解决Redisson无法连接Sentinel, Netty查找DNS失败
前言
- 这里 redisson 的版本为 3.11.2, 对应 netty-all 的版本为 4.1.38.Final
- 如果这篇描述的方法不能解决问题,可以参考另外一篇 Redisson-3.8 查找DNS异常的解决办法
- redisson 其实没问题,问题出在 netty 身上,而且神经得很。
- 之前的 netty 查找 DNS 失败,是因为解析 /etc/resolv.conf 文件有 bug,而这个版本的 netty 则是代码有 bug。
现象
使用 redisson 的应用程序运行时出错,报错信息:
Exception in thread "main" org.redisson.client.RedisConnectionException: At least two sentinels should be defined in Redis configuration! SENTINEL SENTINELS command returns empty result!
at org.redisson.connection.SentinelConnectionManager.<init>(SentinelConnectionManager.java:188)
at org.redisson.config.ConfigSupport.createConnectionManager(ConfigSupport.java:197)
at org.redisson.Redisson.<init>(Redisson.java:120)
at org.redisson.Redisson.create(Redisson.java:160)
at com.ericsson.jee.iam.common.redisson.util.RedissonFactory.initRedissonObject(RedissonFactory.java:27)
at test.Test.main(Test.java:17)
连接使用的 URL:sentinel://redis:26379?. . .
sentinel URL 的说明
你可能会觉得奇怪,报错明明说了至少需要2个 sentinel,但是 URL 却只写了一个 (redis:26379),是不是这里出的问题?
其实不然,redisson 在启动的时候,会通过 URL 中配置的 sentinel 信息,访问 sentinel 节点,然后从 sentinel 节点获取同一集群中其他 sentinel 节点的信息,因此 URL 中只需要一个 sentinel 的信息就可以了。很多时候我们在 URL 中填写多个 sentinel 的连接信息,是出于容错的考虑,如果使用第一个 sentinel 的信息连接不上,那就使用第二个,依次类推。
DNS 环境和配置描述
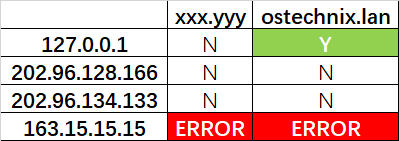
从 URL 中可以看出,sentinel 连接信息使用的是域名 redis,而不是 IP 地址,因此需要先确认 DNS 的可用。本次实验环境在本地安装了 bind9 用以提供 DNS 服务。
helowken@helowken-mint ~ $ ping redis
PING redis.ostechnix.lan (127.0.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from localhost (127.0.0.1): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.016 ms
64 bytes from localhost (127.0.0.1): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.031 ms
64 bytes from localhost (127.0.0.1): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.031 ms
/etc/resolv.conf 内容:
helowken@helowken-mint ~ $ cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 127.0.0.1
nameserver 202.96.128.166
nameserver 202.96.134.133
nameserver 163.15.15.15
search xxx.yyy ostechnix.lan
nameserver 表示 DNS 服务器地址:
- 127.0.0.1 是安装在本地的 DNS 服务器 bind9
- 202.xxx.xxx.xxx 是电信运营商自动生成的
- 163.15.15.15 是一个不存在 IP 地址,用于本次实验
search 表示自动添加到域名后面的搜索域:
- xxx.yyy 是一个没有记录搜索域,用于本次实验
- ostechnix.lan 存在于本地 bind9 的配置中,可以被 bind9 正确解析
使用 nslookup 可以再次确认 DNS 的可用:
helowken@helowken-mint ~ $ nslookup redis 127.0.0.1
Server: 127.0.0.1
Address: 127.0.0.1#53
Name: redis.ostechnix.lan
Address: 127.0.0.1
使用 dig 查询完整的 DNS 记录信息
helowken@helowken-mint ~ $ dig @127.0.0.1 redis.ostechnix.lan
; <<>> DiG 9.10.3-P4-Ubuntu <<>> @127.0.0.1 redis.ostechnix.lan
; (1 server found)
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 5064
;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 2, ADDITIONAL: 3
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;redis.ostechnix.lan. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
redis.ostechnix.lan. 86400 IN A 127.0.0.1
;; AUTHORITY SECTION:
ostechnix.lan. 86400 IN NS pri.ostechnix.lan.
ostechnix.lan. 86400 IN NS sec.ostechnix.lan.
;; ADDITIONAL SECTION:
pri.ostechnix.lan. 86400 IN A 192.168.1.200
sec.ostechnix.lan. 86400 IN A 192.168.1.201
;; Query time: 0 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1)
;; WHEN: Sat Nov 02 02:28:49 CST 2019
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 132
从 dig 的输出中可以看到返回了地址记录:
;; ANSWER SECTION:
redis.ostechnix.lan. 86400 IN A 127.0.0.1
综上所述,可以得知:
- 使用域名 “redis” 时,会自动添加搜索域 “ostechnix.lan”
- 向 nameserver 127.0.0.1 (bind9) 发送 DNS 查询请求 “redis.ostechnix.lan”,会得到实际的地址 127.0.0.1
使用 redis-cli 确认 sentinel 是可以连接的:
helowken@helowken-mint ~/redis-2.8.21 $ src/redis-cli -h redis -p 26379
redis:26379> sentinel get-master-addr-by-name mymaster
1) "127.0.0.1"
2) "6379"
接下来使用 dig 尝试往 “202.96.128.166” 发送查询请求:
helowken@helowken-mint ~ $ dig @202.96.128.166 redis.ostechnix.lan
; <<>> DiG 9.10.3-P4-Ubuntu <<>> @202.96.128.166 redis.ostechnix.lan
; (1 server found)
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NXDOMAIN, id: 18859
;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 0, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 0
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;redis.ostechnix.lan. IN A
;; AUTHORITY SECTION:
. 1800 IN SOA a.root-servers.net. nstld.verisign-grs.com. 2019110101 1800 900 604800 86400
;; Query time: 8 msec
;; SERVER: 202.96.128.166#53(202.96.128.166)
;; WHEN: Sat Nov 02 02:40:34 CST 2019
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 112
没有看到 “ANSWER SECTION”,也就是说没有查找到地址记录。(202.96.134.133 结果类似)
再尝试 dig “163.15.15.15”:
helowken@helowken-mint ~ $ dig @163.15.15.15 redis.ostechnix.lan
; <<>> DiG 9.10.3-P4-Ubuntu <<>> @163.15.15.15 redis.ostechnix.lan
; (1 server found)
;; global options: +cmd
;; connection timed out; no servers could be reached
发现连接超时。
如果依次往所有 nameserver 查询 “redis.xxx.yyy”,会发现:
- 127.0.0.1 和 202.xxx.xxx.xxx 都没有地址记录
- 163.15.15.15 连接超时
Netty 源码分析
因为源码内容较多,这里直接给出主要的逻辑:
- 当满足以下两个条件时,DNS 查找过程将终止:
- allowedQueries 递减为 0
- nameserver 列表已经遍历完
- allowedQueries 表示查找过程总共允许多少次查询,每发起一次查询就减 1。
- 查询会一个接一个 nameserver 地进行尝试,上一个 nameserver 查找失败后(没有记录,超时,网络问题),才会往下一个 nameserver 发送查询请求。
- 查询的时候会把搜索域(search domain)添加到名称的后面形成全路径(如果名称没有以"."结尾)。搜索域也是一个接一个地进行尝试,只要在上一个搜索域遍历完所有 nameserver 后都查找失败,才有可能使用下一个搜索域。
- 查找过程会同时发起 “A” 和 “AAAA” 记录的查询请求。“A” 记录表示 IPv4 的地址记录,“AAAA” 表示 IPv6 的地址记录。
- 如果所有 nameserver 查询 “A” 或 “AAAA” 记录都失败,且满足以下条件,则转为查询 “CNAME” 记录(“CNAME” 表示别名,相当于做多了一次命名映射):
- allowedQueries 还没有递减到 0
- 最后一次使用的 nameserver 没有出现错误
- 查询 “CNAME” 记录时,将重新遍历nameserver 列表,若 “CNAME” 有结果返回,则使用 “CNAME” 的结果再次查询 “A” 或 “AAAA” 记录。
- 如果在查找过程中,任一 nameserver 返回了记录,则终止查找。如果出现了错误,则使用下一个 nameserver 继续进行查询。
- 当 allowedQueries 递减到为 0 时,如果还没有找到 “A” 或 “AAAA” 记录,则返回 UnknownHostException。
- 如果最后一次查询出现了超时或者网络错误,则把 UnknownHostException 的 cause 设置为该错误。
- 检查返回的结果,如果存在 UnknownHostException,则检查它的 cause:
- if 超时或者网络错误,则最终判定为查找失败
- else if 还有搜索域可用,则使用下一个搜索域,重复上述的逻辑,开始新一轮的查找,且 allowedQueries 会重置为初始值
- else 其他的逻辑(当前可以省略)
实验
为了更容易和准确地得到实验结果,我稍微更改了一下 netty 的源码,调整的内容有:
- allowedQueries 根据每个实验进行设置
- 只查询 “A” 记录,不查询 “AAAA” 记录。如果两个都进行查询,会因为异步调用而出现随机性。
- 把查询超时从 5s 修改为 1s,这是为了快速得到结果。
本实验环节为了简单,不配置 CNAME 记录。
实验1
nameserver 127.0.0.1
nameserver 202.96.128.166
nameserver 202.96.134.133
nameserver 163.15.15.15
search xxx.yyy ostechnix.lan
| allowedQueries | Result |
|---|---|
| 1 ~ 3 | Pass |
| >= 4 | Failed |
结果分析:
- 当 allowedQueries 为 1~3 的时候,查询 “redis.xxx.yyy” 都没有记录,因此返回了 UnknownHostException,但因为没有超时或网络错误,且还有 “ostechnix.lan” 这个搜索域可用,所以用 “redis.ostechnix.lan” 开启新一轮查找,最后在 127.0.0.1 上查询到记录。
- 当 allowedQueries >= 4 时,第一轮查询的最后一个 nameserver 是 163.15.15.15,由于网络不可达,返回了超时错误,按照上面源码分析的结果,最终判定查找失败。(即使这时 allowedQueries > 0 也不会查询 “CNAME”,因为最后一次查询出了错)
实验2
nameserver 127.0.0.1
nameserver 202.96.128.166
nameserver 202.96.134.133
nameserver 163.15.15.15
search ostechnix.lan xxx.yyy
| allowedQueries | Result |
|---|---|
| N (N >= 1) | Pass |
结果分析:
- 只要 allowedQueries >= 1,在第一轮查找时,都会在 127.0.0.1 上查询到 “redis.ostechnix.lan” 的地址记录,所以 100% pass。
实验3
nameserver 202.96.128.166
nameserver 202.96.134.133
nameserver 163.15.15.15
nameserver 127.0.0.1
search xxx.yyy ostechnix.lan
| allowedQueries | Result |
|---|---|
| 1 ~ 3 | Failed |
| 4 ~ 6 | Pass |
| 7 | Failed |
| >= 8 | Pass |
结果分析:
- 当 allowedQueries 为 1~3 时,无论使用哪个搜索域,前 3 个 nameserver 都无法返回地址记录(202.xxx.xxx.xxx 是没有查找到记录,而 163.15.15.15 会超时),因为 allowedQueries 不够次数使请求落到 127.0.0.1 上面,所以最终判定查找失败。
- 当 allowedQueries == 4 时,第一轮搜索 “redis.xxx.yyy”,所有 nameserver 都查找失败,这时 allowedQueries 递减到 0,且最后一个 nameserver 是 127.0.0.1,虽然没有查询到记录,但也没有出现超时或者网络错误,于是使用 “redis.ostechnix.lan” 开启新一轮查找。第二轮查找时,最终会在 127.0.0.1 上查询到记录。
- 当 allowedQueries == [5, 6] 时,第一轮搜索 “redis.xxx.yyy”,所有 nameserver 都查找失败,这时 allowedQueries 递减到 2,因为最后一次查询是在 127.0.0.1 上进行的,虽然无记录但没有出错,于是从头遍历 nameserver 列表查找 “CNAME” 记录。但是两台 202.xxx.xxx.xxx 都无法查询到记录,这时 allowedQueries 递减到 0,因为最后一次查询 "CNAME"记录时虽然无记录,但也没有出现超时或者网络错误,于是使用 “redis.ostechnix.lan” 开启新一轮查找,最终在 127.0.0.1 上查询到记录。
- 当 allowedQueries == 7 时,第一轮搜索 “redis.xxx.yyy”,所有 nameserver 都查找失败,这时 allowedQueries 递减到 3,因为最后一次查询是在 127.0.0.1 上进行的,虽然无记录但没有出错,于是从头遍历 nameserver 列表查找 “CNAME” 记录。但是前 3 台 nameserver 都查找失败,这时 allowedQueries 递减到 0,因为最后一次查询 “CNAME” 记录是在 163.15.15.15 上进行的,出现了超时错误,所以最终判定查找失败。
- 当 allowedQueries >= 8 时,第一轮搜索 “redis.xxx.yyy”,所有 nameserver 都查找失败,这时 allowedQueries >= 4,因为最后一次查询是在 127.0.0.1 上进行的,虽然无记录但没有出错,于是从头遍历 nameserver 列表查找 “CNAME” 记录。虽然最后所有 nameserver 都查找失败,但是因为最后的查询请求是落在 127.0.0.1 上的,没有超时或网络错误,所以使用 “redis.ostechnix.lan” 开启新一轮查找,最后在 127.0.0.1 上查询到记录。
PS:你还可以进行更多的实验,根据上面的逻辑进行分析。
结论
解决办法
为了保证 Netty 查找 DNS 能成功,最好遵循以下准则:
- Netty 应用使用的搜索域,尽可能放在 /etc/resolv.conf 文件中 “search” 行的第一位
- 用于解析第1点中的搜索域的 nameserver,尽可能放在 /etc/resolv.conf 文件中 nameserver 列表的最上面
- 尽可能把网络不可达的 nameserver 从 /etc/resolv.conf 文件中删除
PS:
- Netty 对于 DNS 的默认查询超时是 5s,查询是一个接一个搜索域,一个接一个 nameserver 地串行进行的。如果存在 M 个无效的搜索域,N 个网络不可达的 nameserver,那么等待 DNS 查找结果的最差时间就会 >= (M * N * 5 * 2)s。(查找 “CNAME” 记录和查找 “A” 或 “AAAA” 地址记录一样, 所以 *2 )
- Netty 默认的 allowedQueries 为16,不要以为很多,因为是 “A” 和 “AAAA” 查询共用的,再加上 “CNAME” 的查询,能允许犯错的 nameserver 节点其实很少。
- 在实际查询过程中,“A” 和 “AAAA” 都是异步进行的,会存在运行顺序和返回结果先后的不确定性,当 allowedQueries 递减为 0 时,是无法确定最后一次查询使用哪个搜索域以及落在哪台 nameserver 上的,因此不要依赖这种顺序去配置 nameserver 的位置和搜索域的先后次序。
- Netty 查找 DNS 的代码,使用的全是 async 模式,性能虽然好,但是不容易阅读和维护,而且调试中发现不少逻辑存在问题,譬如:
- allowedQueries 递减到 0 了,还继续查询,查询又不断递归,最后直到遍历完所有 nameserver 才终止,但这个过程中其实什么都没干,因为每次进行真正的查询之前都需要检验 allowedQueries > 0
- 当最后一次查询出现错误时,就停止尝试剩余的搜索域
实验涉及到的 Netty 源码文件
查找 DNS:
io.netty.resolver.dns.DnsResolveContext
设置查询超时和 allowedQueries:io.netty.resolver.dns.DnsNameResolverBuilder
额外的测试代码
以下是模拟 Netty 发送 DNS 请求的代码,根据 Netty 的源码得来。
package io.netty.handler.codec.dns;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.PooledByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.util.internal.PlatformDependent;
import io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class DnsClient {
private static final InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 53);
private static final DnsRecordDecoder recordDecoder = DnsRecordDecoder.DEFAULT;
private static final int BUF_LENGTH = 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int id = PlatformDependent.threadLocalRandom().nextInt(65536 - 1) + 1;
DnsQuestion question = new DefaultDnsQuestion(
"redis.ostechnix.lan.",
new DnsRecordType(1, "A")
);
DnsQuery query = new DatagramDnsQuery(null, address, id);
query.setRecursionDesired(true);
query.addRecord(DnsSection.QUESTION, question);
DnsRecord optResource = new AbstractDnsOptPseudoRrRecord(4096, 0, 0) {
};
query.addRecord(DnsSection.ADDITIONAL, optResource);
ByteBuf buf = new PooledByteBufAllocator().ioBuffer(BUF_LENGTH);
new DnsQueryEncoder(DnsRecordEncoder.DEFAULT).encode(query, buf);
byte[] bs = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.getBytes(0, bs);
DnsQuery dnsQuery = sendAndReceive(bs);
print(dnsQuery);
}
private static void print(DnsQuery msg) {
System.out.println(msg);
System.out.println("===========================");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
printSection(sb, msg, DnsSection.ADDITIONAL);
printSection(sb, msg, DnsSection.ANSWER);
System.out.println(sb);
}
private static void printSection(StringBuilder sb, DnsQuery message, DnsSection section) {
final int count = message.count(section);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
DnsRecord record = message.recordAt(section, i);
if (record instanceof DefaultDnsRawRecord)
printRecord((DefaultDnsRawRecord) record, sb);
}
}
private static void printRecord(DefaultDnsRawRecord record, StringBuilder buf) {
final DnsRecordType type = record.type();
if (type == DnsRecordType.OPT)
return;
buf.append(StringUtil.NEWLINE).append(StringUtil.TAB);
buf.append(record.name().isEmpty() ? "" : record.name()).append(" => ");
ByteBuf byteBuf = record.content();
if (type.intValue() == DnsRecordType.A.intValue()) {
byte[] bs = new byte[byteBuf.readableBytes()];
byteBuf.readBytes(bs);
try {
buf.append(
InetAddress.getByAddress(bs)
);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
buf.append(byteBuf.readableBytes()).append("B)");
}
}
private static DnsQuery sendAndReceive(byte[] bs) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bs, bs.length, address);
socket.send(packet);
packet = new DatagramPacket(new byte[BUF_LENGTH], BUF_LENGTH);
socket.receive(packet);
ByteBuf buf = new PooledByteBufAllocator().ioBuffer(BUF_LENGTH);
buf.writeBytes(packet.getData(), 0, packet.getLength());
return decode(buf);
}
private static DnsQuery decode(ByteBuf buf) throws Exception {
final DnsQuery query = newQuery(buf);
final int questionCount = buf.readUnsignedShort();
final int answerCount = buf.readUnsignedShort();
final int authorityRecordCount = buf.readUnsignedShort();
final int additionalRecordCount = buf.readUnsignedShort();
decodeQuestions(query, buf, questionCount);
decodeRecords(query, DnsSection.ANSWER, buf, answerCount);
decodeRecords(query, DnsSection.AUTHORITY, buf, authorityRecordCount);
decodeRecords(query, DnsSection.ADDITIONAL, buf, additionalRecordCount);
return query;
}
private static DnsQuery newQuery(ByteBuf buf) {
final int id = buf.readUnsignedShort();
final int flags = buf.readUnsignedShort();
// if (flags >> 15 == 1) {
// throw new CorruptedFrameException("not a query");
// }
final DnsQuery query =
new DatagramDnsQuery(
null,
address,
id,
DnsOpCode.valueOf((byte) (flags >> 11 & 0xf)));
query.setRecursionDesired((flags >> 8 & 1) == 1);
query.setZ(flags >> 4 & 0x7);
return query;
}
private static void decodeQuestions(DnsQuery query, ByteBuf buf, int questionCount) throws Exception {
for (int i = questionCount; i > 0; i--) {
query.addRecord(DnsSection.QUESTION, recordDecoder.decodeQuestion(buf));
}
}
private static void decodeRecords(
DnsQuery query, DnsSection section, ByteBuf buf, int count) throws Exception {
for (int i = count; i > 0; i--) {
final DnsRecord r = recordDecoder.decodeRecord(buf);
if (r == null) {
break;
}
query.addRecord(section, r);
}
}
}
以下是 本实验中 bind9 的 DNS 配置文件:
helowken@helowken-mint ~ $ cat /etc/bind/for.ostechnix.lan
$TTL 86400
@ IN SOA pri.ostechnix.lan. root.ostechnix.lan. (
2011071001 ;Serial
3600 ;Refresh
1800 ;Retry
604800 ;Expire
86400 ;Minimum TTL
)
$ORIGIN ostechnix.lan.
@ IN NS pri.ostechnix.lan.
@ IN NS sec.ostechnix.lan.
@ IN A 192.168.1.200
@ IN A 192.168.1.201
@ IN A 192.168.1.202
pri IN A 192.168.1.200
sec IN A 192.168.1.201
client IN A 192.168.1.202
redis IN A 127.0.0.1
redis IN AAAA ::1