Linux c/c++文件的基本操作
Linux c/c++文件的基本操作
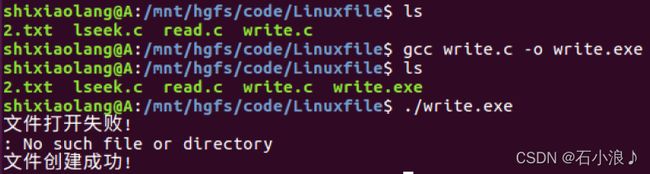
文件的创建以及写入数据
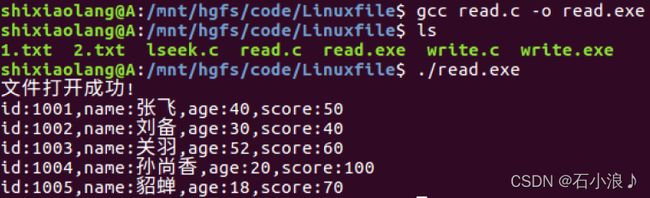
#include 文件的打开以及读取数据
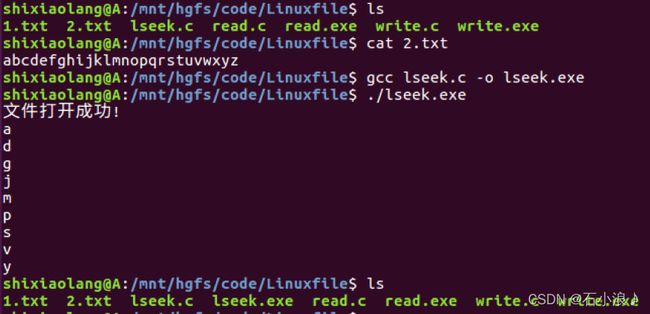
#include 文件描述符fd的位置重置
#include - open()函数
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
//参数1: 文件路径 + 文件名字
//参数2: 文件打开方式或创建方式
//参数3: 文件权限(通常使用三位八进制代替0666表示u g o 均为wr权限)
- write()函数
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);
//参数1: 文件描述符fd
//参数2: 写入的内容的地址
//参数3: 写入内容的大小
- read()函数
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
//参数1: 文件描述符fd
//参数2: 读取使用的缓冲内存地址
//参数3: 读取的大小
- close()函数
int close(int fd);
//参数1: 文件描述符fd
- lseek()函数
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
//参数1: 文件描述符fd
//参数2: 偏移大小
//参数3: 偏移的位置
SEEK_SET 偏移量设置为偏移字节(fd置到偏移文件开头+偏移字节)
SEEK_CUR 偏移量设置为当前位置加偏移字节(fd置到当前位置+偏移字节)
SEEK_END 偏移量设置为文件大小加偏移字节(fd置到文件末尾+偏移字节)
如有错误,还请大佬们指正,嘻嘻嘻!