蓝桥杯刷题总结(省)
文章目录
-
-
- 1. 正确率优先
- 2. 高精度模板
- 3. 前缀和模板 —— 保证不要出现数据0
- 4. 状态转移模板
- 5. 哈希模板
- 6. sqrt()函数 —— 大数 long double 转换
- 7. 直线斜率与截距 —— 利用 a b 关系直接求
- 8. 最短路径模板
- 9. 闰年年月判定模板
- 10. 并查集模板
- 11. 二分模板
- 12. 进制转换细节 —— 如果不是从0 —> x 是不可以直接进制转换的
- 13. 双指针模板 —— 指针位置和所求区间一定要一致
- 14. 审题 —— 边界划分要明确
- 15. 大整数求余 —— 结果保证正数
- 16. 除法操作 —— 除数不能作为0
- 17. 审题 —— 注意限制条件
- xx. 思维题
-
1. 正确率优先
关键1 —— 正确率优先:题目数量有限,并且无法及时得到结果验证。所以一定要先审题 + 多组测试数据检验(或者直接输出求解过程验证),正确率永远是第一位的。
一定要首先保证正确率,题目数量有限并且压轴的思维题有难度可以少写两个都无关紧要,正确率永远是第一位。
关键2 —— 审题必须仔细,相关数是否有大小,倍数等要求,结果的输出一般都会要求唯一(按照字典序结果输出等等), 一定要注意限制条件。
2. 高精度模板
题目链接: 乘积尾0
分析过程:
这个题目的优化思路是将整数进行质因数 2 和 5 的分解,最后去求有多少对完整的2和5就会产生多少个10
但建议能暴力求解的就直接进行暴力求解,因为暴力求解省去了分析思考的过程,这里我们可以直接套用高精度模板进行连乘得到结果.
运行代码:
#include
3. 前缀和模板 —— 保证不要出现数据0
题目链接: 递增三元组
分析过程:
总体思路:先求出 sa[x] 表示 a 数组当中小于等于 x 的元素的个数,再去求 sb[x] 表示数组 b 当中小于等于 x 的元素方案数(可以合法连接上a组当中元素),最后求c 数组直接进行连接即可。
关键:通常我们想要让元素大小从1开始,因为这样我们就不必要对首个元素进行特判处理(如果从0开始不能直接操作 f[x] = f[x] + f[x - 1]),所以我们为了不必要进行特判,所以我们可以让元素全部自加一下,保证最小的元素大小都1.
关键:必须要自加,否则对元素处理的时候会出现错误。例如此题sb[0]是b元素为0能合法连接a的方案数,如果未自加如果b组出现0,sb[0] != 0,这里在之后的递归上面会出现大错误
前缀和为实现元素统一处理(直接从1开始):保证不要出现数据0
运行代码:
#include
4. 状态转移模板
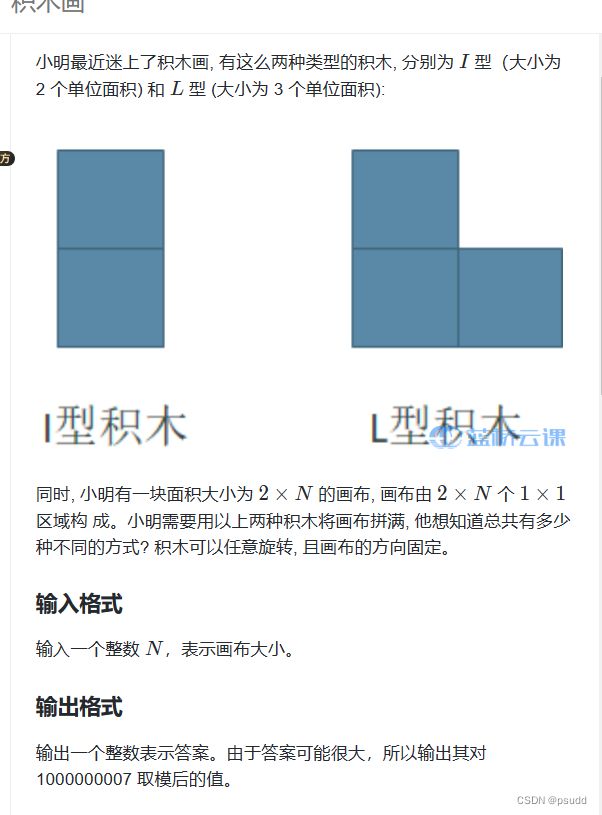
题目链接: 积木画
分析过程:
关键:f[ i ][ j ] 表示处理完前 i - 1 列 且第 i 列状态为 j 的方案数
关键:列出状态转移的方程 + 枚举状态转移 + 结果往往为f[n + 1][0] (处理完前 n 列)
运行代码:
#include
5. 哈希模板
题目链接: 扫雷
分析过程:
关键:将x, y坐标映射成一个唯一的哈希值,记录下该哈希值键对应的炸弹编号和访问状态
运行代码:
#include
6. sqrt()函数 —— 大数 long double 转换
题目链接: 砍竹子
分析过程:
关键:大数开根号的时候使用sqrtl()函数,将默认数据类型提到 long double,防止出现误差
关键:也可以使用sqrt()函数,但是要在数之前加入一个long double的强制数据类型转换也可以要不然sqrt()函数本身在c++ 11里面它可以匹配(double, long double)并不会自动提升数据精度
运行代码:
#include
7. 直线斜率与截距 —— 利用 a b 关系直接求
题目链接: 直线
分析过程:
关键:求直线的斜率和截距。注意因为浮点数类型本身就会造成误差,所以尽可能使用题目本身的变量直接计算相关结果,不要利用求得的浮点数再去求解结果.
关键:利用 y = k * x + b ,消去 k 得到 b,再消去 b 得到 k, 不要利用间接得到的 k 求 b
运行代码:
#include
8. 最短路径模板
题目链接: 路径
分析过程:
正常情况,正权单源最短路 —— Dijkstra算法直接套用就行了
填空题 —— 可以用Floy去写(运行耗时但代码短)快速得结果
运行代码:
Dijkstra算法
#includeFloyd算法
#include
9. 闰年年月判定模板
b. 回文日期

题目链接: 跑步锻炼 回文日期
分析过程:
关键:掌握闰年判断的代码 和 月日合法判断代码
运行代码:
跑步锻炼
#include回文日期
#include
10. 并查集模板
题目链接: 七段码
分析过程:
依次枚举每个状态 + 状态当中并查集判断是否存在唯一的集体
运行代码:
#include
11. 二分模板
题目链接: 杨辉三角形
分析过程:
对称 + 斜着寻找每一斜列结果 + 二分搜索
二分模板 :当最后区间大小为2时,一定要测试判断 mid = l + r + 1 >> 1是否需要 + 1这个操作,能否跳出最终的循坏
二分模板 :当一组有多个答案,想要靠左的答案 mid = l + r >> 1,想要靠右位置的答案一般 mid = l + r + 1 >> 1
运行代码:
#include
12. 进制转换细节 —— 如果不是从0 —> x 是不可以直接进制转换的
题目链接: 年号字串
分析过程:
关键:因为不是从0开始的进制,所以一般是没有规律的.
对于填空题:直接暴力搜结果即可,对于 0 的存在进行特判即可
对于程序题:对每个位进行特判处理不能为0即可。
运行代码:
填空题 —— 暴力结果
#include程序题 —— 特判处理每个位(保证没有0的存在)
#include
13. 双指针模板 —— 指针位置和所求区间一定要一致
题目链接: 统计子矩阵
分析过程:
首先前缀和每一列的区间和, 然后遍历两个横坐标,纵坐标可以用双指针完成
关键:指针移动得到结果的区间一定要和指针位置保持一致,要注意左右指针的自加自减的位置.
运行代码:
#include
14. 审题 —— 边界划分要明确
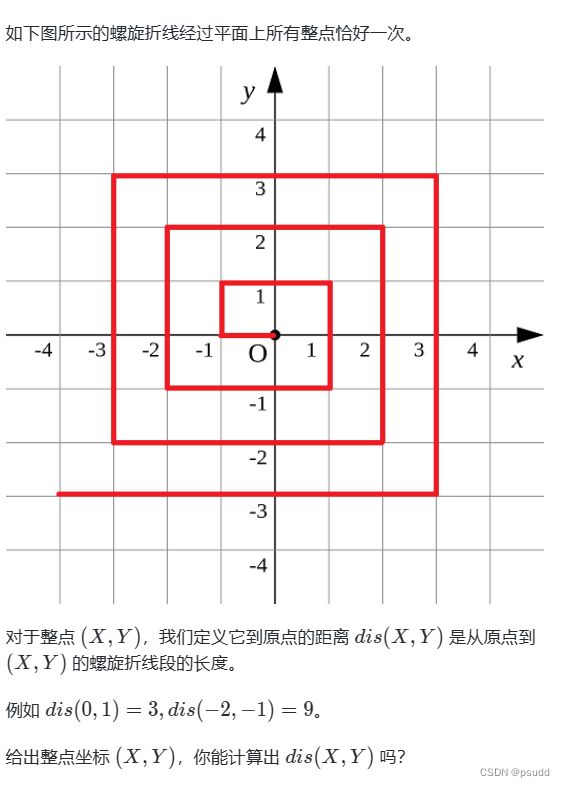
题目链接: 螺旋折线
分析过程:
找规律进行划分,对于每个边界位置点一定要精确划分到某一部分当中(如果没有精确划分到某一个部分,求解的时候可能会在其他方程当中求解到此位置造成误差)
运行代码:
#include
15. 大整数求余 —— 结果保证正数
题目链接: x进制减法
分析过程:
在每一位取最小进制的条件下不断进行求解即可
关键:因为在求解过程当中可能存在某位a[] - b[]为负数,尤其是不同的代码(先对每位结果求余再进行求和操作会出现错误,先求和则不会)最后可能导致结果出现负数的存在(所以涉及求余的结果计算的时候要保证求余完结果为正数)
运行代码:
#include
16. 除法操作 —— 除数不能作为0
题目链接: 等差数列
分析过程:
关键:求差值之间的gcd
关键:当除数为0时要进行特判处理
运行代码:
#include
17. 审题 —— 注意限制条件
题目链接: 砝码称重
分析过程:
类似于背包,注意转移过程方程.
运行代码:
#include
题目链接: 数的分解
分析过程:
审题清楚 —— 注意数字有大小和倍数要求
运行代码:
#include
题目链接: 迷宫
分析过程:
审题清楚 —— 结果要求字典序
运行代码:
#include
xx. 思维题
题目链接: 测试次数
分析过程:
若有多个手机可以区间测(枚举中间层数),单个手机只能从低层开始测
运行代码:
#include 题目链接:字串排序
分析过程:
元素均匀排布含字典序最多(zzyyxx…ccbbaa)。首先求出合法序列最短长度,再从从依次自小到大枚举同时判断当右边剩余部分取最大逆序对时是否满足条件,依次枚举得到最小字母即可.
运行代码:
#include
题目链接: 括号序列
分析过程:
结果左括号和右括号互不干扰,互相单独求解再将结果相乘.
运行代码:
#include
题目链接: 双向排序
分析过程:
找规律:两种操作必须交替出现并且相同类型操作长度必须递减
运行代码:
#include
题目链接: 子串分值和
分析过程:
将字符分为第一次出现和之后出现进行考虑
运行代码:
#include 题目链接: 后缀表达式
分析过程:
分为存在负号和不存在负号进行分别考虑
运行代码:
#include
题目链接: 灵能传输
分析过程:
前缀和分析
运行代码:
#include
题目链接: 平面切分
分析过程:
结论: 每增加一条直线,对平面数的贡献值是其与先前直线的交点数(不重合)+1
涉及精度处理全部使用long double 处理.(保证不出问题)
运行代码:
#include