ntp服务配置
操作场景
ntpd(Network Time Protocol daemon)是 Linux 操作系统的一个守护进程,用于校正本地系统与时钟源服务器之间的时间,完整的实现了 NTP 协议。ntpd 与 ntpdate 的区别是 ntpd 是步进式的逐渐校正时间,不会出现时间跳变,而 ntpdate 是断点更新。本文档以 CentOS 7.5 操作系统云服务器为例,介绍如何安装和配置 ntpd。
注意事项
部分操作系统采用 chrony 作为默认 NTP 服务,请确认 ntpd 正在运行并设置为开机自启动。
使用 systemctl is-active ntpd.service 命令,可查看 ntpd 是否正在运行。
使用 systemctl is-enabled ntpd.service 命令,可查看 ntpd 是否开机自启动。
NTP 服务的通信端口为 UDP 123,设置 NTP 服务之前,请确保您已经开放 UDP 123 端口。
若未开放该端口,请参考 添加安全组规则 进行放行。
操作步骤
安装 ntpd
执行以下命令,判断是否安装 ntpd。
rpm -qa | grep ntp如果返回类似如下结果,表示已安装 ntpd。
如果未安装 ntpd,请使用 yum install ntp 安装 ntpd。
yum -y install ntpntpd 默认为客户端运行方式。
配置 NTP
执行以下命令,打开 NTP 服务配置文件。
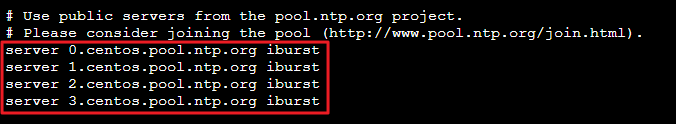
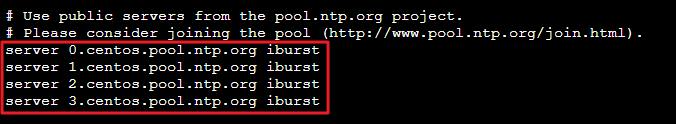
vi /etc/ntp.conf按 i 切换至编辑模式,找到 server 相关配置,将 server 修改为您需要设置的目标 NTP 时钟源服务器(例如 time1.tencentyun.com),并删除暂时不需要的 NTP 时钟源服务器。如下图所示:
按 Esc,输入 :wq,保存文件并返回。
启动 ntpd
执行以下命令,重启 ntpd 服务。
systemctl restart ntpd.service检查 ntpd 状态
根据实际需求,执行以下不同的命令,检查 ntpd 的状态。
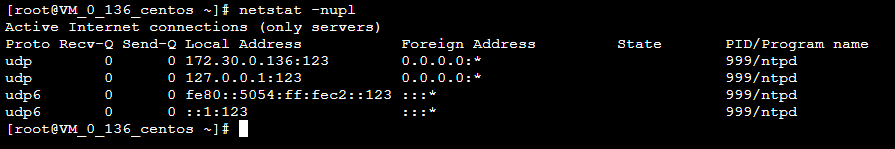
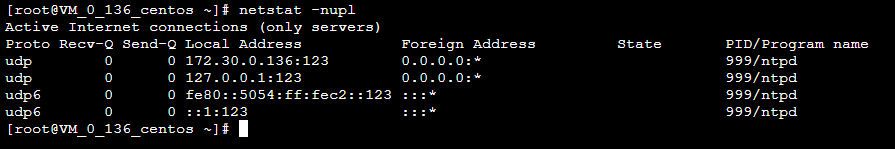
执行以下命令,查看 NTP 服务端口 UDP 123 端口是否被正常监听。
netstat -nupl返回类似如下结果,表示监听正常。
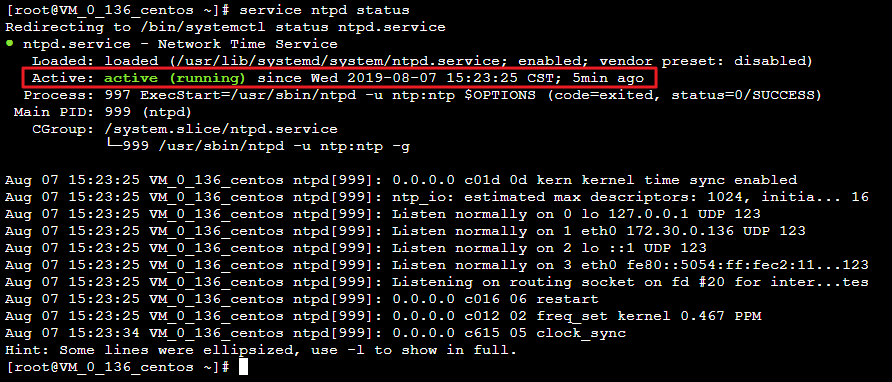
执行以下命令,查看 ntpd 状态是否正常。
service ntpd status返回类似如下结果,表示 ntpd 状态正常。
执行以下命令,获取更详细的 NTP 服务信息。
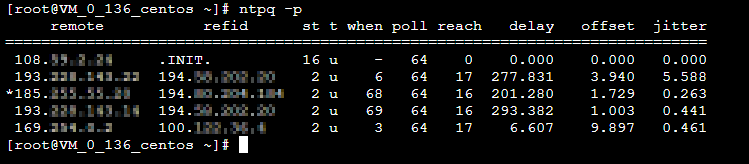
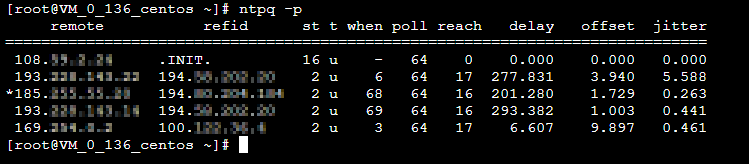
ntpq -p返回类似如下结果:
* : 表示目前使用的 NTP 服务器。
remote:响应这个请求的 NTP 服务器的名称。
refid:NTP 服务器使用的上一级 NTP 服务器。
st:remote 远程服务器的级别。服务器从高到低级别设定为1 - 16,为了减缓负荷和网络堵塞,原则上建议避免直接连接到级别为1的服务器。
when:上一次成功请求之后到现在的秒数。
poll:本地机和远程服务器多少时间进行一次同步(单位为秒)。初始运行 NTP 时,poll 值会比较小,和服务器同步的频率增加,建议尽快调整到正确的时间范围。调整之后,poll 值会逐渐增大,同步的频率也将会相应减小。
reach:八进制值,用来测试能否和服务器连接。每成功连接一次,reach 的值将会增加。
delay:从本地机发送同步要求到 NTP 服务器的 round trip time。
offset:主机通过 NTP 时钟同步与所同步时间源的时间偏移量,单位为毫秒(ms)。offset 越接近于0,主机和 NTP 服务器的时间越接近。
jitter:用来做统计的值。统计在特定连续的连接数里 offset 的分布情况。即 jitter 数值的绝对值越小,主机的时间就越精确。
设置 ntpd 为开机启动
执行以下命令,将 ntpd 设置为开机自启动。
systemctl enable ntpd.service执行以下命令,查看 chrony 是否被设置为开机启动。
systemctl is-enabled chronyd.service如果 chrony 被设置为开机启动,请执行以下命令,将 chrony 从开机启动中移除。
chrony 与 ntpd 冲突,可能引起 ntpd 开机启动失败。
systemctl disable chronyd.service增强 ntpd 安全性
依次执行以下命令,为 /etc/ntp.conf 配置文件增加安全性。
interfaceignorewildcardinterfacelisteneth0操作场景
ntpdate 为断点更新,ntpd 为步进式的逐渐校正时间。对新购实例,您可以使用 ntpdate 同步时间。对已经承载有运行中业务的实例,建议您使用 ntpd 同步时间。本文档以 CentOS 7.5 操作系统云服务器为例,介绍如何将 ntpdate 转换为 ntpd。
前提条件
NTP 服务的通信端口为 UDP 123,转换为 NTP 服务之前,请确保您已经开放 UDP 123端口。
若未开放该端口,请参考 添加安全组规则 进行放行。
操作步骤
您可选择 手动 或者 自动 的方式将 ntpdate 转换为 ntpd。
手动将 ntpdate 转换为 ntpd
关闭 ntpdate
执行以下命令,导出 crontab 配置,并过滤 ntpdate。
crontab -l |grep -v ntpupdate > /tmp/cronfile执行以下命令,更新 ntpdate 配置。
crontab /tmp/cronfile执行以下命令,修改 rc.local 文件。
vim /etc/rc.local按 “i” 切换至编辑模式,删除 ntpupdate 配置行。
按 “Esc”,输入 “:wq”,保存文件并返回。
配置 ntpd
执行以下命令,打开 NTP 服务配置文件。
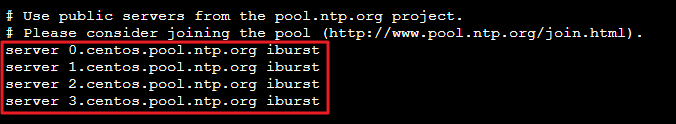
vi /etc/ntp.conf按 i 切换至编辑模式,找到 server 相关配置,将 server 修改为您需要设置的目标 NTP 时钟源服务器(例如 time1.tencentyun.com),并删除暂时不需要的 NTP 时钟源服务器。如下图所示:
按 Esc,输入 :wq,保存文件并返回。
自动将 ntpdate 转换为 ntpd
下载 ntpd_enable.sh 脚本。
wget https://image-10023284.cos.ap-shanghai.myqcloud.com/ntpd_enable.sh执行以下命令,使用 ntpd_enable.sh 脚本将 ntpdate 转换为 ntpd。
sh ntpd_enable.sh相关操作
检查 ntpd 状态
请根据实际需求,执行对应命令,以检查 ntpd 的状态。
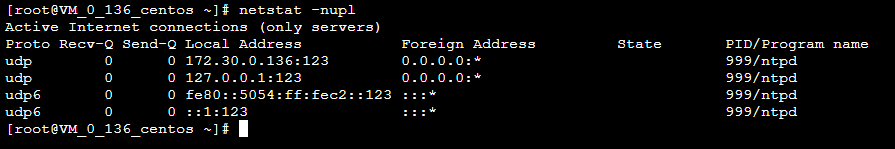
执行以下命令,查看 NTP 服务端口 UDP 123 端口是否被正常监听。
netstat -nupl返回类似如下结果,表示监听正常。
执行以下命令,查看 ntpd 状态是否正常。
service ntpd status返回类似如下结果,表示 ntpd 状态正常。
执行以下命令,获取更详细的 NTP 服务信息。
ntpq -p返回类似如下结果:
* : 表示目前使用的 NTP 服务器。
remote:响应这个请求的 NTP 服务器的名称。
refid:NTP 服务器使用的上一级 NTP 服务器。
st:remote 远程服务器的级别。服务器从高到低级别设定为1 - 16,为了减缓负荷和网络堵塞,原则上建议避免直接连接到级别为1的服务器。
when:上一次成功请求之后到现在的秒数。
poll:本地机和远程服务器多少时间进行一次同步(单位为秒)。初始运行 NTP 时,poll 值会比较小,和服务器同步的频率增加,建议尽快调整到正确的时间范围。调整之后,poll 值会逐渐增大,同步的频率也将会相应减小。
reach:八进制值,用来测试能否和服务器连接。每成功连接一次,reach 的值将会增加。
delay:从本地机发送同步要求到 NTP 服务器的 round trip time。
offset:主机通过 NTP 时钟同步与所同步时间源的时间偏移量,单位为毫秒(ms)。offset 越接近于0,主机和 NTP 服务器的时间越接近。
jitter:用来做统计的值。统计在特定连续的连接数里 offset 的分布情况。即 jitter 数值的绝对值越小,主机的时间就越精确。
操作场景
ntpdate 为断点更新,ntpd 为步进式的逐渐校正时间。对新购实例,您可以使用 ntpdate 同步时间。对已经承载有运行中业务的实例,建议您使用 ntpd 同步时间。本文档以 CentOS 7.5 操作系统云服务器为例,介绍如何将 ntpdate 转换为 ntpd。
前提条件
NTP 服务的通信端口为 UDP 123,转换为 NTP 服务之前,请确保您已经开放 UDP 123端口。
若未开放该端口,请参考 添加安全组规则 进行放行。
操作步骤
您可选择 手动 或者 自动 的方式将 ntpdate 转换为 ntpd。
手动将 ntpdate 转换为 ntpd
关闭 ntpdate
执行以下命令,导出 crontab 配置,并过滤 ntpdate。
crontab -l |grep -v ntpupdate > /tmp/cronfile执行以下命令,更新 ntpdate 配置。
crontab /tmp/cronfile执行以下命令,修改 rc.local 文件。
vim /etc/rc.local按 “i” 切换至编辑模式,删除 ntpupdate 配置行。
按 “Esc”,输入 “:wq”,保存文件并返回。
配置 ntpd
执行以下命令,打开 NTP 服务配置文件。
vi /etc/ntp.conf
#!/bin/bash -
set -o nounset # Treat unset variables as an error
check_os_type()
{
# ostype: tlinux|opensuse|suse|centos|redhat|ubuntu|debian
while [ true ];do
if [ -f /etc/tlinux-release ];then
echo tlinux
return
fi
if [ -f /etc/SuSE-release ];then
grep -i "opensuse" /etc/SuSE-release >/dev/null 2>/dev/null && echo "opensuse" || echo "suse"
return
fi
if [ -f /etc/centos-release ];then
echo centos
return
fi
#centos5 and redhat5
if [ -f /etc/redhat-release ];then
grep "Red Hat" /etc/redhat-release >/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo redhat
return
fi
grep CentOS /etc/redhat-release >/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo centos
return
fi
fi
break
done
for os in ubuntu debian coreos;do grep ^ID=${os}$ /etc/os-release >/dev/null 2>/dev/null && echo ${os} && return; done
grep -i =ubuntu /etc/lsb-release >/dev/null 2>/dev/null && echo ubuntu && return
[ -f /etc/freebsd-update.conf ] && echo FreeBSD
}
time_daemon_config_recheck_ntpdate()
{
echo "time_daemon_config_recheck_ntpdate run..."
crontab -l |grep -v ntpupdate > /tmp/cronfile
crontab /tmp/cronfile
rm -rf /tmp/cronfile
echo "time_daemon_config_recheck_ntpdate done"
}
# This function is only called in cloud-init path.
# So it
time_daemon_config()
{
echo "time_daemon_config run..."
if [ "`which ntpd &> /dev/null;echo $?`" == 0 ];then
# NTPD mode
local cfg=/etc/ntp.conf
[ ! -f $cfg ] && echo "time_daemon_config $cfg NOT FOUND. failed" && return
local srv=ntpd
[ "$ostype" == "ubuntu" ] && srv=ntp
elif [ "`which chronyd &> /dev/null;echo $?`" == 0 ];then
# CHRONYD mode
local cfg=/etc/chrony.conf
[ ! -f $cfg ] && cfg=/etc/chrony/chrony.conf
[ ! -f $cfg ] && echo "time_daemon_config $cfg NOT FOUND. failed" && return
local srv=chronyd
else
echo "time_daemon_config FAILED. No supported time daemon here"
return
fi
[ ! -f $cfg ] && echo "$cfg not found. exit time_daemon_config" && return
echo "time_daemon_config delete old config"
# delete tencent config and mask others
sed -i '/tencent/d' $cfg
sed -i 's/\(server.*\)/#\1/g' $cfg
sed -i 's/\(pool.*\)/#\1/g' $cfg
echo "time_daemon_config add servers"
# add time* config
echo server time1.tencentyun.com iburst >> $cfg
echo server time2.tencentyun.com iburst >> $cfg
echo server time3.tencentyun.com iburst >> $cfg
echo server time4.tencentyun.com iburst >> $cfg
echo server time5.tencentyun.com iburst >> $cfg
echo "time_daemon_config add ntp local listening rules"
# add ntp local listening rules
if [[ $cfg =~ 'ntp' ]];then
sed -i '/interface ignore wildcard/d' $cfg
sed -i '/interface listen eth/d' $cfg
echo "interface ignore wildcard" >> $cfg
[ -L /sys/class/net/eth0 ] && echo "interface listen eth0" >> $cfg ||
echo "interface listen eth1" >> $cfg
fi
echo "time_daemon_config ban ntpdate in crontab"
# ban ntpdate in crontab
time_daemon_config_recheck_ntpdate
echo "time_daemon_config restart service"
# restart ntpd compatible for sysvinit and systemd
if [ "`which systemctl &> /dev/null;echo $?`" == 0 ];then
systemctl enable $srv
systemctl restart $srv
elif [ "`which chkconfig &> /dev/null;echo $?`" == 0 ];then
chkconfig --level 3 $srv on
echo service $srv restart
service $srv restart
elif [ "`which update-rc.d &> /dev/null;echo $?`" == 0 ];then
update-rc.d $srv enable 3
service $srv restart
fi
echo "time_daemon_config done..."
}
function pre_check()
{
nslookup time1.tencentyun.com &> /dev/null
}
# RUN FROM HERE
ostype=`check_os_type`
pre_check
if [ $? != 0 ];then
echo "can't resolve time1.tencentyun.com. failed"
exit 1
fi
time_daemon_config
按 i 切换至编辑模式,找到 server 相关配置,将 server 修改为您需要设置的目标 NTP 时钟源服务器(例如 time1.tencentyun.com),并删除暂时不需要的 NTP 时钟源服务器。如下图所示:
按 Esc,输入 :wq,保存文件并返回。
自动将 ntpdate 转换为 ntpd
下载 ntpd_enable.sh 脚本。
wget https://image-10023284.cos.ap-shanghai.myqcloud.com/ntpd_enable.sh执行以下命令,使用 ntpd_enable.sh 脚本将 ntpdate 转换为 ntpd。
sh ntpd_enable.sh
#!/bin/bash -
set -o nounset # Treat unset variables as an error
check_os_type()
{
# ostype: tlinux|opensuse|suse|centos|redhat|ubuntu|debian
while [ true ];do
if [ -f /etc/tlinux-release ];then
echo tlinux
return
fi
if [ -f /etc/SuSE-release ];then
grep -i "opensuse" /etc/SuSE-release >/dev/null 2>/dev/null && echo "opensuse" || echo "suse"
return
fi
if [ -f /etc/centos-release ];then
echo centos
return
fi
#centos5 and redhat5
if [ -f /etc/redhat-release ];then
grep "Red Hat" /etc/redhat-release >/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo redhat
return
fi
grep CentOS /etc/redhat-release >/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo centos
return
fi
fi
break
done
for os in ubuntu debian coreos;do grep ^ID=${os}$ /etc/os-release >/dev/null 2>/dev/null && echo ${os} && return; done
grep -i =ubuntu /etc/lsb-release >/dev/null 2>/dev/null && echo ubuntu && return
[ -f /etc/freebsd-update.conf ] && echo FreeBSD
}
time_daemon_config_recheck_ntpdate()
{
echo "time_daemon_config_recheck_ntpdate run..."
crontab -l |grep -v ntpupdate > /tmp/cronfile
crontab /tmp/cronfile
rm -rf /tmp/cronfile
echo "time_daemon_config_recheck_ntpdate done"
}
# This function is only called in cloud-init path.
# So it
time_daemon_config()
{
echo "time_daemon_config run..."
if [ "`which ntpd &> /dev/null;echo $?`" == 0 ];then
# NTPD mode
local cfg=/etc/ntp.conf
[ ! -f $cfg ] && echo "time_daemon_config $cfg NOT FOUND. failed" && return
local srv=ntpd
[ "$ostype" == "ubuntu" ] && srv=ntp
elif [ "`which chronyd &> /dev/null;echo $?`" == 0 ];then
# CHRONYD mode
local cfg=/etc/chrony.conf
[ ! -f $cfg ] && cfg=/etc/chrony/chrony.conf
[ ! -f $cfg ] && echo "time_daemon_config $cfg NOT FOUND. failed" && return
local srv=chronyd
else
echo "time_daemon_config FAILED. No supported time daemon here"
return
fi
[ ! -f $cfg ] && echo "$cfg not found. exit time_daemon_config" && return
echo "time_daemon_config delete old config"
# delete tencent config and mask others
sed -i '/tencent/d' $cfg
sed -i 's/\(server.*\)/#\1/g' $cfg
sed -i 's/\(pool.*\)/#\1/g' $cfg
echo "time_daemon_config add servers"
# add time* config
echo server time1.tencentyun.com iburst >> $cfg
echo server time2.tencentyun.com iburst >> $cfg
echo server time3.tencentyun.com iburst >> $cfg
echo server time4.tencentyun.com iburst >> $cfg
echo server time5.tencentyun.com iburst >> $cfg
echo "time_daemon_config add ntp local listening rules"
# add ntp local listening rules
if [[ $cfg =~ 'ntp' ]];then
sed -i '/interface ignore wildcard/d' $cfg
sed -i '/interface listen eth/d' $cfg
echo "interface ignore wildcard" >> $cfg
[ -L /sys/class/net/eth0 ] && echo "interface listen eth0" >> $cfg ||
echo "interface listen eth1" >> $cfg
fi
echo "time_daemon_config ban ntpdate in crontab"
# ban ntpdate in crontab
time_daemon_config_recheck_ntpdate
echo "time_daemon_config restart service"
# restart ntpd compatible for sysvinit and systemd
if [ "`which systemctl &> /dev/null;echo $?`" == 0 ];then
systemctl enable $srv
systemctl restart $srv
elif [ "`which chkconfig &> /dev/null;echo $?`" == 0 ];then
chkconfig --level 3 $srv on
echo service $srv restart
service $srv restart
elif [ "`which update-rc.d &> /dev/null;echo $?`" == 0 ];then
update-rc.d $srv enable 3
service $srv restart
fi
echo "time_daemon_config done..."
}
function pre_check()
{
nslookup time1.tencentyun.com &> /dev/null
}
# RUN FROM HERE
ostype=`check_os_type`
pre_check
if [ $? != 0 ];then
echo "can't resolve time1.tencentyun.com. failed"
exit 1
fi
time_daemon_config
相关操作
检查 ntpd 状态
请根据实际需求,执行对应命令,以检查 ntpd 的状态。
执行以下命令,查看 NTP 服务端口 UDP 123 端口是否被正常监听。
netstat -nupl返回类似如下结果,表示监听正常。
执行以下命令,查看 ntpd 状态是否正常。
service ntpd status返回类似如下结果,表示 ntpd 状态正常。
执行以下命令,获取更详细的 NTP 服务信息。
ntpq -p返回类似如下结果:
* : 表示目前使用的 NTP 服务器。
remote:响应这个请求的 NTP 服务器的名称。
refid:NTP 服务器使用的上一级 NTP 服务器。
st:remote 远程服务器的级别。服务器从高到低级别设定为1 - 16,为了减缓负荷和网络堵塞,原则上建议避免直接连接到级别为1的服务器。
when:上一次成功请求之后到现在的秒数。
poll:本地机和远程服务器多少时间进行一次同步(单位为秒)。初始运行 NTP 时,poll 值会比较小,和服务器同步的频率增加,建议尽快调整到正确的时间范围。调整之后,poll 值会逐渐增大,同步的频率也将会相应减小。
reach:八进制值,用来测试能否和服务器连接。每成功连接一次,reach 的值将会增加。
delay:从本地机发送同步要求到 NTP 服务器的 round trip time。
offset:主机通过 NTP 时钟同步与所同步时间源的时间偏移量,单位为毫秒(ms)。offset 越接近于0,主机和 NTP 服务器的时间越接近。
jitter:用来做统计的值。统计在特定连续的连接数里 offset 的分布情况。即 jitter 数值的绝对值越小,主机的时间就越精确。