并发编程(十)-ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor源码分析
一、ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 概述
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 是 Java 中的一个线程池实现,它继承自 ThreadPoolExecutor 类,并实现了 ScheduledExecutorService 接口,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor内部维护了一个任务队列和一组线程,可以执行周期性和延迟性任务,并且可以动态地调整线程池的大小。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 的核心原理是:
- 将任务添加到任务队列中,任务可以通过 schedule、scheduleAtFixedRate 或 scheduleWithFixedDelay 等方法来指定任务的延迟时间或周期性时间来计算任务的执行时间,在执行时间到达时从任务队列中取出任务并交给线程池中的线程执行。
- ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 通过 ScheduledFutureTask 类来表示任务,并使用 DelayedWorkQueue 来存储任务队列,这个队列可以根据任务的执行时间进行排序,保证优先执行先到期的任务。
- ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 的线程池大小可以根据需要进行动态调整,当任务的执行时间到达时,如果当前线程池中的线程数小于核心线程数,就会创建新的线程来执行任务;如果当前线程池中的线程数大于等于核心线程数,就会将任务添加到任务队列中等待执行。当任务队列太长或者任务执行时间比较长时,线程池中的线程数会逐渐增加,直到达到最大线程数为止。
- ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 可以通过 shutdown 方法来关闭线程池,将队列中的任务执行完毕并停止线程池中的所有线程。在关闭线程池之前,如果有周期性任务在执行,需要将这些任务取消掉,避免对下一次任务的启动时间产生影响。
总之,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 通过线程池和任务队列来管理任务的执行,并通过 DelayQueue 和 ScheduledFutureTask 来实现任务的延迟执行和周期性执行。它具有线程池的优点,可以复用线程、控制线程数量等,同时也支持延迟执行和周期性执行,适用于需要执行定时任务的场景。
二、ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor如何使用
使用 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,需要按照以下步骤进行操作:
- 创建 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 对象,可以使用默认的构造函数或者使用带参数的构造函数设置线程池的大小和拒绝策略等参数。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, handler);
- 使用 executor 提交任务,可以使用 schedule、scheduleAtFixedRate、scheduleWithFixedDelay 等方法提交任务。
// 这个任务将在指定的延迟时间之后执行一次。
executor.schedule(() -> {
// 执行任务
},
delay, // 任务的延迟时间
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS // 时间单位
);
// 周期性地执行任务【这个任务将在 initialDelay 时间之后开始执行,然后每隔 period 时间执行一次。】
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate((Runnable) () -> {
// 执行任务
},
initialDelay, // 任务的初始延迟时间
period, // 任务的周期时间
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS // 表示时间单位
);
- 如果需要取消任务,可以使用 ScheduledFuture 对象的 cancel 方法。
ScheduledFuture<?> future = executor.schedule(() -> {
// 执行任务
},
delay, // 任务的延迟时间
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS // 时间单位
);
// 取消任务
future.cancel(true);
- 在所有任务执行完毕后,需要关闭线程池以释放资源。可以使用 executor 对象的 shutdown 方法。
executor.shutdown();
需要注意的是,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 中的周期性任务执行时间不能超过指定的时间间隔,否则会影响下一次任务的启动时间。此外,在任务的实现中,也需要注意线程安全问题,避免对共享资源的竞争和冲突。
三、源码分析
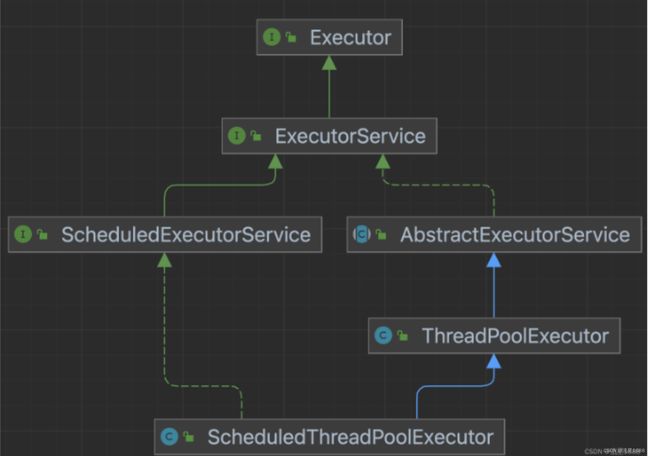
3.1 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor Diagrams
3.2 构造方法
3.2.1 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) 构造方法
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize)构造方法,用于创建一个可调度的线程池。该线程池会在指定时间内执行给定的任务,并且可以按照指定的时间间隔重复执行任务。
参数说明:
- corePoolSize 表示线程池中的核心线程数。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize)构造方法调用其父类(ThreadPoolExecutor)构造方法,参数含义如下:
- corePoolSize:核心线程池大小。
- maximumPoolSize:线程池的最大线程数,这里设置为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,表示线程数没有上限。
- keepAliveTime:线程池中空闲线程的存活时间,这里设置为 0,表示空闲线程会立即被回收。
- unit:空闲线程存活时间的时间单位,这里设置为 NANOSECONDS,表示单位为纳秒。
- workQueue:用于存储等待执行的任务的阻塞队列,这里使用 DelayedWorkQueue,它是一个基于堆的延迟队列,用于存储延迟执行的任务。
该构造方法继承自 ThreadPoolExecutor类的构造方法,因此ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor实际上是基于 ThreadPoolExecutor实现的,它添加了调度功能,能够支持延迟执行和周期性执行任务。
注意:由于maximumPoolSize设置是Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建大量的线程,从而导致OOM。
3.2.2 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory)构造方法
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory);
}
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory),用于创建一个可调度的线程池。该线程池会在指定时间内执行给定的任务,并且可以按照指定的时间间隔重复执行任务。
参数说明:
- corePoolSize:核心线程池大小,表示线程池中最少需要保持的线程数。
- threadFactory:线程工厂,用于创建新的线程。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory)构造方法调用其父类 ThreadPoolExecutor 构造方法,参数含义如下:
- corePoolSize:核心线程池大小。
- maximumPoolSize:线程池最大线程数,这里设置为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,表示线程数没有上限。
- keepAliveTime:线程池中非核心线程的存活时间,超过这个时间,非核心线程会被回收。这里设置为 0,表示空闲线程会立即被回收。
- unit:空闲线程存活时间的时间单位,这里设置为 NANOSECONDS,表示单位为纳秒。
- workQueue:用于存储等待执行的任务的阻塞队列,这里使用 DelayedWorkQueue,它是一个基于堆的延迟队列,用于存储延迟执行的任务。
- threadFactory:线程工厂,用于创建新的线程。
注意:由于maximumPoolSize设置是Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建大量的线程,从而导致OOM。
3.2.3 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)构造方法
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), handler);
}
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)构造函数,用于创建一个可调度的线程池。该线程池会在指定时间内执行给定的任务,并且可以按照指定的时间间隔重复执行任务。
参数说明:
- corePoolSize:核心线程池大小,表示线程池中最少需要保持的线程数。
- handler:线程池中的拒绝策略,用于处理任务提交时无法处理的任务。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory)构造方法调用其父类 ThreadPoolExecutor 构造方法,参数含义如下:
- corePoolSize:核心线程池大小。
- maximumPoolSize:线程池最大线程数,这里设置为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,表示线程数没有上限。
- keepAliveTime:线程池中非核心线程的存活时间,超过这个时间,非核心线程会被回收。这里设置为 0,表示空闲线程会立即被回收。
- unit:空闲线程存活时间的时间单位,这里设置为 NANOSECONDS,表示单位为纳秒。
- workQueue:用于存储等待执行的任务的阻塞队列,这里使用 DelayedWorkQueue,它是一个基于堆的延迟队列,用于存储延迟执行的任务。
- handler:线程池中的拒绝策略,用于处理任务提交时无法处理的任务。
构造函数中,maximumPoolSize被设置为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,表示线程池中的线程数没有上限,这是因为该线程池是一个可调度的线程池,任务执行的时间不确定,因此无法确定线程池的最大线程数。同时,使用了一个 DelayedWorkQueue作为任务队列,该队列可以按照任务延迟的时间进行排序,从而实现任务的定时执行。而线程池中的拒绝策略则由传入的 handler参数决定,用于处理任务提交时无法处理的任务,例如队列已满或者线程池已经关闭等情况。
注意:由于maximumPoolSize设置是Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建大量的线程,从而导致OOM。
3.2.4 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)构造方法
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory, handler);
}
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)构造函数,用于创建一个可调度的线程池。该线程池会在指定时间内执行给定的任务,并且可以按照指定的时间间隔重复执行任务。
参数说明:
- corePoolSize:核心线程池大小,表示线程池中最少需要保持的线程数。
- threadFactory:用于创建新线程的工厂对象。
- handler:线程池中的拒绝策略,用于处理任务提交时无法处理的任务。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)构造函数构造方法调用其父类 ThreadPoolExecutor 构造方法,参数含义如下:
- corePoolSize:核心线程池大小。
- maximumPoolSize:线程池最大线程数,这里设置为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,表示线程数没有上限。
- keepAliveTime:线程池中非核心线程的存活时间,超过这个时间,非核心线程会被回收。这里设置为 0,表示空闲线程会立即被回收。
- unit:空闲线程存活时间的时间单位,这里设置为 NANOSECONDS,表示单位为纳秒。
- workQueue:用于存储等待执行的任务的阻塞队列,这里使用 DelayedWorkQueue,它是一个基于堆的延迟队列,用于存储延迟执行的任务。
- threadFactory:用于创建新线程的工厂对象。
- handler:线程池中的拒绝策略,用于处理任务提交时无法处理的任务。
注意:由于maximumPoolSize设置是Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建大量的线程,从而导致OOM。
3.3 内部类
3.3.1 ScheduledFutureTask
ScheduledFutureTask 继承自 FutureTask,同时实现了 RunnableScheduledFuture 接口,提供了定时执行和周期性执行任务的能力。
在 ScheduledFutureTask 中,任务的执行时间可以通过构造函数或者 setTime 方法来设置,任务的执行时间可以是固定的时间点,也可以是相对时间,例如在当前时间的基础上延迟一段时间后执行。任务的周期性执行可以通过 setPeriod`方法来设置,当任务执行完成后,会在指定的时间间隔后重新执行。
该类的主要方法包括:
- run:实现了 Runnable 接口的方法,用于执行任务。
- getDelay:实现了 Delayed 接口的方法,用于获取任务还要延迟多少时间才能被执行。
- compareTo:实现了 Comparable 接口的方法,用于比较两个任务的执行时间。
- isPeriodic:用于判断该任务是否为周期性执行任务。
ScheduledFutureTask 类是 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类中使用的任务类,用于实现定时任务和周期性任务的调度和执行。在 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 中,任务会被封装成 ScheduledFutureTask 对象,然后加入任务队列中等待执行。在任务执行时,会调用 ScheduledFutureTask的 run方法来执行任务,当任务执行完成后,如果是周期性任务,会重新计算下一次执行时间,并将任务重新加入任务队列中等待执行。
3.3.2 DelayedWorkQueue
DelayedWorkQueue实现了 BlockingQueue接口。它用于存储那些被延迟执行的任务,并根据任务的延迟时间进行排序。延迟时间短的任务排在队列的前面,这样就能保证队列头部的任务是最近需要执行的任务。
DelayedWorkQueue 中的每个元素都是一个 ScheduledFutureTask 对象,包含了一个要被执行的任务以及它的延迟时间。在每个任务被加入队列时,DelayedWorkQueue 会根据这个延迟时间将任务插入到适当的位置。当队列头部的任务的延迟时间已经过去时,它就会被取出并执行。
需要注意的是,DelayedWorkQueue 是一个有界队列,其容量由 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor构造函数中传入的 queueSize 参数决定。如果队列已满,那么新的任务将无法加入队列中,直到有任务被取出并执行。如果队列中的任务全部都是周期性任务(通过 scheduleAtFixedRate 或 scheduleWithFixedDelay方法添加),并且这些任务的周期时间都很短,那么队列中可能会出现任务堆积的情况,这时就需要适当地调整队列的容量。
3.4 方法
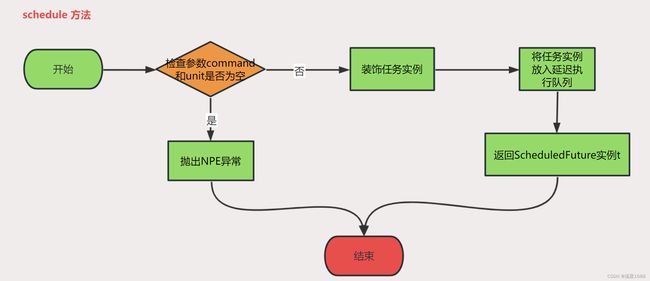
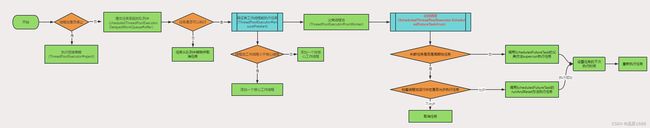
3.4.1 schedule方法
public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (callable == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableScheduledFuture<V> t = decorateTask(callable,
new ScheduledFutureTask<V>(callable,
triggerTime(delay, unit)));
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
- 检查参数callable和unit是否为null,如果是则抛出NullPointerException异常。
- 创建一个ScheduledFutureTask对象,其中包含任务callable和执行时间(triggerTime(delay, unit))等信息。
- 通过decorateTask方法将ScheduledFutureTask对象包装成RunnableScheduledFuture对象t。
- 将t添加到DelayedWorkQueue中,等待执行。
- 返回对象t。
Scheduled方法是延迟一定时间(delay)后执行一个任务(callable),ScheduledFutureTask对象会被添加到DelayedWorkQueue中,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor会在任务到达执行时间时从队列中取出任务并执行。如果任务执行过程中发生异常,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor会根据任务的重试次数和重试间隔重新将任务添加到DelayedWorkQueue中,等待下次执行。需要注意的是,如果任务的执行时间超过了设定的延迟时间,那么任务会立即开始执行,不会等待当前执行结束。返回的ScheduledFuture对象可以用于取消。
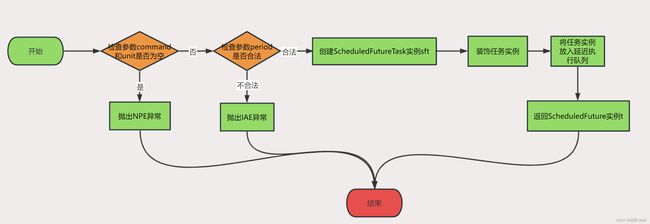
3.4.2 scheduleAtFixedRate 方法
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
ScheduledFutureTask<Void> sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(period));
RunnableScheduledFuture<Void> t = decorateTask(command, sft);
sft.outerTask = t;
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
- 如果command或unit为空,则抛出NullPointerException异常;
- 如果period小于等于0,则抛出IllegalArgumentException异常
- 创建一个 ScheduledFutureTask 对象 sft,其中包含了传入的 command、计算出的 initialDelay 和 period 参数。
- 使用 decorateTask() 方法对 sft 进行装饰,返回一个 RunnableScheduledFuture 对象 t。
- 将 t 赋值给 sft 的 outerTask 属性。
- 将 t 提交给线程池进行延迟执行。
- 返回RunnableScheduledFuture对象。
scheduleAtFixedRate方法是将一个任务按照固定频率(period)执行,每次执行的时间间隔为period,第一次执行的延迟时间为initialDelay。ScheduledFutureTask对象会被添加到DelayedWorkQueue中,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor会在任务到达执行时间时从队列中取出任务并执行。如果任务执行过程中发生异常,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor会根据任务的重试次数和重试间隔重新将任务添加到DelayedWorkQueue中,等待下次执行。需要注意的是,如果任务的执行时间超过了执行频率,那么下一次执行会立即开始,不会等待当前执行结束。
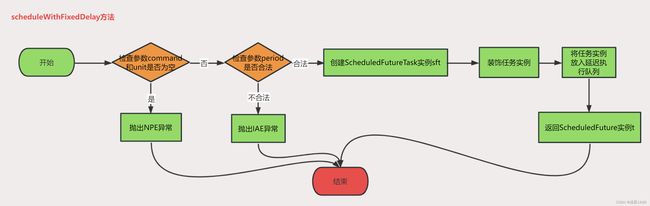
3.4.3 scheduleWithFixedDelay 方法
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (delay <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
ScheduledFutureTask<Void> sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(-delay));
RunnableScheduledFuture<Void> t = decorateTask(command, sft);
sft.outerTask = t;
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
- 如果command或unit为空,则抛出NullPointerException异常;
- 如果period小于等于0,则抛出IllegalArgumentException异常
- 创建一个ScheduledFutureTask对象sft,其中包含任务command、执行时间(initialDelay)和延迟时间(delay)等信息。
- 使用 decorateTask() 方法对 sft 进行装饰,返回一个 RunnableScheduledFuture 对象 t。
- 将 t 赋值给 sft 的 outerTask 属性。
- 将 t 提交给线程池进行延迟执行。
- 返回RunnableScheduledFuture对象。
scheduleWithFixedDelay方法是将一个任务按照固定延迟时间(delay)多次执行,每次执行的时间间隔为delay,第一次执行的延迟时间为initialDelay。ScheduledFutureTask对象会被添加到DelayedWorkQueue中,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor会在任务到达执行时间时从队列中取出任务并执行。如果任务执行过程中发生异常,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor会根据任务的重试次数和重试间隔重新将任务添加到DelayedWorkQueue中,等待下次执行。
3.3.4 delayedExecute 方法
private void delayedExecute(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> task) {
if (isShutdown())
reject(task);
else {
super.getQueue().add(task);
// 已经关闭并且任务不满足当前执行状态,即不能在当前状态下执行,那么将任务从队列中移除并取消任务。
if (isShutdown() &&
!canRunInCurrentRunState(task.isPeriodic()) &&
remove(task))
task.cancel(false);
else
ensurePrestart();
}
}
- 首先判断线程池是否已经关闭,如果已经关闭,则拒绝任务。
- 否则,将任务添加到任务队列中。
- 如果线程池已经关闭,同时当前线程池的状态不允许执行该任务,并且任务已经被成功从任务队列中移除,则取消该任务。
- 否则,确保至少有一个线程在等待任务,以便在任务可用时立即执行。
delayedExecute方法是将任务添加到DelayedWorkQueue中,并确保线程池中至少有一个线程在运行。如果ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor已经关闭并且任务不满足当前执行状态,那么任务将被取消。需要注意的是,DelayedWorkQueue是一个有序队列,按照任务的执行时间排序,因此任务会按照执行时间的顺序执行。另外,当任务执行时,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor会将任务包装成FutureTask对象并提交给ThreadPoolExecutor进行执行。