MyBatis 二级缓存
介绍
二级缓存与具体的命名空间绑定,一个 Mapper 中有一个 Cache ,相同 Mapper 中的 MappedStatement 共⽤⼀个 Cache。
收到查询请求时Mybatis会先查询二级缓存,若二级缓存未命中,则查询一级缓存,若一级缓存未命中则查询数据库。
启用二级缓存
1、开启全局二级缓存配置
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
settings>
2、在需要使用二级缓存的mapper文件中配置标签:
<cache>cache>
3、在CRUD标签上配置:
<select id="findAllList" resultType="User" useCache="true">
select * from user
select>
源码的具体实现:
解析< cache/> 标签
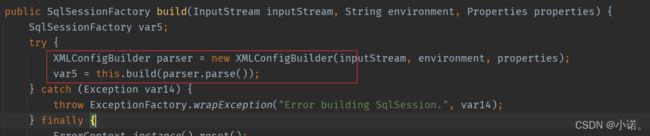
从build中开始,由XMLConfigBuilder.parse()⽅法来实现具体解析

![]()
解析mapper.xml

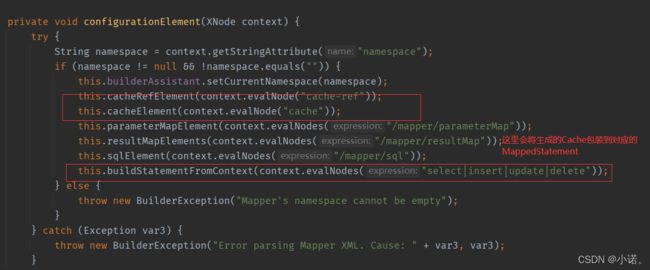
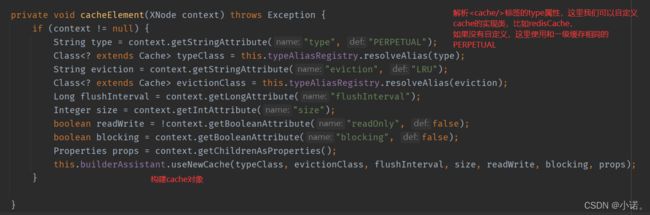
开始构建cache对象:Mapper.xml只会解析一次标签,也就是只会创建一次Cache对象,放进configuration,并将cache赋值给MapperBuilderAssistant.currentCache:
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass, Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass, Long flushInterval, Integer size, boolean readWrite, boolean blocking, Properties props) {
//⽣成Cache对象
Cache cache = (new CacheBuilder(this.currentNamespace))
//这⾥如果我们定义了buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes(“select|insert|update|delete”));将Cache
包装到MappedStatement
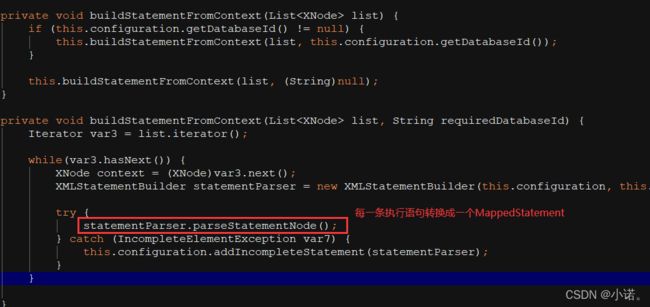
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(String id, SqlSource sqlSource, StatementType statementType, SqlCommandType sqlCommandType, Integer fetchSize, Integer timeout, String parameterMap, Class<?> parameterType, String resultMap, Class<?> resultType, ResultSetType resultSetType, boolean flushCache, boolean useCache, boolean resultOrdered, KeyGenerator keyGenerator, String keyProperty, String keyColumn, String databaseId, LanguageDriver lang, String resultSets) {
if (this.unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
} else {
id = this.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = (new org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement
.Builder(this.configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType))
.resource(this.resource).fetchSize(fetchSize)
.timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty)
.keyColumn(keyColumn)
.databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered)
.resultSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(this.getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id)).
resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired((Boolean)this.valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache((Boolean)this.valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
//在这⾥将之前⽣成的Cache封装到MappedStatement
.cache(this.currentCache);
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = this.getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
this.configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}
将Mapper中创建的Cache对象,加⼊到了每个MappedStatement对象中,也就是同⼀个
Mapper中。
CachingExecutor,源码跟踪:

public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
// 从 MappedStatement 中获取 Cache,注意这⾥的 Cache 是从MappedStatement中获取的,
//也就是我们上⾯解析Mapper中,则 cache 为空
if (cache != null) {
//如果需要刷新缓存的话就刷新:flushCache="true" ,
//如果设置了flushCache="true",则每次查询都会刷新缓存
this.flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
this.ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
List<E> list = (List)this.tcm.getObject(cache, key);
// 访问⼆级缓存
if (list == null) {
// 如果没有值,则执⾏查询,这个查询实际也是先⾛⼀级缓存查询,⼀级缓存也没有的话,则进⾏DB查询
list = this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
// 将查询结果进行缓存
this.tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);
}
return list;
}
}
return this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
由于 MappedStatement 存在于全局配置中,可以多个 CachingExecutor 获取到,这样就会出现线程安全问题。除此之外,若不加以控制,多个事务共⽤⼀个缓存实例,会导致脏读问题。⾄于脏读问题,需要借助其他类来处理,也就是上⾯代码中 tcm 变量对应的类型。
TransactionalCacheManager(事物管理器)源码跟踪:
public class TransactionalCacheManager {
// Cache 与 TransactionalCache 的映射关系表
private final Map<Cache, TransactionalCache> transactionalCaches = new HashMap();
public TransactionalCacheManager() {
}
// 获取 TransactionalCache 对象,并调⽤该对象的 clear ⽅法
public void clear(Cache cache) {
this.getTransactionalCache(cache).clear();
}
// 直接从TransactionalCache中获取缓存
public Object getObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key) {
return this.getTransactionalCache(cache).getObject(key);
}
// 直接存⼊TransactionalCache的缓存中
public void putObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key, Object value) {
this.getTransactionalCache(cache).putObject(key, value);
}
public void commit() {
Iterator var1 = this.transactionalCaches.values().iterator();
while(var1.hasNext()) {
TransactionalCache txCache = (TransactionalCache)var1.next();
txCache.commit();
}
}
public void rollback() {
Iterator var1 = this.transactionalCaches.values().iterator();
while(var1.hasNext()) {
TransactionalCache txCache = (TransactionalCache)var1.next();
txCache.rollback();
}
}
private TransactionalCache getTransactionalCache(Cache cache) {
// 从映射表中获取 TransactionalCache
TransactionalCache txCache = (TransactionalCache)this.transactionalCaches.get(cache);
if (txCache == null) {
// TransactionalCache 也是⼀种装饰类,为 Cache 增加事务功能
// 创建⼀个新的TransactionalCache,并将真正的Cache对象存进去
txCache = new TransactionalCache(cache);
this.transactionalCaches.put(cache, txCache);
}
return txCache;
}
}
TransactionalCacheManager 内部维护了 Cache 实例与 TransactionalCache 实例间的映射关系,该类也仅负责维护两者的映射关系,真正做事的还是 TransactionalCache。TransactionalCache 是⼀种缓 存装饰器,可以为 Cache 实例增加事务功能。我在之前提到的脏读问题正是由该类进⾏处理的。
TransactionalCache 源码跟踪:
public class TransactionalCache implements Cache {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(TransactionalCache.class);
//真正的缓存对象,和上⾯的Map中的Cache是同⼀个
private final Cache delegate;
private boolean clearOnCommit;
// 在事务被提交前,所有从数据库中查询的结果将缓存在此集合中
private final Map<Object, Object> entriesToAddOnCommit;
private final Set<Object> entriesMissedInCache;
public TransactionalCache(Cache delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
this.clearOnCommit = false;
this.entriesToAddOnCommit = new HashMap();
this.entriesMissedInCache = new HashSet();
}
public String getId() {
return this.delegate.getId();
}
public int getSize() {
return this.delegate.getSize();
}
public Object getObject(Object key) {
// 查询的时候是直接从delegate中去查询的,也就是从真正的缓存对象中查询
Object object = this.delegate.getObject(key);
if (object == null) {
// 缓存未命中,则将 key 存⼊到 entriesMissedInCache 中
this.entriesMissedInCache.add(key);
}
return this.clearOnCommit ? null : object;
}
public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() {
return null;
}
public void putObject(Object key, Object object) {
// 将键值对存⼊到 entriesToAddOnCommit 这个Map中中,⽽⾮真实的缓存对象delegate 中
this.entriesToAddOnCommit.put(key, object);
}
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return null;
}
public void clear() {
this.clearOnCommit = true;
// 清空 entriesToAddOnCommit,但不清空 delegate 缓存
this.entriesToAddOnCommit.clear();
}
public void commit() {
if (this.clearOnCommit) {
// 根据 clearOnCommit 的值决定是否清空 delegate
this.delegate.clear();
}
// 刷新未缓存的结果到 delegate 缓存中
this.flushPendingEntries();
// 重 置 entriesToAddOnCommit 和 entriesMissedInCache
this.reset();
}
public void rollback() {
this.unlockMissedEntries();
this.reset();
}
private void reset() {
this.clearOnCommit = false;
// 清空集合
this.entriesToAddOnCommit.clear();
this.entriesMissedInCache.clear();
}
private void flushPendingEntries() {
Iterator var1 = this.entriesToAddOnCommit.entrySet().iterator();
while(var1.hasNext()) {
Entry<Object, Object> entry = (Entry)var1.next();
// 将 entriesToAddOnCommit 中的内容转存到 delegate 中
this.delegate.putObject(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
var1 = this.entriesMissedInCache.iterator();
while(var1.hasNext()) {
Object entry = var1.next();
if (!this.entriesToAddOnCommit.containsKey(entry)) {
// 存⼊空值
this.delegate.putObject(entry, (Object)null);
}
}
}
private void unlockMissedEntries() {
Iterator var1 = this.entriesMissedInCache.iterator();
while(var1.hasNext()) {
Object entry = var1.next();
try {
// 调⽤ removeObject 进⾏解锁
this.delegate.removeObject(entry);
} catch (Exception var4) {
log.warn("Unexpected exception while notifiying a rollback to the cache adapter.Consider upgrading your cache adapter to the latest version. Cause: " + var4);
}
}
}
}
存储⼆级缓存对象的时候是放到了TransactionalCache.entriesToAddOnCommit这个map中,但是每 次查询的时候是直接从TransactionalCache.delegate中去查询的,所以这个⼆级缓存查询数据库后,设 置缓存值是没有⽴刻⽣效的,主要是因为直接存到 delegate 会导致脏数据问题。
只有SqlSession提交或关闭之后二级缓存才生效。
SqlSession.commit() 方法源码跟踪:
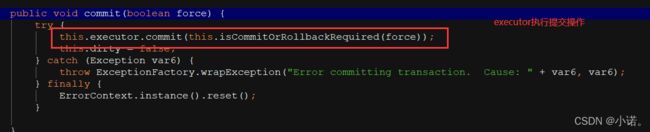
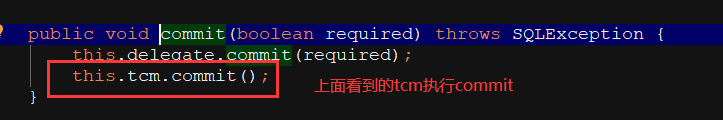

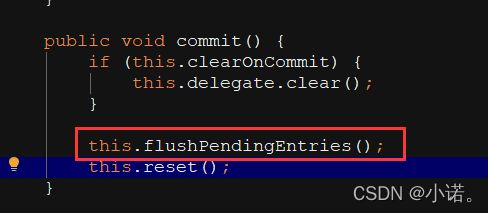

二级缓存的刷新:
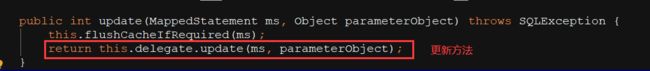
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
//获取MappedStatement对应的Cache,进⾏清空
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
//SQL需设置flushCache="true" 才会执⾏清空
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
this.tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
⼀但数据变 更,MyBatis会清空缓存,因此⼆级缓存不适⽤于经常进⾏更新的数据,只适⽤于不常进⾏增、删、改的数据。