X264简介-Android使用(二)
X264简介-Android使用(二)
4、Ubuntu上安装ffmpeg:
检查更新本地软件包(如果未更新,reboot Vmware):
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
官网下载的source文件安装: http://ffmpeg.org/
下载完成后,到根目录执行:
make
make install
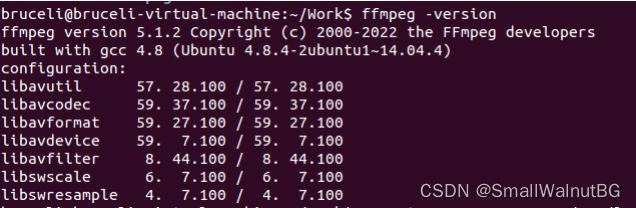
查看FFMpeg版本:
ffmpeg –version
Tips 如果查看ffmpeg出现如下错误:
解办法->配置ffmpeg的环境变量:
环境变量:
vi /etc/profile
#set ffmpeg path environment
PATH=$PATH:/snap/ffmpeg/current/bin
export PATH
编译ffmpeg
sh脚本"build_ffmpeg.sh":
#!/bin/bash
export NDK=/home/bruceli/Work/android-ndk-r25d
export PREBUILD=$NDK/toolchains/llvm/prebuilt
export CROSS_PREFIX=${PREBUILD}/linux-x86_64/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-
export CC=$PREBUILD/linux-x86_64/bin/armv7a-linux-androideabi21-clang
export NM=$CROSS_PREFIXnm
export AR=$CROSS_PREFIXar
export PREFIX=./android/armeabi-v7a
function build_so
{
./configure \
--prefix=$PREFIX \
--cc=$CC \
--nm=$NM \
--ar=$AR \
--enable-small \
--disable-programs \
--disable-avdevice \
--disable-encoders \
--disable-muxers \
--disable-filters \
--cross-prefix=$CROSS_PREFIX \
--target-os=android \
--arch=arm \
--disable-shared \
--enable-static \
--enable-cross-compile
}
make clean
build_so
make -j4
make install
}
将以上脚本放置与ffmpeg的根目录,并执行:
./build_ffmpeg.sh
Tips 出现以下错误
错误: make: *** [libavfilter/libavfilter.a] 错误 127
解决方案一->授权r25c文件夹权限(NG):
chmod +777 -R android-ndk-r25c/
解决方案二->install libavfilter(NG):
sudo apt-get install -y libavfilter-dev
解决方案三->配置 android-ndk-r21e 版本的NDK(SUCCESS):
...
export NDK=/home/bruceli/Work/android-ndk-r21e
...
文件生成路径:/home/bruceli/Work/ffmpeg-5.1.2/android/armeabi-v7a
下载NDK:
LINK1:
wget -c http://dl.google.com/android/ndk/android-ndk-r25c-linux-x86_64.bin
LINK2: https://developer.android.google.cn/ndk/downloads?hl=zh-cn
DOC: https://developer.android.google.cn/ndk/guides/other_build_systems?hl=zh-cn
配置NDK环境变量: 编辑
sudo gedit ~/.bashrc
文件末尾添加路径
export NDK=/文件夹路径
export PATH=${PATH}:$NDK
保存文件
source ~/.bashrc
build ndk:
ndk-build
5、编译X264:
官网连接: https://www.videolan.org/developers/x264.html
编译配置:
./configure --disable-asm --enable-shared --enable-pic
编译和安装:
make
make install
x264编译脚本:
脚本(build_x264.sh):
新建以下文件:
vim build_x264.sh
文件内容:
#!/bin/bash
export NDK=/home/bruceli/Work/android-ndk-r21e
export TOOLCHAIN=$NDK/toolchains/llvm/prebuilt/linux-x86_64
export API=21
function build_one
{
./configure \
--prefix=$PREFIX \
--disable-cli \
--enable-static \
--enable-pic \
--host=$my_host \
--cross-prefix=$CROSS_PREFIX \
--sysroot=$NDK/toolchains/llvm/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/sysroot \
make clean
make -j8
make install
}
#arm64-v8a
PREFIX=./android/arm64-v8a
my_host=aarch64-linux-android
export TARGET=aarch64-linux-android
export CC=$TOOLCHAIN/bin/$TARGET$API-clang
export CXX=$TOOLCHAIN/bin/$TARGET$API-clang++
CROSS_PREFIX=$TOOLCHAIN/bin/aarch64-linux-android-
build_one
#armeabi-v7a
PREFIX=./android/armeabi-v7a
my_host=armv7a-linux-android
export TARGET=armv7a-linux-androideabi
export CC=$TOOLCHAIN/bin/$TARGET$API-clang
export CXX=$TOOLCHAIN/bin/$TARGET$API-clang++
CROSS_PREFIX=$TOOLCHAIN/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-
build_one
开启文件权限:
chmod +777 build_x264.sh
放置x264文件夹下并执行
./build_x264.sh
1> /home/bruceli/Work/x264/android/arm64-v8a
2> /home/bruceli/Work/x264/android/armeabi-v7a
使用
Android Studio
CmakeList配置文件
# For more information about using CMake with Android Studio, read the
# documentation: https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html
# Sets the minimum version of CMake required to build the native library.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
# Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC
# or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code.
# You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds them for you.
# Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK.
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
native-lib
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
queue.c
native-lib.c)
set(distribution_DIR ../../../../libs)
add_library(libx264
SHARED
IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(libx264
PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libx264.a)
add_library(librtmp
SHARED
IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(librtmp
PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/librtmp.a)
add_library(libfaac
SHARED
IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(libfaac
PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libfaac.a)
# Searches for a specified prebuilt library and stores the path as a
# variable. Because CMake includes system libraries in the search path by
# default, you only need to specify the name of the public NDK library
# you want to add. CMake verifies that the library exists before
# completing its build.
find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable.
log-lib
# Specifies the name of the NDK library that
# you want CMake to locate.
log)
# Specifies libraries CMake should link to your target library. You
# can link multiple libraries, such as libraries you define in this
# build script, prebuilt third-party libraries, or system libraries.
target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library.
native-lib
libx264
librtmp
libfaac
# Links the target library to the log library
# included in the NDK.
${log-lib})
交叉编译后生成文件放置的位置:
配置参数及说明
///setVideoOptions
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_com_example_smallwalnut_jni_PushNative_setVideoOptions(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance,
jint width, jint height, jint bitrate,
jint fps) {
//x264流程:
//x264_encoder_encode 编码
//x264_encoder_close( h ) 关闭编码器,释放资源
//x264_param_default_preset 设置
x264_param_t param;
//"ultrafast" - "medium" ... 与速度和画质有关 ,zerolatency ->可降低在线转码的编码延迟
x264_param_default_preset(¶m, "ultrafast", "zerolatency");
//编码输入的像素格式
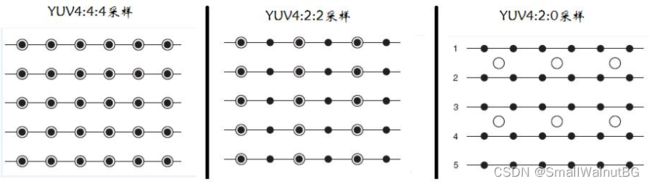
//YUV 4:4:4采样,每一个Y对应一组UV分量。
//YUV 4:2:2采样,每两个Y共用一组UV分量。
//YUV 4:2:0采样,每四个Y共用一组UV分量。
param.i_csp = X264_CSP_I420;
param.i_width = width;
param.i_height = height;
y_len = width * height;
u_len = y_len / 4;
v_len = u_len;
//参数i_rc_method表示码率控制,CQP(恒定质量),CRF(恒定码率),ABR(平均码率)
//恒定码率,会尽量控制在固定码率
param.rc.i_rc_method = X264_RC_CRF;
param.rc.i_bitrate = bitrate / 1000; //* 码率(比特率,单位Kbps)
param.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate = bitrate / 1000 * 1.2; //瞬时最大码率
//码率控制不通过timebase和timestamp,而是fps
param.b_vfr_input = 0;
param.i_fps_num = fps; //* 帧率分子
param.i_fps_den = 1; //* 帧率分母
param.i_timebase_den = param.i_fps_num;
param.i_timebase_num = param.i_fps_den;
param.i_threads = 1;//并行编码线程数量,0默认为多线程
//码率控制不通过timebase和timestamp,而是fps
//是否把sps和pts放入一个关键帧
//SPS Sequence Parameter Set 参数序列集,PPs Picture Params Set图像参数集
//为了提高图像的纠错能力
param.b_repeat_headers = 1;
//设置级别level
param.i_level_idc = 51;
//x264_param_apply_profile 设置档次
x264_param_apply_profile(¶m, "baseline");
//x264_picture_alloc(x264_picture_t输入图像)初始化
x264_picture_alloc(&pic_in, param.i_csp, param.i_width, param.i_height);
pic_in.i_pts = 0;
//x264_encoder_open 打开编码器
video_encode_handle = x264_encoder_open(¶m);
if (video_encode_handle) {
LOGI("%s", "打开编码器成功");
} else {
LOGI("%s", "打开编码器失败");
throwNativeError(env,INIT_FAILED);
}
}
YUV
YUV格式有两大类:planar和packed。
对于planar的YUV格式,先连续存储所有像素点的Y,紧接着存储所有像素点的U,随后是所有像素点的V。
对于packed的YUV格式,每个像素点的Y,U,V是连续交叉存储的。
YUV分为三个分量,Y表示明亮度(Luminance或Luma),也就是灰度值;而U和V表示的则是色度(Chrominance或Chroma),作用是描述影像色彩及饱和度,用于指定像素的颜色。
与我们熟知的RGB类似,YUV也是一种颜色编码方法,主要用于电视系统以及模拟视频领域,它将亮度信息(Y)与色彩信息(UV)分离,没有UV信息一样可以显示完整的图像,只不过是黑白的,这样的设计很好地解决了彩色电视机与黑白电视的兼容问题。并且,YUV不像RGB那样要求三个独立的视频信号同时传输,所以用YUV方式传送占用极少的频宽。
采样方式
YUV码流的存储格式其实与其采样的方式密切相关,主流的采样方式有三种,YUV4:4:4,YUV4:2:2,YUV4:2:0,用三个图来直观地表示采集的方式,以黑点表示采样该像素点的Y分量,以空心圆圈表示采样该像素点的UV分量。
start
///startPush
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_com_example_smallwalnut_jni_PushNative_startPush(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance, jstring url_) {
//
jobj_push_native = (*env)->NewGlobalRef(env, instance);
jclass j_cls_push_native_temp = (*env)->GetObjectClass(env, jobj_push_native);
jcls_push_native = (*env)->NewGlobalRef(env,j_cls_push_native_temp);
//PushNative.throwNativeError
jmid_throw_native_error = (*env)->GetMethodID(env, jcls_push_native,
"throwNativeError",
"(I)V");
// jmid_throw_native_error = (*env)->NewGlobalRef(env,throw_native_error_mid_temp);//jmethodId 不能全局引用
const char *url_cstr = (*env)->GetStringUTFChars(env, url_, 0);
LOGI("播放地址:%s", url_cstr);
//utl赋值
rtmp_path = malloc(strlen(url_cstr) + 1);
//数组初始化,临时变量清0
memset(rtmp_path, 0, strlen(url_cstr) + 1);
memcpy(rtmp_path, url_cstr, strlen(url_cstr));
//初始化互斥锁和条件变量
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);
//创建
create_queue();
//init
//启动消费者线程(从队列中能够不断拉取RTMPPacket发送给流媒体服务器)
pthread_t push_thread_id;
pthread_create(&push_thread_id, NULL, push_thread, NULL);
(*env)->ReleaseStringUTFChars(env, url_, url_cstr);
}
视频编码
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_com_example_smallwalnut_jni_PushNative_fireVideo(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance,
jbyteArray data_) {
jbyte *nv21_buffer = (*env)->GetByteArrayElements(env, data_, NULL);
//视频数据转为yuv420p
//nv21->yuv420p
jbyte *u = (jbyte *) pic_in.img.plane[1];
jbyte *v = (jbyte *) pic_in.img.plane[2];
memcpy(pic_in.img.plane[0], nv21_buffer, y_len);
int i = 0;
for (; i < u_len; i++) {//notice
*(u + i) = *(nv21_buffer + y_len + i * 2 + 1);
*(v + i) = *(nv21_buffer + y_len + i * 2);
}
//x264编码得到NALU指针数组
x264_nal_t *nal = NULL;
int n_nal = -1;//nalu的个数
//进行h264编码
if (x264_encoder_encode(video_encode_handle, &nal, &n_nal, &pic_in, &pic_out) < 0) {
LOGI("%s", "编码失败");
throwNativeError(env,INIT_FAILED);
return;
}
//使用rtmp协议将数据发送到流媒体服务器
//帧分为关键帧和普通帧,为了提高画面的纠错率,关键帧必须包含sps和pps数据
unsigned char sps[100];
unsigned char pps[100];
int sps_len, pps_len;
memset(sps, 0, 100);
memset(pps, 0, 100);
pic_in.i_pts += 1;//顺序叠加
i = 0;//遍历NALU数组,根据NALU的类型判断(SPS PPS )
for (; i < n_nal; i++) {
if (nal[i].i_type == NAL_SPS) {
//复制sps数据
sps_len = nal[i].i_payload - 4;
memcpy(sps, nal[i].p_payload + 4, sps_len);//不复制4字节起始码
} else if (nal[i].i_type == NAL_PPS) {
//复制pps数据
pps_len = nal[i].i_payload - 4;
memcpy(pps, nal[i].p_payload + 4, pps_len);//不复制4字节起始码
//发送序列信息
//将sps和pps数据添加到h264关键帧发送
add_264_key_header(pps, sps, pps_len, sps_len);
} else {
//发送普通帧信息
add_264_body(nal[i].p_payload, nal[i].i_payload);
}
}
// TODO
(*env)->ReleaseByteArrayElements(env, data_, nv21_buffer, 0);
}
在H.264标准协议中规定了多种不同的NAL
Unit类型,其中类型7表示该NAL Unit内保存的数据为Sequence Paramater
Set。在H.264的各种语法元素中,SPS中的信息至关重要。如果其中的数据丢失或出现错误,那么解码过程很可能会失败。SPS及后续将要讲述的图像参数集PPS在某些平台的视频处理框架(比如iOS的VideoToolBox等)还通常作为解码器实例的初始化信息使用。
SPS即Sequence Paramater Set,又称作序列参数集。SPS中保存了一组编码视频序列(Coded video sequence)的全局参数。所谓的编码视频序列即原始视频的一帧一帧的像素数据经过编码之后的结构组成的序列。而每一帧的编码后数据所依赖的参数保存于图像参数集中。一般情况SPS和PPS的NAL Unit通常位于整个码流的起始位置。但在某些特殊情况下,在码流中间也可能出现这两种结构,主要原因可能为:
解码器需要在码流中间开始解码;
编码器在编码的过程中改变了码流的参数(如图像分辨率等);
在做视频播放器时,为了让后续的解码过程可以使用SPS中包含的参数,必须对其中的数据进行解析。
除了序列参数集SPS之外,H.264中另一重要的参数集合为图像参数集Picture Paramater
Set(PPS)。通常情况下,PPS类似于SPS,在H.264的裸码流中单独保存在一个NAL Unit中,只是PPS NAL
Unit的nal_unit_type值为8;而在封装格式中,PPS通常与SPS一起,保存在视频文件的文件头中。
发送frame信息
///发送帧信息
void add_264_body(unsigned char *buf, int len) {
//去掉起始码(界定符)
if (buf[2] == 0x00) { //00 00 00 01
buf += 4;
len -= 4;
} else if (buf[2] == 0x01) { // 00 00 01
buf += 3;
len -= 3;
}
int body_size = len + 9;
RTMPPacket *packet = malloc(sizeof(RTMPPacket));
RTMPPacket_Alloc(packet, body_size);
unsigned char *body = packet->m_body;
//当NAL头信息中,type(5位)等于5,说明这是关键帧NAL单元
//buf[0] NAL Header与运算,获取type,根据type判断关键帧和普通帧
//00000101 & 00011111(0x1f) = 00000101
int type = buf[0] & 0x1f;
//Inter Frame 帧间压缩
body[0] = 0x27;//VideoHeaderTag:FrameType(2=Inter Frame)+CodecID(7=AVC)
//IDR I帧图像
if (type == NAL_SLICE_IDR) {
body[0] = 0x17;//VideoHeaderTag:FrameType(1=key frame)+CodecID(7=AVC)
}
//AVCPacketType = 1
body[1] = 0x01; /*nal unit,NALUs(AVCPacketType == 1)*/
body[2] = 0x00; //composition time 0x000000 24bit
body[3] = 0x00;
body[4] = 0x00;
//写入NALU信息,右移8位,一个字节的读取?
body[5] = (len >> 24) & 0xff;
body[6] = (len >> 16) & 0xff;
body[7] = (len >> 8) & 0xff;
body[8] = (len) & 0xff;
/*copy data*/
memcpy(&body[9], buf, len);
packet->m_hasAbsTimestamp = 0;
packet->m_nBodySize = body_size;
packet->m_packetType = RTMP_PACKET_TYPE_VIDEO;//当前packet的类型:Video
packet->m_nChannel = 0x04;
packet->m_headerType = RTMP_PACKET_SIZE_LARGE;
// packet->m_nTimeStamp = -1;
packet->m_nTimeStamp = RTMP_GetTime() - start_time;//记录了每一个tag相对于第一个tag(File Header)的相对时间
add_rtmp_packet(packet);
}
Native class
public class PushNative {
public static final int CONNECTION_FAILED=101;
public static final int INIT_FAILED=102;
static {
System.loadLibrary("native-lib");
}
LiveStateChangeListener liveStateChangeListener;
public void setLiveStateChangeListener(LiveStateChangeListener liveStateChangeListener) {
this.liveStateChangeListener = liveStateChangeListener;
}
public void removeLiveStateChangeLitener(){
if (liveStateChangeListener != null){
liveStateChangeListener =null;
}
}
/**
* 接收native抛出的错误
*/
public void throwNativeError(int code) {
if (liveStateChangeListener != null) {
liveStateChangeListener.onError(code);
}
}
public native void startPush(String url);
public native void releasePush();
public native void stopPush();
//设置音频参数
public native void setAudioOptions(int sampleRateInHz, int channel);
//设置视频参数
public native void setVideoOptions(int width, int height, int bitrate, int fps);
//发送视频
public native void fireVideo(byte[] data);
//发送音频
public native void fireAudio(byte[] bytes, int len);
}