Dynamic A*(D*) 路径规划算法C++高效实现(开源,OOP)
为何用C++?
- 网上基本都是py或者matlab,C++较少。
- 路径规划算法一般需要落地,C++是沟通硬件的语言,py或matlab不太直接。
- C++实现算法更考验编程。
- 高效,C++速度更快。
何谓D*搜索算法
D*也称为动态A*算法,顾名思义,在应对动态环境下D*更高效。为什么?因为它不会replan,也就是不会重规划,而是局部重规划,降低了运算量。
关于D*算法的讲解下面几篇blog讲得不错:
https://blog.csdn.net/lqzdreamer/article/details/85055569
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/142721264
https://blog.csdn.net/banzhuan133/article/details/100532206?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-baidujs_title-0&spm=1001.2101.3001.4242
原论文传送门:http://web.mit.edu/16.412j/www/html/papers/original_dstar_icra94.pdf
算法的两个大步骤:
- 从目标点出发使用类似dijkstr的方法计算每个节点的h,直到起始点被OPEN表弹出。此时得到了静态环境下所有节点的信息(h and k)。
- 从起始点开始利用第一步获得的指针b(从一个节点指向下一个节点)一步步走向终点,但是此时障碍是动态的,若在某一步发现会碰撞,那么将该节点的h置为无穷大后放入OPEN表,开始更新指针b(h也会更新),从而更新规划路径,这样只会改变周围节点的信息而无需replan,大大减少了规划时间。
- 原文伪代码(process_state核心函数)
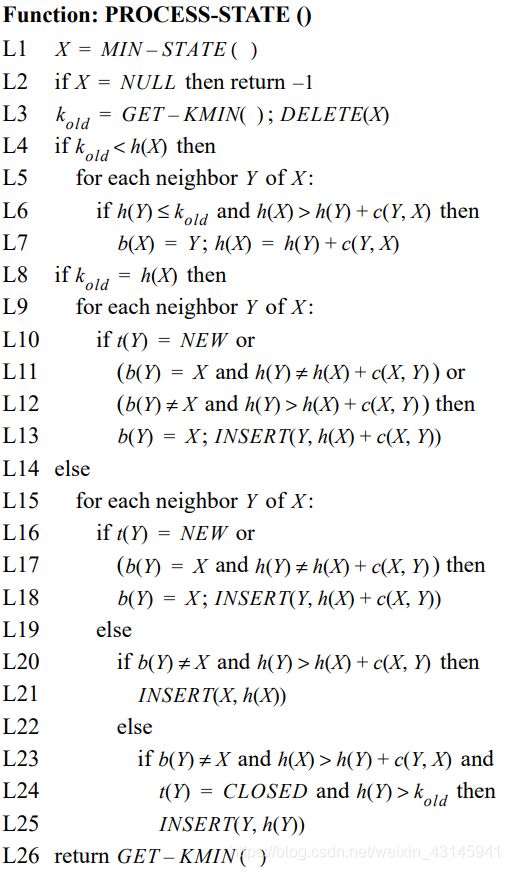
这份伪代码我其实想吐槽的,最后一个if-else明显else多余,但是不影响算法…
代码
github
代码分三个文件(也可以一个文件,但是分文件更规范):mydstar.cpp Dstar.cpp myDstar.h
这份代码默认以整数值坐标作为节点表示,事实上如果想表示小数可以扩大整数空间用整数表示小数。
起点和终点在构造函数中改,障碍球起始静态坐标也在构造函数中,动态障碍位置再run成员函数中修改。
代码采用OOP编程,函数都是传引用,不用数组全用STL实现,另外还有tuple。
代码运行后会将路径保存在.csv文件下,用matlab或者其他工具可以绘图。
环境vs2017,稳定运行。
Dstar.cpp
这是主函数:
# includemyDstar.h
这是一个类:
#pragma once
#includemydstar.cpp
这是类的实现:
#include "myDstar.h"
using namespace std;
D_star::D_star()
{
// 初始化
for (int i = -1; i < 2; i++)
{
for (int j = -1; j < 2; j++)
{
for (int k = -1; k < 2; k++)
{
tuple<int, int, int> t(i, j, k);
double d = sqrt(i * i + j * j + k * k);
this->Alldirec.insert(make_pair(t, d));
}
}
}
this->b.clear();
this->OPEN.clear();
this->h.clear();
this->tag.clear();
this->path.clear();
start = make_tuple(4, 4, 3); // 这里是起始点(填整数,整数也能外推到小数的情况)
goal = make_tuple(16, 16, 3); // 这里是终止点
obs_r = 2; // 初始障碍球半径
obs_pos = make_tuple(10, 10, 3); // 初始障碍球位置
count = 0;
}
void D_star::check_state(tuple<int, int, int>&t)
{
if (this->h.find(t) == this->h.end())
{
this->h.insert(make_pair(t, 0));
}
if (this->tag.find(t) == this->tag.end())
{
this->tag.insert(make_pair(t, "New"));
}
}
double D_star::get_kmin()
{
/*拿到OPEN中最小值*/
if (!this->OPEN.empty())
{
double min_value = 1000;
for (auto it = OPEN.begin(); it != OPEN.end(); ++it)
{
if (it->second < min_value)
{
min_value = it->second;
}
}
return min_value;
}
return -1;
}
tuple<tuple<int, int, int>,double> D_star::min_state()
{
/*弹出OPEN最小值*/
if (!this->OPEN.empty())
{
double min_value = this->get_kmin();
for (auto it = OPEN.begin(); it != OPEN.end(); ++it)
{
if (it->second == min_value)
{
tuple<tuple<int, int, int>, double> t = make_tuple(it->first, min_value); // 找了一天bug,就是这句double写成int了
OPEN.erase(it);
return t;
}
}
}
tuple<tuple<int, int, int>, int> t = make_tuple(tuple<int, int, int>(-1,-1,-1), -1);
return t;
}
void D_star::insert(tuple<int, int, int>&x, double& h_new)
{
/*插入OPEN表并更新h*/
double kx;
if (tag[x] == "New")
{
kx = h_new;
}
if (tag[x] == "Open")
{
kx = OPEN[x] < h_new ? OPEN[x] : h_new;
}
if (tag[x] == "Closed")
{
kx = h[x] < h_new ? h[x] : h_new;
}
if (x == tuple<int, int, int>(7, 7, 3))
{
int aaa = 0;
}
OPEN[x] = kx;
h[x] = h_new;
tag[x] = "Open";
}
double D_star::cost(tuple<int, int, int>&a, tuple<int, int, int>&b)
{
/*欧式距离函数,当碰撞时返回一个非常大的值*/
int x1 = get<0>(a);
int y1 = get<1>(a);
int z1 = get<2>(a);
int x2 = get<0>(b);
int y2 = get<1>(b);
int z2 = get<2>(b);
int obs_x = get<0>(obs_pos);
int obs_y = get<1>(obs_pos);
int obs_z = get<2>(obs_pos);
if ((sqrt((x1 - obs_x)*(x1 - obs_x) + (y1 - obs_y)*(y1 - obs_y) + (z1 - obs_z)*(z1 - obs_z)) < obs_r) ||
(sqrt((x2 - obs_x)*(x2 - obs_x) + (y2 - obs_y)*(y2 - obs_y) + (z2 - obs_z)*(z2 - obs_z)) < obs_r))
{
return 1000;
}
else
{
return sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2)*(y1 - y2) + (z1 - z2)*(z1 - z2));
}
}
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> D_star::children(tuple<int, int, int>& x)
{
/*获取子节点坐标*/
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> allchild;
for (auto it = Alldirec.begin(); it != Alldirec.end(); ++it)
{
auto direc = it->first;
int xx = get<0>(x) + get<0>(direc);
int yy = get<1>(x) + get<1>(direc);
int zz = get<2>(x) + get<2>(direc);
tuple<int, int, int> child = make_tuple(xx, yy, zz);
int obs_x = get<0>(obs_pos);
int obs_y = get<1>(obs_pos);
int obs_z = get<2>(obs_pos);
if (sqrt((xx - obs_x)*(xx - obs_x) + (yy - obs_y)*(yy - obs_y) + (zz - obs_z)*(zz - obs_z)) <= obs_r) continue;
if(xx < 0 || xx > 20 ||
yy < 0 || yy > 20 ||
zz < 0 || zz > 10) continue;
allchild.push_back(child);
}
return allchild;
}
double D_star::process_state()
{
/*核心函数*/
tuple<tuple<int, int, int>, double> temp = this->min_state();
tuple<int, int, int> x = get<0>(temp);
double kold = get<1>(temp);
this->tag[x] = "Closed";
if (x == tuple<int, int, int>(-1, -1, -1)) return -1;
this->check_state(x);
if (kold < h[x])
{
auto allchild = children(x);
for (auto it = allchild.begin(); it != allchild.end(); ++it)
{
tuple<int, int, int> y = *it;
check_state(y);
double a = h[y] + cost(y, x);
if (h[y] <= kold && h[x] > a)
{
b[x] = y;
h[x] = a;
}
}
}
if (kold == h[x])
{
auto allchild = children(x);
for (auto it = allchild.begin(); it != allchild.end(); ++it)
{
tuple<int, int, int> y = *it;
check_state(y);
double bb = h[x] + cost(x, y);
if (tag[y] == "New" || (b[y] == x && h[y] != bb) || (b[y] != x && h[y] > bb))
{
b[y] = x;
insert(y, bb);
}
}
}
else
{
auto allchild = children(x);
for (auto it = allchild.begin(); it != allchild.end(); ++it)
{
tuple<int, int, int> y = *it;
check_state(y);
double bb = h[x] + cost(x, y);
if (tag[y] == "New" || (b[y] == x && h[y] != bb))
{
b[y] = x;
insert(y, bb);
}
else
{
if (b[y] != x && h[y] > bb)
{
insert(x, h[x]);
}
else
{
if (b[y] != x && h[y] > bb && tag[y] == "Closed" && h[y] == kold)
{
insert(y, h[y]);
}
}
}
}
}
return get_kmin();
}
void D_star::modify_cost(tuple<int, int, int>& x)
{
auto xparent = b[x];
if (tag[x] == "Closed")
{
double temp = h[xparent] + cost(x, xparent);
insert(x,temp);
}
}
void D_star::modify(tuple<int, int, int>& x)
{
modify_cost(x);
while (true)
{
double kmin = process_state();
if (kmin >= h[x]) break;
}
}
void D_star::get_path()
{
/*获取路径*/
path.clear();
tuple<int, int, int> s = goal;
tuple<int, int, int> x = start;
path.push_back(x);
do
{
x = b[x];
path.push_back(x);
} while (x != s);
}
void D_star::run()
{
// D* 算法首先需要计算静态环境下的h
OPEN[goal] = 0;
tag[start] = "New";
while (true)
{
cout << "程序正向执行了"<<++count <<"个迭代回合。"<< endl;
process_state();
if (tag[start] == "Closed") break;
}
get_path();
save_path("path1.csv");
cout << "记录已经保存" << endl;
// D*面对变化后的环境进行小范围replan
for (int i = 1; i < 3; ++i)
{
obs_pos = make_tuple(9-i, 9-i, 3); // 新的障碍位置(这里可以设置为动态变化的位置,一个道理)
auto s = start;
while (s != goal)
{
auto sparent = b[s];
if (cost(s, sparent) > 500)
{
modify(s);
continue;
}
s = sparent;
}
get_path();
char load_dir[10];
sprintf_s(load_dir, "%s%d%s", "path", i + 1, ".csv");
save_path(load_dir);
cout << "记录已经保存" << endl;
}
}
void D_star::save_path(string load_dir)
{
/*保存数据*/
ofstream ofs;
ofs.open(load_dir, ios::out);
for (auto it = path.begin(); it != path.end(); ++it)
{
tuple<int, int, int>xyz = *it;
int x = get<0>(xyz);
int y = get<1>(xyz);
int z = get<2>(xyz);
if (it != path.end() - 1)
{
ofs << x << "," << y << "," << z << endl;
}
else
{
ofs << x << "," << y << "," << z;
}
}
ofs.close();
}
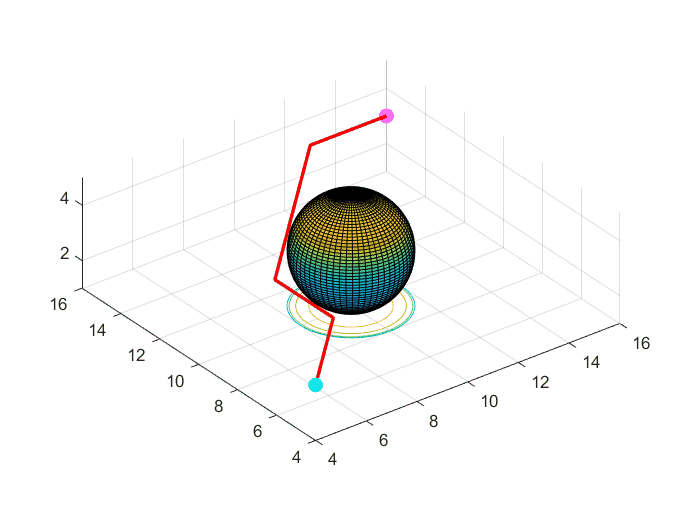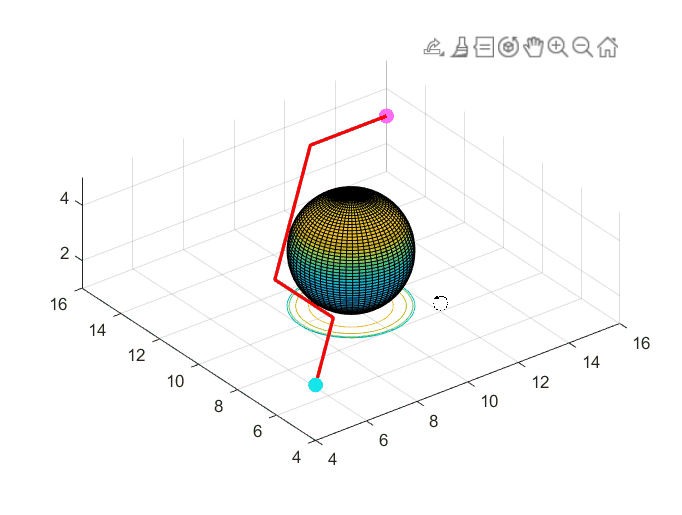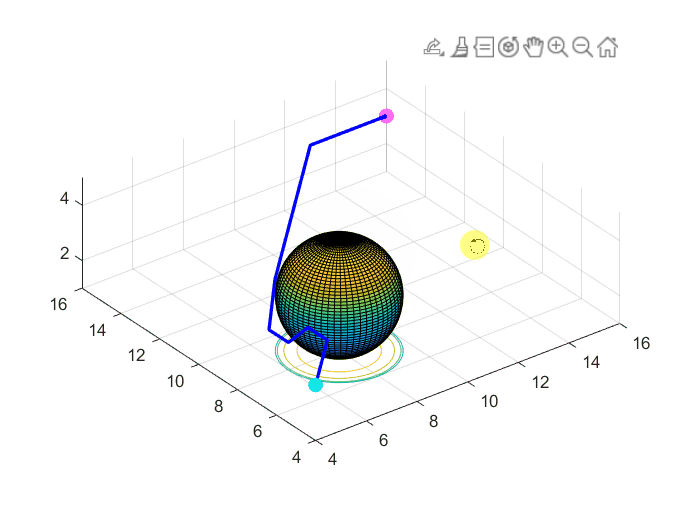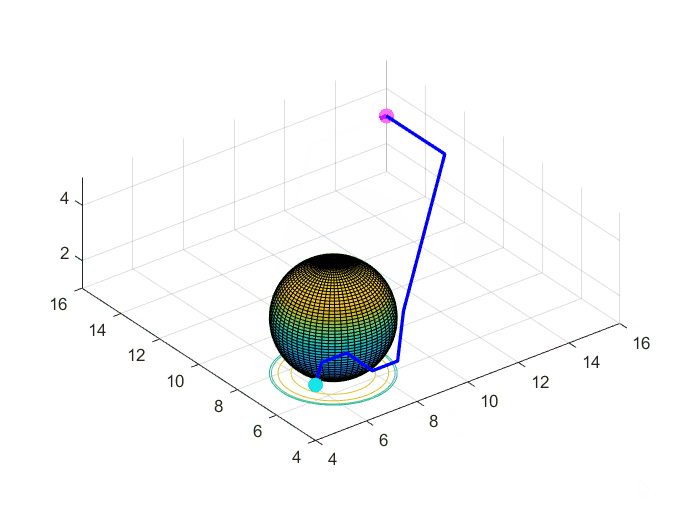
效果展示
方便绘图,给出matlab代码(画图还是请它来):
用实时脚本打开:
里面的参数需要改成和C++代码一致,就是几个点的修改。
clc;clear;close all;
path1 = csvread("path1.csv");
path2 = csvread("path2.csv");
path3 = csvread("path3.csv");
figure(1);
scatter3(path1(1,1),path1(1,2),path1(1,3),80,"cyan",'filled','o');
hold on;
scatter3(path1(end,1),path1(end,2),path1(end,3),80,"magenta",'filled','o');
b = drawSphere([10,10,3],2);
h = plot3(path1(:,1),path1(:,2),path1(:,3),'LineWidth',2,"Color",'r');
axis equal;
waitforbuttonpress;
delete(h);delete(b);
b = drawSphere([8,8,3],2);
h = plot3(path2(:,1),path2(:,2),path2(:,3),'LineWidth',2,"Color",'b');
axis equal;
waitforbuttonpress;
delete(h);delete(b);
drawSphere([7,7,3],2);
plot3(path3(:,1),path3(:,2),path3(:,3),'LineWidth',2,"Color",'b');
axis equal;
function h = drawSphere(pos, r)
[x,y,z] = sphere(60);
h = surfc(r*x+pos(1), r*y+pos(2), r*z+pos(3));
hold on;
end