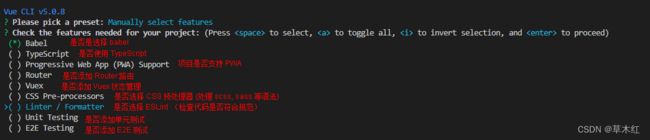
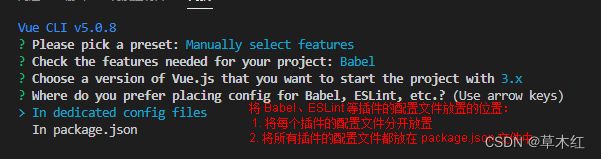
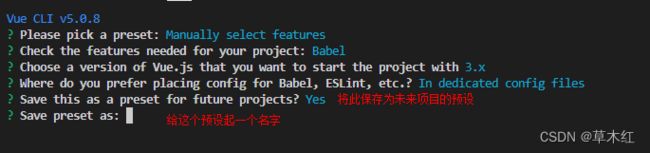
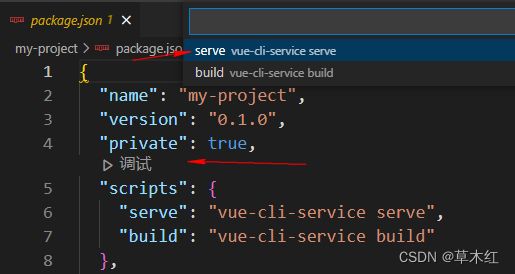
#创建一个名字为 my-project 的文件夹 vue create my-project - 配置 vue-cli
特别注意点空格是选中,回车是下一步
2. 使用 vite 搭建 vue3
vite 要求Node 版本是大于12版本的
-
进入要放置项目的文件夹 ,初始化 vite,并创建vite-project 项目文件夹, 并依次选择 如图
npm init vite
-
进入到项目目录 vite-project ,执行下面命令进行安装 vue-cli
npm install -
启动 vue
npm run dev -
解释index.html 文件中的几个重点:
<body> <div id="app">div> <script type="module" src="/src/main.js">script> body> -
在 main.js 文件中加载主要的文件
//结构 vue 中的 createApp函数 import { createApp } from 'vue' import './style.css' import App from './App.vue' // 将 app文件挂载到 id为 app的dom元素上 createApp(App).mount('#app')
3. 对 man.js 文件的一个简单说明
//程序的主入口文件
//引入createApp函数,创建对应的应用,产生应用的实例对象
import { createApp } from 'vue'
//引入 App组件(所有组件的父级组件)
import App from './App.vue'
// 将 app文件挂载到 id为 app的dom元素上
createApp(App).mount('#app')
三、常用的 Composition API (组合式 API)
1. setup
-
setup执行的时机
- 在beforeCreate之前执行(一次), 此时组件对象还没有创建
- this是undefined, 不能通过this来访问data/computed/methods / props
- 其实所有的composition API相关回调函数中也都不可以
-
setup的返回值
- 一般都返回一个对象: 为模板提供数据, 也就是模板中可以直接使用此对象中的所有属性/方法
- 返回对象中的属性会与data函数返回对象的属性合并成为组件对象的属性
- 返回对象中的方法会与methods中的方法合并成功组件对象的方法
- 如果有重名, setup优先
- 注意:
- 一般不要混合使用: methods中可以访问setup提供的属性和方法, 但在setup方法中不能访问data和methods
- setup不能是一个async函数: 因为返回值不再是return的对象, 而是promise, 模板看不到return对象中的属性数据
-
setup的参数
- setup(props, context) / setup(props, {attrs, slots, emit})
- props: 子级组件中使用 props 参数接收到父级组件传递的数据,是一个对象。
- attrs: 包含没有在props配置中声明的属性的对象, 相当于 this.$attrs (获取当前组件标签上的所有属性的对象)
- slots: 包含所有传入的插槽内容的对象, 相当于 this.$slots
- emit: 用来分发自定义事件的函数, 相当于 this.$emit
<template>
<div>
<son msg="hahhahahah" />
div>
template>
<script>
import Son from "./son.vue";
export default {
components: {
Son,
},
};
script>
<template>
<p>{{ msg }}p>
template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
msg: {
type: String,
default: ''
}
},
setup(props) {
//{msg: 'hahhahahah'}
console.log(props)
}
}
script>
2. ref 函数创建响应式的基本数据类型
- 经过 ref 函数包装的基本数据类型返回一个 ref 对象
{ value: 0 } - ref 的语法糖
$ref该语法糖还处在实验阶段 - 模板中的解包是浅层的解包
1). setup 经典风格
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ msg }}p>
<p>{{ info.msg }}p>
<p>{{ info.msg.value }}p>
<p>{{ info2.msg }}p>
<button @click="updateMsg">点击修改msgbutton>
div>
template>
<script >
import { ref, reactive } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
//使用 ref 函数定义一个响应式的基本数据类型
const msg = ref('我是一个字符串变量')
const info = {
msg
}
//{"msg":{"__v_isShallow":false,"__v_isRef":true,"_rawValue":"我是一个字符串变量","_value":"我是一个字符串变量"}}
console.log(JSON.stringify(info));
const info2 = reactive({
msg
})
function updateMsg() {
// 修改和读取变量 都是 对 变量 的value进行操作
//其实 this.msg = "新消息" 和下边的效果一样,但是不知道为什么不这么写
console.log(this)
msg.value = '新消息'
}
//将定义的方法和变量暴露出来
return { msg, info, info2, updateMsg }
}
}
script>
2). setup 语法糖风格
<template>
<div>
{{ msg }}
<button @click="updateMsg">点击修改msgbutton>
div>
template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from "vue";
//使用 ref 函数定义一个响应式的基本数据类型
const msg = ref("我是一个字符串变量");
const updateMsg = () => {
// 修改和读取变量 都是 对 变量 的value进行操作
msg.value = "修改msg";
console.log(msg.value)
};
script>
3. reactive 函数创建响应式的引用数据类型
- 接收一个想普通对象然后返回该普通对象的响应式代理器对象
- 响应式转换是 “深层的”:会影响对象内部所有嵌套的属性
<template>
<div>
name: {{ obj.name }} <br />
address: {{ obj.otherInfo.address }}<br />
road: {{ obj.otherInfo.road }}<br />
wifeName:{{ obj?.wife?.name }}<br /><br />
<button @click="setName">点击修改namebutton><br />
<button @click="setAddress">点击修改深层属性addressbutton><br />
<button @click="addProperty">添加对象wife与roadbutton><br />
<button @click="delProperty">删除对象wifebutton><br />
div>
template>
<script >
import { reactive } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
const obj = reactive({
name: "张三",
age: 33,
otherInfo: {
address: "梧桐街",
},
});
//响应式修改
function setName() {
obj.name = "李四";
}
//响应式修改
function setAddress() {
obj.otherInfo.address = "凤阳街";
}
//新添加的属性 也是响应式的
function addProperty() {
obj.wife = {
name: "小红",
age: 23,
};
obj.otherInfo.road = "工人路";
console.log(obj);
}
//响应式删除
function delProperty() {
delete obj.wife;
console.log(obj);
}
//将定义的方法和变量暴露出来
return { obj, setName, setAddress, addProperty, delProperty };
},
};
script>
4. reactive 与 ref 的区别
- ref 用来处理基本类型数据, reactive用来处理对象(递归深度响应式)
- 如果用 ref 处理对象/数组, 内部会自动将对象/数组转换为reactive的代理对象
- ref 内部: 通过给value属性添加getter/setter来实现对数据的劫持
- reactive 内部: 通过使用Proxy来实现对对象内部所有数据的劫持, 并通过Reflect操作对象内部数据
- ref的数据操作: 在js中要.value, 在模板中不需要(内部解析模板时会自动添加.value)
<template>
<div>
{{ user.wife.name }}
<button @click="editWifeName">修改wife的namebutton>
div>
template>
<script>
import { ref } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
//ref 处理对象
let user = ref({
name: "张三",
wife: {
name: "小红",
},
});
//修改时要用 .value
function editWifeName() {
user.value.wife.name = "小白";
}
return { user, editWifeName };
},
};
script>
5. toRef / toRefs 函数使解构后的数据重新获得响应式
- 作用: 创建一个 ref 对象,其 value 值指向另一个对象中的某个属性
- 语法:
const name = toRef(对象, key) - 应用: 要将响应式对象中的某个属性单独提供给外部使用时
- 扩展:
toRefs与toRef功能一致,但可以批量创建多个 ref 对象,语法:toRefs(person)
<template>
<div>
<p>name:{{ name }}p>
<p>age:{{ age }}p>
<p>salary:{{ salary }}p>
<button @click="edit">修改personbutton>
div>
template>
<script>
import { toRef, reactive, toRefs } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
const person = reactive({
name: '张三',
age: 12,
salary: 50
})
//将name直接结构出来, 非响应式
const { name } = person
//通过 toRef 将 salary 结构出来,响应式
const salary = toRef(person, 'salary')
//通过 toRefs 将 age 结构出来,响应式
const { age } = toRefs(person)
function edit() {
person.name += '*'
person.age++
person.salary++
}
return { name, age, salary, edit }
}
}
script>
6. 计算属性
<template>
<div>
姓氏:<input type="text" v-model="user.firstName" /><br />
名字:<input type="text" v-model="user.lastName" /><br />
计算属性,自动填充姓氏和名字<input type="text" v-model="fullName" /><br />
修改计算属性,反向填充姓氏和名字<input type="text" v-model="fullName2" /><br />
div>
template>
<script>
import { computed, reactive } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
const user = reactive({
firstName: "",
lastName: "",
});
//默认是 getter 方法
const fullName = computed(() => {
return user.firstName + "_" + user.lastName;
});
//有getter与setter的计算属性
const fullName2 = computed({
get() {
return user.firstName + "_" + user.lastName;
},
set(newVal) {
console.log("新值为:" + newVal);
const nameArr = newVal.split("_");
user.firstName = nameArr[0];
user.lastName = nameArr[1];
},
});
return { user, fullName, fullName2 };
},
};
script>
7. watch 监听函数
- watch(被监听的响应式引用, 回调函数 [, 其他可选参数])
- 其他可选参数:
- immediate:在侦听器创建时立即触发回调。第一次调用时旧值是 undefined。
- deep:如果源是对象,强制深度遍历,以便在深层级变更时触发回调。
- flush:调整回调函数的刷新时机。
pre默认值,在元素 挂载 或者 更新 之前执行;post将会使侦听器延迟到组件渲染之后再执行;sync在响应式依赖发生改变时立即触发侦听器。该设置应谨慎使用,因为如果有多个属性同时更新,这将导致一些性能和数据一致性的问题。 - onTrack / onTrigger:调试侦听器的依赖。
- 监听 reactive 定义的响应式数据时,无法正确的获取 oldValue、强制开启了深度监听(deep 配置失效)
- 监听 reactive 定义的响应式对象中的属性时,需要将该属性放在一个函数中返回,作为 watch 函数的第一个参数
<template>
<div>
{{ msg }}<br />
{{ obj.name }}<br />
{{ subject }}<br />
{{ obj.job.salary }}<br />
<button @click="updateMsg">修改msgbutton><br />
<button @click="updateName">修改obj的namebutton><br />
<button @click="updateSubject">修改subjectbutton><br />
<button @click="updateSalary">修改obj.job.salarybutton><br />
div>
template>
<script >
import { reactive, ref, watch, toRefs } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
const msg = ref("一个消息");
const subject = ref("一个话题");
const obj = reactive({
name: "张三",
age: 22,
job: {
salary: 20,
},
});
function updateMsg() {
msg.value = "一个新消息";
}
function updateName() {
obj.name = "李四";
}
function updateSubject() {
subject.value = "另一个话题";
}
function updateSalary() {
obj.job.salary ++;
}
watch(msg, function (newVal, oldVal) {
console.log("msg旧值:", oldVal);
console.log("msg新值:", newVal);
});
//监听多个变量
watch([msg, subject], (newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log("监听多个属性的方法被调用", newVal, oldVal);
});
//监听对象中的属性,即使是深度监听也不行
watch(
obj,
(newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log("obj 旧值:", oldVal);
console.log("obj 新值:", newVal);
},
{ deep: true }
);
//监听对象中的属性,无法监听,会报一个警告
watch(
obj.name,
(newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log("深度监听obj.name旧值:", oldVal);
console.log("深度监听obj.name新值:", newVal);
},
{ deep: true }
);
//监听对象属性的方法一
watch(
() => obj.name,
(newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log("方法一:obj.name旧值:", oldVal);
console.log("方法一:obj.name新值:", newVal);
}
);
//监听对象属性的方法二
const { name: tempName } = toRefs(obj);
watch(tempName, (newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log("方法二:obj.name旧值:", oldVal);
console.log("方法二:obj.name新值:", newVal);
});
//监听对象的对象属性, 需要开启 deep
watch(() => obj.job, (newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log("job 旧值:", oldVal);
console.log("job 新值:", newVal);
}, {deep: true});
//这时不需要开启 deep
watch(obj.job, (newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log("job 旧值2:", oldVal);
console.log("job 新值2:", newVal);
}, {deep: false});
return { msg, updateMsg, obj, updateName, subject, updateSubject, updateSalary };
},
};
script>
8. watchEffect 监听函数
- 不用直接指定要监视的数据, 回调函数中使用的哪些响应式数据就监视哪些响应式数据
- 默认初始时就会执行第一次, 从而可以收集需要监视的数据
- 监视数据发生变化时回调
- watchEffect 函数会返回一个函数,可以利用该函数停止数据的监听
- watchEffect 有点像 copmputed:
- 但 computed 注重的是计算出来的值 (回调函数的返回值) ,所以必须要写返回值
- 而 watchEffect 更注重的是过程 (回调函数的函数体), 所以不用写返回值
- 给watchEffect传入的函数被回调时,其实可以获取到一个参数:onInvalidate
- 当副作用即将重新执行 或者 侦听器被停止 时会执行该函数传入的回调函数;
- 可以在传入的回调函数中,执行一些清楚工作;
<template>
<div>
{{ msg }}<br />
{{ obj.name }}<br />
<button @click="updateMsg">修改msgbutton><br />
<button @click="updateSalary">修改salarybutton><br />
<button @click="stopWatchEffect">停止监听数据button><br />
div>
template>
<script >
import { ref, reactive, watchEffect } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
const msg = ref('我是一个消息')
const obj = reactive({
name: '张三',
age: 22,
job: {
salary: 20
}
})
function updateMsg() {
msg.value = '一个新消息'
}
function updateSalary() {
obj.job.salary++
}
const stop = watchEffect((onInvalidate) => {
console.log(arguments)
console.log('salary变化了', obj.job.salary)
console.log('msg变化了', msg.value)
//改函数会比上边的 log 中的内容先执行
// stop 函数被调用时也会执行
onInvalidate(() => {
console.log(123)
})
})
function stopWatchEffect(){
stop()
}
return { msg, obj, updateMsg, updateSalary, stopWatchEffect }
}
}
script>
9. 生命周期
-
vue3 中可以继续使用 vue2 的声明周期钩子,但是 vue3 将 beforeDestroy 和 destroyed 两个生命周期函数改名为:beforeUnmount 和 unmounted
-
vue3中的声明周期回调函数比 vue2 中的生命周期 回调函数执行的早
-
与 2.x 版本生命周期相对应的组合式 API
beforeCreate -> 使用 setup()
created -> 使用 setup()
beforeMount -> onBeforeMount
mounted -> onMounted
beforeUpdate -> onBeforeUpdate
updated -> onUpdated
beforeDestroy -> onBeforeUnmount
destroyed -> onUnmounted
errorCaptured -> onErrorCaptured
parent.vue
<template>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">切换child组件状态button>
<Child v-if="isShow" />
template>
<script>
import Child from "./07.child.vue";
import { ref } from "vue";
export default {
name: "Parent",
// data() {
// return {
// isShow: true,
// };
// },
components: {
Child,
},
setup() {
let isShow = ref(true);
return { isShow };
},
};
script>
child.vue
<template>
<span>{{ msg }}span>
<button @click="updateMsg">更改Msgbutton>
template>
<script>
import {
ref,
onMounted,
onUpdated,
onUnmounted,
onBeforeMount,
onBeforeUpdate,
onBeforeUnmount,
} from "vue";
export default {
name: "Child",
beforeCreate() {
console.log("vue2 的 beforeCreate");
},
created() {
console.log("vue2 的 created");
},
beforeMount() {
console.log("vue2 的 beforeMount");
},
mounted() {
console.log("vue2 的 mounted");
},
beforeUpdate() {
console.log("vue2 的 beforeUpdate");
},
updated() {
console.log("vue2 的 updated");
},
// vue3 将 beforeDestroy 和 destroyed 两个生命周期函数改名为:beforeUnmount unmounted
beforeUnmount() {
console.log("vue2 的 beforeUnmount");
},
unmounted() {
console.log("vue2 的 unmounted");
},
setup() {
console.log("setup被调用,充当 beforeCreate 和 created");
onBeforeMount(() => {
console.log("vue3 的 onBeforeMount");
});
onMounted(() => {
console.log("vue3 的 onMounted");
});
onBeforeUpdate(() => {
console.log("vue3 的 onBeforeUpdate");
});
onUpdated(() => {
console.log("vue3 的 onUpdated");
});
onBeforeUnmount(() => {
console.log("vue3 的 onBeforeUnmount");
});
onUnmounted(() => {
console.log("vue3 的 onUnmounted");
});
let msg = ref("一个消息");
function updateMsg() {
msg.value = "一个新消息";
}
return { msg, updateMsg };
},
};
script>
10. 自定义 hook 函数
- hook 本质是一个函数,把 setup 函数中使用的 Componsition API 进行了封装
- 类似于 Vue 2 中的 mixin
- 自定义 hoook 的优势: 复用代码,让 setup 中的逻辑更清楚易懂
-
在 src 目录下新建 hooks 文件夹,在 hooks 文件夹中新建 userPoint.js 文件 (hooks 文件夹中的文件一般以 user 开头)
import { reactive, onMounted, onBeforeUnmount } from 'vue' export default function () { let point = reactive({ x: 0, y: 0 }) function getCursorPoint(event) { point.x = event.pageX point.y = event.pageY } // 创建组件时 挂载事件监听 onMounted(() => { window.addEventListener('click', getCursorPoint) }) // 组件销毁时 取消事件监听 onBeforeUnmount(() => { window.removeEventListener('click', getCursorPoint) }) return point } -
创建组件,并应用 hooks/userPoint.js
<template> <p>鼠标点击的位置:X: {{ point.x }},Y: {{ point.y }}p> template> <script> import userPoint from "./../hooks/userPoint"; export default { name: "Point", setup() { let point = userPoint(); console.log(point) return { point }; }, }; script>
11. 比较 Vue2 与 Vue3 的响应式
1). Vue2 的响应式
-
核心:
- 对象: 通过defineProperty对对象的已有属性值的读取和修改进行劫持(监视/拦截)
- 数组: 通过重写数组更新数组一系列更新元素的方法来实现元素修改的劫持
-
问题
- 对象直接新添加的属性或删除已有属性, 界面不会自动更新
- 直接通过下标替换元素或更新length, 界面不会自动更新 如: arr[1] = {}
Object.defineProperty(data, 'count', { get () {}, set () {} })
1). Vue3 的响应式
-
核心:
- 通过Proxy(深度代理): 拦截对data任意属性的任意(13种)操作, 包括属性值的读写, 属性的添加, 属性的删除等…
- 通过 Reflect(反射): 动态对被代理对象的相应属性进行特定的操作
new Proxy(data, { // 拦截读取属性值 get (target, prop) { return Reflect.get(target, prop) }, // 拦截设置属性值或添加新属性 set (target, prop, value) { return Reflect.set(target, prop, value) }, // 拦截删除属性 deleteProperty (target, prop) { return Reflect.deleteProperty(target, prop) } // ... 其他方法 }) proxy.name = 'tom'
四、其它 Composition API
1. shallowRef 与 shallowReactive
1). shallowRef
- 在 shallowRef 中传入基本的数据类型时,shallowRef 与 ref 没有区别
- shallowRef 中传入对象数据类型时,不会对数据进行响应式处理
<template>
<div>
<p>refVal:{{ refVal }}p>
<p>shollowRefVal:{{ shollowRefVal }}p>
<button @click="refVal++">refVal ++button>
<button @click="shollowRefVal--">shollowRefVal --button>
<p>refObjVal:{{ refObjVal.msg }}p>
<p>shollowRefObjVal:{{ shollowRefObjVal.msg }}p>
<button @click="refObjVal.msg += '*'">refMsg ++button>
<button @click="shollowRefObjVal.msg += '^'">shollowRefMsg --button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { ref, shallowRef } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
let refVal = ref(0);
let shollowRefVal = shallowRef(100);
let refObjVal = ref({
msg: "ref的消息",
});
let shollowRefObjVal = shallowRef({
msg: "shallowRef的消息",
});
console.log(refVal);
console.log(shollowRefVal);
console.log(refObjVal); // value值为 proxy
console.log(shollowRefObjVal); // 在控制台中点开后,value值不一样,为 Object
return { refVal, shollowRefVal, refObjVal, shollowRefObjVal };
},
};
script>
2). shallowReactive
- shallwReactive 只对数据的最外层进行响应式处理(浅响应式),reactive 会对数据的深层进行响应式处理
<template>
<div>
<p>reactiveObj:name:{{ reactiveObj.name }}p>
<p>shallowReactiveObj:name:{{ shallowReactiveObj.name }}p>
<p>reactiveObj:salary:{{ reactiveObj.obj.salary }}p>
<p>shallowReactiveObj:salary:{{ shallowReactiveObj.obj.salary }}p>
<button @click="reactiveObj.name += '*'">reactiveObj.namebutton>
<button @click="shallowReactiveObj.name += '^'"> shallowReactiveObj.name button>
<button @click="reactiveObj.obj.salary += 1">reactiveObj.obj.salarybutton>
<button @click="shallowReactiveObj.obj.salary += 1"> shallowReactiveObj.obj.salary button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { reactive, shallowReactive } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
let reactiveObj = reactive({
name: "张三",
obj: {
salary: 20,
},
});
let shallowReactiveObj = shallowReactive({
name: "李四",
obj: {
salary: 10,
},
});
return { reactiveObj, shallowReactiveObj };
},
};
script>
2. readonly与 shallowReadonly
- readonly: 让一个响应式数据变为只读的 (深只读)
- const info = readonly(obj),info对象是不允许被修改的; 当响应式的obj 被修改时,readonly返回的info对象也会被修改;
- 其实本质上就是readonly返回的对象的setter方法被劫持了而已;
- shallowReadonly: 让一个响应式数据变为只读的 (浅只读)
<template>
<div>
<p>obj1.name:{{ obj1.name }}p>
<p>obj2.name:{{ obj2.name }}p>
<p>obj3.name:{{ obj3.name }}p>
<p>obj4.name:{{ obj4.name }}p>
<p>obj1.job.salary:{{ obj1.job.salary }}p>
<p>obj2.job.salary:{{ obj2.job.salary }}p>
<p>obj3.job.salary:{{ obj3.job.salary }}p>
<p>obj4.job.salary:{{ obj4.job.salary }}p>
<p>tempObj.job.salary:{{ tempObj.job.salary }}p>
<p>info.job.salary:{{ info.job.salary }}p>
<button @click="obj1.name += '*'">obj1.namebutton>
<button @click="obj2.name += '^'">obj2.namebutton>
<button @click="obj3.name += '#'">obj3.namebutton>
<button @click="obj4.name += '#'">obj4.namebutton>
<button @click="obj1.job.salary++">obj1.job.salarybutton>
<button @click="obj2.job.salary++">obj2.job.salarybutton>
<button @click="obj3.job.salary++">obj3.job.salarybutton>
<button @click="obj4.job.salary++">obj4.job.salarybutton>
<button @click="tempObj.job.salary++">tempObj.job.salarybutton>
<button @click="info.job.salary++">info.job.salarybutton>
<button @click="printResult">打印最终结果button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { reactive, readonly, shallowReadonly } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
let info = {
name: '张三',
job: {
salary: 20
}
}
let tempObj = reactive(info)
let obj1 = readonly(tempObj)
let obj2 = readonly({
name: '李四',
job: {
salary: 17
}
})
let obj3 = shallowReadonly({
name: '王五',
job: {
salary: 6
}
})
let obj4 = shallowReadonly(tempObj)
function printResult() {
console.log('info:' + JSON.stringify(info), info) //object
console.log('obj1:' + JSON.stringify(obj1), obj1) //proxy
console.log('obj2:' + JSON.stringify(obj2), obj2) //proxy
console.log('obj3:' + JSON.stringify(obj3), obj3) //proxy
console.log('obj4:' + JSON.stringify(obj4), obj4) //proxy
console.log('-----------------------------')
}
return { info, tempObj, obj1, obj2, obj3, obj4, printResult }
}
}
script>
3. toRaw 与 markRaw
- toRaw: 将一个由
reactive生成的 响应式对象 转为 普通对象 - markRaw: 标记一个对象,使其永远不会再成为响应式对象
<template>
<div>
<p>obj.name:{{ obj.name }}p>
<p>obj.car:{{ obj.car?.name }}p>
<p>obj.house:{{ obj.house?.name }}p>
<button @click="addCarInfo">添加car信息button>
<button @click="addHouseInfo">添加horse信息button>
<button @click="editCarInfo">修改car信息button>
<button @click="editHouseInfo">修改horse信息button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { markRaw, reactive, toRaw } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
let obj = reactive({
name: "张三",
obj: {
salary: 20,
},
});
function addCarInfo() {
//添加的car是响应式的
obj.car = { name: "兰博基尼" };
}
function editCarInfo() {
//修改是响应式的
obj.car.name = "五菱";
}
function addHouseInfo() {
//添加一个非响应式的属性
obj.house = markRaw({ name: "大房子" });
}
function editHouseInfo() {
//可以修改属性 但是 为 非响应式的
obj.house.name = "小房子";
console.log(obj.house.name); //小房子
}
console.log(obj); //proxy
console.log(toRaw(obj)); //普通对象 {name: ...}
return { obj, addCarInfo, addHouseInfo, editCarInfo, editHouseInfo };
},
};
script>
4. customRef
- 创建一个自定义的 ref, 并对其依赖项跟踪和更新触发进行显示控制
- customRef 中需要一个回调函数,回调函数中有两个参数分别是
用于追踪的 track与用于触发响应的 trigger,并需要返回一个一个带有 get 和 set 属性的对象 - 一般来说,track() 应该在 get() 内部调用,trigger() 应该在 set() 内部调用。但是,您可以完全控制何时调用它们,或者是否应该调用它们。
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="msg" />
<p>{{ msg }}p>
div>
template>
<script>
import { customRef } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
function myRef(value, delay) {
let timer;
return customRef((track, trigger) => {
return {
get() {
console.log(`get函数被调用,value值为:${value}`);
track(); // 通知 Vue 跟踪 value 的变化
return value;
},
set(newValue) {
console.log(`set函数被调用`);
//实现数据防抖
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(() => {
value = newValue;
trigger(); // 通知 Vue 去重新解析模板
}, delay);
},
};
});
}
var msg = myRef("一个消息", 500);
return { msg };
},
};
script>
5. provide 与 inject
- 在组合式 API 中使用 provide/inject,两个只能在 setup 期间调用,使用之前,必须从 vue 显示导入 provide/inject 方法。
- 实现跨层级组件(祖孙)间通信
- provide( name,value ) :name,定义提供 property 的 name ;value,property 的值。
- inject(name,default): name,接收 provide 提供的属性名;default,设置默认值,可以不写,是可选参数。
祖先组件:parent.vue
<template>
<div style="border: 1px solid red">
<p>名字{{ name }}p>
<p>车:{{ car.name }},{{ car.price }}Wp>
<p>房:{{ house.name }},{{ house.price }}Wp>
<button @click="car.price++">更改车的价格button>
<Child />
div>
template>
<script>
import { ref, reactive, provide } from "vue";
import Child from "./child.vue";
export default {
components: {
Child,
},
setup() {
let car = reactive({
name: "奔驰",
price: 20,
});
let name = ref("张三");
let house = reactive({
name: "碧桂园",
price: 50,
});
//提供给后代组件可使用的值
provide("car", car);
provide("name", name);
provide("house", house);
return {
name,
car,
house,
};
},
};
script>
中间组件 child.vue
<template>
<div style="border: 1px solid green">
中间组件
<Descendant />
div>
template>
<script>
import Descendant from "./descendant.vue";
export default {
components: {
Descendant,
},
};
script>
后代组件 descendant.vue
<template>
<div style="border: 1px solid blue">
<p>{{ name }}p>
<p>{{ house }}p>
<p>{{ car }}p>
div>
template>
<script>
import { inject } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
//接收从祖先组件传递的值
const car = inject("car");
const house = inject("house");
const name = inject("name");
//因为祖先组件传递的是响应式的数据所以得到的数据也是响应式的
console.log(car, house, name);
return { car, house, name };
},
};
script>
6. 响应式数据的判断
- isRef: 检查一个值是否为一个 ref 对象
- isReactive: 检查一个对象是否是由 reactive 创建的响应式代
- isReadonly: 检查一个对象是否是由 readonly 创建的只读代理
- isProxy: 检查一个对象是否是由 reactive 或者 readonly 方法创建的代理
- unref:
val = isRef(val) ? val.value : val的语法糖函数
7. 自定义指令
- 局部自定义指令:组件中通过 directives 选项,只能在当前组件中使用;
- 全局自定义指令:app的 directive 方法,可以在任意组件中被使用;
- 自定义指令的生命周期:
- created:在绑定元素的 attribute 或事件监听器被应用之前调用;
- beforeMount:当指令第一次绑定到元素并且在挂载父组件之前调用;
- mounted:在绑定元素的父组件被挂载后调用;
- beforeUpdate:在更新包含组件的 VNode 之前调用;
- updated:在包含组件的 VNode 及其子组件的 VNode 更新后调用;
- beforeUnmount:在卸载绑定元素的父组件之前调用;
- unmounted:当指令与元素解除绑定且父组件已卸载时,只调用一次
局部自定义指令:
<template>
<input type="input" v-focus />
template>
<script>
export default {
// 局部自定义指令
directives: {
//定义一个focus
focus: {
// 在指令的 mounted 生命周期挂载
mounted(el, binding, vnode, prevNode) {
el.focus()
}
}
}
}
script>
全局自定义指令:在main.js文件中
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import './style.css'
import App from './App.vue'
const app = createApp(App)
app.directive('focus', {
mounted(el, binding, vnode, prevNode) {
el.focus()
},
})
app.mount('#app')
五、新的组件
1. Teleport
- Teleport 是一种能够将我们的组件HTML结构移动到指定位置的技术
接收一个 to prop 来指定传送的目标。to 的值可以是一个 CSS 选择器字符串,也可以是一个 DOM 元素对象。这段代码的作用就是告诉 Vue“把以下模板片段传送到 body 标签下”。
<template>
<div>
<button @click="open = true">Open Modalbutton>
<Teleport to="body">
<div v-if="open" class="modal">
<p>Hello from the modal!p>
<button @click="open = false">Closebutton>
div>
Teleport>
div>
template>
<script>
import { ref } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
const open = ref(false);
return {
open,
};
},
};
script>
2. mitt 事件总线
Vue3从实例中移除了 $on、$off 和 $once 方法,所以我们如果希望继续使用全局事件总线,要通过第三方的库:Vue3官方有推荐一些库,例如 mitt 或 tiny-emitter;
- 进入到项目文件夹中,安装 mitt 库
npm install mitt - 创建 eventbus.js 文件
import mitt from 'mitt' const emmiter = mitt(); // 可以创建多个事件总线 // export const emmiter1 = mitt(); export default emmiter; - 创建 parent.vue 文件
<template> <div> <son v-if="showSon" /> <button @click="sendInfo">触发sendInfo方法button> <button @click="sendOther">触发sendOther方法button> <button @click="destroySon">销毁子组件button> div> template> <script> import emmiter from "./eventbus"; import { ref } from "vue"; import Son from "./son.vue"; export default { components: { Son, }, setup() { const showSon = ref(true); function sendInfo() { console.log("infoEmit被触发"); // 在事件总线上 触发 infoEmit 事件, 并传递参数 emmiter.emit("infoEmit", { componentName: "parent", type: "emit" }); } function sendOther() { console.log("sendOther被触发"); // 在事件总线上 触发 isendOther 事件, 并传递参数 emmiter.emit("sendOther", { name: "123", age: 24 }); } function destroySon() { showSon.value = false } return { showSon, sendInfo, sendOther, destroySon }; }, }; script> - 创建 son.vue 文件
<template> <div style="width: 50px; height: 50px; border: 1px solid blue"> 我是子组件 div> template> <script> import emmiter from "./eventbus"; import { onBeforeUnmount } from "vue"; export default { setup() { function infoEmitFn(info) { console.log("infoEmitFn被触发"); console.log(info); } function sendOtherFn(other) { console.log("sendOtherFn被触发"); console.log(other); } //一般是在声明周期的 created 阶段挂载监听事件总线 emmiter.on("infoEmit", infoEmitFn); emmiter.on("sendOther", sendOtherFn); //监听事件总线上的所有事件 emmiter.on("*", (eventName, playload) => { console.log("*被触发", eventName, playload); }); //在声明周期的 onBeforeUnmount 阶段取消事件的监听 onBeforeUnmount(() => { console.log("子组件被销毁"); //取消监听和挂载监听必须是同一个回调函数 //如果不取消监听,注册时的回调方法仍然会被触发 emmiter.off("infoEmit", infoEmitFn); emmiter.off("sendOther", sendOtherFn); //取消所有的监听 emmiter.all.clear(); }); }, }; script>
六、自己实现 Vue3 源码
- vue 的 github 源码地址:https://github.com/vuejs/core
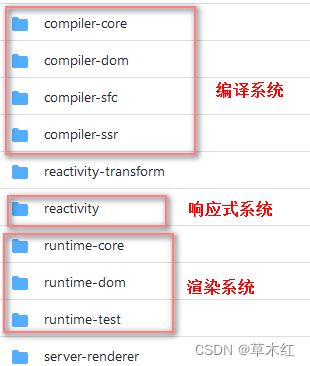
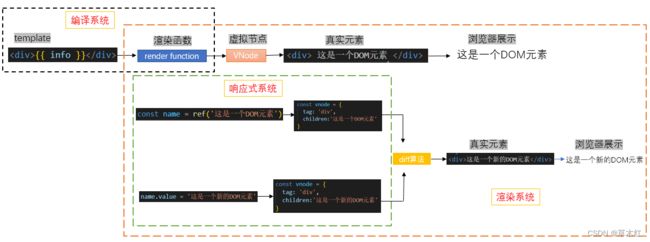
- vue源码包含三大核心:
1. 渲染系统
1). h函数
用于返回一个 VNode (虚拟节点)对象
- 在 renderer.js 文件中创建 h 函数
/**
* 将 vnode 转为 javascript 对象
* @param {标签名称} tag
* @param {属性} props
* @param {子元素} children
* @returns
*/
const h = (tag, props, children) => {
// 返回一个 vnode
return {
tag,
props,
children,
el: null // 存放 DOM节点
}
}
2). mount 函数
用于将 VNode 改在到 DOM 上
- 在 renderer.js 文件中创建 mount 函数
/**
* 将 vnode 挂载到 container
* @param {虚拟节点} vnode
* @param {需要挂载的节点} container
*/
const mount = (vnode, container) => {
// 1.将 vnode 转为 DOM
const el = vnode.el = document.createElement(vnode.tag)
// 2.将 props 作为 DOM 属性
if (vnode.props) {
for (const key in vnode.props) {
if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(vnode.props, key)) {
const value = vnode.props[key]
// 处理事件
if (key.startsWith('on')) {
el.addEventListener(key.slice(2).toLowerCase(), value)
} else { //处理属性
el.setAttribute(key, value)
}
}
}
}
// 3.处理子节点, 只处理字符串和数组
if (vnode.children) {
if (typeof vnode.children === 'string') {
el.textContent = vnode.children
} else if (Array.isArray(vnode.children)) {
vnode.children.forEach(item => {
mount(item, el) //回调
});
}
}
// 4.将子节点挂载到container
container.appendChild(el)
}
3). patch 函数
用于对比两个 VNode ,决定如何处理新的 VNode
- 在 renderer.js 文件中创建 mount 函数
/**
* 对比两个 vnode 用 newVnode 替换 oldVnode
* @param {*} oldVnode
* @param {*} newVnode
*/
const patch = (oldVnode, newVnode) => {
const el = newVnode.el = oldVnode.el
// 1. 元素类型不一样, 直接替换
if (oldVnode.tag !== newVnode.tag) {
const parentEle = oldVnode.el.parentElement
parentEle.removeChild(el)
mount(newVnode, parentEle)
} else { // 2. 元素类型一样
// 2.1 将 newVnode 上独有的属性 prop 添加到元素上
for (const key in newVnode.props) {
if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(newVnode.props, key)) {
const oldProp = oldVnode.props[key];
const newProp = newVnode.props[key];
if (oldProp !== newProp) {
//添加新的事件
if (key.startsWith('on')) {
el.addEventListener(key.slice(2).toLowerCase(), newProp)
} else {
el.setAttribute(key, newProp)
}
}
}
}
// 2.2 删除 n1(旧元素) 上独有的属性
for (const key in oldVnode.props) {
if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(oldVnode.props, key)) {
const oldProp = oldVnode.props[key];
const newProp = newVnode.props[key];
if (oldProp !== newProp) {
if (key.startsWith('on')) {
el.removeEventListener(key.slice(2).toLowerCase(), oldProp)
} else {
el.removeAttribute(key)
}
}
}
}
// 2.3 处理 children
const oldVnodeChildren = oldVnode.children
const newVnodeChildren = newVnode.children
// 2.3.1 newVnode.children 是字符串,
if (typeof newVnodeChildren === 'string') {
if (typeof oldVnodeChildren === 'string' && oldVnodeChildren !== newVnodeChildren) {
el.textContent = newVnodeChildren
}
} else { //2.3.2 newVnodeChildren 是数组
// oldVnodeChildren 是字符串
if (typeof oldVnodeChildren === 'string') {
el.textContent = ''
newVnodeChildren.forEach(item => {
mount(item, el)
})
} else {
const oldVnodeChildrenLength = oldVnodeChildren.length
const newVnodeChildrenLength = newVnodeChildren.length
const minLength = Math.min(oldVnodeChildrenLength, newVnodeChildrenLength)
// oldVnodeChildrenLength === oldVnodeChildrenLength 时也会在这里处理
for (let i = 0; i < minLength; i++) {
patch(oldVnodeChildren[i], newVnodeChildren[i])
}
// 删除 oldVnodeChildrenLength 中多余的 child
if (oldVnodeChildrenLength > newVnodeChildrenLength) {
oldVnodeChildren.slice(minLength).forEach(item => {
el.removeChild(item.el)
})
}
// 添加 newVnodeChildren 中多余的 child
if (oldVnodeChildrenLength < newVnodeChildrenLength) {
newVnodeChildren.slice(minLength).forEach(item => {
mount(item, el)
})
}
}
}
}
}
4). 使用 h 函数、mount 函数和 patch 函数
<body>
<div id="app">div>
<script src="./renderer.js">script>
<script>
//通过 h 函数创建 vnode
const vnode = h('div', { class: 'box', 'data-id': '#div' }, [
h('h2', null, 'h函数的实现'),
h('button', { onClick: function () { console.log("按钮被点击") } }, '按钮')
])
//将 vnode 挂在到 #app
mount(vnode, document.getElementById('app'))
const newVnode = h('div', { id: 'user', 'data-id': '#div' }, [
h('p', null, '我是一段文字'),
h('button',{ onClick: function () { console.log("按钮2被点击") } }, '按钮2'),
])
patch(vnode, newVnode)
script>
body>
2. 响应式系统
1). reactive 函数
- reactive.js 文件
class Dep {
constructor() {
this.subscribers = new Set()
}
//添加收集到的依赖
depend() {
if (activeEffect) {
this.subscribers.add(activeEffect)
}
}
//触发收集到的依赖
notify() {
this.subscribers.forEach(effect => {
effect()
})
}
}
//将要被收集的依赖
let activeEffect = null
function watchEffect(effect) {
activeEffect = effect
effect() //直接执行一次,执行后会将依赖收集
activeEffect = null
}
//存储所有数据,
//假设需要监听的数据为:info = {name: '张三', age: 13} ,将以 target 的值(对象)作为 WeakMap 的key, 以map 为值
//map 中以 target 中的 key 作为 map中的key, 以 target[key] 的值 作为 map[key] 的值
// 类似于:{{name: '张三', age: 13}:{name: dep, age: dep}}
const targetMap = new WeakMap();
function getDep(target, key) {
let depsMap = targetMap.get(target)
if (!depsMap) {
depsMap = new Map()
targetMap.set(target, depsMap)
}
let dep = depsMap.get(key)
if (!dep) {
dep = new Dep();
depsMap.set(key, dep)
}
return dep
}
// 响应式 入口
function reactive(raw) {
//返回的是 proxy 的实例
return new Proxy(raw, {
get(target, key) {
const dep = getDep(target, key) // 将raw 中的 key 存储在 targetMap 中
dep.depend() //进行依赖收集
return target[key]
},
set(target, key, newvalue) {
const dep = getDep(target, key) // 将raw 中的 key 存储在 targetMap 中, 包含新增的key
target[key] = newvalue;
dep.notify() // 执行所有依赖
}
})
}
// 测试用例
// const info = reactive({ name: '张三', age: 13 })
// watchEffect(function(){
// console.log('info.name :' + info.name)
// })
// info.name = '李四'
3. 整合渲染系统与响应式系统
1). createApp 函数
function createApp(rootComponent) {
return {
mount(selector) { //自己的mount函数
const container = document.querySelector(selector);
let isMounted = false;
let oldVNode = null;
watchEffect(function () { // 数据更新时 更新 DOM
if (!isMounted) { // 判断是否已经挂载
oldVNode = rootComponent.render();
mount(oldVNode, container); // 渲染系统中的mount函数
isMounted = true;
} else {
const newVNode = rootComponent.render();
patch(oldVNode, newVNode);
oldVNode = newVNode;
}
})
}
}
}
4. 使用渲染系统、响应式系和createApp函数
<body>
<div id="app">div>
<script src="./renderer.js">script>
<script src="./reactive.js">script>
<script src="./createApp.js">script>
<script>
const App = {
data: reactive({
counter: 0
}),
render() {
return h('div', null, [
h('p', null, `counter:${this.data.counter}`),
h('button', {
onClick: () => {
this.data.counter++
}
}, '增加1')
])
}
}
const app = createApp(App)
app.mount('#app')
script>
body>