SpringBoot高级: (一)缓存
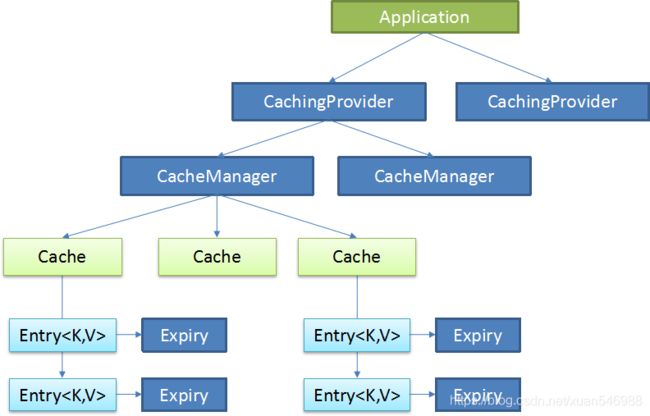
JSR107
Java Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry 和 Expiry。
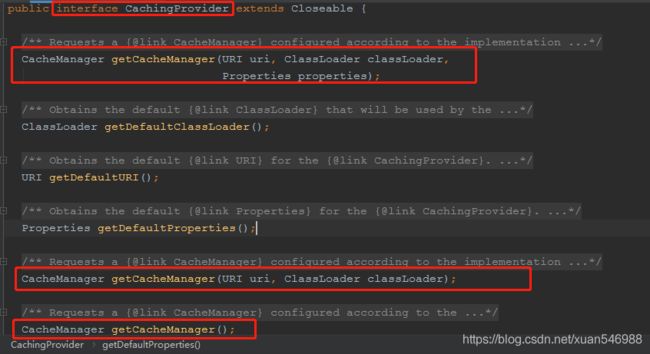
CachingProvider
定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
CacheManager
定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
![]()

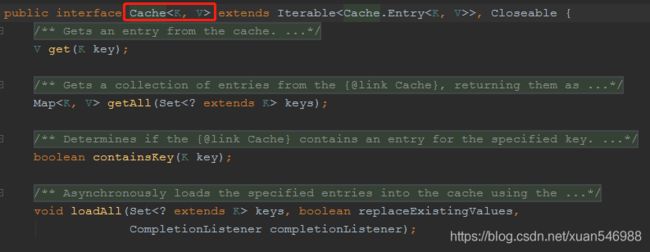
Cache
是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有。
Entry
是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
Expiry
每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
/**
*导入maven
*/
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.cache</groupId>
<artifactId>cache-api</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
Spring缓存抽象
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache
和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术;
并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发;
Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache , ConcurrentMapCache等;
每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点;
1、确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
2、从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据
缓存注解
@Cacheable 和 @CachePut区别
@Cacheable: 只会被调用一次,再次调用缓存中有就读缓存中的。
@CachePut: 方法总会被调用,调用结果会被更新到缓存中。
基本环境搭建
/**
* sql脚本
*/
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for department
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `department`;
CREATE TABLE `department` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`departmentName` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for employee
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employee`;
CREATE TABLE `employee` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`lastName` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`gender` int(2) DEFAULT NULL,
`d_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/**
* pom.xml
*/
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
/**
* application.yml
*/
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://XX.XXX.XX.XX:3306/any?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT%2b8
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# 开启驼峰识别开关
mybatis:
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
# 开启数据库sql打印
logging:
level:
com:
springboot01cache:
cache:
mapper: debug
/**
* Department实体类
*/
package com.springboot01cache.cache.pojo;
public class Department {
private Integer id;
private String departmentName;
public Department() {
super();
}
public Department(Integer id, String departmentName) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.departmentName = departmentName;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getDepartmentName() {
return departmentName;
}
public void setDepartmentName(String departmentName) {
this.departmentName = departmentName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Department [id=" + id + ", departmentName=" + departmentName + "]";
}
}
/**
* Employee实体类
*/
package com.springboot01cache.cache.pojo;
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private Integer gender; //性别 1男 0女
private Integer dId;
public Employee() {
super();
}
public Employee(Integer id, String lastName, String email, Integer gender, Integer dId) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
this.gender = gender;
this.dId = dId;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(Integer gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public Integer getdId() {
return dId;
}
public void setdId(Integer dId) {
this.dId = dId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email=" + email + ", gender=" + gender + ", dId="
+ dId + "]";
}
}
/**
* DepartmentMapper类
*/
package com.springboot01cache.cache.mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface DepartmentMapper {
}
/**
* EmployeeMapper类
*/
package com.springboot01cache.cache.mapper;
import com.springboot01cache.cache.pojo.Employee;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
@Mapper
public interface EmployeeMapper {
@Select("select * from employee where id = #{id}")
public Employee employee(Integer id);
@Update("update employee set email = #{email} where id = #{id}")
public void updateEmployee(Employee employee);
@Delete("delete from employee where id = #{id}")
public void deleteEmployee(Integer id);
@Insert("insert into employee(lastName,email,gender,d_id) values(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender},#{dId})")
public void insertEmployee(Employee employee);
@Select("select * from employee where lastName = #{lastName}")
public Employee getEmployeeByLastName(String lastName);
}
/**
* EmployeeService
*/
package com.springboot01cache.cache.service;
import com.springboot01cache.cache.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.springboot01cache.cache.pojo.Employee;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* 抽取缓存的公共配置
*/
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = {"emp", "temp"})
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
/**
* 将方法的运行结果进行缓存,以后再要查询相同的数据,直接从缓存中获取,不用调用方法
* CacheManager管理多个Cache组件的,对缓存真正的CRUD操作是在Cache组件中,每一个缓存组件都有自己唯一的名字
* cacheNames/value: 指定缓存组件的名字,将方法的返回结果放在哪个缓存中,是数组的方式,可以指定多个缓存
* key: 缓存数据使用的key,可以使用它来指定,默认使用方法的参数值
* 支持spel表达式
* keyGenerator: key的生成器 和key二选一
* cacheManager: 指定缓存管理器
* cacheResolver: 指定缓存解析器 和缓存管理器二选一
* condition: 符合条件的情况下才缓存
* unless: 否定缓存,当true时方法的返回值就不会被缓存
* sync: 是否使用异步模式
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp", "temp"},
key = "#id",
condition = "#id>0",
unless = "#result == null")
public Employee employee(Integer id) {
System.out.println("查询" + id + "号员工");
return employeeMapper.employee(id);
}
/**
* @param employee
* @return
* @CachePut 即调用方法, 又更新缓存
* 修改数据库中某个数据,同时更新缓存
* 运行时机:
* 1. 先调用目标方法
* 2. 将目标方法的结果缓存起来
*/
@CachePut(value = {"emp", "temp"}, key = "#employee.id"/**,key = "#result.id"*/)
public Employee updateEmployee(Employee employee) {
employeeMapper.updateEmployee(employee);
return employee;
}
/**
* 清除缓存
* allEntries: 删除这个缓存中所有的key缓存
* beforeInvocation: 缓存的清除是否在方法之前执行
*
* @param id
*/
@CacheEvict(value = {"emp", "temp"}, allEntries = true, beforeInvocation = true)
public void updateEmployee(Integer id) {
employeeMapper.deleteEmployee(id);
}
/**
* @param lastName
* @return
* @Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则
*/
@Caching(cacheable = {
@Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp", "temp"},
key = "#id",
condition = "#id>0",
unless = "#result == null")
},
put = {@CachePut(value = {"emp", "temp"}, key = "#employee.id"),
@CachePut(value = {"emp", "temp"}, key = "#employee.email")})
public Employee getEmployeeByLastName(String lastName) {
return employeeMapper.getEmployeeByLastName(lastName);
}
}
/**
* EmployeeController
*/
package com.springboot01cache.cache.controller;
import com.springboot01cache.cache.pojo.Employee;
import com.springboot01cache.cache.service.EmployeeService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
EmployeeService employeeService;
@RequestMapping("/emp/{id}")
public Employee employee(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return employeeService.employee(id);
}
}
/**
* 启动类 扫描mapper 开始注解缓存
*/
package com.springboot01cache.cache;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan({"com.springboot01cache.cache.mapper"})
@EnableCaching // 标注开启注解缓存
public class CacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Cacheable/@CachePut/@CacheEvict 主要的参数
Cache SpEL available metadata
原理
(1). 自动配置类: CacheAutoConfiguration
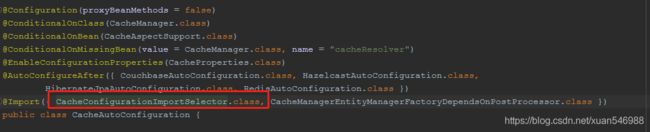
(2). 缓存配置类

(3). 默认生效的配置类:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration
(4). 给容器中注册了一个CacheManager: ConcurrentMapCacheManager 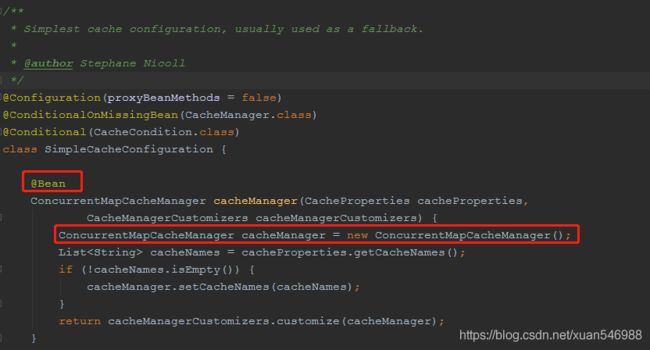
(5). 可以获取和创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的缓存组件,作用将数据保存在ConcurrentMap中。

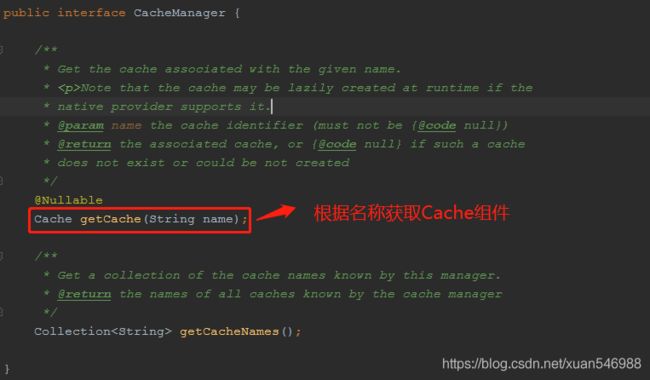

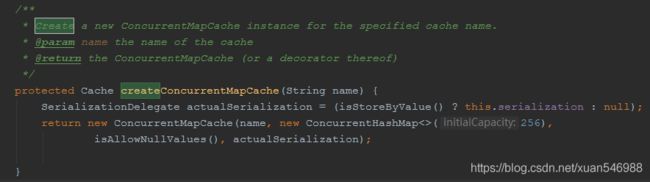
ConcurrentMapCache类:
![]()
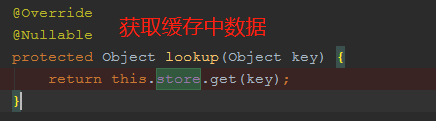
运行流程
@Cacheable
1、方法运行之前, 先去查询Cache缓存组件,按照cacheNams指定的名称获取,(CacheManager先获取相应的缓存),第一次获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建。
2、去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数。
key是按照某种策略生成的,默认使用keyGenerator生成的,默认是SimpleKeyGenerator生成key。
SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的默认策略:
1) 如果没有参数,key=new SimpleKey();
2) 如果有一个参数,key=参数的值
3)如果有多个参数,key=new SimpleKey(params);
3、没有查到缓存就调用目标方法。
4、将目标方法返回的结果放进缓存中。
@Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先来检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存,如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存中,以后再来调用就可以直接使用缓存中的数据。
核心:
1、使用CacheManager【ConcurrentMapCacheManager】按照名字得到Cache【ConcurrentMapCache】
2、key使用keyGenerator生成的,默认是SimpleKeyGenerator