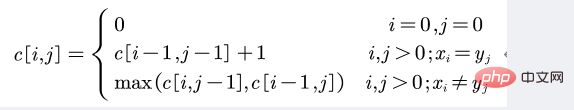最长公共子序列算法 java,算法学习——java实现最长公共子序列,
算法学习——java实现最长公共子序列学习——java实现最长公共子序列的算法,
实验目的:
输入两个同类型的序列,用动态规划的方法计算它们最长的公共子序列的长度和序列。
(推荐教程: Java视频教程
思考:
1.首先,使用二维数组存储最长公共子序列的长度,并记录每个值的状态
2.根据记录值的状态,递归计算最长的公共子序列
3.递归方程:
代码实现:
Package c最长公共子序列;
导入Java . util . scanner;
/**
* @作者德拉科
* @参见最长公共子序列(最长公共缺失)
* @版本
* @ date-time 2020-04-27-4:2:36。
*/
LCS公开课
公共静态void main(String[] args) {
//测试字符串:ABCBDAB BDCABA
扫描仪扫描仪=新扫描仪(system . in);
System.out.println(‘注意:第一个字符串比第二个字符串长’);
System.out.print(‘请输入第一个字符串:’);
string 1=scanner . next();
System.out.print(‘请输入第二个字符串:’);
string string 2=scanner . next();
String str1=string1
String str2=string2
//String str 1=’ ABCBDAB ‘;
//String str 2=’ BDCABA ‘;
int[][]c=GetSubstingMatriX(str 1,str 2);
String[][] b=getTrace(str1,str 2);
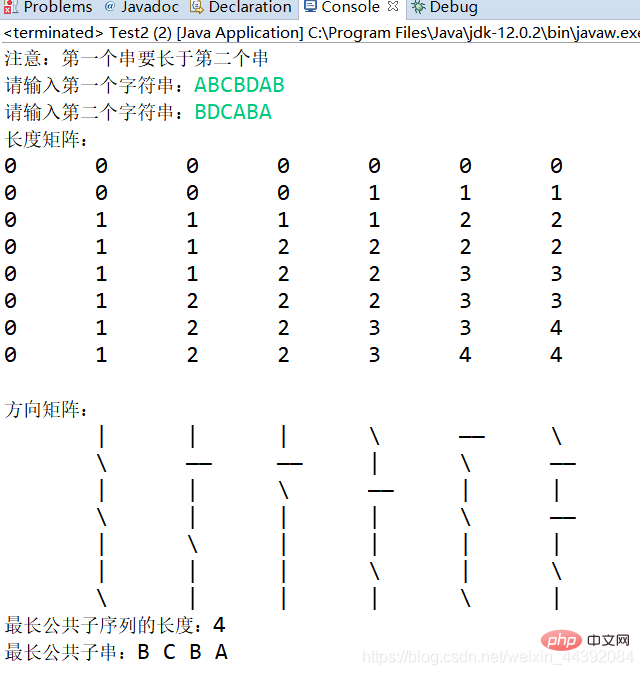
System.out.println(‘长度矩阵:’);
show(c);
system . out . println();
System.out.println(‘方向矩阵:’);
showforsting(b);
System.out.println(‘最长公共子序列的长度:’ c[str 1 . length()][str 2 . length()]);
string SMax=str 1 . length()str 2 . length()?str1 : str2//选择最长的字符串,因为你要取出最大的子字符串
string SMin=str 1 . length()str 2 . length()?str1 : str2//选择最小的字符串
System.out.print(‘最长的公共子字符串:’);
print(b,sMax,sMax.length(),SMin . length());
{}
/**
* @参见找出子序列的矩阵,其中最后一行和最后一列是最长子序列的长度
* @param x第一个字符串
* @param y第二个字符串
* @返回长度矩阵
*/
public static int[][]GetSubscriptingStrix(String x,String y) {
int Xlen=x . length()1;//添加1是因为第一个被初始化为0
int YLen=y . length()1;
int rLen=xLen yLen?xLen : yLen//大字符串按行排列
int cLen=xLen yLen?xLen : yLen//小字符串按列排列
int[][]c=new int[RLen][CLen];//保存矩阵c的状态
for(int I=1;i rLeni ) {
for(int j=1;j cLenj ) {
if(x . CharaT(I-1)=y . CharaT(j-1)){
//相等,对角线1
c[I][j]=c[I-1][j-1]1;
} else if (c[i – 1][j]=c[i][j – 1]) {
//不相等,请选择较大的
c[I][j]=c[I-1][j];
} else {
c[I][j]=c[I][j-1];
{}
{}
{}
返回c;//长度矩阵
{}
/**
* @see记录每个值的状态,便于回溯递归
* @param x第一个字符串
* @param y第二个字符串
* @返回方向矩阵
*/
公共静态字符串[][] getTrace(字符串x,字符串y) {
int Xlen=x . length()1;
int YLen=y . length()1;
//为矩阵c和b设置行和列。
int rLen=xLen yLen?xLen : yLen//大字符串按行排列
int cLen=xLen yLen?xLen : yLen//小字符串按列排列
int[][]c=new int[RLen][CLen];
String[][]b=new String[RLen][CLen];
for(int I=1;i rLeni ) {
for(int j=1;j cLenj ) {
if(x . charat(I-1)==y . charat(j-1)){//等于
c[I][j]=c[I-1][j-1]1;
b[I][j]=’ \ \ \ \ ‘;//指向左上角
} else if(c[I-1][j]=c[I][j-1]){//不相等
//当上述值较大时
c[I][j]=c[I-1][j];
b[I][j]=’ | ‘;//指向顶部
} else {
//当下列值较大时
c[I][j]=c[I][j-1];
b[I][j]=’ —— ‘;//指向左边
{}
{}
{}
返回b;//方向矩阵
{}
/**
* @参见递归实现回溯,然后打印出最长的公共子序列
* @param b方向矩阵
* @param s长字符串
* @param i较长字符串的长度
* @param j较短字符串的长度
*/
public static void print(String[][]b,String s,int i,int j) {
//递归终止的条件
if (i==0 || j==0) {
返回;
{}
//判断递归的条件
if (b[i][j]。等于(‘ \ \ \ \ ‘){
//遇到斜线,递归到左上角
print(b,s,i – 1,j-1);
系统。出去。print(s . charat(I-1)’ ‘);
} else if (b[i][j]).等于(“|”)
//遇到竖线,递归到上边
print(b,s,i – 1,j);
} else if (b[i][j]).equals(‘ —— ‘){
//遇到横线,递归到左边
print(b,s,I,j-1);
{}
{}
/**
* @参见打印二维数组
* @param b一个二维数组
*/
public static void show(int[][]b){
for(int w=0;w b。长度;w ) {
for(int p=0;p b[w].长度;p ) {
系统。出去。print(b[w][p]’ \ \ t ‘);
if (p==b[w]).长度- 1) {
系统。出去。println();
{}
{}
{}
{}
/**
* @参见打印字符串的二维数组
* @param b一个字符串的二位数组
*/
public static void showforsting(String[][]b){
for(int w=1;w b。长度;w ) {
系统。出去。print(‘ \ \ t ‘);
for(int p=1;p b[w].长度;p ) {
系统。出去。print(b[w][p]’ \ \ t ‘);
if (p==b[w]).长度- 1) {
系统。出去。println();
{}
{}
{}
{}
{}运行结果: