刷题计划-图论
刷题计划1 ——洛谷题单-省选图论
P3758 [TJOI2017]可乐
题目描述:给一个无向无环图, n n n 个点 ( 1 − n ) (1 - n) (1−n) m m m 条边, 总时间为 t t t,一个机器人从点 1 1 1 出发, 三种行为: 停在原地,去下一个相邻的城市,自爆。 问经过了 t t t 秒,机器人的行为方案数是多少 ? ? ?
数据范围
1 < t ≤ 1 0 6 1
0 < M < 100 0
1 ≤ u 1 \leq u 1≤u, v ≤ N v \leq N v≤N
一开始看到这题感觉数据很水,想当然的写了个爆搜看下能过几个点,结果当然是Wa了 一个点没过。
真实思路:
我们先考虑 D p Dp Dp: 令 f [ i , j ] f[i, j] f[i,j] 表示 从点 i i i 走到 点 j j j 的方案数 ,那么 更新方式:
f [ i , j ] + = f [ i , k ] ∗ f [ k ] [ j ] f[i, j] += f[i, k] * f[k][j] f[i,j]+=f[i,k]∗f[k][j]
我们在设置一个点0 连接所有边来表示自爆, 增加自环表示停顿即可。
状态转移代码:
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i ++)
for(int j = 0; j <= n; j ++)
for(int k = 0; k <= n; k ++)
f[i][j] = (f[i][j] + f[i][k] * f[k][j]) % 2017;
但是这样没办法处理走 t t t 步
然后我们发现,这个代码好像就是矩阵的乘法, 一个邻接矩阵 A A A, A k A^k Ak 就可以表示从 i i i 到 j j j 经过 k k k 步的路径方案总数。
然后写一个矩阵的 k k k次方的快速幂即可。
最后统计一下点 1 1 1 到所有点的方案数总和即可
代码;
#include P1772 [ZJOI2006]物流运输
题目描述:
物流公司要把一批货物从码头 A A A 运到码头 B B B。由于货物量比较大,需要 n n n 天才能运完。货物运输过程中一般要转停好几个码头。
物流公司通常会设计一条固定的运输路线。有的时候某个码头会无法装卸货物。这时候就必须修改运输路线,让货物能够按时到达目的地。而修改线路会导致额外 k k k 的花费。 求 n n n天运输的最小花费。
数据范围: 1 ≤ n ≤ 100 , 1 ≤ m ≤ 20 。 1 \le n \le 100,1\le m \le 20。 1≤n≤100,1≤m≤20。
思路:
- 由于这题的数据量很小, 我们可以选择预处理处出 f ( i , j ) f(i, j) f(i,j), 表示第 i i i 天到第 j j j 天的最小花费(1 ~ m的最短路)。
- 采用动态规划的方法: d p ( i ) dp(i) dp(i) 表示第 i i i 天的最小花费, 第 j j j ( j < i ) (j < i) (j<i) 天的时候更换了线路,那么状态转移方程:
d p ( i ) = d p ( j ) + ( i − j ) ∗ f ( j + 1 ) ( i ) + k dp(i) = dp(j) + (i - j) * f(j + 1)(i) + k dp(i)=dp(j)+(i−j)∗f(j+1)(i)+k 取 m i n min min 那么答案就是 d p [ n ] dp[n] dp[n]
代码:
#include P4438 [HNOI/AHOI2018]道路
题目描述: 太麻烦了点击进去自己看。
思路:
记忆化搜索 + + + 树形 D p Dp Dp
f ( i , j , k ) f(i, j, k) f(i,j,k) 表示第 i i i 个点到根经过 j j j 个未被修复的公路, k k k 个未被修复的铁路,所得到的最小值。
状态转移:当更新到乡村的时候:
f [ x ] [ p ] [ q ] = m i n ( d f s ( s o n [ x ] [ 0 ] , p , q ) + d f s ( s o n [ x ] [ 1 ] , p , q + 1 ) , d f s ( s o n [ x ] [ 1 ] , p , q ) + d f s ( s o n [ x ] [ 0 ] , p + 1 , q ) ) f[x][p][q]=min(dfs(son[x][0],p,q)+dfs(son[x][1],p,q+1),dfs(son[x][1],p,q)+dfs(son[x][0],p+1,q)) f[x][p][q]=min(dfs(son[x][0],p,q)+dfs(son[x][1],p,q+1),dfs(son[x][1],p,q)+dfs(son[x][0],p+1,q))
答案就是 f ( 1 , p , q ) f(1, p, q) f(1,p,q) 根节点经过 p p p 条公路和 q q q 条铁路所得到的最小值
这里用 s o n ( x , 1 / 0 ) son(x, 1/0) son(x,1/0) 表示 x x x 的左儿子为公路所连接点, 右儿子为马路所连点。
用 ( 1 (1 (1 ~ n − 1 ) n - 1) n−1) 表示城市 ( n (n (n ~ 2 n − 1 ) 2n - 1) 2n−1) 表示乡村。
代码:
#include P1131 [ZJOI2007] 时态同步
题目描述:给定一颗树和一个树的根节点,求使得从根节点开始,到每个叶子节点的时间相同需要对每条边增加的边权值的最小值。
数据范围:
N ≤ 500000 N≤500000 N≤500000
思路:
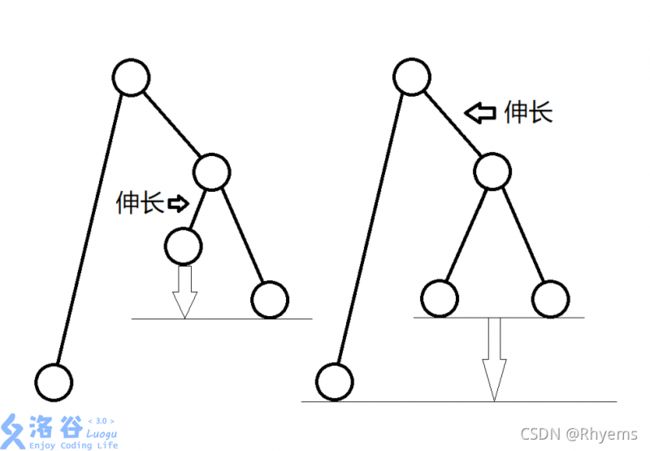
- 对于每条边,我们应当先伸长靠近叶子节点的边,然后再伸长靠近根节点的边,这样得到的结果应当才是最小值。后伸长靠近根节点的边会使得根节点下的所有点到根节点的长度增加,这样最优。
- 所以我们先 d f s dfs dfs 到叶子节点,然后从下往上跟新 d i s t [ u ] dist[u] dist[u] (表示某一子树的根节点 u u u 到其所有叶子节点的距离中的最大值),更新方式: d i s t [ u ] = m a x ( d i s t [ j ] + w [ i ] ) dist[u] = max(dist[j] + w[i]) dist[u]=max(dist[j]+w[i]) 其中 j j j 是 u 的子节点。
- 然后再从叶子节点向根节点跟新答案 a n s ans ans, 更新方式: a n s + = d i s t [ u ] − ( d i s t [ j ] + w [ i ] ) ans += dist[u] - (dist[j] + w[i]) ans+=dist[u]−(dist[j]+w[i]),其中 w [ i ] w[i] w[i] 为 子节点 j j j 到子树根节点 u u u 的边的权值。这一步在统计该子树中需要增加的边的长度,只需与该子树最长叶子节点保持一致即可。
代码:
#include C. Game On Leaves
【思维题】
题目概述:
两个人玩游戏,每次可以拿走图中一个叶子节点,当有人拿到唯一的特殊节点时就获胜吗,问谁会赢。
思路:
- 把图中的边分成两个部分,第一部分为直接与特殊节点相连的边,第二部分为其他边。
- 对于第一部分,如果为奇数,则先手必赢,反之必输(画个图看看)。
- 对于第二部分,如果边的数量为奇数,则会改变第一部分的先手与后手,为偶数则不会。
- 如果只有一条边或者没有边与特殊节点相连,那么直接先手赢。
- 否则将以上两个情况同时考虑即可。
代码:
#include C. Cycle
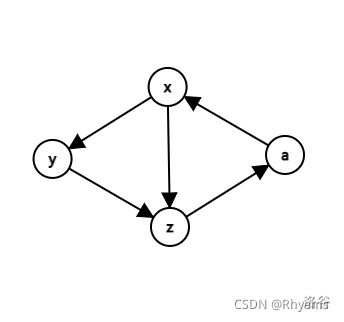
题目概述:
一个竞赛图中找大小为 3 3 3 的环,输出任意一个,如果没有就输出 − 1 -1 −1。
竞赛图:若有向简单图 G G G 满足任意不同两点间都有恰好一条边(单向),则称 G G G 为 竞赛图 ( T o u r n a m e n t g r a p h ) (Tournament graph) (Tournamentgraph)。
- 如果直接使用 T a r j a n Tarjan Tarjan 计算环的大小,那么这个环的大小会被记为 5 5 5 但是图中是有一个大小为 3 3 3 的环 z , a , x z, a, x z,a,x, 因此我们考虑另外一种做法。
- 因为竞赛图保证任意两点之间有一条有向边,如果上述情况出现时, 在删掉 x x x—> z z z 后, 不论 y , z y, z y,z 之间的边方向如何,都会有一个新的大小为 3 3 3 的环。
- 当我们删掉这样的边后,我们使得每个点的出度都为 1 1 1, 这样,我们只需呀枚举 点 i i i, 点 i i i 直接到达的点 t o [ i ] to[i] to[i] 和点 j j j 三者之间能否构成环即可。
代码:
#include CF437C The Child and Toy
题目概述:
n n n 个点 m m m 条边,每删一个点需要花费与该点直接相连的点 i i i 的 v [ i ] v[i] v[i],问删完整个图的最小花费。
本题考虑删点过于麻烦,因为要把图删完,所以删边也是一样的效果。
对于删掉的每条边,最小花费是边的两个节点的最小 v [ i ] v[i] v[i],将每条边的最小花费加起来就是最后的答案。
#include