.NET Core MVC使用基于角色的授权
你还在为不会使用.NET Core做登录注册角色分配而烦恼吗?现在,这篇文章即将告诉你如何使用.NET Core的组件进行简单的登录注册和角色分配的功能,文章将会教你实现以下功能:
1、.NET Core自带的Identity组件的安装与使用;
2、实现注册功能;
3、实现登录功能;
4、实现退出与修改密码功能;
5、角色分配与授权;
6、数据库的简单CRUD
1、使用Identity组件
使用vs2022的.NET 6进行演示。我们需要以下nuget包:
第一个包就是我们需要的Identity相关组件,安装完成后,需要进行如下步骤:
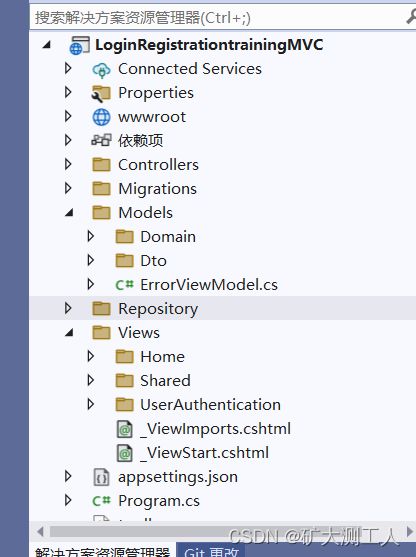
创建Domain层用于存放聚合根和Dto,文件位置如下:
创建用户基本信息,由于是演示,我们不需要组件。
public class ApplicationUser:IdentityUser
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string? ProfilePicture { get; set; }
}创建聚合根。
public class DatabaseContext:IdentityDbContext
{
public DatabaseContext(DbContextOptions options) : base(options)
{
}
} 在program里进行依赖注入。
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllersWithViews();
builder.Services.AddDbContext(options => options.UseSqlite(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("conn")));
//安全组件添加
builder.Services.AddIdentity()
.AddEntityFrameworkStores()
.AddDefaultTokenProviders();
//添加cookie
builder.Services.ConfigureApplicationCookie(options => options.LoginPath = "/UserAuthentication/Login");
var app = builder.Build(); 配置连接字符串。
"ConnectionStrings": {
"conn": "Data Source=to.db"
}
重定义路由。
app.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=UserAuthentication}/{action=Login}/{id?}");添加授权鉴权。
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();使用如下指令进行迁移:
add-migration init
update-database现在,你已经连接了sqlite数据库,当然,连接其他的数据库也可以。
2、实现注册的功能
现在,我们需要把Repository完善,然后依赖注入。首先需要的是实现注册登录退出相关的功能,我们使用Identity和DTO层来完成数据平面化。
关于注册的DTO层建立代码如下。
public class Register_Dto
{
[Required]
public string FirstName { get; set; }
[Required]
public string LastName { get; set; }
[Required]
[EmailAddress]
public string Email { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Username { get; set; }
[Required]
[RegularExpression("^(?=.*?[A-Z])(?=.*?[a-z])(?=.*?[0-9])(?=.*[#$^+=!*()@%&]).{6,}$", ErrorMessage = "最小长度为6,必须包含1个大写、1个小写、1个特殊字符和1个数字")]
public string Password { get; set; }
[Required]
[Compare("Password")]
public string PasswordConfirm { get; set; }
public string? Role { get; set; }
}在AuthRepository的注册实现方法如下:
public async Task RegisterAsync(Register_Dto model)
{
var status = new Status();
var userExists = await userManager.FindByNameAsync(model.Username);
if (userExists != null)
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "用户已存在";
return status;
}
ApplicationUser user = new ApplicationUser()
{
Email = model.Email,
SecurityStamp = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(),
UserName = model.Username,
FirstName = model.FirstName,
LastName = model.LastName,
EmailConfirmed = true,
PhoneNumberConfirmed = true,
};
var result = await userManager.CreateAsync(user, model.Password);
if (!result.Succeeded)
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "注册失败";
return status;
}
if (!await roleManager.RoleExistsAsync(model.Role))
await roleManager.CreateAsync(new IdentityRole(model.Role));
if (await roleManager.RoleExistsAsync(model.Role))
{
await userManager.AddToRoleAsync(user, model.Role);
}
status.StatusCode = 1;
status.StatusMessage = "注册成功";
return status;
} 在控制器的注册方法如下:
public IActionResult Registration()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task Registration(Register_Dto model)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
return View(model);
model.Role = "User";
var result = await repository.RegisterAsync(model);
TempData["msg"]=result.StatusMessage;
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Registration));
} 前端界面大致如下:
@model LoginRegistrationtrainingMVC.Models.Dto.Register_Dto
@{
Layout = null;
}
@Html.ValidationSummary()
Registration
可以看到,我们使用了Identity的许多方法,这样我们就可以专心于业务逻辑而非数据库的CRUD。
3、实现登录功能
对于登录功能,我们同样需要DTO。我们不用AutoMapper,而是自己实现数据库与DTO的映射。
DTO的代码如下:
public class Login_Dto
{
[Required]
public string Username { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Password { get; set; }
}Repository的代码如下:
public async Task LoginAsync(Login_Dto model)
{
var status = new Status();
var user = await userManager.FindByNameAsync(model.Username);
if (user == null)
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "查无此人";
return status;
}
if (!await userManager.CheckPasswordAsync(user, model.Password))
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "修改密码失败";
return status;
}
var signInResult = await signInManager.PasswordSignInAsync(user, model.Password, false, true);
if (signInResult.Succeeded)
{
var userRoles = await userManager.GetRolesAsync(user);
var authClaims = new List
{
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, user.UserName),
};
foreach (var userRole in userRoles)
{
authClaims.Add(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, userRole));
}
status.StatusCode = 1;
status.StatusMessage = "成功";
}
else if (signInResult.IsLockedOut)
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "用户退出";
}
else
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "错误";
}
return status;
} 在控制器的代码如下:
public IActionResult Login()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public async TaskLogin(Login_Dto model)
{
if(!ModelState.IsValid)
return View(model);
var result = await repository.LoginAsync(model);
if (result.StatusCode==1)
return RedirectToAction("Index","Home");
else
{
TempData["msg"] = result.StatusMessage;
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Login));
}
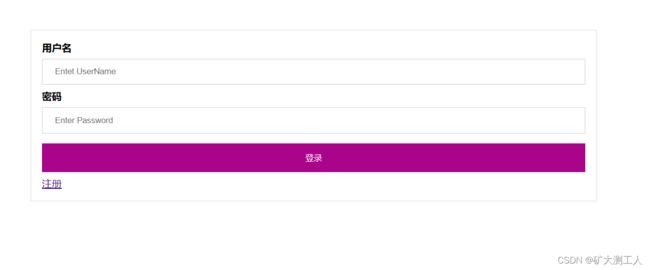
} 前端界面如下:
@model LoginRegistrationtrainingMVC.Models.Dto.Login_Dto
@{
Layout = null;
}
登录
4、实现退出与修改密码功能
退出功能如下:
[Authorize]
public async Task Logout()
{
await repository.LogoutAsync();
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Login));
} public async Task LogoutAsync()
{
await signInManager.SignOutAsync();
}修改密码的DTO层如下:
public class ChangePassword_Dto
{
[Required]
public string? CurrentPassword { get; set; }
[Required]
[RegularExpression("^(?=.*?[A-Z])(?=.*?[a-z])(?=.*?[0-9])(?=.*[#$^+=!*()@%&]).{6,}$", ErrorMessage = "最小长度为6,必须包含1个大写、1个小写、1个特殊字符和1个数字")]
public string? NewPassword { get; set; }
[Required]
[Compare("NewPassword")]
public string? PasswordConfirm { get; set; }
}Repository设计如下:
public async Task ChangePasswordAsync(ChangePassword_Dto model, string username)
{
var status = new Status();
var user = await userManager.FindByNameAsync(username);
if (user == null)
{
status.StatusMessage = "用户不存在";
status.StatusCode = 0;
return status;
}
var result = await userManager.ChangePasswordAsync(user, model.CurrentPassword, model.NewPassword);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
status.StatusMessage = "密码更新成功";
status.StatusCode = 1;
}
else
{
status.StatusMessage = "密码更新失败";
status.StatusCode = 0;
}
return status;
} 控制器设计如下:
[Authorize]
public IActionResult ChangePassword()
{
return View();
}
[Authorize]
[HttpPost]
public async Task ChangePassword(ChangePassword_Dto model)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
return View(model);
var result = await repository.ChangePasswordAsync(model, User.Identity.Name);
TempData["msg"] = result.StatusMessage;
return RedirectToAction(nameof(ChangePassword));
} 前端界面如下:
@model LoginRegistrationtrainingMVC.Models.Dto.ChangePassword_Dto
Registration
5、角色分配与授权鉴权
我们使用Cookie来完成这一切。首先我们需要在program里面使用Cookie,然后使用授权组件(包括 AuthorizeAttribute 和 AllowAnonymousAttribute 属性)完成我们的角色分配与授权。
当用户属于admin时,我们赋予用户角色,然后由授权中间件来完成后续步骤,例如:
[Authorize(Roles ="admin")]
public IActionResult Privacy()
{
return View();
}只有admin才可以访问该页面,其他人是无法访问的。
与此同时,我们使用ASP对前端进行修改,不让非admin用户看到相应的菜单栏,例如:
@if (User.IsInRole("admin"))
{
Privacy
}对于需要登录才可以查看的页面,我们可以使用以下属性:
[Authorize]
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}而对于用户角色的设置,我们在用户注册时就选定好了;而对于管理者,可以实现使用种子数据,或者直接到数据库里修改。
[HttpPost]
public async Task Registration(Register_Dto model)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
return View(model);
model.Role = "User";
var result = await repository.RegisterAsync(model);
TempData["msg"]=result.StatusMessage;
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Registration));
} 在Repository层,我们使用Identity的组件来对用户角色进行绑定。由于项目较小,我们不使用Service层,故直接在控制器里使用Repository。
public async Task RegisterAsync(Register_Dto model)
{
var status = new Status();
var userExists = await userManager.FindByNameAsync(model.Username);
if (userExists != null)
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "用户已存在";
return status;
}
ApplicationUser user = new ApplicationUser()
{
Email = model.Email,
SecurityStamp = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(),
UserName = model.Username,
FirstName = model.FirstName,
LastName = model.LastName,
EmailConfirmed = true,
PhoneNumberConfirmed = true,
};
var result = await userManager.CreateAsync(user, model.Password);
if (!result.Succeeded)
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "注册失败";
return status;
}
if (!await roleManager.RoleExistsAsync(model.Role))
await roleManager.CreateAsync(new IdentityRole(model.Role));
if (await roleManager.RoleExistsAsync(model.Role))
{
await userManager.AddToRoleAsync(user, model.Role);
}
status.StatusCode = 1;
status.StatusMessage = "注册成功";
return status;
} 这也是我们使用DTO的目的,此时用户的角色绑定过程如下:
DTO的角色与数据库的用户通过Identity实现绑定。
public class Register_Dto
{
[Required]
public string FirstName { get; set; }
[Required]
public string LastName { get; set; }
[Required]
[EmailAddress]
public string Email { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Username { get; set; }
[Required]
[RegularExpression("^(?=.*?[A-Z])(?=.*?[a-z])(?=.*?[0-9])(?=.*[#$^+=!*()@%&]).{6,}$", ErrorMessage = "最小长度为6,必须包含1个大写、1个小写、1个特殊字符和1个数字")]
public string Password { get; set; }
[Required]
[Compare("Password")]
public string PasswordConfirm { get; set; }
public string? Role { get; set; }
}6、数据库的简单CRUD
使用EF Core进行简单的CRUD,代码如下:
public class BaseRepository : IBaseRepository where T : class
{
private readonly DatabaseContext context;
public BaseRepository(DatabaseContext context)
{
this.context = context;
}
public bool Create(T entity)
{
context.Set().Add(entity);
if( context.SaveChanges()>0)
return true;
return false;
}
public bool Delete(T entity)
{
context.Set().Remove(entity);
if (context.SaveChanges() > 0)
return true;
return false;
}
public T? FindById(int id)
{
return context.Set().Find(id);
}
public IQueryable GetAll()
{
return context.Set().AsNoTracking();
}
public IQueryable GetAll(Expression> exception)
{
return context.Set().Where(exception).AsNoTracking();
}
public bool Update(T entity)
{
context.Update(entity);
if (context.SaveChanges() > 0)
return true;
return false;
}
} 7、补充
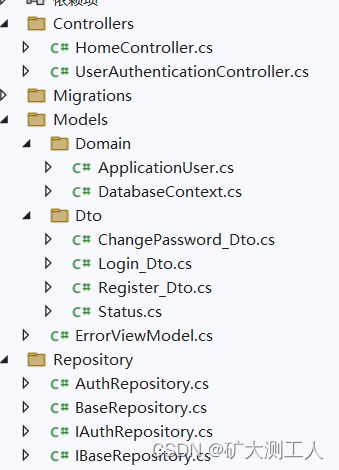
项目完整结构目录如下:
public interface IBaseRepository
{
IQueryable GetAll();
IQueryable GetAll(Expression>exception);
T? FindById(int id);
bool Create(T entity);
bool Update(T entity);
bool Delete(T entity);
}
部分代码:
public interface IAuthRepository
{
Task LoginAsync(Login_Dto model);
Task LogoutAsync();
Task RegisterAsync(Register_Dto model);
Task ChangePasswordAsync(ChangePassword_Dto model, string username);
} public interface IBaseRepository
{
IQueryable GetAll();
IQueryable GetAll(Expression>exception);
T? FindById(int id);
bool Create(T entity);
bool Update(T entity);
bool Delete(T entity);
} public class AuthRepository : IAuthRepository
{
private readonly UserManager userManager;
private readonly RoleManager roleManager;
private readonly SignInManager signInManager;
public AuthRepository(UserManager userManager,
SignInManager signInManager, RoleManager roleManager)
{
this.userManager = userManager;
this.roleManager = roleManager;
this.signInManager = signInManager;
}
public async Task RegisterAsync(Register_Dto model)
{
var status = new Status();
var userExists = await userManager.FindByNameAsync(model.Username);
if (userExists != null)
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "用户已存在";
return status;
}
ApplicationUser user = new ApplicationUser()
{
Email = model.Email,
SecurityStamp = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(),
UserName = model.Username,
FirstName = model.FirstName,
LastName = model.LastName,
EmailConfirmed = true,
PhoneNumberConfirmed = true,
};
var result = await userManager.CreateAsync(user, model.Password);
if (!result.Succeeded)
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "注册失败";
return status;
}
if (!await roleManager.RoleExistsAsync(model.Role))
await roleManager.CreateAsync(new IdentityRole(model.Role));
if (await roleManager.RoleExistsAsync(model.Role))
{
await userManager.AddToRoleAsync(user, model.Role);
}
status.StatusCode = 1;
status.StatusMessage = "注册成功";
return status;
}
public async Task LoginAsync(Login_Dto model)
{
var status = new Status();
var user = await userManager.FindByNameAsync(model.Username);
if (user == null)
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "查无此人";
return status;
}
if (!await userManager.CheckPasswordAsync(user, model.Password))
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "修改密码失败";
return status;
}
var signInResult = await signInManager.PasswordSignInAsync(user, model.Password, false, true);
if (signInResult.Succeeded)
{
var userRoles = await userManager.GetRolesAsync(user);
var authClaims = new List
{
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, user.UserName),
};
foreach (var userRole in userRoles)
{
authClaims.Add(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, userRole));
}
status.StatusCode = 1;
status.StatusMessage = "Logged in successfully";
}
else if (signInResult.IsLockedOut)
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "用户退出";
}
else
{
status.StatusCode = 0;
status.StatusMessage = "Error on logging in";
}
return status;
}
public async Task LogoutAsync()
{
await signInManager.SignOutAsync();
}
public async Task ChangePasswordAsync(ChangePassword_Dto model, string username)
{
var status = new Status();
var user = await userManager.FindByNameAsync(username);
if (user == null)
{
status.StatusMessage = "用户不存在";
status.StatusCode = 0;
return status;
}
var result = await userManager.ChangePasswordAsync(user, model.CurrentPassword, model.NewPassword);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
status.StatusMessage = "密码更新成功";
status.StatusCode = 1;
}
else
{
status.StatusMessage = "密码更新失败";
status.StatusCode = 0;
}
return status;
}
} using LoginRegistrationtrainingMVC.Models.Domain;
using LoginRegistrationtrainingMVC.Repository;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllersWithViews();
builder.Services.AddDbContext(options => options.UseSqlite(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("conn")));
//安全组件添加
builder.Services.AddIdentity()
.AddEntityFrameworkStores()
.AddDefaultTokenProviders();
//添加cookie
builder.Services.ConfigureApplicationCookie(options => options.LoginPath = "/UserAuthentication/Login");
//添加组件
builder.Services.AddScoped();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
// The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=UserAuthentication}/{action=Login}/{id?}");
app.Run();
public class UserAuthenticationController : Controller
{
private readonly IAuthRepository repository;
public UserAuthenticationController(IAuthRepository repository)
{
this.repository = repository;
}
public IActionResult Login()
{
return View();
}
public IActionResult Registration()
{
return View();
}
[Authorize]
public async Task Logout()
{
await repository.LogoutAsync();
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Login));
}
[Authorize]
public IActionResult ChangePassword()
{
return View();
}
[Authorize]
[HttpPost]
public async Task ChangePassword(ChangePassword_Dto model)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
return View(model);
var result = await repository.ChangePasswordAsync(model, User.Identity.Name);
TempData["msg"] = result.StatusMessage;
return RedirectToAction(nameof(ChangePassword));
}
[HttpPost]
public async TaskLogin(Login_Dto model)
{
if(!ModelState.IsValid)
return View(model);
var result = await repository.LoginAsync(model);
if (result.StatusCode==1)
return RedirectToAction("Index","Home");
else
{
TempData["msg"] = result.StatusMessage;
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Login));
}
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task Registration(Register_Dto model)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
return View(model);
model.Role = "User";
var result = await repository.RegisterAsync(model);
TempData["msg"]=result.StatusMessage;
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Registration));
}
}