ElasticSearch 高级查询及索引原理
这里写目录标题
- 高级查询
-
- ==匹配查询[match_all]==
- ==关键词查询[term]==
- 范围查询[range]
- 前缀查询[prefix]
- 通配符查询[wildcard]
- 通过id数组查询[ids]
- 模糊查询[fuzzy]
- 布尔查询[bool]
-
- must查询
- should查询
- must_not查询
- filter查询
- 布尔组合查询
- 多字段查询[multi_match]
- 默认字段分词查询[query_string]
- 高亮查询[highlight]
- 返回指定条数[size]
- 分页查询[form]
- 指定字段排序[sort]
- 返回指定字段[_source]
- 索引原理
高级查询
ES中提供了一种强大的检索数据方式,这种检索方式称之为Query DSL ,Query DSL是利用Rest API传递JSON格式的请求体(Request Body)数据与ES进行交互,这种方式的丰富查询语法让ES检索变得更强大,更简洁。
匹配查询[match_all]
- match_all: 返回索引中的全部文档
- match:会将搜索词先分词处理,再与目标查询字段进行匹配,若分词中的任意一个词与目标字段匹配上,则可查询到
- match_phrase: 不将搜索词分词,要求搜索词与字段内容,有序连贯匹配上,需要全部单词和顺序完全一样,标点符号除外
- match_phrase_prefix :与match_phrase用法类似,区别就在于允许使用前缀匹配
用一个例子说明它们之间的区别
- 首先存入一条数据
i like eating and cooking默认分词器应该将内容分为 “i” “like” “eating” “and” “kuing”
| 查询词/匹配类型 | match | m_phrase | m_p_prefix |
|---|---|---|---|
| i | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| i like | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| i like singing | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| i like ea | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| and | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
总结:
match会将搜索词分词后再去匹配,match_phrase和match_phrase_prefix不会将搜索词分词match和match_phrase属于精准匹配,match_phrase要求搜索词与字段内容有序连贯的匹配match_phrase_prefix不属于精准匹配,它在match_phrase的基础上,允许最后一个词使用前缀匹配
关键词查询[term]
term关键字:使用关键词查询
- keyword类型:使用term查询
keyword类型的字段时,需要全部内容匹配上 - integer类型、double类型、date类型:不分词,得全部匹配
- text类型:默认es标准分词器,中文单字分词,英文单词 分词
所以除了text类型,其余类型均不分词
es中默认使用的是标准分词器,中文单字分词 ,英文 单词分词
#查询语句
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"title": {
"value": "猪猪侠"
}
}
}
}
#结果
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.2039728,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "products",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "rj5iCYABiB8dDekOlCwE",
"_score" : 1.2039728,
"_source" : {
"id" : 2,
"title" : "猪猪侠",
"price" : 0.5,
"created_at" : "2022-04-08",
"description" : "5毛钱一包"
}
}
]
}
范围查询[range]
range关键字:用来查询指定范围内的文档
#范围查询 range
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"字段名": {
"gte": 2, #下界
"lte": 4 #上界
}
}
}
}
前缀查询[prefix]
prefix关键字:按照文档的前缀进行查询
#前缀查询 prefix
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"FIELD": {
"value": ""
}
}
}
}
通配符查询[wildcard]
可使用通配符查询:
?匹配一个字符*匹配多个字符
#通配符查询
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"FIELD": {
"value": "VALUE"
}
}
}
}
通过id数组查询[ids]
通过一个id数组去查询文档
#通过一组id查询
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": [1,2]
}
}
}
模糊查询[fuzzy]
模糊查询含有指定关键字的文档
注意: fuzzy 模糊查询 最大模糊错误 必须在0-2之间
- 搜索关键词长度为 2 不允许存在模糊
- 搜索关键词长度为3-5 允许一次模糊
- 搜索关键词长度大于5 允许最大2模糊
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"FIELD": "xxxx"
}
}
}
布尔查询[bool]
Elasticsearch可以使用bool 关键字用来组合多个条件实现复杂查询,类似于在SQL中使用AND、OR以及NOT的运算
Elasticsearch支持的布尔逻辑类型包括有以下几种:
类型包括有以下几种:
-
must:文档必须符合其中所有的查询条件,包含多个条件时类似于SQL中的AND,运算符中的&& -
should:文档必须符合其中任意一个及以上查询条件(可由minimum_should_match指定需要满足的条件数量),包含多个条件时类似于SQL中的OR,运算符中的|| -
must_not:文档必须不符合其中所有的查询条件,类似于SQL中的NOT,且不参与分值的计算,返回的分支都是0 -
filter::先筛选出符合条件的文档,并且不计算得分。一般情况下,我们应该先使用过滤操作过滤掉一部分数据,然后使用查询去精准匹配数据,提高查询效率
must查询
当使用must查询时,文档必须符合其中包括的所有查询条件。
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
"term": {
"age": 20
}
]
}
}
}
该查询等同于下面对应的SQL语句
SELECT * FROM xxx WHERE age = 20;
使用must时可以同时指定多个查询条件,在DSL中它以数组的形式表示,效果类似于SQL中的AND运算。例如下面的例子:
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "term": { "age": 20 } },
{ "term": { "gender": "male" } }
]
}
}
}
should查询
should查询类似于SQL中的OR语句,当其中包括两个及两个以上的条件时,其查询的结果必须至少满足其中一个。当只有一个查询条件时,即结果必须满足该条件。
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{ "term": { "age": 20 } },
{ "term": { "gender": "male" } },
{ "range": { "height": { "gte": 170 } } },
]
}
}
}
该查询等同于下面对应的SQL语句:
SELECT * FROM xxx WHERE age = 20 OR gender = "male" or height >= 170;
should查询与SQL中的OR运算较为不同的一点是,should查询可以使用minimum_should_match参数指定至少需要满足几个条件。例如下面的例子中,查询的结果需要满足两个或两个以上的查询条件:
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{ "term": { "age": 20 } },
{ "term": { "gender": "male" } },
{ "term": { "height": 170 } },
],
"minimum_should_match": 2
}
}
}
在同一个bool语句中若不存在must或filter时,minimum_should_match默认的值为1,即至少要满足其中一个条件;但若有其它must或filter存在时,minimum_should_match默认值为0。就是说should查询会默认失效
例如下面的查询,所有返回的文档age值必定为20,但其中可能包括有status值不为"active"的文档。若需要二者同时生效,可入上面例子中一样在bool查询中增加一个参数"minimum_should_match": 1。
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"term": {
"age": 20
},
},
"should": {
"term": {
"status": "active"
}
},
"minimum_should_match": 1
}
}
}
must_not查询
must_not查询类似于SQL语句中的NOT运算,它将只返回不满足指定条件的文档。例如:
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{ "term": { "age": 20 } },
{ "term": { "gender": "male" } }
]
}
}
}
该查询等同于下面的SQL查询语句(由于MySQL不支持下面语句使用NOT,于是改写为使用!=实现):
SELECT * FROM xxx WHERE age != 20 AND gender != "male";
另外,must_not与filter相同,采用过滤器执行而不需要计算文档的得分,所以返回的结果对应的分值为0。
filter查询
使用filter查询时其效果等同于must查询,但不同于must查询的是,先筛选出符合条件的文档,并且不计算得分
例如下面的查询中,将返回所有status的值为"active"的文档,其得分均为0.0。
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"status": "active"
}
}
}
}
}
布尔组合查询
我们也可以在各个查询中进行嵌套查询。但需要注意的是,布尔查询必须包含在bool查询语句中,所以在嵌套查询中必须在内部再次使用bool查询语句。
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"bool": {
"should": [
{ "term": { "age": 20 } },
{ "term": { "age": 25 } }
]
}
},
{
"range": {
"level": {
"gte": 3
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
该查询语句等同于以下SQL语句:
SELECT * FROM xxx WHERE (age = 20 OR age = 25) AND level >= 3;
多字段查询[multi_match]
会先将查询条件分词之后,再单独的拿去查询
比如说泡面,会分成“泡”和“面”然后单独拿去查询
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "泡面",
"fields": ["title","description"]
}
}
}
默认字段分词查询[query_string]
- 如果查询字段的类型是不分词的,就不分词查询
- 如果查询字段的类型是分词的,就分词查询
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"default_field": "description",
"query": "xxxx"
}
}
}
高亮查询[highlight]
可以让符合条件的文档中的关键词高亮
- 只有字段类型为text可分词的才能高亮显示
*表示匹配所以字段- 高亮并没有修改原始的文档,只是把高亮的结果放在了一个highlight里
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "泡面"
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"*":{}
}
}
}
自定义高亮html标签: 可以在highlight中使用
pre_tags和post_tags
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "xxx"
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"post_tags": [""],
"pre_tags": [""],
"fields": {
"*":{}
}
}
}
多字段高亮 使用
require_field_match开启多个字段高亮
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "xxx"
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"require_field_match": "false",
"post_tags": [""],
"pre_tags": [""],
"fields": {
"*":{}
}
}
}
返回指定条数[size]
size 关键字: 指定查询结果中返回指定条数。 默认返回值10条
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 5
}
分页查询[form]
from 关键字: 用来指定起始返回位置,和size关键字连用可实现分页效果
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 5,
"from": 0 #(page-1)*
}
指定字段排序[sort]
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
返回指定字段[_source]
_source 关键字: 是一个数组,在数组中用来指定展示那些字段
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"_source": ["title","description"]
}
索引原理
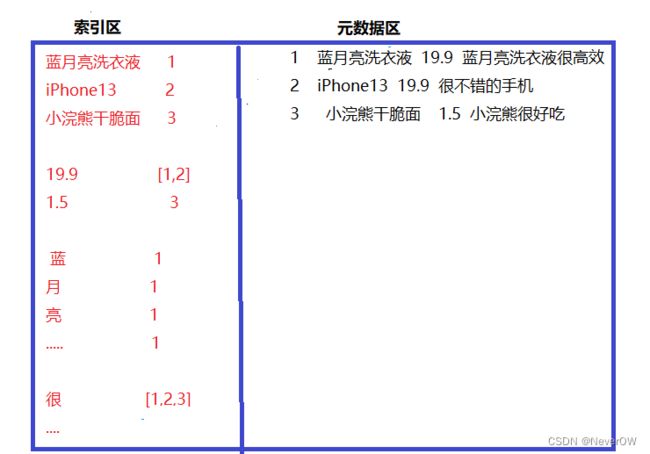
倒排索引也叫反向索引,有正向就有反向。正向索引就是通过key去找value,反向索引则是通过value找key。
ES底层在检索时,底层使用的就是反向索引
测试用例
现有索引和映射如下:
{
"products" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"description" : {
"type" : "text"
},
"price" : {
"type" : "float"
},
"title" : {
"type" : "keyword"
}
}
}
}
录入如下数据
| _id | title | price | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 蓝月亮洗衣液 | 19.9 | 蓝月亮洗衣液很高效 |
| 2 | iphone13 | 19.9 | 很不错的手机 |
| 3 | 小浣熊干脆面 | 1.5 | 小浣熊很好吃 |
可视化表示
- es根据字段是否能分词建立索引,能分词的就分词建立索引,不能分词的就整个字段建立索引:
- 例如keyword类型不能分词:建立索引的时候就以整个字段值作为索引
- text类型能分词,建立索引前会先将字段值进行分词,然后建立索引
- es索引和mysql的innodb引擎建立索引类型,索引结构的key存储索引字段,value存储整条数据的id值,查询时先通过索引找到id值,再去元数据区根据id值找到对应的整条文档记录