全卷积网络FCN详解与代码实现
简单粗暴——FCN
- 一、学习目标
- 二、CNN 与 FCN 的区别
- 三、FCN结构
- 四、FCN缺点
- 五、VGG网络的FCN化
先附上 FCN论文
Pytorch实现 https://github.com/wkentaro/pytorch-fcn
一、学习目标
1、理解FCN原理
2、掌握FCN的关键技术
3、掌握FCN的实现
二、CNN 与 FCN 的区别
FCN与CNN的区域在把于CNN最后的全连接层换成卷积层。
对于一般的分类CNN网络,如VGG和Resnet,都会在网络的最后加入一些全连接层,经过softmax后就可以获得类别概率信息。但是这个概率信息是1维的,即只能标识整个图片的类别,不能标识每个像素点的类别,所以这种全连接方法不适用于图像分割。
而FCN提出可以把后面几个全连接都换成卷积,这样就可以获得一张2维的feature map,后接softmax获得每个像素点的分类信息,从而解决了分割问题,如下图。
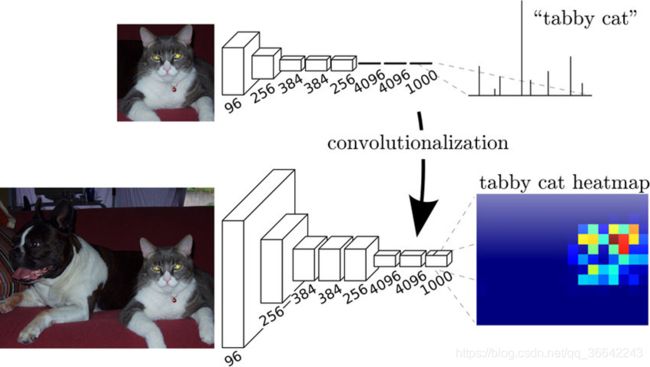
经过多次卷积和pooling以后,得到的图像越来越小,分辨率越来越低。其中图像到 最小的一层时,所产生图叫做heatmap热图,热图就是我们最重要的高维特诊图,得到高维特征的heatmap之后就是最重要的一步也是最后的一步对原图像进行upsampling,把图像进行放大到原图像的大小。
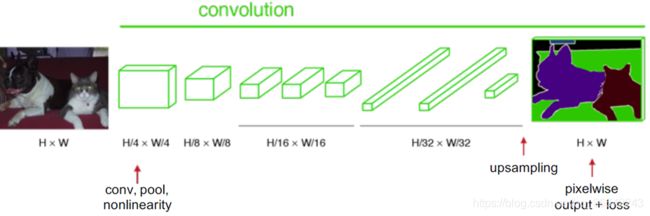
最后的输出是1000张heatmap经过upsampling变为原图大小的图片,为了对每个像素进行分类预测label成最后已经进行语义分割的图像,这里有一个小trick,就是最后通过逐个像素地求其在1000张图像该像素位置的最大数值描述(概率)作为该像素的分类。因此产生了一张已经分类好的图片,如上图右侧有狗猫图。
三、FCN结构
1、image经过多个conv和+一个max pooling变为pool1 feature,宽高变为1/2
2、pool1 feature再经过多个conv+一个max pooling变为pool2 feature,宽高变为1/4
3、pool2 feature再经过多个conv+一个max pooling变为pool3 feature,宽高变为1/8
4、pool3 feature再经过多个conv+一个max pooling变为pool4 feature,宽高变为1/16
5、直到pool5 feature,宽高变为1/32。

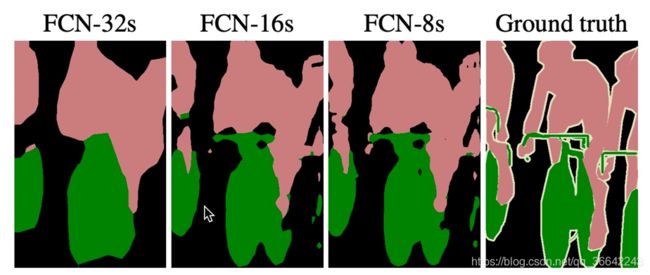
1、对于FCN-32s,直接对pool5 feature进行32倍上采样获得32x upsampled feature,再对32x upsampled feature每个点做softmax prediction获得32x upsampled feature prediction(即分割图)。
2、对于FCN-16s,首先对pool5 feature进行2倍上采样获得2x upsampled feature,再把pool4 feature和2x upsampled feature逐点相加,然后对相加的feature进行16倍上采样,并softmax prediction,获得16x upsampled feature prediction。
3、对于FCN-8s,首先进行pool4+2x upsampled feature逐点相加,然后又进行pool3+2x upsampled逐点相加,即进行更多次特征融合。具体过程与16s类似,不再赘述。

关于Skip Architecture 注意点
1、维度一致才能相加:spatial/channel
2、1 x 1 Convolution
作者在原文种给出3种网络结果对比,明显可以看出效果:FCN-32s < FCN-16s < FCN-8s,即使用多层feature融合有利于提高分割准确性。
四、FCN缺点
1、FCN-8s的结果还是不够精细
2、没有充分考虑像素之间的关系
五、VGG网络的FCN化
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.init as init
# 建立block
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch):
super(Block, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_ch, out_ch, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_ch)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.relu1(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
return out
# 建立Layer
def make_layers(in_channels, layer_list):
layers = []
for v in layer_list:
layers += [Block(in_channels, v)]
in_channels = v # 下次输入为上次输出
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
class Layer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, layer_list):
super(Layer, self).__init__()
self.layer = make_layers(in_channels, layer_list)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.layer(x)
return out
# VGG 19
# [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = Layer(3, [64, 64])
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.layer2 = Layer(64, [128, 128])
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.layer3 = Layer(128, [256, 256, 256, 256])
self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.layer4 = Layer(256, [512, 512, 512, 512])
self.pool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.layer5 = Layer(512, [512, 512, 512, 512])
self.pool5 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
def forward(self, x):
f1 = self.pool1(self.layer1(x))
f2 = self.pool2(self.layer2(f1))
f3 = self.pool3(self.layer3(f2))
f4 = self.pool4(self.layer4(f3))
f5 = self.pool5(self.layer5(f4))
return [f3, f4, f5]
# 建立上采样模块
class MergeUpsample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_cha1, in_cha2, out_chan):
super(MergeUpsample, self).__init__()
self.conv11 = Block(in_chan1, out_ch)
self.conv12 = Block(in_chan2, out_ch)
self.conv2 = Block(out_ch, out_ch)
self.upsample = nn.ConvTranspose2d(out_chan1,
out_chan2 ,2 ,stride=2)
def forward(self, x, y):
p1 = self.conv11(self.upsample(x))
p2 = self.conv12(y)
out = self.conv2(p1+p2)
return out
class FCNDecode(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n, in_channels, out_channels, upsample_ratio):
super(FCNDecode, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = Layer(in_channels, [out_channels]*n)
self.trans_conv1 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(
out_channels,
out_channels,
upsample_ratio,
stride=upsample_ratio)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.trans_conv1(self.conv1(x))
return out
# 建立FCN_Seg模型
class FCNSeg(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n, in_channels, out_channels, upsample_ratio):
super(FCNSeg, self).__init__()
self.encode = VGG()
self.decode = FCNDecode(n, in_channels, out_channels, upsample_ratio)
self.classifier = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, 10, 3, padding=1)
def forward(self, x):
feature_list = self.encode(x)
out = self.decode(feature_list[-1])
pro = self.classifier(out)
return out
x = torch.randn((10, 3, 256, 256)) # batchsize, channel, h, w
model = FCNSeg(4, 512, 256, 32) # 卷积层, 输入通道, 输出通道,上采32
model.eval()
y = model(x)
y.size() #torch.Size([10, 256, 256, 256])