Buffer.from和Nodejs支持的字符编码
Node.js 目前支持的字符编码包括以下八种:
ascii - 仅支持 7 位 ASCII 数据。如果设置去掉高位的话,这种编码是非常快的。
utf8 - 多字节编码的 Unicode 字符。许多网页和其他文档格式都使用 UTF-8 。
utf16le - 2 或 4 个字节,小字节序编码的 Unicode 字符。支持代理对(U+10000 至 U+10FFFF)。
ucs2 - utf16le 的别名。
base64 - Base64 编码。
latin1 - 一种把 Buffer 编码成一字节编码的字符串的方式。
binary - latin1 的别名。
hex - 将每个字节编码为两个十六进制字符。
Buffer.from()和Buffer.alloc()
// 从字符串创建一个buffer
const buffer1 = Buffer.from('regis');
console.log(buffer1);
// 输出结果
<Buffer 72 65 67 69 73>
// 从一个数组创建一个buffer
const buffer2 = Buffer.from([1, 2, 3, 4]);
console.log(buffer2);
// 输出结果
<Buffer 01 02 03 04>
// 创建一个长度20的空buffer
const buffer3 = Buffer.alloc(20);
console.log(buffer3);
// 输出结果
<Buffer 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00>
// 向buffer2的buffer中写入数字12,类型为int8,(int8 只占用两位),从图中第1个位置写入,
buffer2.writeInt8(12, 1);
// 写入后的结果,与上面比较,只有第1个位置的值换为0c, 其余的值因为没有写入数据,所以不变
console.log(buffer2);
<Buffer 01 0c 03 04>
// 向buffer2中写入数字512,并且写入位置从第2个位置写入, 因为是Int16,所以需要占用两位,512的十六进制数字为 02 00 2*16^2=512
buffer2.writeInt16BE(512, 2);
console.log(buffer2);
// 输出结果
<Buffer 01 0c 02 00>
// 注意writeInt16BE 与 writeInt16LE的区别
// 高低位的顺序不一样,正好相反, BE的高位在左侧, 而LE的高位在右侧
buffer2.writeInt16LE(512, 2);
console.log(buffer2);
// 输出结果
<Buffer 01 0c 00 02>
// 创建一个包含 Latin-1 字节 [0x74, 0xe9, 0x73, 0x74] 的 Buffer。
const buf6 = Buffer.from('tést', 'latin1');
console.log(buf6);
// 输出结果
<Buffer 74 e9 73 74>
Buffer的API
- Buffer.alloc(size[, fill[, encoding]]): 返回一个指定大小的 Buffer 实例(参数:size是大小,fill是用什么填充(默认为0),encoding是编码格式,可以参考上面Buffer与字符编码这个标题的内容)
- Buffer.allocUnsafe(size): 返回一个指定大小的 Buffer 实例,但是它不会被初始化,所以它可能包含敏感的数据
- Buffer.allocUnsafeSlow(size): 返回一个指定大小的 Buffer 实例, 如果 size 大于 buffer.constants.MAX_LENGTH 或小于 0,则抛出 ERR_INVALID_OPT_VALUE。 如果 size 为 0,则创建一个长度为零的 Buffer。以这种方式创建的 Buffer 实例的底层内存是未初始化的。 Buffer 的内容是未知的,可能包含敏感数据。
- Buffer.from(array): 返回一个被 array 的值初始化的新的 Buffer 实例(传入的 array 的元素只能是数字,不然就会自动被 0 覆盖)
- Buffer.from(arrayBuffer[, byteOffset[, length]]): 返回一个新建的与给定的 ArrayBuffer 共享同一内存的 Buffer。
- Buffer.from(buffer): 复制传入的 Buffer 实例的数据,并返回一个新的 Buffer 实例
- Buffer.from(string[, encoding]): 返回一个被 string 的值初始化的新的 Buffer 实例【encoding - 使用的编码。默认为 ‘utf8’ 】
Buffer.from(string, encoding)支持哪些编码?
意思是:从一个包含指定encoding的字节中创建Buffer。你得确定这个字节的编码是啥?乱写会造成错误。
Node.js 目前支持的字符编码包括:
- ascii - 仅支持 7 位 ASCII 数据。如果设置去掉高位的话,这种编码是非常快的。
- utf8 - 多字节编码的 Unicode 字符。许多网页和其他文档格式都使用 UTF-8 。
- utf16le - 2 或 4 个字节,小字节序编码的 Unicode 字符。支持代理对(U+10000 至 U+10FFFF)。
- ucs2 - utf16le 的别名。
- base64 - Base64 编码。
- latin1 - 一种把 Buffer 编码成一字节编码的字符串的方式。
- binary - latin1 的别名。
- hex - 将每个字节编码为两个十六进制字符。
不同编码之间可以通过Buffer作为中间转换工具
let str = "我是待编码的字符串"
console.log(str)
// 输出:
我是待编码的字符串
let buffer = Buffer.from(str, 'utf-8')
console.log(buffer)
// 输出
<Buffer e6 88 91 e6 98 af e5 be 85 e7 bc 96 e7 a0 81 e7 9a 84 e5 ad 97 e7 ac a6 e4 b8 b2>
str = buffer.toString('base64')
console.log(str)
// 输出
'5oiR5piv5b6F57yW56CB55qE5a2X56ym5Liy'
// 指定正确encoding✅
buffer = Buffer.from(str, 'base64')
console.log(buffer)
// 输出
<Buffer e6 88 91 e6 98 af e5 be 85 e7 bc 96 e7 a0 81 e7 9a 84 e5 ad 97 e7 ac a6 e4 b8 b2>
// 如果指定错了encoding,就会得到错误的结果❎
let bufferError = Buffer.from(str, 'utf-8')
console.log(bufferError)
// 输出
<Buffer 35 6f 69 52 35 70 69 76 35 62 36 46 35 37 79 57 35 36 43 42 35 35 71 45 35 61 32 58 35 36 79 6d 35 4c 69 79>
// 接着正确✅的Buffer来
str = buffer.toString('utf-8')
console.log(str)
// 输出
'我是待编码的字符串'
Express框架中res.write、res.end及res.send 、res.json方法之间的区别?
- res.write()与res.end()总是且必须成对出现
// res.writeHead(200, {
// 'Content-Type': 'text/html;charset=utf-8'
// });
let show = "888
";
res.write(show);
res.write('商品列表');
res.end();
res.send() & res.end()的区别
- res.send([body]):body的参数可以是Buffer,String,对象或Array
- res.end(xxx): 只限定字符串和Buffer. 字符串必须指定 ‘content-type’: ‘text/html’,不然中文会乱码
res.end([data <string | Buffer>[, encoding]][, callback])
res.send([body[,statusCode]])
// body 参数可以是 Buffer、Object、String、Boolean 或 Array。
res.send(new Buffer('whoop'));
res.send({ some: 'json' });
res.send('some html
');
res.status(404).send('Sorry, we cannot find that!');
res.status(500).send({ error: 'something blew up' });
如果不指定Content-Type,框架如express会怎么设置默认值?
根据send的内容不同,设置不同值:
res.send({hello:"word"});
header: 'content-type': 'application/json'
body:{ hello: 'word' }
res.send(["hello","word"]);
header: 'content-type': 'application/json'
body:[ 'hello', 'word' ]
res.send(helloword);
header: 'text/html; charset=utf-8'body:helldworld
body:helldworld(postman 及浏览器测试)
res.send(new Buffer('helloworld'));
header:'application/octet-stream'
body:<Buffer 68 65 6c 6c 6f 77 6f 72 6c 64>
对比
相同点
Express 的 res.end() 和 res.send() 方法的相同点:
二者最终都是回归到 http.ServerResponse.Use 的 response.end() 方法。
二者都会结束当前响应流程。
不同点
Express 的 res.end() 和 res.send() 方法的不同点:
前者只能发送 string 或者 Buffer 类型,后者可以发送任何类型数据。
从语义来看,前者更适合没有任何响应数据的场景,而后者更适合于存在响应数据的场景。
Buffer和Stream(或二进制)
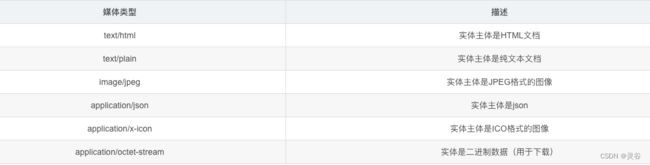
APPLICATION_ATOM_XML("application/atom+xml"), // ATOM XML聚合格式
APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED("application/x-www-form-urlencoded"), // 表单默认格式
APPLICATION_JSON("application/json"), // JSON数据格式
APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM("application/octet-stream"), // 二进制流格式
APPLICATION_SVG_XML("application/svg+xml"), //
APPLICATION_XHTML_XML("application/xhtml+xml"), // XHTML格式
APPLICATION_XML("application/xml"), // XML格式
APPLICATION_PDF("application/pdf"), // PDF格式
APPLICATION_WORD("application/msword"), // WORD格式
APPLICATION_ZIP("application/zip"), // ZIP格式
IMAGE_BMP("image/bmp"), // BMP图片格式
IMAGE_GIF("image/gif"), // GIF图片格式
IMAGE_JPEG("image/jpeg"), // JPEG图片格式
IMAGE_PNG("image/png"), // PND图片格式
IMAGE_SVG("image/svg+xml"), // SVG图片格式
IMAGE_TIFF("image/tiff"), // TIFF图片格式
IMAGE_WEBP("image/webp"), // WEBP图片格式
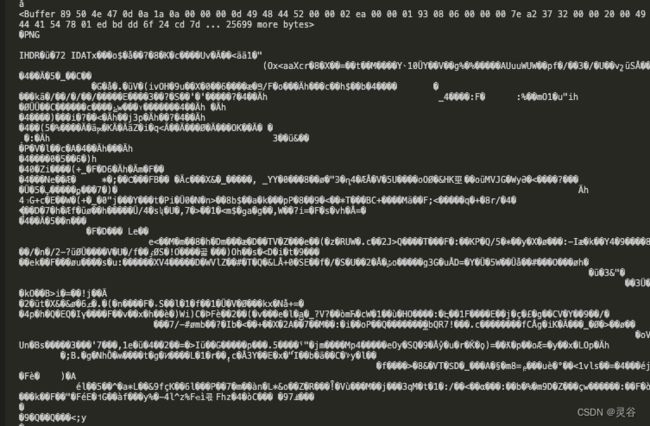
res.end返回buffer后,得到如下格式文件
fs.createWriteStream(path.resolve(__dirname, 'a.txt')).write(data)
const stream = require('stream');
const bufferStream = new stream.PassThrough();
const streams = bufferStream.end(Buffer);