线程池详解+springboot整合线程池(超级详细简洁代码可直接执行)
一、概念
与数据库连接池的原理类似,线程池就是将多个线程对象放入一个池子里面,之后从该池子中获取、实用和回收线程。有两点需要明确。1. 每一个线程,在一段时间内只能执行一个任务。2. 线程池中的各个线程是可以重复使用的。
二、线程池的创建方式
-
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor() 创建只有一个线程的线程池。其底层源码如下:
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue())); } 其中可以发现,线程只有一个,但是等待队列是Integer.MAX_VALUE大的。
-
Executors.newCachedThreadPool() 创建可以放多个线程的线程池。其底层源码如下:
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0,Integer.MAX_VALUE,60L,TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue());
} 其中可以发现,线程有Integer.MAX_VALUE个,其中SynchronousQueue没有容量,是无缓冲等待队列,是一个不存储元素的阻塞队列。
3. Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5) 创建固定线程数的线程池。其底层源码如下:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads,nThreads,0L,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue());
} 其中可以发现,线程数是指定的,等待队列是Integer.MAX_VALUE大的。
4. Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() 创建一个可用于任务调度的线程池。其底层源码如下:
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() {
return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1));
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS, new DelayedWorkQueue());
}其中可以发现核心线程数为1,但是最大线程数为Integer.MAX_VALUE,等待队列是一个延迟无界队列
5. Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5) 创建一个可用于任务调度的线程池,并且线程是有多个的。
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS, new DelayedWorkQueue());
}可以发现,除了核心线程数跟newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor()不一样,其他的都一样。
特别说明:
阿里巴巴编程规范中特意强调,禁止使用上面五种方式创建线程池。其实我们也可以从中发现,以上线程池中,要么是最大线程数没有限制,要么是其中的等待队列的大小没有限制(Integer.MAX_VALUE可以被认为是没有限制),那么就有可能将内存撑爆,导致系统崩溃。所以工作中一定不要用上面的方式创建数据库。
那么应该怎样创建数据库呢?
创建数据库的正确姿势如下:
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1,2,3, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10),new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());其实就是上面那些创建线程池有系统自动赋值的参数,改成我们手动赋值
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
} 线程池的参数说明:
-
corePoolSize:核心线程数
-
maximumPoolSize:最大线程数
-
keepAliveTime:最大空闲时间
-
unit:最大空闲时间单位
-
workQueue:任务队列
-
handler:拒绝策略,有以下四种
(1)ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy 丢弃任务,并抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常。
(2)ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy:该任务被线程池拒绝,由调用 execute方法的线程执行该任务。
(3)ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy : 抛弃队列最前面的任务,然后重新尝试执行任务。
(4)ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy,丢弃任务,不过也不抛出异常。
也可以自己实现RejectedExecutionHandler接口来自定义拒绝策略
下面附上SpringBoot整合线程的代码:
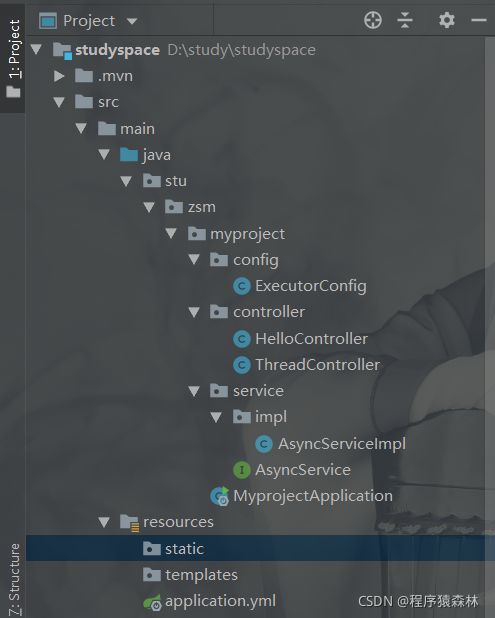
代码的结构图,方便读者查看
@RestController
public class ThreadController {
@Autowired
private AsyncService asyncService;
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPool;
@RequestMapping("test")
public void testAsync() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("testAsync 执行开始");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
asyncService.executeAsync();
System.out.println("testAsync 执行完毕");
}
@RequestMapping("testThreadPool")
public void testThreadPool() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("testThreadPool start");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
threadPool.execute(() -> System.out.println("threadPool testThreadPool"));
System.out.println("testThreadPool end");
}
}public interface AsyncService {
/**
* 执行异步任务
*/
void executeAsync();
}@Service
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncServiceImpl.class);
@Async("asyncServiceExecutor")
// @Resource(name = "asyncServiceExecutor")
@Override
public void executeAsync() {
logger.info("start executeAsync");
System.out.println("start executeAsync");
System.out.println("当前运行的线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
logger.info("end executeAsync");
System.out.println("end executeAsync");
}
}@Configuration
@EnableAsync
@Data
public class ExecutorConfig {
@Value("${async.executor.thread.core_pool_size}")
private int corePoolSize;
@Value("${async.executor.thread.max_pool_size}")
private int maxPoolSize;
@Value("${async.executor.thread.queue_capacity}")
private int queueCapacity;
@Value("${async.executor.thread.name.prefix}")
private String namePrefix;
@Bean(name = "asyncServiceExecutor")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor asyncServiceExecutor(){
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setKeepAliveSeconds(3);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix(namePrefix);
// rejection-policy:当pool已经达到max size的时候,如何处理新任务
// CALLER_RUNS:不在新线程中执行任务,而是由调用者所在的线程来执行
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
//加载
threadPoolTaskExecutor.initialize();
return threadPoolTaskExecutor;
}
}application.yml配置
async:
executor:
thread:
# 配置核心线程数
core_pool_size: 10
# 配置最大线程数
max_pool_size: 20
# 配置队列大小
queue_capacity: 999
name:
prefix: async-service-以上就是springboot整合线程池的代码,读者可以直接拷贝下来运行。这里整合Controller里面有两种用法,一种是用service的实现方法去异步执行;另外一种是直接将ThreadPoolTaskExecutor注入到Controller中来调用执行。读者可以自行体会。