MyBatis核心源码剖析(SqlSession XML解析 Mapper executor SQL执行过程 自定义类型处理器 缓存 日志)
MyBatis核心源码剖析
- MyBatis核心源码剖析
-
- 1 MyBatis源码概述
-
- 1.1 为什么要看MyBatis框架的源码
- 1.2 如何深入学习MyBatis源码
- 1.3 源码分析的5大原则
- 2 MyBatis架构体系深入剖析
-
- 2.1 MyBatis的整体架构体系
- 2.2 MyBatis的工作机制和实现原理
- 2.3 代码回顾
-
- 2.3.1 JDBC代码回顾
- 2.3.2 mybatis代码回顾
- 2.3.3 思考
- 3 整体流程分析
-
- 3.1 获取SqlSession
-
- 3.1.1 接口层
- 3.1.2 流程分析
- 3.2 配置文件解析
-
- 3.2.1 数据处理核心层
- 3.2.2 Configuration对象
- 3.3 SQL解析(SqlSource)
- 3.4SQL执行(Executor)
- 3.5 基础支撑层
-
- 缓存机制
- 数据源/连接池
- 事务管理
- 反射
- IO 模块
- 解析器
- 4 MyBatis的核心配置文件解析原理
-
- 4.1 解析的目的
- 4.2 XML 解析流程
-
- 4.2.1 入口
- 4.2.2 XMLConfigBuilder
- 4.3 mapper映射文件解析原理
-
- 4.3.1 XMLMapperBuilder
- 5 初始化流程
-
- 5.1 相关解析类
- 5.2 映射器关键类
- 5.3 Mapper文件解析
- 6 核心执行器executor详解
-
- 6.1 jdbc回顾
-
- 6.1.1 回顾JDBC执行过程
- 6.1.2 MyBatis对JDBC封装的执行过程
- 6.2 MyBatis的核心执行组件介绍
-
- 6.2.1 四个核心组件
-
- 6.2.2 SqlSession
- 6.2.3 Executor
- 6.2.4 StatementHandler
- 6.3 Executor执行器分析
-
- 6.3.2 Executor继承结构分析
- Executor接口
- Executor的创建:
- 7 MyBatis源码之SQL执行过程
-
- SQL执行的入口分析
- 执行代理逻辑
- 查询语句的执行过程分析
-
- selectOne方法分析
- sql获取
- 参数设置
- SQL执行和结果集的封装
- 更新语句的执行过程分析
-
- sqlsession增删改方法分析:
- sql获取
- 参数设置
- SQL执行
- 8 自定义类型处理器 TypeHandler
-
- 8.1 架构
- 8.2 原理
- 8.3 自定义类型处理器
- 8.4 案例
-
- 8.4.1 DesensitizationTypeHandler
- 8.4.2 在Mapper中配置
- 9 MyBatis进阶之缓存原理
-
- 9.1 一级缓存
-
- 一级缓存示意图:
- 9.2 二级缓存
- CachingExecutor剖析
-
- 缓存执行器流程分析
- 10 日志模块解析
-
- 10.1 概述
- 10.2 日志接口Log
- 10.3 日志工厂LogFactory
- 10.4 日志系统转换
- 11设计模式
-
- 装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)
-
- 什么是装饰器模式
- 角色
- 优缺点
- 适用场景
- 案例
- 11.2 适配器模式(Adapter Pattern)
-
- 11.2.1 什么是适配器模式
- 11.2.2 角色
- 优点
- 缺点
- 适用场景
- 案例
MyBatis核心源码剖析
1 MyBatis源码概述
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,也是当前最流行的java持久层框架之一,它内部封装了jdbc,使开发者只需要关注sql语句本身,而不需要花费精力去处理加载驱动、创建连接、创建statement等繁杂的过程。
采用ORM思想解决了实体和数据库映射的问题,对jdbc进行了封装,屏蔽了jdbc api底层访问细节,使我们不用与jdbc api打交道,就可以完成对数据库的持久化操作。
mybatis通过xml或注解的方式将要执行的各种statement配置起来,并通过java对象和statement中sql的动态参数进行映射生成最终执行的sql语句,最后由mybatis框架执行sql并将结果映射为java对象并返回。
为了更好地学习和理解mybatis背后的设计思路,作为高级开发人员,有必要深入研究了解优秀框架的源码,以便更好的借鉴其思想。同时,框架作为设计模式的主要应用场景,通过研究优秀框架的源码,可以更好的领会设计模式的精髓。
1.1 为什么要看MyBatis框架的源码
通过学习开源框架MyBatis的源码,我们可以深入学习到框架的解析思路和底层的实现原理,掌握源码的剖析办法,快速增加查看源码的经验;
- 在使用MyBatis框架进行开发时,如果你对其源码有所了解,可以最大化地减少出故障的可能;
- 学习源码分析的最大好处是可以开阔思维,提升架构设计能力,通过看源码,看别人如何设计,然后领悟到这样设计的好处,理解优秀的代码设计思想;
- 互联网大厂对有经验的开发人员的招聘,对架构思想和底层的理解能力考察方面比较重视,学习完有助于提高自己的竞争力;
- 可以在深入的学习、剖析后,可以对框架进行改造,进而自定义MyBatis框架,提升架构能力。
1.2 如何深入学习MyBatis源码
- 查看MyBatis官方文档
[https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html](https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html) - 断点跟进源码,参照主线,一步步分析;
- 手动自定义MyBatis框架,加深对框架源码的理解,掌握源码的学习方法,进而提升自身架构能力;
1.3 源码分析的5大原则
- 紧跟入口
- 看图梳理
- 先粗后细
- 精略结合
- 猜想验证
2 MyBatis架构体系深入剖析
2.1 MyBatis的整体架构体系
2.2 MyBatis的工作机制和实现原理
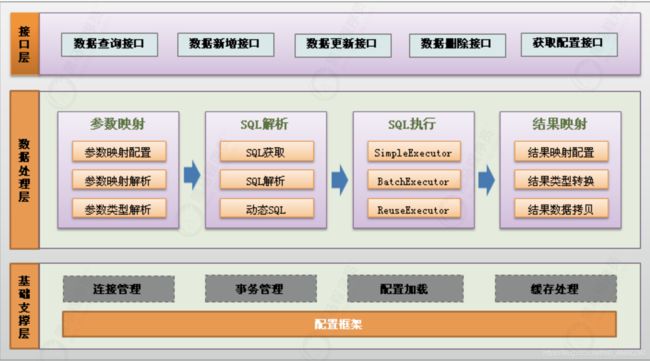
2.2.1 接口层
提供给外部使用的接口API,开发人员通过这些本地API来操纵数据库。
接口层一接收到调用请求就会调用数据处理层来完成具体的数据处理。
2.2.2 数据处理核心层
负责具体的SQL查找、SQL解析、SQL执行和执行结果映射处理等。
它主要的目的是根据调用的请求完成一次数据库操作。
2.2.3 基础支撑层
负责最基础的功能支撑,包括连接管理、事务管理、配置加载和缓存处理,这些都是共用的东西,
将他们抽取出来作为最基础的组件。
为上层的数据处理层提供最基础的支撑。
2.3 代码回顾
2.3.1 JDBC代码回顾
public class JDBCTest {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JDBCTest.class);
private static final Integer p = 101;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、注册驱动
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
// 2、建立连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/employees?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8", "root", "root");
// 3、编写sql,进行预编译
String sql = "SELECT * FROM user";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//ps.setInt(1, p);
// 4、执行查询,得到结果集
ps.execute();
ResultSet rs = ps.getResultSet();
while (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String username = rs.getString("username");
logger.debug("====> id=" + id + "\tname=" + username);
}
//5、关闭事务
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.3.2 mybatis代码回顾
public class MybatisTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.读取配置文件
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//2.创建SqlSessionFactory工厂
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(in);
//关闭输入流
in.close();
//3.使用工厂生产SqlSession对象
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//List userList = session.selectList("com.heima.mapper.UserMapper.findAll");
//4.使用SqlSession创建Dao接口的代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
List<User> userList = userMapper.findAll();
//userMapper.saveUser();
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}
//6.释放资源
session.close();
in.close();
}
}
2.3.3 思考
mybatis为我们做了什么?
- mybatis如何获取数据源连接信息?
- mybatis如何获取到需要执行的sql语句?
- mybatis是如何完成sql执行的?
- mybatis如何完成参数映射和结果封装?
3 整体流程分析
3.1 获取SqlSession
3.1.1 接口层
对应 session 模块。
接口层相对简单,其核心是 SqlSession 接口,该接口中定义了 MyBatis 暴露给应用程序调用的API,也就是上层应用与 MyBatis 交互的桥梁。接口层在接收到调用请求时,会调用核心处理层的相应模块来完成具体的数据库操作。
作用
使用SqlSession接口和Mapper接口通知调用哪个sql还有关联参数。
- 可以实现数据的增/删/改/查接口
- 配置信息维护接口,进行动态的更改配置
3.1.2 流程分析
Mybatis工作的主要顶层API,表示和数据库交互的会话,完成必要数据库增删改查功能
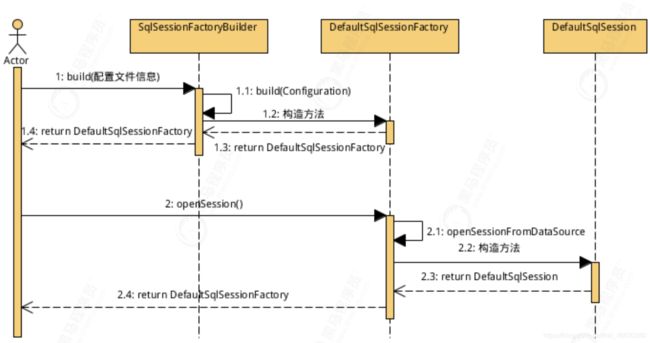
3.2 配置文件解析
3.2.1 数据处理核心层
在核心处理层中,实现了 MyBatis 的核心处理流程。
其中包括 MyBatis 的初始化以及完成一次数据库操作的涉及的全部流程 。
概述
对应 builder 和 mapping 模块。前者为配置解析过程,后者主要为 SQL 操作解析后的映射
解析流程
在 MyBatis 初始化过程中,会加载 mybatis-config.xml 配置文件、映射配置文件以及 Mapper接口中的注解信息,解析后的配置信息会形成相应的对象并保存到 Configuration 对象中。
利用该 Configuration 对象创建 SqlSessionFactory对象。待 MyBatis 初始化之后,开发人员可以通过初始化得到 SqlSessionFactory 创建 SqlSession 对象并完成数据库操作。
3.2.2 Configuration对象
概述:是一个所有配置信息的容器对象
实战分析:Configuration对象涉及到的配置信息分析
简单的理解:MyBatis初始化的过程,就是创建 Configuration对象,加载各种配置信息的过程
3.3 SQL解析(SqlSource)
对应 scripting 模块
MyBatis 中的 scripting 模块,会根据用户传入的实参,解析映射文件中定义的动态 SQL 节点,并形成数据库可执行的 SQL 语句。之后会处理 SQL 语句中的占位符,绑定用户传入的实参负责根据用户传递的parameterObject,动态地生成SQL语句,将信息封装到BoundSql对象中,并返回。
** SqlSource 接口继承体系**

RawSqlSource 负责处理静态 SQL 语句,它们最终会把处理后的 SQL 封装StaticSqlSource 进行返回。
StaticSqlSource 处理包含的 SQL 可能含有 “?” 占位符,可以被数据库直接执行。
DynamicSqlSource 负责处理动态 SQL 语句。
ProviderSqlSource 实现 SqlSource 接口,基于方法上的 @ProviderXXX 注解的 SqlSource 实现类。
3.4SQL执行(Executor)
对应 executor 模块,是MyBatis执行器,是MyBatis 调度的核心,负责SQL语句的生成和查询缓存的维护。
SQL 语句的执行涉及多个组件 ,其中比较重要的是 Executor、StatementHandler、
ParameterHandler 和 ResultSetHandler 。
** Executor主要负责维护一级缓存和二级缓存,并提供事务管理的相关操作,它会将数据库相关操作委托给StatementHandler完成。
** StatementHandler首先通过 ParameterHandler 完成 SQL 语句的实参绑定,然后通过 java.sql.Statement 对象执行 SQL 语句并得到结果集,最后通过 ResultSetHandler 完成结果集的映射,得到结果对象并返回。
** 流程分析**

3.5 基础支撑层
基础支持层,包含整个 MyBatis 的基础模块,这些模块为核心处理层的功能提供了良好的支撑。
对应 logging 包
Mybatis提供了详细的日志输出信息,还能够集成多种日志框架,其日志模块的主要功能就是集成第三方日志框架。
- 设计模式分析:使用的适配器模式分析
缓存机制
对应 cache 包
一级缓存
Session或Statement作用域级别的缓存,默认是Session,BaseExecutor中根据
MappedStatement的Id、SQL、参数值以及rowBound(边界)来构造CacheKey,并使用
BaseExccutor中的localCache来维护此缓存。
实战应用场景分析:默认开启的缓存
二级缓存
全局的二级缓存,通过CacheExecutor来实现,其委托TransactionalCacheManager来保存/获取缓存
实战应用场景分析:缓存的效率以及应用场景
注意点
两级缓存与Mybatis以及整个应用是运行在同一个JVM中的,共享同一块内存,如果这两级缓存中的数据量较大,则可能影响系统中其它功能,需要缓存大量数据时,优先考虑使用Redis、Memcache等缓存产品。
数据源/连接池
对应 datasource 包
Mybatis自身提供了相应的数据源实现,也提供了与第三方数据源集成的接口。
主要实现类是PooledDataSource,包含了最大活动连接数、最大空闲连接数、最长取出时间(避免某个线程过度占用)、连接不够时的等待时间。
事务管理
对应 transaction 包
Mybatis自身对数据库事务进行了抽象,提供了相应的事务接口和简单实现。
注意点:一般地,Mybatis与Spring框架集成,由Spring框架管理事务。
反射
对应 reflection 包
对Java原生的反射进行了很好的封装,提供了简易的API,方便上层调用,并且对反射操作进行了一系列的优化,提高了反射操作的性能。
缓存了类的元数据(MetaClass)
对象的元数据(MetaObject)
IO 模块
对应 io 包
资源加载模块,主要是对类加载器进行封装,确定类加载器的使用顺序,并提供了加载类文件以及其他资源文件的功能 。
解析器
对应 parsing 包
解析器模块,主要提供了两个功能:
- 对 XPath 进行封装,为 MyBatis 初始化时解析 mybatis-config.xml 配置文件以及映射配置文件提供支持。
- 为处理动态 SQL 语句中的占位符提供支持。
4 MyBatis的核心配置文件解析原理
在 MyBatis 初始化过程中,会加载 mybatis-config.xml 配置文件、映射配置文件以及 Mapper接口中的注解信息,解析后的配置信息会形成相应的对象并保存到 Configuration 对象中
4.1 解析的目的
通过资源类Resources读入“SqlMapConfig.xml”文件
使用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类生成我们需要的SqlSessionFactory类。
mybatis解析配置文件最本质的目的是为了获得Configuration对象;
然后,利用该 Configuration 对象创建 SqlSessionFactory对象。待 MyBatis 初始化之后,可以通过初始化得到 SqlSessionFactory 创建 SqlSession 对象并完成数据库操作。
4.2 XML 解析流程
4.2.1 入口
MyBatis 的初始化流程的入口是 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 的 build 方法:
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
//对XMLConfigBuilder进行基础环境配置
//创建xmlconfigbuilder对象
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
//解析配置文件的入口
//执行xml解析,创建Defaultsqlsessionfactory对象
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
4.2.2 XMLConfigBuilder
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLConfigBuilder ,继承 BaseBuilder 抽象类,XML 配
置构建器;
主要负责解析 mybatis-config.xml 配置文件:
//构造设置Propertise
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
//创建Configuration对象
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
//设置Configuration的variables属性
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
this.parsed = false;
this.environment = environment;
this.parser = parser;
}
//判断是否解析过
public Configuration parse() {
//若已解析,抛出builderException异常
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
//标记已解析
parsed = true;
//解析XML Configuration节点
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
//解析configuration节点
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
// issue #117 read properties first
//解析new Configuration()
配置文件解析的本质就是获得Configuration对象
很多需要的成员变量需要根据 XML 配置文件解析后来赋值
parser.parse()
该函数就是XML解析的核心
解析全局配置文件,调用parse.evalNode()方法,将指定路径的config配置文件转换为XNode对象调用parseConfiguration()方法逐步解析配置文件中的各个节点
build(configuration)
该函数用来创建一个具体的SqlSessionFactory对象。
创建DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象, 并将configuration赋值给相应的成员变量
核心解析逻辑
org.apache.ibatis.parsing.XPathParser ,基于 Java XPath 解析器,用于解析 MyBatis
mybatis-config.xml 和 Mapper.xml 等 XML 配置文件。属性如下:
public class XPathParser {
// XML Document对象
private final Document document;
//是否校验
private boolean validation;
//XML实体解析器
private EntityResolver entityResolver;
//变量 Properties对象
private Properties variables;
// java xpath对象
private XPath xpath;
//构造Xpathparser对象
public XPathParser(String xml, boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
commonConstructor(validation, variables, entityResolver);
this.document = createDocument(new InputSource(new StringReader(xml)));
}
//公用的构造方法逻辑
private void commonConstructor(boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
this.validation = validation;
this.entityResolver = entityResolver;
this.variables = variables;
XPathFactory factory = XPathFactory.newInstance();
this.xpath = factory.newXPath();
}
//创建Document对象-->将XML文件解析成Document对象
private Document createDocument(InputSource inputSource) {
// important: this must only be called AFTER common constructor
try {
//创建DocumentbuilderFactory对象
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
factory.setFeature(XMLConstants.FEATURE_SECURE_PROCESSING, true);
factory.setValidating(validation);//设置是否验证XML
factory.setNamespaceAware(false);
factory.setIgnoringComments(true);
factory.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(false);
factory.setCoalescing(false);
factory.setExpandEntityReferences(true);
//创建DocumentBuilder对象
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
builder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver); //设置实体解析器
builder.setErrorHandler(new ErrorHandler() {
@Override
public void error(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void fatalError(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void warning(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
// NOP
}
});
//解析XML文件
return builder.parse(inputSource);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error creating document instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperEntityResolver ,实现 EntityResolver 接口,
MyBatis 自定义 EntityResolver 实现类,用于加载本地的 mybatis-3-config.dtd 和 mybatis-3- mapper.dtd 这两个 DTD 文件。代码如下:
public class XMLMapperEntityResolver implements EntityResolver {
private static final String IBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM = "ibatis-3-config.dtd";
private static final String IBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM = "ibatis-3-mapper.dtd";
private static final String MYBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM = "mybatis-3-config.dtd";
private static final String MYBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM = "mybatis-3-mapper.dtd";
private static final String MYBATIS_CONFIG_DTD = "org/apache/ibatis/builder/xml/mybatis-3-config.dtd";
private static final String MYBATIS_MAPPER_DTD = "org/apache/ibatis/builder/xml/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd";
@Override
public InputSource resolveEntity(String publicId, String systemId) throws SAXException {
try {
if (systemId != null) {
String lowerCaseSystemId = systemId.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
//本地 mybatis-config.dtd文件
if (lowerCaseSystemId.contains(MYBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM) || lowerCaseSystemId.contains(IBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM)) {
return getInputSource(MYBATIS_CONFIG_DTD, publicId, systemId);
/本地 mybatis-mapper.dtd文件
} else if (lowerCaseSystemId.contains(MYBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM) || lowerCaseSystemId.contains(IBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM)) {
return getInputSource(MYBATIS_MAPPER_DTD, publicId, systemId);
}
}
return null;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SAXException(e.toString());
}
}
private InputSource getInputSource(String path, String publicId, String systemId) {
InputSource source = null;
if (path != null) {
try {
//创建inputsource对象
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(path);
source = new InputSource(in);
//设置publicId,systemId属性
source.setPublicId(publicId);
source.setSystemId(systemId);
} catch (IOException e) {
// ignore, null is ok
}
}
return source;
}
}
4.3 mapper映射文件解析原理
其实XMLConfigBuilder在解析核心配置文件中mappers节点时,会进一步解析mapper映射文件。
加载 Mapper 映射配置文件这个步骤的主体是 XMLMapperBuilder
mapper文件示意:

4.3.1 XMLMapperBuilder
【解析xml文件中的节点】
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperBuilder ,继承 BaseBuilder 抽象类,Mapper
XML 配置构建器,主要负责解析 Mapper 映射配置文件
配置package,会遍历该包下所有的类
指定mapper文件的路径resource/url/class
具体解析逻辑通过XMLMapperBuilder类来完成,解析xml文件中的节点
parse() 方法
public void parse() {
// <1> 判断当前 Mapper 是否已经加载过
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
//解析mapper标签
// <2> 解析 `configurationElement(XNode context) 方法
解析 节点。
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
// <1> 获得 namespace 属性
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.isEmpty()) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
// <1> 设置 namespace 属性
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
// <2> 解析 cacheRefElement(XNode context) 方法
解析 节点。
private void cacheRefElement(XNode context) {
if (context != null) {
// <1> 获得指向的 namespace 名字,并添加到 configuration 的 cacheRefMap 中
configuration.addCacheRef(builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(), context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
// <2> 创建 CacheRefResolver 对象,并执行解析
CacheRefResolver cacheRefResolver = new CacheRefResolver(builderAssistant, context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
try {
cacheRefResolver.resolveCacheRef();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// <3> 解析失败,添加到 configuration 的 incompleteCacheRefs 中
configuration.addIncompleteCacheRef(cacheRefResolver);
}
}
}
cacheElement(XNode context) 方法
private void cacheElement(XNode context) {
if (context != null) {
// <1> 获得负责存储的 Cache 实现类
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
// <2> 获得负责过期的 Cache 实现类
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
// <3> 获得 flushInterval、size、readWrite、blocking 属性
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
// <4> 获得 Properties 属性
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// <5> 创建 Cache 对象
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}
resultMapElements(List list) 方法
解析 节点们。代码如下
// 解析 buildStatementFromContext(List list) 方法
解析 、 、 、 节点们。代码如下
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list) {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
buildStatementFromContext(list, null);
}
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
// <1> 遍历 XMLStatementBuilder
【解析mapper.xml文件中的crud节点】
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLStatementBuilder ,继承 BaseBuilder 抽象类,
Statement XML 配置构建器,主要负责解析 Statement 配置,即 、 、 、 标签。
开启SQL节点解析,源码开始解析的入口parseStatementNode
public void parseStatementNode() {
// <1> 获得 id 属性,编号。
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
// <2> 获得 databaseId , 判断 databaseId 是否匹配
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
//获取标签内容
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
//将标签内容转换成对应的执行类型
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
//判断释放是 select 类型的sql
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: and were parsed and removed)
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
// <13.1> 优先,从 configuration 中获得 KeyGenerator 对象。如果存在,意味着是 databaseIdMatchesCurrent(String id, String databaseId, String
requiredDatabaseId) 方法
判断 databaseId 是否匹配。
private boolean databaseIdMatchesCurrent(String id, String databaseId, String requiredDatabaseId) {
// 如果不匹配,则返回 false
if (requiredDatabaseId != null) {
return requiredDatabaseId.equals(databaseId);
}
// 如果未设置 requiredDatabaseId ,但是 databaseId 存在,说明还是不匹配,则返回 false
if (databaseId != null) {
return false;
}
}// 判断是否已经存在
id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
if (!this.configuration.hasStatement(id, false)) {
return true;
}
// skip this statement if there is a previous one with a not null databaseId
// 若存在,则判断原有的sqlFragment是否databaseId 为空。因为,当前databaseId为空,这样 两者才能匹配。
MappedStatement previous = this.configuration.getMappedStatement(id, false); // issue #2
return previous.getDatabaseId() == null;
}
** XMLIncludeTransformer**
【解析节点】
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLIncludeTransformer ,XML 标签的转
换器;
解析节点,该过程会将其替换成节点中定义的SQL片段,并将其中的”${xxx}“占位符替换为真实的参数
#applyIncludes(Node source) 方法
将 标签,替换成引用的 。
public void applyIncludes(Node source) {
// <1> 创建 variablesContext ,并将 configurationVariables 添加到其中
Properties variablesContext = new Properties();
Properties configurationVariables = configuration.getVariables();
Optional.ofNullable(configurationVariables).ifPresent(variablesContext::putAll);
// <2> 处理 applyIncludes(Node source, final Properties variablesContext, boolean included)方 法
使用递归的方式,将 标签,替换成引用的 。代码如下:
private void applyIncludes(Node source, final Properties variablesContext, boolean included) {
// <1> 如果是 findSqlFragment(String refid, Properties variables)方法
获得对应的 节点。代码如下:
private Node findSqlFragment(String refid, Properties variables) {
// 因为 refid 可能是动态变量,所以进行替换
refid = PropertyParser.parse(refid, variables);
// 获得完整的 refid ,格式为 "${namespace}.${refid}"
refid = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(refid, true);
try {
// 获得对应的 ** SqlSourceBuilder创建 SqlSource**
org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlSource ,SQL 来源接口。
代表从 Mapper XML 或方法注解上,读取的一条 SQL 内容。代码如下:
public interface SqlSource {
/**
* 根据传入的参数对象,返回 BoundSql 对象
*
* @param parameterObject 参数对象
* @return BoundSql 对象
*/
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
}
- RawSqlSource 负责处理静态 SQL 语句,它们最终会把处理后的 SQL 封装 StaticSqlSource 进行返回。
使用 #{} 表达式,或者不使用任何表达式的情况,所以它是静态的,仅需要在构造方法中,
直接生成对应的 SQL 。
- StaticSqlSource处理包含的 SQL 可能含有 “?” 占位符,可以被数据库直接执行。
- DynamicSqlSource负责处理动态 SQL 语句。
使用了 OGNL 表达式,或者使用了 ${} 表达式的 SQL ,所以它是动态的,需要在每次执行
#getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) 方法,根据参数,生成对应的 SQL 。
- ProviderSqlSource 实现 SqlSource 接口,基于方法上的 @ProviderXXX 注解的 SqlSource实现类。
org.apache.ibatis.builder.SqlSourceBuilder ,SqlSource 构建器。
负责将 SQL 语句中的 #{} 替换成相应的 ? 占位符,并获取该 ? 占位符对应的 ParameterMapping对象。
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
// <1> 创建 ParameterMappingTokenHandler 对象
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters);
// <2> 创建 GenericTokenParser 对象
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
String sql;
// <3> 执行解析
if (configuration.isShrinkWhitespacesInSql()) {
sql = parser.parse(removeExtraWhitespaces(originalSql));
} else {
sql = parser.parse(originalSql);
}
// <4> 创建 StaticSqlSource 对象
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}
//注意:ParameterMappingTokenHandler 是 SqlSourceBuilder 的内部私有静态类。
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
// <1> 构建 ParameterMapping 对象,并添加到 parameterMappings 中
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
// <2> 返回 ? 占位符
return "?";
}
5 初始化流程
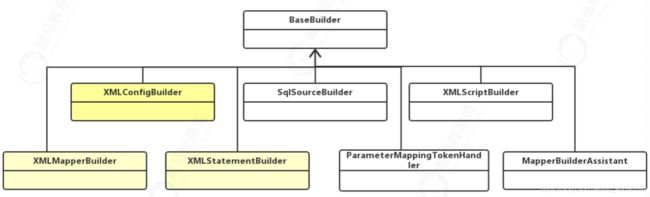
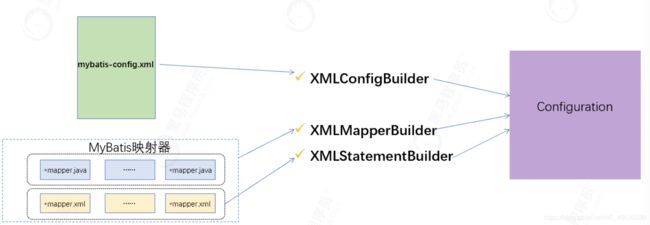
5.1 相关解析类
XMLConfigBuilder、 XMLMapperBuilder、 XMLStatementBuilder 这三个类在配置文件加载过程中非常重要,具体分工如下图所示:
5.1.1 BaseBuilder
所有解析器的父类,包含配置文件实例,为解析文件提供的一些通用的方
5.1.2 XMLConfigBuilder
主要负责解析mybatis-config.xml;
5.1.3 XMLMapperBuilder
主要负责解析映射配置文件;
5.1.4 XMLStatementBuilder
主要负责解析映射配置文件中的SQL节点;
5.2 映射器关键类
5.2.1 Configuration
Mybatis启动初始化的核心就是将所有xml配置文件信息加载到Configuration对象中,
Configuration是单例的,生命周期是应用级的;
5.2.2 MapperRegistry
mapper接口动态代理工厂类的注册中心。在MyBatis中,通过mapperProxy实现
InvocationHandler接口,MapperProxyFactory用于生成动态代理的实例对象;
5.2.3 ResultMap
用于解析mapper.xml文件中的resultMap节点,使用ResultMapping来封装id,result等子元素;
5.2.4 MappedStatement
用于存储mapper.xml文件中的select、insert、update和delete节点,同时还包含了这些节点的很多重要属性;
5.2.5 SqlSource
mapper.xml文件中的sql语句会被解析成SqlSource对象,经过解析SqlSource包含的语句最终仅仅包含?占位符,可以直接提交给数据库执行
5.3 Mapper文件解析
逐一读取Mapper.xml文件内的各个元素。为了更为直观的了解xml元素至Mybatis的内部数据结构

6 核心执行器executor详解
6.1 jdbc回顾
6.1.1 回顾JDBC执行过程
添加jar包 -> 获得连接 -> 预编译SQL -> 执行SQL,读取结果 -> 关闭事务
public static void main(String[]args)throws Exception{
// 1、注册驱动
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
// 2、建立连接
Connection con=
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?
useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=GMT", " root", " root");
// 3、编写sql,进行预编译
String sql=" select * from tb_brand;";
PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement(sql);
// 4、执行查询,得到结果集
ResultSet rs=ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
int bid=rs.getInt("bid");
String bname=rs.getString("bname");
System.out.println("====> bid="+bid+"\tbname="+bname);
}
//5、关闭事务
rs.close();
ps.close();
con.close();
}
6.1.2 MyBatis对JDBC封装的执行过程
6.2 MyBatis的核心执行组件介绍
在Mybatis中,SqlSession对数据库的操作,将委托给执行器Executor来完成都将委托给执行器Executor来完成;
Mybatis执行过程,主要的执行模块是: SqlSession->Executor->StatementHandler->数据库
6.2.1 四个核心组件
- 动态代理 MapperProxy
- SQL会话 SqlSession
- 执行器 Executor
- JDBC处理器 StatementHandler
6.2.2 SqlSession
SqlSession采用了门面模式方便来让我们使用。他不能跨线程使用,一级缓存生命周期和它一致;
基本功能:增删改查基本的操作功能;
辅助功能:提交、关闭会话;
门面模式:提供一个统一的门面接口API,使得系统更加容易使用。
6.2.3 Executor
Executor 主要负责维护一级缓存和二级缓存,并提供事务管理的相关操作,它会将数据库相关操作委托给 StatementHandler完成。
基本功能:改、查、维护缓存;
辅助功能:提交、关闭执行器、批处理刷新;
6.2.4 StatementHandler
经过执行器处理后交给了StatementHandler(声明处理器);
StatementHandler 首先通过 ParameterHandler 完成 SQL 语句的实参绑定,然后通过
java.sql.Statement 对象执行 SQL 语句并得到结果集,最后通过 ResultSetHandler 完成结果集的映射,得到结果对象并返回。
主要作用就是:参数处理、结果处理;
6.3 Executor执行器分析
JDBC有三种执行器分别是
Statement
简单执行器:基本功能:执行静态SQL
PreparedStatement
预处理执行器:设置预编译,防止SQL注入
CallableStatement
存储过程执行器:设置出参、读取参数(用于执行存储过程)
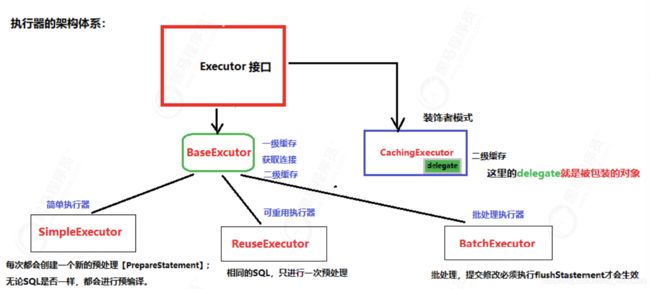
6.3.2 Executor继承结构分析
- SimpleExecutor(简单执行器)、
- ResuseExecutor(可重用执行器)、
- BathExecutor(批处理执行器)
这三个执行器继承了一个BaseExecutor(基础执行器),而这个基础执行器实现了Executor接口,其中简单执行器是默认的执行器。
其实还有一种执行器CachingExecutor(二级缓存执行器)你开启二级缓存则会实例化它,在
BaseExecutor 的基础上,实现二级缓存功能。 (注意: BaseExecutor 的本地缓存,就是一级缓存。)
Executor接口
org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor ,执行器接口。
主要定义了以下内容:
读和写操作相关的方法
事务相关的方法
缓存相关的方法
设置延迟加载的方法
设置包装的 Executor 对象的方法
public interface Executor {
// 空 ResultHandler 对象的枚举
ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null;
// 更新 or 插入 or 删除,由传入的 MappedStatement 的 SQL 所决定
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
// 查询,带 ResultHandler + CacheKey + BoundSql
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
// 查询,带 ResultHandler
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
// 查询,返回值为 Cursor
<E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException;
// 刷入批处理语句
List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException;
// 提交事务
void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException;
// 回滚事务
void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException;
// 创建 CacheKey 对象
CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql);
// 判断是否缓存
boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key);
// 清除本地缓存
void clearLocalCache();
// 延迟加载
void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType);
// 获得事务
Transaction getTransaction();
// 关闭事务
void close(boolean forceRollback);
// 判断事务是否关闭
boolean isClosed();
// 设置包装的 Executor 对象
void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor);
}
BaseExecutor(基础执行器)
基础执行器:维护一级缓存,是simple、reuse、batch这三个执行器的父类。主要逻辑是维护缓存,其他实现交给子类。 org.apache.ibatis.executor.BaseExecutor 实现 Executor 接口,提供骨架方法,从而使子类只要实现指定的几个抽象方法即可。
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(BaseExecutor.class);
//事务对象
protected Transaction transaction;
//包装的 Executor 对象
protected Executor wrapper;
//DeferredLoad( 延迟加载 ) 队列
protected ConcurrentLinkedQueue<DeferredLoad> deferredLoads;
//本地缓存,即一级缓存
protected PerpetualCache localCache;
//本地输出类型的参数的缓存
protected PerpetualCache localOutputParameterCache;
protected Configuration configuration;
//记录嵌套查询的层级
protected int queryStack;
//是否关闭
private boolean closed;
// clearLocalCache() 方法,清理一级(本地)缓存
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
if (!closed) {
// 清理 localCache
localCache.clear();
// 清理 localOutputParameterCache
localOutputParameterCache.clear();
}
}
//createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) 方法,创建 CacheKey 对象
// isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key) 方法,判断一级缓存是否存在
// query方法
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//封装SQL
// <1> 获得 BoundSql 对象
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
//生成缓存key // <2> 创建 CacheKey 对象
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
// <3> 查询
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
// update方法
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId());
// <1> 已经关闭,则抛出 ExecutorException 异常
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// <2> 清空本地缓存
clearLocalCache();
// <3> 执行写操作
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
SimpleExecutor(简单执行器)
每次读或写操作都会创建一个新的预处理器(PrepareStatement);
每次执行的的SQL都会进行一次预编译;
执行完成后,关闭该 Statement 对象。
org.apache.ibatis.executor.SimpleExecutor ,继承 BaseExecutor 抽象类,简单的 Executor 实现类。
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
super(configuration, transaction);
}
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//生成handler对象
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//获取Statement对象
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
protected <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, null, boundSql);
Statement stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
Cursor<E> cursor = handler.queryCursor(stmt);
stmt.closeOnCompletion();
return cursor;
}
@Override
public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
//获取连接 并设置是否自动提交
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
//设置参数
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
}
ReuseExecutor(可重用执行器)
每次开始读或写操作,以sql作为key,查找Statement对象优先从缓存中获取对应的
Statement 对象。如果不存在,才进行创建。( 只要是相同的SQL只会进行一次预处理)
执行完成后,不关闭该 Statement 对象,而是放置于Map
使用。
其它的,和 SimpleExecutor 是一致的。
原理:
//可重用的执行器内部用了一个map,用来缓存SQL语句对应的Statement对象
//Key是我们的SQL语句,value是我们的Statement对象
private final Map<String, Statement> statementMap = new HashMap<>();
org.apache.ibatis.executor.ReuseExecutor ,继承 BaseExecutor 抽象类,可重用的 Executor实现类。
主要方法
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// 存在
if (hasStatementFor(sql)) {
// <1.1> 从缓存中获得 Statement 或 PrepareStatement 对象
stmt = getStatement(sql);
// <1.2> 设置事务超时时间
applyTransactionTimeout(stmt);
} else {
// 不存在 <2.1> 获得 Connection 对象
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// <2.2> 创建 Statement 或 PrepareStatement 对象
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// <2.3> 添加到缓存中
putStatement(sql, stmt);
}
// <2> 设置 SQL 上的参数,例如 PrepareStatement 对象上的占位符
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
- ReuseExecutor 考虑到重用性,但是 Statement 最终还是需要有地方关闭。答案就在
#doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) 方法中。而 BaseExecutor 在关闭 #close() 方 法中,最终也会调用该方法,从而完成关闭缓存的 Statement 对象们 - BaseExecutor 在提交或者回滚事务方法中,最终也会调用该方法,也能完成关闭缓存的 Statement 对象们。
** BatchExecutor(批处理执行器)**
- 批处理只对增删改SQL有效(没有select,JDBC批处理不支持select);
- 将所有增删改sql都添加到批处理中(addBatch()),等待统一执行(executeBatch()),它缓存了多个Statement对象,每个Statement对象都是addBatch()完毕后,等待逐一执行
executeBatch()批处理的; - 执行sql需要满足三个条件才能使用同一个Statement(使用同一个Statement是为了压缩体 积、减少SQL预处理)
1.sql相同
2.同一个MappedStatement(sql标签的配置都在这里面)
3.执行的顺序必须是连续的
org.apache.ibatis.executor.BatchExecutor ,继承 BaseExecutor 抽象类,批量执行的
Executor 实现类。
public class BatchExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
public static final int BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE = Integer.MIN_VALUE + 1002;
private final List<Statement> statementList = new ArrayList<>();
private final List<BatchResult> batchResultList = new ArrayList<>();
private String currentSql;
private MappedStatement currentStatement;
public BatchExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
super(configuration, transaction);
}
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
final Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
final StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameterObject, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
final BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql();
final String sql = boundSql.getSql();
final Statement stmt;
// 如果匹配最后一次 currentSql 和 currentStatement ,则聚合到 BatchResult 中
if (sql.equals(currentSql) && ms.equals(currentStatement)) {
//获得最后一次的 Statement 对象
int last = statementList.size() - 1;
stmt = statementList.get(last);
//设置事务超时时间
applyTransactionTimeout(stmt);
//设置 SQL 上的参数,例如 PrepareStatement 对象上的占位符
handler.parameterize(stmt);// fix Issues 322
//获得最后一次的 BatchResult 对象,并添加参数到其中
BatchResult batchResult = batchResultList.get(last);
batchResult.addParameterObject(parameterObject);
} else {
//如果不匹配最后一次 currentSql 和 currentStatement ,则新建 BatchResult 对象
Connection connection = getConnection(ms.getStatementLog());
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
//设置 SQL 上的参数,例如 PrepareStatement 对象上的占位符
handler.parameterize(stmt); // fix Issues 322
//重新设置 currentSql 和 currentStatement
currentSql = sql;
currentStatement = ms;
//添加 Statement 到 statementList 中
statementList.add(stmt);
// 创建 BatchResult 对象,并添加到 batchResultList 中
batchResultList.add(new BatchResult(ms, sql, parameterObject));
}
//批处理
handler.batch(stmt);
return BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE;
}
- doUpdate代码上 if (sql.equals(currentSql) &&ms.equals(currentStatement)) 可
以看出上一个添加的是否是这个sql(currentSql)并且是同一个MappedStatement
currentStatement(映射语句); - 满足条件就将参数放到当前这个BatchResult对象中的参数。属性是(parameterObject)
【batchResult.addParameterObject(parameterObject);】 - 不满足条件则获取一个Statement实例 再实例化BatchResult对象。最后放到list中去,再给current和MappedStatement currentStatement赋值
- 批处理提交必须执行flushStatements才会生效(会将一个个的Statement提交)可以减少与数 据库交互次数
Executor的创建:
在上面的学习中,我们已经理解了各种 Executor 的实现代码。
那么,Executor 对象究竟在 MyBatis 中,是如何被创建的呢?
其实Configuration 类中,提供 newExecutor 方法,代码如下:
// 创建 Executor 对象 -----------------在创建SqlSession执行
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
// <1> 获得执行器类型 //可以通过在 mybatis-config.xml 配置 - 我们可以在 ExecutorType 中看到,枚举了三种类型: SIMPLE 、REUSE 、BATCH
- 如果没有指定类型,默认为 SimpleExecutor 对象
- 如果开启缓存,创建 CachingExecutor 对象,进行包装
7 MyBatis源码之SQL执行过程
SQL执行的入口分析
为Mapper接口创建代理对象
// 方式1:
User user = session.selectOne("com.itheima.dao.UserMapper.findUserById", 101);
// 方式2:
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> userList = mapper.findAll();
执行代理逻辑
session是DefaultSqlSession类型的,因为sqlSessionFactory默认生成的SqlSession是
DefaultSqlSession类型。
selectOne()会调用selectList()。
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// CURD操作是交给Excetor去处理的
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
获取代理对象:
//DefaultSqlSession类 ====================>
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
// Configuration类 ====================>
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
//MapperRegistry ----> apperProxyFactory.newInstance ====================>
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//从缓存中获取该Mapper接口的代理工厂对象
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>)
knownMappers.get(type);
//如果该Mapper接口没有注册过,则抛异常
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the
MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
//【使用代理工厂创建Mapper接口的代理对象】
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e,
e);
}
}
//MapperProxyFactory --->此时生成代理对象 ====================>
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
//Mybatis底层是调用JDK的Proxy类来创建代理实例
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new
Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession,
mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
代理对象执行逻辑
//代理对象执行的方法,代理以后,所有Mapper的方法调用时,都会调用这个invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
//如果是Object方法,则调用方法本身
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
//调用接口方法:根据被调用接口的Method对象,从缓存中获取MapperMethodInvoker对象
//apper接口中的每一个方法都对应一个MapperMethodInvoker对象,而MapperMethodInvoker 对象里面的MapperMethod保存着对应的SQL信息和返回类型以完成SQL调用
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
//缓存Invoker
//获取缓存中MapperMethodInvoker,如果没有则创建一个,而MapperMethodInvoker内部封装这一 个MethodHandler
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(methodCache, method, m -> {
if (m.isDefault()) {
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
//会走这个方法
//如果调用的普通方法(非default方法),则创建一个PlainMethodInvoker并放 入缓存,其中MapperMethod保存对应接口方法的SQL以及入参和出参的数据类型等信息
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
//调用Invok方法
// 当cacheInvoker返回了PalinMethodInvoker实例之后,紧接着调用了这个实例的 PlainMethodInvoker:invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
//Mybatis实现接口方法的核心: MapperMethod::execute方法:
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
// 将args进行解析,如果是多个参数则,则根据@Param注解指定名称将参数转换为Map, 如果是封装实体则不转换
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
//解析参数,因为SqlSession::selectOne方法参数只能传入一个,但是我们 Mapper中可能传入多个参数,
//有可能是通过@Param注解指定参数名,所以这里需要将Mapper接口方法中的多个参 数转化为一个ParamMap,
//也就是说如果是传入的单个封装实体,那么直接返回出来;如果传入的是多个参数, 实际上都转换成了Map
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//可以看到动态代理最后还是使用SqlSession操作数据库的
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
// 此时我们发现: 回到了sqlsession中
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List<E> result;
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// issue #510 Collections & arrays support
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
} else {
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
}
return result;
}
查询语句的执行过程分析
selectOne方法分析
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
// //selectOne()会调用selectList()。
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
sql获取
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获取绑定的sql命令,比如"SELECT * FROM xxx"
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
//真正执行query操作的是SimplyExecutor代理来完成的,SimplyExecutor的父类BaseExecutor的 query方法中:
// BaseExecutor类:SimplyExecutor的父类 =================>
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
//是否必须刷新缓存
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
//清除本地缓存
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
//localCache是一级缓存,如果找不到就调用queryFromDatabase从数据库中查找
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
//第一次,没有缓存,所以会调用queryFromDatabase方法来执行查询。
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
//设置执行占位
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 查询
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//生成handler对象
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//获取Statement对象
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 2:SQL查询操作和结果集的封装
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
参数设置
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
//获取连接 并设置是否自动提交
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 调用prepare方法来获取一个Statement
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
//设置参数
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
// RoutingStatementHandler ============================>
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
delegate.parameterize(statement);
}
// PreparedStatementHandler ============================>
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
// DefaultParameterHandler ============================> 此时参数设置成功
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
//获取参数映射列表
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
//获取TypeHandler
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
//获取JDBCType
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
//设置参数
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
SQL执行和结果集的封装
// RoutingStatementHandler ============================>
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
return delegate.query(statement, resultHandler);
}
// PreparedStatementHandler ============================>
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 这里就到了熟悉的PreparedStatement了
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
// 执行SQL查询操作
ps.execute();
// 结果交给ResultHandler来处理
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
// DefaultResultSetHandler类(封装返回值,将查询结果封装成Object对象)
@Override
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
//获取结果集包装
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
//获取需要包装的对象
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
//包装结果集
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
更新语句的执行过程分析
- Executor 的 update 方法分析
insert、update 和 delete 操作都会清空一二级缓存 - doUpdate 方法
- PreparedStatementHandler 的 update 方法
默认是创建PreparedStatementHandler,然后执行prepareStatement方法。
执行结果为受影响行数
执行更新语句的SQL
sqlsession增删改方法分析:
@Override
public int insert(String statement) {
return insert(statement, null);
}
@Override
public int insert(String statement, Object parameter) {
return update(statement, parameter);
}
@Override
public int update(String statement) {
return update(statement, null);
}
@Override
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
@Override
public int delete(String statement) {
return update(statement, null);
}
@Override
public int delete(String statement, Object parameter) {
return update(statement, parameter);
}
sql获取
// CachingExecutor ===============>
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
// 执行增删改,清除缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 跳转BaseExecutor
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
BaseExecutor ===============>
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 清除 LocalCache 一级缓存
clearLocalCache();
//执行 doUpdate
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
// SimpleExecutor ===============>
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
// 【1】.获取statement,并进行参数映射
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 【2】.handler.update()方法执行具体sql指令
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
参数设置
// SimplyExecutor类 ============================> //【1】 prepareStatement
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
//获取连接 并设置是否自动提交
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 使用connection对象信息创建statement,并将超时时间绑定
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
//设置参数 parameterize方法设置sql执行时候需要的参数
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
// RoutingStatementHandler ============================>
// PreparedStatementHandler ============================>
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
// DefaultParameterHandler ============================> 此时参数设置成功
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
//获取参数映射列表
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
//获取TypeHandler
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
//获取JDBCType
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
//设置参数
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
SQL执行
// RoutingStatementHandler ============================>
@Override
public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
return delegate.update(statement);
}
// PreparedStatementHandler ============================>
@Override
public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
// 这里就是底层JDBC的PreparedStatement 操作了
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
// 执行SQL增删改操作
ps.execute();
// 获取影响的行数
int rows = ps.getUpdateCount();
Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject();
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator();
keyGenerator.processAfter(executor, mappedStatement, ps, parameterObject);
// 返回影响的行数
return rows;
}
mybatis执行SQL的流程都是:
1.根据statement字符串从configuration中获取对应的mappedStatement;
2.根据获取的mappedStatement创建相应的Statement实例;
3.根据传入的参数对statement实例进行参数设置;
4.执行statement并执行后置操作;
8 自定义类型处理器 TypeHandler
当大家使用mybatis作为持久层框架时,在存储和查询数据时,只需要在mapper.xml文件中配置好对应字段的JdbcType和JavaType,mybatis就可以帮我们转化对应的类型。这背后是有mybatis内置的类型转换器做转换(可见源码TypeHandlerRegistry)。但是有时候,我们会对某些字段做特殊处理,比如加密和解密、状态转换、类型转换等。这个时候我们需要自定义类型转换器。
8.1 架构

从上面的图中可以看出MyBatis中整个类型处理器实现架构,TypeHandler接口定义了类型处理器,而TypeReference抽象类则定义了一个类型引用,用于引用一个泛型类型(此处很抽象,不好理解,详见后续解析),BaseTypeHandler则是类型处理器的基础,是所有类型处理器的公共模块,几乎所有的类型处理器都是通过直接继承BaseTypeHandler来实现的。
8.2 原理
使用场景:mybatis在预处理语句(PreparedStatement)中设置一个参数时,或者从结果集
(ResultSet)中取出一个值时,都会用到TypeHandler。它的作用就是将java类型(javaType)转化为jdbc类型(jdbcType),或者将jdbc类型(jdbcType)转化为java类型(javaType)。
8.3 自定义类型处理器
实现TypeHandler接口或者继承BaseTypehandler
TypeHandler是一个接口,它定义了如下四个方法,实现类必须去实现,方法如下
public interface TypeHandler<T> {
void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException;
T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException;
T getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
T getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
}
setParameter:通过preparedStatement对象设置参数,将T类型的数据存入数据库。
getResult:通过列名或者下标来获取结果数据,也可以通过CallableStatement获取数据。
8.4 案例
对银行卡号进行脱敏,一个银行卡号19位例如 4424634402341054214 脱敏后需要变成
442463*********4214 ,前六后四保留,其他位用 * 代替,因为我们们的jdbc类型以及java类型都是String,我们可以继承 StringTypeHandler 来实现
8.4.1 DesensitizationTypeHandler
public class DesensitizationTypeHandler extends StringTypeHandler {
/**
* 根据列明获取结果
* @param rs
* @param columnName
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Override
public String getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName)
throws SQLException {
return CommonUtils.cardId(rs.getString(columnName));
}
/**
* 根据下标获取结果
* @param rs
* @param columnIndex
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Override
public String getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex)
throws SQLException {
return CommonUtils.cardId(rs.getString(columnIndex));
}
}
8.4.2 在Mapper中配置
<resultMap id="userResultMap" type="com.heima.domain.User">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<result column="address" property="address"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="card_id" property="cardId" typeHandler="com.heima.typeHandel.DesensitizationTypeHandler"/>
resultMap>
9 MyBatis进阶之缓存原理
Mybatis 提供了缓存策略,通过缓存策略来减少数据库的查询次数,从而提高性能。
Mybatis的缓存分为:一级缓存和二级缓存
9.1 一级缓存
当我们使用MyBatis开启一次和数据库的会话,MyBatis会创建出一个SqlSession对象表示一次数据库会话,建立一个简单的缓存,将每次查询到的结果缓存起来,当下次查询的时候,如果判断先前有个完全一样的查询,会直接从缓存中直接将结果取出,返回给用户,不需要再进行一次数据库查询了。
说明:对于会话(Session)级别的数据缓存,我们称之为一级数据缓存,简称一级缓存。
特点:
一级缓存是默认开启的
一级缓存是基于SqlSession生命周期的
一级缓存示意图:
SqlSession -- DefaultSqlSession
Executor -- BaseExecutor -- “PerpetualCache localCache”
测试一级缓存:
测试1: 测试多次查询同一条数据
@Test
public void testLocalCache01() {
User user = userMapper.findUserById(101);
System.out.println("第一次查询:"+user);
User user2 = userMapper.findUserById(101);
System.out.println("第二次查询:"+user2);
}
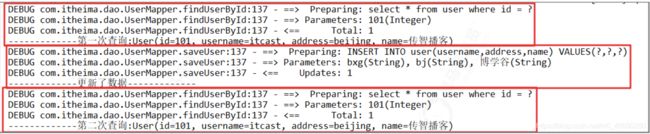
查询结果查看:
调用了两次dao查询方法,但只执行了一条sql语句,说明第二次查询获得的对象是从缓存中取的,并未执行sql语句

测试2:测试修改后再查询:
/**
* 在两次查询中间 执行 更新操作:
*/
@Test
public void testLocalCache02() {
User user = userMapper.findUserById(101);
System.out.println("-------------第一次查询:"+user);
userMapper.saveUser(new User(null,"bxg","bj","博学谷"));
System.out.println("-------------更新了数据-------------");
User user2 = userMapper.findUserById(101);
System.out.println("-------------第二次查询:"+user2);
}
查询结果查看:
在一次数据库会话中,如果对数据库发生了修改操作,在修改操作后执行的相同查询,查询了数据库,一级缓存失效。
一级缓存生命周期
当会话结束时,SqlSession对象及其内部的Executor对象还有PerpetualCache对象也一并释放掉
如果SqlSession调用了close()方法,会释放掉一级缓存PerpetualCache对象,一级缓存将不可用
如果SqlSession调用了clearCache(),会清空PerpetualCache对象中的数据,但是该对象仍可使用
SqlSession中执行了任何一个update操作(update()、delete()、insert()) ,都会清空
PerpetualCache对象的数据,但是该对象可以继续使用
9.2 二级缓存
一级缓存中,其最大的共享范围就是一个 SqlSession 内部;
如果多个 SqlSession 之间需要共享缓存,则需要使用到二级缓存。
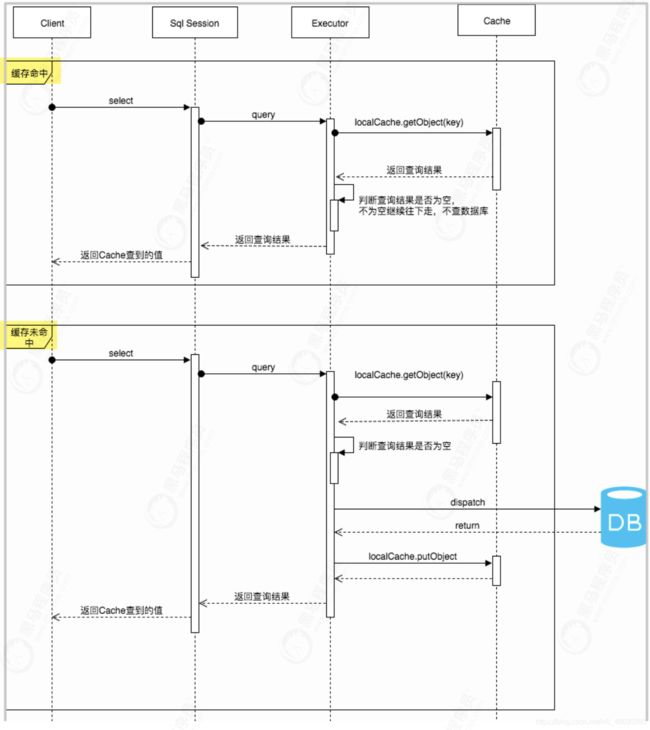
开启二级缓存后,会使用 CachingExecutor 装饰 Executor ,进入一级缓存的查询流程前,
先在 CachingExecutor 进行二级缓存的查询。
二级缓存示意图

解读
开启二级缓存后,执行器Executor会被CachingExecutor包装一层。(装饰器模式)
二级缓存是手动开启的,作用域为sessionfactory
二级缓存则是全局级别的,不同的session共用同一个二级缓存
维护二级缓存,只有在提交事务之后二级缓存才会保存 (查询的时候先走二级缓存再走一级缓存【开启二级缓存的条件下】)
它采用的是装饰器模式它里面有个属性是 Executor delegate;(实例化哪个自己配置的,默认是SimpleExecutor,使用有参构造给属性赋值)这里存的就是你三种执行器中的一种。
装饰者模式:在不改变原有类和继承的情况下,通过包装原对象去扩展一个新的功能。
开启二级缓存配置
// MyBatis的配置文件中二级缓存: 默认已开启
<settings>
<setting name = "cacheEnabled" value = "true" />
settings>
//mapper映射XML中配置cache或者 cache-ref: cache标签用于声明这个namespace使用二级缓存,并且可以自定义配置。
<cache/>
CachingExecutor剖析
org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor ,实现 Executor 接口,支持二级缓存的 Executor的实现类。
先从缓存中获取查询结果,存在就返回;
不存在,再委托给Executor delegate去数据库取;
delegate可以是SimpleExecutor、ReuseExecutor、BatchExecutor。
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// <1> 获得 Cache 对象,即当前 MappedStatement 对象的二级缓存。
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
// <2.1> 如果需要清空缓存,则进行清空
// 注意: 注意,此时清空的仅仅,当前事务中查询数据产生的缓存。而真正的清空,在事务的提 交时。
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// <2.3> 从二级缓存中,获取结果
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
// 如果需要清空缓存,则进行清空
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 执行 delegate 对应的方法
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
解析:
- 获得 Cache 对象,即当前 MappedStatement 对象的二级缓存
- 如果没有 Cache 对象,说明该 MappedStatement 对象,未设置二级缓存,则调用delegate 属性的 #query(…) 方法,直接从数据库中查询。
- 如果有 Cache 对象,说明该 MappedStatement 对象,有设置二级缓存:
缓存执行器流程分析
- 在优化系统性能时,优化数据库性能是非常重要的一个环节,而添加缓存则是优化数据库时 最有效的手段之一。
- 正确、合理地使用缓存可以将一部分数据库请求拦截在缓存这一层。
- MyBatis 中提供的一级缓存和二级缓存,而这两级缓存都是依赖于基础支持层中的缓 存模块实现的。这里需要注意的是,在分布式环境下,由于默认的MyBatis Cache实现都是基于本地的,占用系统资源,并且有一定安全性问题,建议直接使用Redis、Memcached等分布式 缓存可能成本更低,安全性也更高。
10 日志模块解析
10.1 概述
mybatis 没有提供日志的实现类,需要接入第三方的日志组件,但第三方日志组件都有各自的Log级别,且各不相同。而Mybatis统一提供了trace/ debug/ warn/ error四个级别,mybatis使用适配器模式进行日志加载,我们来欣赏下mybatis源码的魅力。
10.2 日志接口Log
mybatis 封装了统一的日志接口,其他日志接口接入需要实现该日志接口。
该接口只提供了trace/ debug/ warn/ error四个级别的日志输出
public interface Log {
boolean isDebugEnabled();
boolean isTraceEnabled();
void error(String s, Throwable e);
void error(String s);
void debug(String s);
void trace(String s);
void warn(String s);
10.3 日志工厂LogFactory
在这里定义了日志框架的加载顺序
slf4j -> commonsLoging -> Log4J2 -> Log4J -> JdkLog
使得日志框架优雅的嵌入到mybatis中
- 到这里是整个日志的加载顺序,尝试找到一个可用的构造方法,找到后返回该日志框架的实例
- 这里面用到了Runable接口的钩子方法,也可以叫做接口回调,并没有使用多线程编程。
public final class LogFactory {
/**
* Marker to be used by logging implementations that support markers.
*/
public static final String MARKER = "MYBATIS";
//记录正在使用的是那个日志框架的构造方法
private static Constructor<? extends Log> logConstructor;
/**
* 顺序尝试找到一个可用的日志框架
*
* :: 双冒号运算符就是java中的方法引用 方法引用的格式是 类名::方法名。
* person ->person.getAge(); 可以替换为 Person::getAge
* ()-> new HashMap<>(); 可以替换为 HashMap::new
* 双冒号操作符返回的是一个接口的匿名实现
*/
static {
//尝试使用某一种日志框架 第一个不成功到第二个 一直找到一个合适的
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useSlf4jLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useCommonsLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useLog4J2Logging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useLog4JLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useJdkLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useNoLogging);
}
private LogFactory() {
// disable construction
}
//返回具体实现的实现类
public static Log getLog(Class<?> clazz) {
return getLog(clazz.getName());
}
public static Log getLog(String logger) {
try {
//使用当前可用的构造方法进行创建对象
return logConstructor.newInstance(logger);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new LogException("Error creating logger for logger " + logger + ". Cause: " + t, t);
}
}
public static synchronized void useCustomLogging(Class<? extends Log> clazz) {
setImplementation(clazz);
}
public static synchronized void useSlf4jLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.slf4j.Slf4jImpl.class);
}
public static synchronized void useCommonsLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.commons.JakartaCommonsLoggingImpl.class);
}
public static synchronized void useLog4JLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.log4j.Log4jImpl.class);
}
public static synchronized void useLog4J2Logging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.log4j2.Log4j2Impl.class);
}
public static synchronized void useJdkLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdk14.Jdk14LoggingImpl.class);
}
public static synchronized void useStdOutLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl.class);
}
public static synchronized void useNoLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.nologging.NoLoggingImpl.class);
}
/**
* 咋一看好像是多线程
* 其实不然,只用用了下Runnable接口的钩子方法
* 不用再自定义接口内部类实现了,用现成的Runnable接口
* @param runnable
*/
private static void tryImplementation(Runnable runnable) {
if (logConstructor == null) {
try {
runnable.run();
} catch (Throwable t) {
// ignore
}
}
}
private static void setImplementation(Class<? extends Log> implClass) {
try {
//获取具体实现类的构造方法
Constructor<? extends Log> candidate = implClass.getConstructor(String.class);
//创建一个实现类 并打印日志
Log log = candidate.newInstance(LogFactory.class.getName());
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Logging initialized using '" + implClass + "' adapter.");
}
//设置否则方法为当前可用构造方法
logConstructor = candidate;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new LogException("Error setting Log implementation. Cause: " + t, t);
}
}
}
10.4 日志系统转换
这里采用了很多日志框架,使用了适配器模式进行日志的转换,装饰着模式可以查看我的设计模式
一节这里我们就拿比较负责的sl4j来查看源码
public class Slf4jImpl implements Log {
private Log log;
public Slf4jImpl(String clazz) {
//logger的方式创建日志类
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(clazz);
//如果返回的是 LocationAwareLogger 对象
if (logger instanceof LocationAwareLogger) {
try {
// check for slf4j >= 1.6 method signature
//检查sl4j 版本是否>=1.6
logger.getClass().getMethod("log", Marker.class, String.class, int.class, String.class, Object[].class, Throwable.class);
//使用 Slf4jLocationAwareLoggerImpl 实例
log = new Slf4jLocationAwareLoggerImpl((LocationAwareLogger) logger);
return;
} catch (SecurityException | NoSuchMethodException e) {
// fail-back to Slf4jLoggerImpl
}
}
//sl4j 版本小于1.6 使用Slf4jLoggerImpl
// Logger is not LocationAwareLogger or slf4j version < 1.6
log = new Slf4jLoggerImpl(logger);
}
@Override
public boolean isDebugEnabled() {
return log.isDebugEnabled();
}
@Override
public boolean isTraceEnabled() {
return log.isTraceEnabled();
}
@Override
public void error(String s, Throwable e) {
log.error(s, e);
}
@Override
public void error(String s) {
log.error(s);
}
@Override
public void debug(String s) {
log.debug(s);
}
@Override
public void trace(String s) {
log.trace(s);
}
@Override
public void warn(String s) {
log.warn(s);
}
}
这里注意下Slf4j版本控制,如果Slf4j版本>=1.6 使用 Slf4jLocationAwareLoggerImpl 否则使用Slf4jLoggerImpl
11设计模式
装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)
装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern),动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责,就增加功能来说,装饰器模式比生成子类更灵活
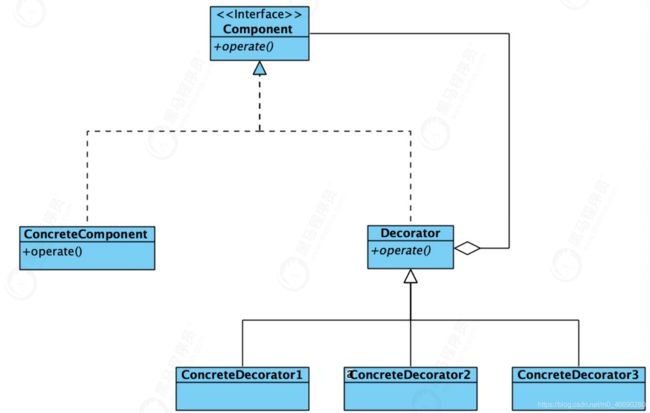
什么是装饰器模式
允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其结构。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它是作为现有的类的一个包装。
这种模式创建了一个装饰类,用来包装原有的类,并在保持类方法签名完整性的前提下,提供了额外的功能。
动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。就增加功能来说,装饰器模式相比生成子类更为灵活
角色
Component(抽象构件)
给出一个抽象接口,装饰器模式中公共方法的类,在装饰器模式结构图的顶层,以规范准备接收附加责任的对象。
ConcreteComponent(具体构件)
是要动态扩展的对象,转换器模式中具体的被装饰的类,它继承自Component。
Decorator(装饰器)
持有一个构件(Component)对象的实例,它是装饰器模式中的核心对象,所有具体装饰器对象的父类,完成装饰器的部分职能。可以只对被装饰的对象进行一些简单的包裹,也可包含对Component中方法的实现。
ConcreteDecorator(具体装饰)
完成具体的装饰功能。装饰功能的实现是通过调用被装饰对象对应的方法,加上装饰对象自身的方法。这是装饰器模式动机中的添加额外功能的关键。
优缺点
优点
- 装饰类和被装饰类可以独立发展,不会相互耦合,装饰模式是继承的一个替代模式,装饰模式可以动态扩展一个实现类的功能。
- 装饰模式与继承关系的目的都是要扩展对象的功能,但是装饰模式可以提供比继承更多的灵活性。
- 装饰模式允许系统动态决定“贴上”或者除掉一个“装饰”,继承关系是静态的,它在系统运行前就决定了;
- 通过使用不同的具体装饰类以及这些装饰类的排列组合,设计师可以创造出很多不同行为的组合;
- 装饰者类可以在被装饰者的行为前面或后面加上自己的行为,甚至取代被装饰者的行为,达到特定的目的;
- 装饰者一般对组件的客户是透明的,除非客户程序依赖于组件的具体类型
缺点
- 多层装饰比较复杂。
- 由于使用装饰模式,可以比使用继承关系需要较少数目的类。使用较少的类,当然使设计比较易于
- 进行。但是,在另一方面,使用装饰模式会产生比使用继承关系更多的对象。更多的对象会使得查错变得困难,特别是这些对象看上去都很相像。
适用场景
运行时,你需要动态地为对象增加额外职责时;
当你需要一个能够代替子类的类,借助它提供额外方法时。
在不影响其他对象的情况下,以动态、透明的方式给单个对象添加职责;
处理那些可以撤销的职责;
当不能采用生成子类的方式进行扩充时。
案例
假设我去买咖啡,首先服务员给我冲了一杯原味咖啡,我希望服务员给我加些牛奶和白糖混合入原味咖啡中。使用装饰器模式就可以解决这个问题。
咖啡接口
定义了获取花费和配料的接口。
public interface Coffee {
/**
* 获取价格
* @return
*/
public float getPrice();
/**
* 获取咖啡
* @return
*/
public String getCoffee();
}
原味咖啡
实现Coffe接口,花费1元,配料中,只有咖啡
public class OriginalCoffee implements Coffee {
@Override
public float getPrice() {
return 1;
}
@Override
public String getCoffee() {
return "原味咖啡";
}
}
装饰器类
咖啡对象的装饰器类,同样实现Coffee接口,定义一个Coffe对象的引用,在构造器中进行初始化。并且将getPrice()和getCoffee()方法转发给被装饰对象。
/**
* 咖啡的"装饰器",可以给咖啡添加各种"配料"
* 该类是一个抽象类需要具体子类来实现
*/
public class DecoratorAbstractCoffee implements Coffee {
/**
* 具体咖啡的接口
*/
protected final Coffee coffee;
/**
* 构造方法,初始化咖啡对象的引用
* @param coffee
*/
public DecoratorAbstractCoffee(Coffee coffee) {
this.coffee = coffee;
}
/**
* 获取价格,装饰器父类中直接转发"请求"至引用对象
* @return
*/
@Override
public float getPrice() {
return coffee.getPrice();
}
/**
* 获取咖啡,装饰器父类中直接转发"请求"至引用对象
* @return
*/
@Override
public String getCoffee() {
return coffee.getCoffee();
}
}
具体的装饰器类
添加牛奶
具体的装饰器类,负责往咖啡中“添加”牛奶,注意看getPrice()方法和getCoffee()方法,可以在转发请求之前或者之后,增加功能。如果是代理模式,这里的结构就有所不同,通常代理模式根据运行时的条件来判断是否转发请求。
/**
* 混合牛奶到蜂蜜中
*/
public class CreamCoffee extends DecoratorAbstractCoffee {
private float price = (float) 0.5;
/**
* 调用父类的构造方法
* @param coffee
*/
public CreamCoffee(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
/**
* 增加配料需要加钱
* @return
*/
@Override
public float getPrice() {
return coffee.getPrice()+price;
}
/**
* 对咖啡进行加工
* @return
*/
@Override
public String getCoffee() {
return coffee.getCoffee()+";添加牛奶";
}
}
添加糖
另一个具体装饰器类,用来给咖啡加蜂蜜,一样的逻辑。
public class HoneyCoffee extends DecoratorAbstractCoffee {
private float price = (float) 1.4;
public HoneyCoffee(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
@Override
public float getPrice() {
return coffee.getPrice()+price;
}
@Override
public String getCoffee() {
return coffee.getCoffee()+";添加蜂蜜";
}
}
测试
public class DecoratorMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//是不是很像 javaIO中的 stream流
Coffee coffee = new CreamCoffee(new HoneyCoffee(new OriginalCoffee()));
System.out.println(coffee.getCoffee());
System.out.println(coffee.getPrice());
}
}
11.2 适配器模式(Adapter Pattern)
11.2.1 什么是适配器模式
将一个接口转换成客户希望的另一个接口,使接口不兼容的那些类可以一起工作,其别名为包装器(Wrapper)。适配器模式既可以作为类结构型模式,也可以作为对象结构型模式。
在适配器模式中,我们通过增加一个新的适配器类来解决接口不兼容的问题,使得原本没有任何关系的类可以协同工作。
根据适配器类与适配者类的关系不同,适配器模式可分为对象适配器和类适配器两种,在对象适配器模式中,适配器与适配者之间是关联关系;在类适配器模式中,适配器与适配者之间是继承(或实现)关系。
缺省适配器模式(Default Adapter Pattern):当不需要实现一个接口所提供的所有方法时,可先设计一个抽象类实现该接口,并为接口中每个方法提供一个默认实现(空方法),那么该抽象类的子类可以选择性地覆盖父类的某些方法来实现需求,它适用于不想使用一个接口中的所有方法的情况,又称为单接口适配器模式。缺省适配器模式是适配器模式的一种变体,其应用也较为广泛。在JDK类库的事件处理包java.awt.event中广泛使用了缺省适配器模式,如WindowAdapter、KeyAdapter、MouseAdapter等。
11.2.2 角色
Target(目标抽象类):目标抽象类定义客户所需接口,可以是一个抽象类或接口,也可以是具体类。
Adapter(适配器类):适配器可以调用另一个接口,作为一个转换器,对Adaptee和Target进行适配,适配器类是适配器模式的核心,在对象适配器中,它通过继承Target并关联一个Adaptee对象使二者产生联系。
Adaptee(适配者类):适配者即被适配的角色,它定义了一个已经存在的接口,这个接口需要适配,适配者类一般是一个具体类,包含了客户希望使用的业务方法,在某些情况下可能没有适配者类的源代码。
优点
可以让任何两个没有关联的类一起运行。
提高了类的复用。
增加了类的透明度。
灵活性好。
缺点
过多地使用适配器,会让系统非常零乱,不易整体进行把握。比如,明明看到调用的是 A 接口,其实内部被适配成了 B 接口的实现,一个系统如果太多出现这种情况,无异于一场灾难。因此如果不是很有必要,可以不使用适配器,而是直接对系统进行重构。
由于 JAVA 至多继承一个类,所以至多只能适配一个适配者类,而且目标类必须是抽象类。
适用场景
- 想要使用一个已经存在的类,但是它却不符合现有的接口规范,导致无法直接去访问,这时创建一个适配器就能间接去访问这个类中的方法。
- 我们有一个类,想将其设计为可重用的类(可已经被多处访问了),我们可以创建适配器来将这个类来适配其他没有提供合适接口的类。
- 想要使用接口中的某个或者某些方法,但是接口中有太多不是自己需要的方法了,接口在实现时必须实现其中的所有方法,这个时候就要使用抽象类来实现接口,并不对所有方法进行实现(进置空),然后我们再继承这个抽象类来重写想要的方法。这个抽象类就是适配器
案例
我们用电源适配器举例,我们笔记本电脑以及电动车都需要电源适配器才能够接入220V的市电,那这个电源适配器就是我们需要实现的适配器类
/**
* 电源适适配器接口
*/
public interface PowerAdaper {
/**
* 适配接口就
*/
public void adaper();
/**
* 电源转换器
*/
public int transfor();
}
public class UtilityPower {
/**
* 220V供电
*/
public int supply220V() {
System.out.println("供应220V交流电");
return 220;
}
}
需要适配的电动车
public class EVChar {
/**
* 336V供电接口
*/
public void supply336V() {
System.out.println("进行24V供电");
}
}
** 电动汽车适配器**
/**
* 电动车适配器
*/
public class EVCharAdaper extends UtilityPower implements PowerAdaper {
private EVChar evChar = new EVChar();
@Override
public void adaper() {
transfor();
evChar.supply336V();
}
@Override
public int transfor() {
int voltage = supply220V();
//转换成对应的电压
return 336;
}
}
需要适配的电动车
/**
* 笔记本电脑
*/
public class NotebookComputer {
/**
* 24V供电接口
*/
public void supply24V() {
System.out.println("进行24V供电");
}
}
/**
* 笔记本电脑适配器
*/
public class NotebookComputerAdaper extends UtilityPower implements PowerAdaper {
private NotebookComputer computer = new NotebookComputer();
@Override
public void adaper() {
transfor();
computer.supply24V();
}
@Override
public int transfor() {
int voltage = supply220V();
//转换成对应的电压
return 24;
}
}