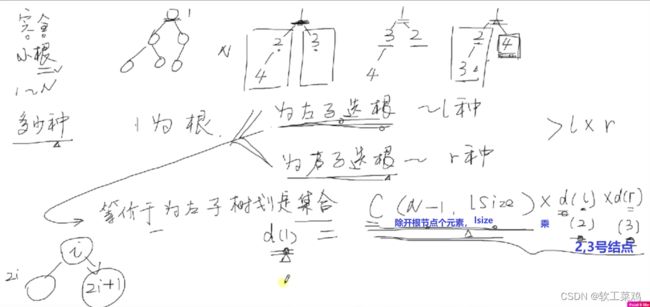
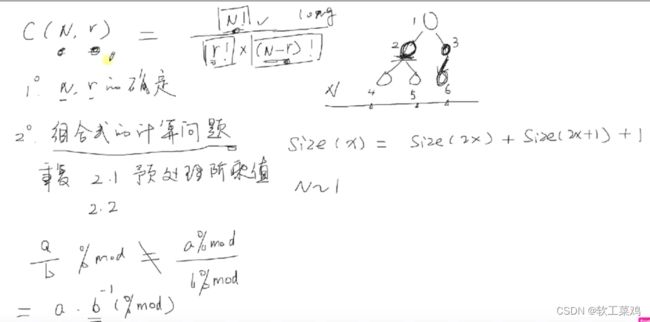
第十四届 蓝桥杯java组备赛考纲解读 技巧 查找 深搜宽搜 DFS 动态规划 数论 暴力枚举
CSDN客服说是广告我就删减了一部分
大佬经验
第一次参赛获Java B组国二,给蓝桥杯Beginners的6700字保姆级经验分享
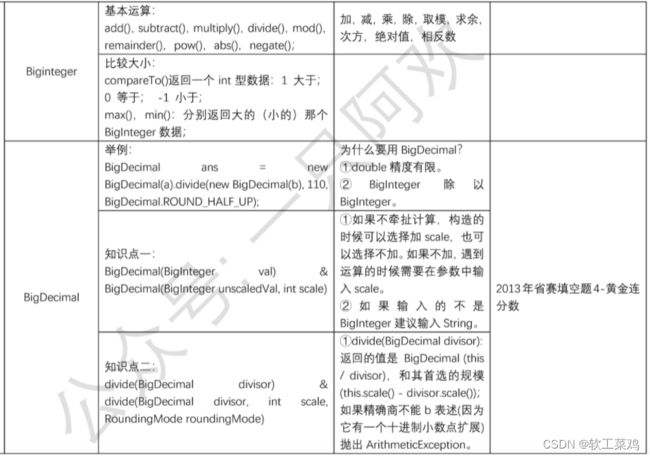
Java常用API
4. 集合API、集合遍历、排序(建议掌握)
7. 数学知识(建议掌握)
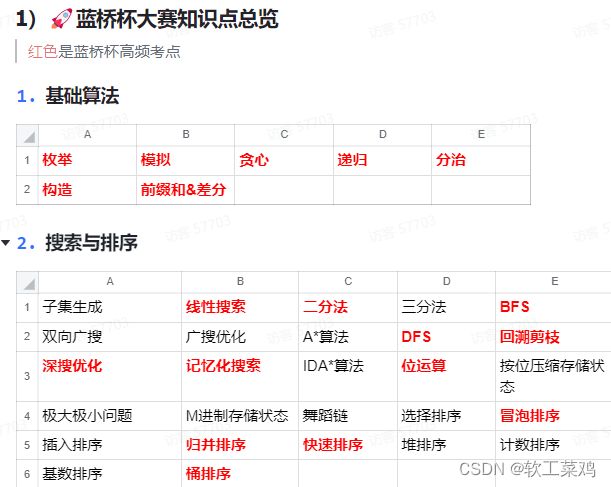
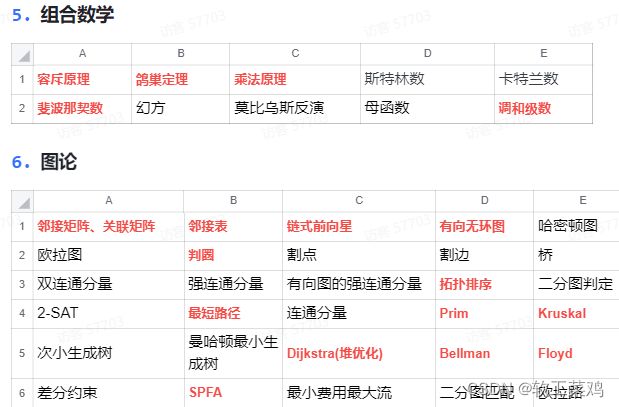
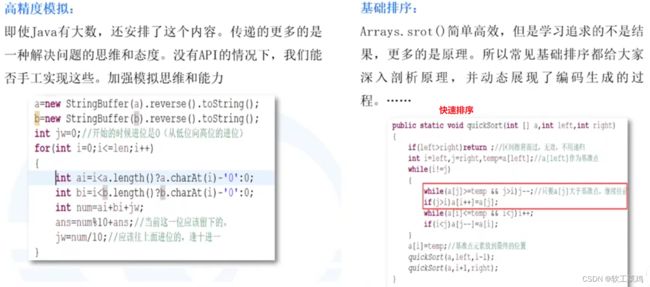
三、蓝桥杯官方常考点总结
官方竞赛大纲讲解
题型分值
【距省赛仅1个多月!蓝桥杯的比赛流程和必考点,你还不清楚?】听说省二四五道题就行
CC150给出算法题的五种解法
手算&填空题技巧
巧用编辑器
心算手数
巧用Excel
购物单
Excel文本转为列
巧用Python(字符、大数、日期)
平方和 确实 python处理字符简单一点哈
建议刷题
枚举和查找
!最少刷题数-蓝桥杯2022年第十三届省赛真题
https://www.dotcpp.com/oj/problem2673.html
时间限制: 1s 内存限制: 512MB 提交: 1843 解决: 211
题目描述
小蓝老师教的编程课有 N 名学生,编号依次是 1 . . . N。第 i 号学生这学期刷题的数量是 Ai。
对于每一名学生,请你计算他至少还要再刷多少道题,才能使得全班刷题比他多的学生数不超过刷题比他少的学生数。
输入格式
第一行包含一个正整数 N。
第二行包含 N 个整数:A1, A2, A3, . . . , AN.
输出格式
输出 N 个整数,依次表示第 1 . . . N 号学生分别至少还要再刷多少道题。
样例输入
5
12 10 15 20 6
样例输出
0 3 0 0 7
提示
对于 30% 的数据,1 ≤ N ≤ 1000, 0 ≤ Ai ≤ 1000.
对于 100% 的数据,1 ≤ N ≤ 100000, 0 ≤ Ai ≤ 100000.//自己做的 超时
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int[] arr=new int[n];
int[] brr=new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int[] crr=arr.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int m=crr[i];
for (int j = i ; j < n; j++) {
if(m>crr[j]) {
m=crr[j];
crr[j]=crr[i];
crr[i]=m;
}
crr[i]=m;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int count=0;
int k=0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(j时间复杂度:O(N*log(max(A))*logN)
二分找需要刷题数目a, 设已经刷了多少题为x,再二分找符合 < a + x - 1 与 > a + x + 1 的人数,根据题目要求比较即可。
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main{
static int[] a, b;
static int n;
static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static BufferedWriter log = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
n = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
String[] s = reader.readLine().split(" ");
a = new int[n];
b = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
a[i] = Integer.parseInt(s[i]);
b[i] = a[i];
}
Arrays.sort(b);
int[] res = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res[i] = getMin(a[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
log.write(res[i] + " ");
}
// 释放资源
reader.close();
log.flush();
log.close();
}
//lowerBound
public static int getMin(int nums) {
int l = 0, r = b[n - 1];
while(l < r) {
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(getR(nums + mid - 1, mid) < getL(nums + mid + 1)) {
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid;
}
}
return l;
}
public static int getR(int tar, int e) {
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
while(l < r) {
int mid = l + r + 1>> 1;
if(b[mid] <= tar) {
l = mid;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
return e == 0 ? l + 1 : l;
}
public static int getL(int tar) {
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
while(l < r) {
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(b[mid] < tar) {
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid;
}
}
return tar > b[n - 1] ? 0 : n - l;
}
}力扣869. 重新排序得到 2 的幂
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reordered-power-of-2/solution/zhong-xin-pai-xu-de-dao-2-de-mi-by-leetc-4fvs/
class Solution {
boolean[] vis;
public boolean reorderedPowerOf2(int n) {
char[] nums = Integer.toString(n).toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(nums);
vis = new boolean[nums.length];
return backtrack(nums, 0, 0);
}
public boolean backtrack(char[] nums, int idx, int num) {
if (idx == nums.length) {
return isPowerOfTwo(num);
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
// 不能有前导零
if ((num == 0 && nums[i] == '0') || vis[i] || (i > 0 && !vis[i - 1] && nums[i] == nums[i - 1])) {
continue;
}
vis[i] = true;
if (backtrack(nums, idx + 1, num * 10 + nums[i] - '0')) {
return true;
}
vis[i] = false;
}
return false;
}
public boolean isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
return (n & (n - 1)) == 0;
}
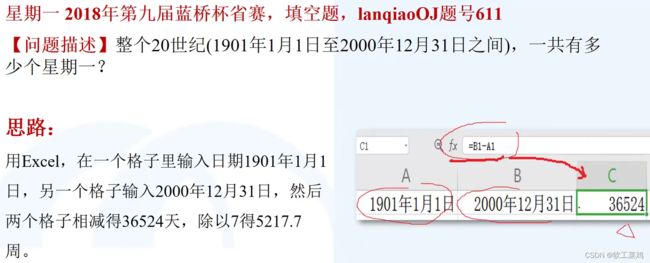
}*世纪末的星期
幸运数
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
int m=scanner.nextInt();
int n=scanner.nextInt();
ArrayList aee = new ArrayList();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(i%2!=0)
aee.add(i);
}
//System.out.println(aee);
int l=3;
for(int j=1;jj;i--){
if( (i+1)%l==0 ) {
aee.remove(i);
}
}
if(j!=aee.size()-1)
l=aee.get(j+1);
}
// System.out.println(aee);
int c=0;
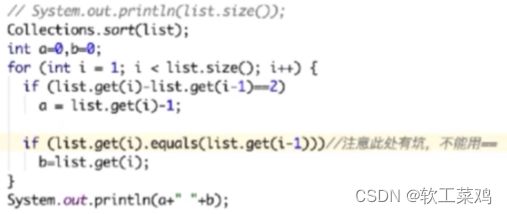
for(int i=0;im&&r 错误票据
猜字母 太简单了
分糖果
return;
}
}
}字符串子序列
我自己写的拿了66.7 后面的超时了; 感觉写法稀碎,乱的一批!
public class Main {
static int c=0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
String s=sc.next().toLowerCase();
int m=sc.nextInt();
String z=sc.next().toLowerCase();
for (int j = 0,i = 0; j < n&&ipublic class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
char[] s1=sc.next().toLowerCase().toCharArray();
int m=sc.nextInt();
char[] s2=sc.next().toLowerCase().toCharArray();
int j=0;
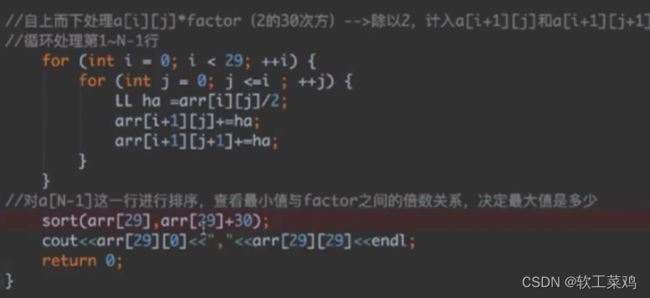
for(int i=0;i*承压计算 本题坑在于两次计量单位怎么试出来 先扩大倍数防止精度丢失,然后缩小
<<1(更快!)等价于*2;乘factor保证除30次没有小数,防止精度丢失;
最终试错发现最小的电子秤是题目给的两倍,说明试的factor不对
卡片 真服了
public class Main {//自己作的
static int[] arr={2021,2021,2021,2021,2021,2021,2021,2021,2021,2021};
static int ans=1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
while(true){
ans++;
if(!check(ans)){//检查不合法
break;
}
}
System.out.println(ans-1);//ans-2答案正确,但是我就觉得是-1呀!
}
public static boolean check(int x){
while(x>0){
int a=x%10;
if(arr[a]>0){
arr[a]--;
}
else{
return false;
}
x/=10;
}
return true;
}
}
------------------------------以下是官方题解
public class Main {
static int[] num = {2021,2021,2021,2021,2021,2021,2021,2021,2021,2021};
static int check(int x){
while(x > 0){
int now = x % 10;
if(num[now] > 0) num[now]--;
else return 0;
x /= 10;
}
return 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 1;;i++) {
if (check(i) == 0) {
System.out.println(i - 1);
break;
}
}
}
}深搜DFS宽搜BFS(A组*题目) 回溯算法
*带分数
其实感觉这道题10层循环也可以吧
public class Main02 {
static int ans; //全局变量 return最终结果
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int N=sc.nextInt();
int[] arr= {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
f(arr,0,N);
System.out.println(ans);
}
//确认某排列的第k位
private static void f(int[] arr, int k,int n) {
//全排列全部确认
if(k==9) {
Check(arr,n);
return;
}
//选定第k位
for(int i=k;in) return false;
// // /后面至少有1个数字,前面
// for (int j = i+1; j < 8-i; j++) {
// mid += (int) (arr[j]*Math.pow(10, j-i-1));
// right += (int) (arr[j+1]*Math.pow(10, j-i-2));
// if(mid=n )
continue;
// /后面至少有1个数字,前面
for (int j = 1; j <= 8-i; j++) {
int num2=toInt(arr,i,j);
int num3=toInt(arr,j+i,9-(i+j));
if(num3==0) return;
if(num2%num3==0&&num1+num2/num3==n)
ans++;
}
}
}
//把数组元素拼接 成数字
private static int toInt(int[] arr, int pos, int len) {
int t=1;//10,100,1000...
int ans=0;
for (int i = pos+len-1; i >= pos; i--) {
ans+=arr[i]*t;//进位
t*=10;
}
return ans;
}
} 46. 全排列
47. 全排列 II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations-ii/solution/quan-pai-lie-ii-by-leetcode-solution/
地宫取宝 没看懂
dsf(坐标x,坐标y,最大值,物品数);//第一个值可能是0所以传-1,
扑克序列(全排列+check)
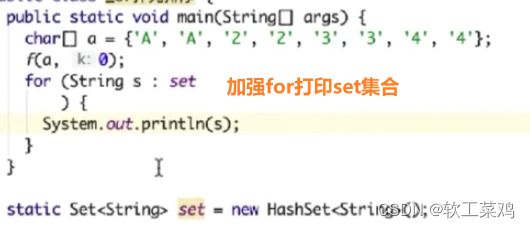
技巧7: 重复元素去重用set;
凑算式 凑分式相加res=整数(通分)
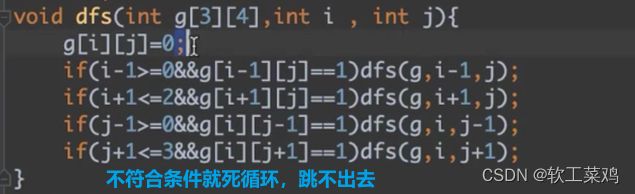
!剪邮票 DFS连通性
!生命之树
首先暴力枚举所有子集30:DFS探测是否连通
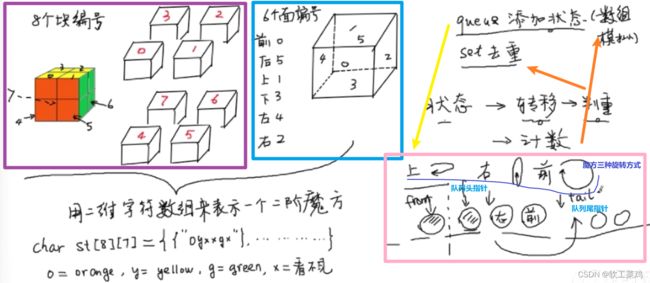
魔方状态 空间状态搜索。模拟操作+判重
#include
using namespace std;
typedef char st[8][7];
st state[2000000];
set all;
st begin={{"oybbgb"},{"oygbbb"},{"bygbby"},{"bybbgy"},{"obbogb"},{"obgobb"},{"bbgoby"},{"bbbogy"}};
//st begin={{"oooooo"},{"oooooo"},{"oooooo"},{"oooooo"},{"oooooo"},{"oooooo"},{"oooooo"},{"oooooo"}};
//只有一个颜色的魔方 ans=1
//st begin={{"rykkbk"},{"rygkkk"},{"kygkko"},{"kykkbo"},{"rkkwbk"},{"rkgwkk"},{"kkgwko"},{"kkkwbo"}};
//正常2阶魔方状态 r红 y黄 b蓝 g绿 w白 o橙 k黑(红对橙,白对黄,蓝对绿,颜色相近的相对)这里白为底 前为红
//需要将state大小改为4000000
//这个测试用例跑了20分钟左右 560M内存 ans=3674160 与实际二阶魔方状态数相同 见下截图
int front, tail;
void ucell(char *a){swap(a[0], a[2]); swap(a[2], a[5]); swap(a[5], a[4]);}
void rcell(char *a){swap(a[1], a[0]); swap(a[0], a[3]); swap(a[3], a[5]);}
void fcell(char *a){swap(a[2], a[1]); swap(a[1], a[4]); swap(a[4], a[3]);}
void u(st &s)//顶层顺时针旋转
{
ucell(s[0]);
ucell(s[1]);
ucell(s[2]);
ucell(s[3]);
swap(s[1], s[0]);
swap(s[2], s[1]);
swap(s[3], s[2]);
}
void uwhole(st &s)//整个魔方从顶部看 顺时针转 用于判重
{
u(s);
ucell(s[4]);
ucell(s[5]);
ucell(s[6]);
ucell(s[7]);
swap(s[5], s[4]);
swap(s[6], s[5]);
swap(s[7], s[6]);
}
void f(st &s)//前面一层 顺时针转
{
fcell(s[0]);
fcell(s[1]);
fcell(s[4]);
fcell(s[5]);
swap(s[1], s[5]);
swap(s[0], s[1]);
swap(s[4], s[0]);
}
void fwhole(st &s)//整个魔方从前面看 顺时针转 用于判重
{
f(s);
fcell(s[2]);
fcell(s[6]);
fcell(s[7]);
fcell(s[3]);
swap(s[2], s[6]);
swap(s[3], s[2]);
swap(s[7], s[3]);
}
void r(st &s)//魔方右层顺时针转
{
rcell(s[1]);
rcell(s[2]);
rcell(s[6]);
rcell(s[5]);
swap(s[2], s[1]);
swap(s[5], s[1]);
swap(s[6], s[5]);
}
void rwhole(st &s)//整个魔方从右边看 顺时针转 用于判重
{
r(s);
rcell(s[0]);
rcell(s[3]);
rcell(s[4]);
rcell(s[7]);
swap(s[3], s[7]);
swap(s[0], s[3]);
swap(s[4], s[0]);
}
string convert(st &s)//魔方状态二维字符数组 转化为string
{
string ss;
for(int i=0; i<8; i++)ss+=s[i];
return ss;
}
bool try_to_insert(int tail)//判重
{
st k;
memcpy((void*)k, (void*)state[tail], sizeof(state[tail]));
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
fwhole(k);
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
uwhole(k);
for(int q=0; q<4; q++)
{
rwhole(k);
if(all.count(convert(k))==1)
{
return false;
}
}
}
}
all.insert(convert(k));
return true;
}
int main()
{
front=0,tail=1; //队列中的首尾
all.insert(convert(begin));
memcpy((void*)state[0],(void*)begin,sizeof(begin));
while(front!=tail)
{
//对当前状态分别模拟三种操作U R F 然后判重
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
memcpy((void*)state[tail], (void*)state[front], sizeof(state[front]));
if(i==0)
{
u(state[tail]);
if(try_to_insert(tail))tail++;
}
else if(i==1)
{
r(state[tail]);
if(try_to_insert(tail))tail++;
}
else if(i==2)
{
f(state[tail]);
if(try_to_insert(tail))tail++;
}
}
front++;
}
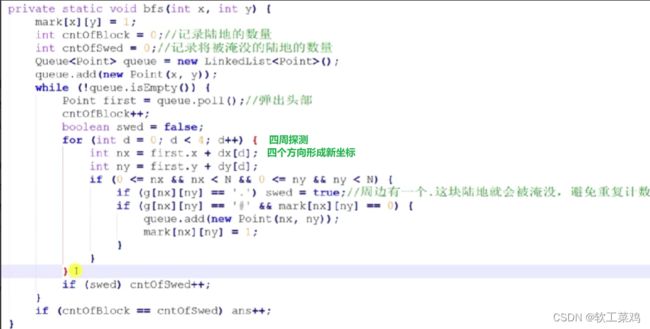
cout< 全球变暖BFS宽搜连通块模板
BFS=自定义对象+队列;
纸牌三角形 全排列
正三角形,三边和相等的旋转3种,镜像3种 都算同种,所以有六种重复ans/6;
最大公共子串
动态规划(逆向思维+分类讨论)
我觉得用数组代替函数这个思想非常哇塞
暴力dfs-->记忆化搜索-->递推-->动态规划;层层优化
*李白打酒
//自己写的垃圾,还错了
public class Main {
static int ans=0;
static StringBuilder s=new StringBuilder();
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println( dp(2,5,9)+dp(2,4,10) ) ;
}
static int dp(float count,int a,int b){
if(b==0&&count==1&&a==0) {
ans++;
return ans;
}else if(b==2&&count==2&&a==0) {
return dp( count, a, b-=2);
}else if(b==2&&count==1&&a==1) {
return dp(count, a-1, b-=2);
}
return dp(count-1, a-1, b)+dp(count-1, a, b-1);
}
}李白打酒加强版
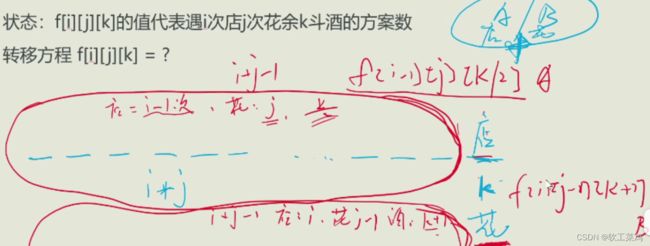
因为题目要求最后一个是遇到花,所以可以少枚举一个
DP一般以样例为例子: 一直分类下图是 前两次的分法
5店8花2斗的方案分类
*198. 打家劫舍
https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber/solution/da-jia-jie-she-by-leetcode-solution/
class Solution {//自己写的
public int rob(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length-1;
if(n==0) return nums[0];
else if(n==1) return Math.max(nums[0],nums[1]);
int[] db=new int[nums.length];
db[0]=nums[0];
db[1]=nums[1];
for(int i=2;iclass Solution {//官方
public int rob(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int length = nums.length;
if (length == 1) {
return nums[0];
}
int[] dp = new int[length];
dp[0] = nums[0];
dp[1] = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 2] + nums[i], dp[i - 1]);
}
return dp[length - 1];
}
}振兴中华
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(f(0,0));
}
public static int f(int a,int b){
if(a==3||b==4)
return 1;
return f(a+1,b)+f(a,b+1);
}
}牌型总数
k代表考虑到第几张牌,cnt代表手里牌的总数
归结为 每个牌出现0~4次,超过13不行,超过13的return;
70. 爬楼梯
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int[] a=new int[n+1];
a[1]=1;a[0]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
a[i]=(a[i-1])+(a[i-2]);
}
return a[n];
}
}官方题解 滚动数组
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int p = 0, q = 0, r = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
p = q;
q = r;
r = p + q;
}
return r;
} }118. 杨辉三角
我的想法就根据上一行 递归 跟官方思路也一样;但是集合brr 的静态改变不如动态函数传参
class Solution {
public List> generate(int numRows) {
ArrayList> list=new ArrayList<>();
List first=new ArrayList<>();
first.add(1);
list.add(first);
List second=new ArrayList<>();
if(numRows>=2)
{
second.add(1);
second.add(1);
list.add(second);
}
for(int i=3;i<=numRows;i++){
List arr=new ArrayList<>();
arr.add(1);
List brr=second;
for(int j=1;j class Solution {
public List> generate(int numRows) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
List firstRow = new ArrayList<>();
firstRow.add(1);
res.add(firstRow);
func(res, firstRow, numRows);
return res;
}
private void func(List> res, List lastRow, int numRows) {
if (lastRow.size() == numRows) {
return;
}
List curRow = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < lastRow.size() - 1; i++) {
curRow.add(lastRow.get(i) + lastRow.get(i + 1));
}
curRow.add(0, 1);
curRow.add(curRow.size(), 1);
res.add(curRow);
func(res, curRow, numRows);
} } 数学解法(官方)
class Solution {
public List> generate(int numRows) {
List> ret = new ArrayList>();
for (int i = 0; i < numRows; ++i) {
List row = new ArrayList();
for (int j = 0; j <= i; ++j) {
if (j == 0 || j == i) {
row.add(1);
} else {
row.add(ret.get(i - 1).get(j - 1) + ret.get(i - 1).get(j));
}
}
ret.add(row);
}
return ret;
} } class Solution {
public List> generate(int numRows) {
if (numRows < 1) return new ArrayList<>();
List> ans = new ArrayList<>();
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(){{add(1);}});
for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {
Integer[] arr = new Integer[i + 1];
arr[0] = arr[i] = 1;
for (int x = 1; x < i; x++)
arr[x] = ans.get(i - 1).get(x) + ans.get(i - 1).get(x - 1);
ans.add(Arrays.asList(arr));
}
return ans;
}
} 很巧妙的找规律
我刚开始看到这个思路感觉很巧妙,但是细细照着这个思路做了半个小时,作者做的是Python所以这个思路很适合,首先我认为就是这个思路做java不合适,因为java的要求是返回List
如果用这个思路做,就必须先把一行组装成一个int,前面+0,后面+0再相加; 然后 再次拆分成一个个 个位数add到小List,add到大List 很浪费时间就下面这个代码效率很差
class Solution {
public List> generate(int numRows) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(numRows == 0) return res;
res.add( new ArrayList<>() {{ add(1); }} );//第一行
int size = res.size();
while(size < numRows){
LinkedList first = new LinkedList<>();
first.addFirst(0);
LinkedList second = new LinkedList<>();
second.addLast(0);
for(int x: res.get(size-1)){
first.addFirst(x);
second.addLast(x);
}
List newRow = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i !垒骰子_15
!测试次数
if手机摔坏,初始3个,3--
!堆的计数
!取球博弈
博弈问题 身份互换 三判定
技巧13:判断奇数( (a&1)==1);判偶( (a&1) ==0)
优化重复数据组合,减小规模,缓存实现记忆性递归
记忆性递归技巧:在函数出口下面查
数学思维和知识
修改数组
public class Main {//自己写的40%
static int[] arr;
static int[] brr;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
//在此输入您的代码...
int n=scan.nextInt();
arr=new int[n];
for(int i=0;iimport java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int[] count=new int[1000001]; //记录每一个Ai出现的次数
long[] arr=new long[n]; //最终数组
for(int i=0;i黄金连分数-大数
.ROUNG_HALF_DOWN四舍五入
阶乘约数_国20-大数
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(scan.next());很神奇的题解?为甚?
立方变自身
当99的时候就不可能成立了所以上限99即可
连号区间数
三羊献瑞
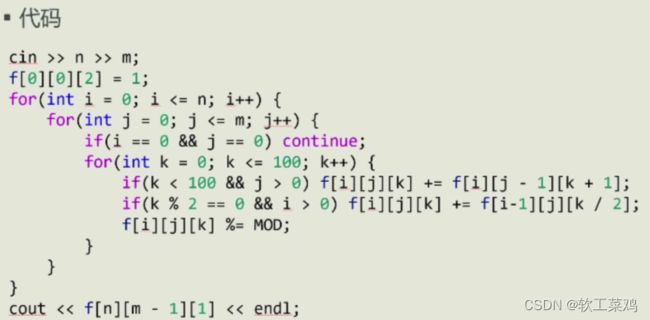
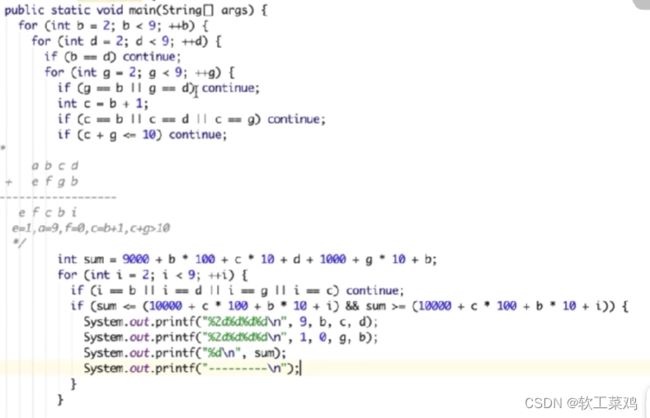
不能直接枚举,太麻烦。先观察几个再枚举,我就觉得e=1没毛病,但是a=8后面进位也有可能,他应该验证一下8不对,不能跳了直接到a=9
武功秘籍 我觉得很怪
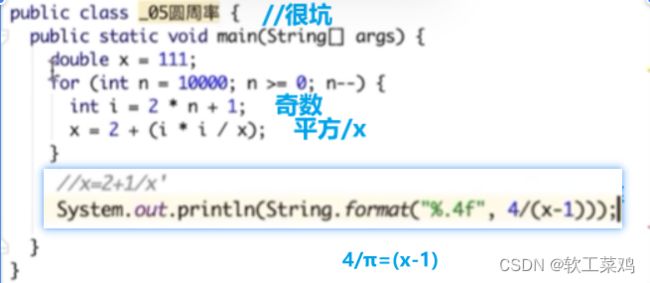
圆周率
抽签
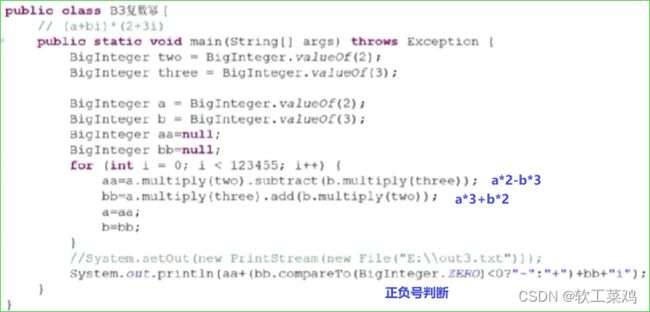
复数幂 (大数)
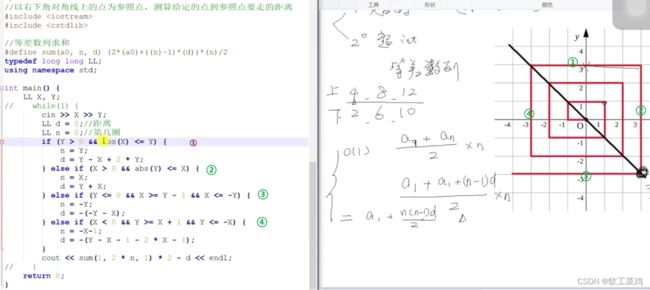
螺旋折线
n代表等差数列有多少项,d代表减的距离。
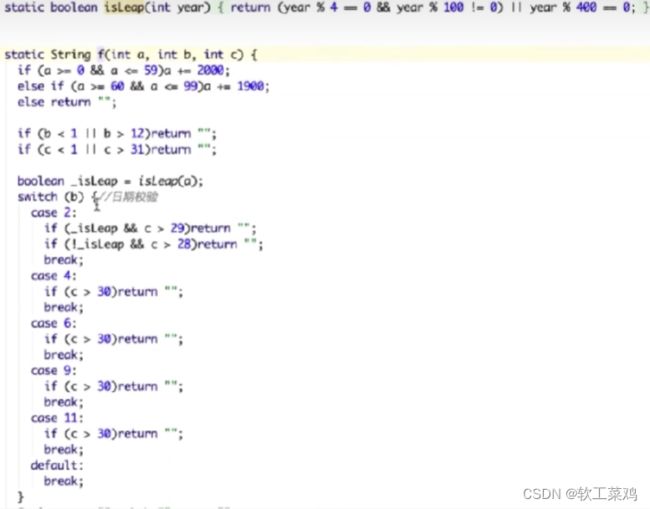
日期问题
我的想法就是 挨个判断 但是老师的讲法就是 不符合的return“”;剩下的情况就是对的!
还有用treeset排序去重!我自己写的忘记了去重
public class Main
{ public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=scanner.next();
int a=Integer.parseInt(str.split("/")[0]);
int ar=Integer.parseInt(str.split("/")[1]);
int arr=Integer.parseInt(str.split("/")[2]);
panduan(a, ar, arr);
panduan(arr, ar, a);
panduan(arr, a, ar);
}
public static void panduan(int a,int b,int c) {
if(a<60&&b<12) {
LocalDate ld=LocalDate.of(2000+a, b+1, 1);
LocalDate ld2=ld.minusDays(1);
int day2=ld2.getDayOfMonth();
if(c<=day2) {
if(b<10&&c>=10)
System.out.println(2000+a+"-0"+b+"-"+c);
else if(b<10&&c<10)
System.out.println(2000+a+"-0"+b+"-0"+c);
else if(b>=10&&c<10)
System.out.println(2000+a+"-"+b+"-0"+c);
else
System.out.println(2000+a+"-"+b+"-"+c);
}
}
else if(a<60&&b==12) {
LocalDate ld=LocalDate.of(2001+a, 1, 1);
LocalDate ld2=ld.minusDays(1);
int day2=ld2.getDayOfMonth();
if(c<=day2) {
if(b<10&&c>=10)
System.out.println(2000+a+"-0"+b+"-"+c);
else if(b<10&&c<10)
System.out.println(2000+a+"-0"+b+"-0"+c);
else if(b>=10&&c<10)
System.out.println(2000+a+"-"+b+"-0"+c);
else
System.out.println(2000+a+"-"+b+"-"+c);
}
}
else if(a>=60&&b<12) {
LocalDate ld=LocalDate.of(1900+a, b+1, 1);
LocalDate ld2=ld.minusDays(1);
int day2=ld2.getDayOfMonth();
if(c<=day2) {
if(b<10&&c>=10)
System.out.println(1900+a+"-0"+b+"-"+c);
else if(b<10&&c<10)
System.out.println(1900+a+"-0"+b+"-0"+c);
else if(b>=10&&c<10)
System.out.println(1900+a+"-"+b+"-0"+c);
else
System.out.println(1900+a+"-"+b+"-"+c);
}
}
else if(a>=60&&b==12) {
LocalDate ld=LocalDate.of(1901+a, 1, 1);
LocalDate ld2=ld.minusDays(1);
int day2=ld2.getDayOfMonth();
if(c<=day2) {
if(b<10&&c>=10)
System.out.println(1900+a+"-0"+b+"-"+c);
else if(b<10&&c<10)
System.out.println(1900+a+"-0"+b+"-0"+c);
else if(b>=10&&c<10)
System.out.println(1900+a+"-"+b+"-0"+c);
else
System.out.println(1900+a+"-"+b+"-"+c);
}
}
}
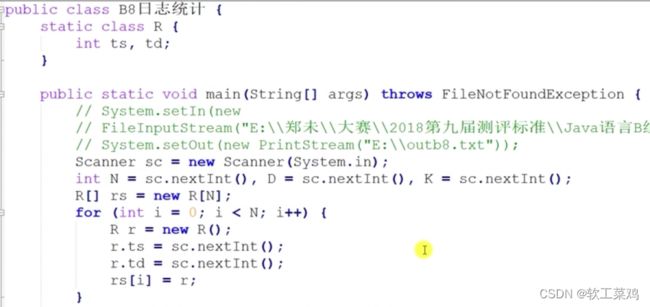
}!日志统计map尺取法
暴力枚举
一直不知道啥意思,其实很简单,就是猜或者遍历
生日蜡烛
四平方和 因为a最小 所以a²取值范围≤N/4 四次遍暴力枚举超时
暴力枚举优化1减少变量取值范围,变量个数;数据缓存到hashMap,减少变量个数
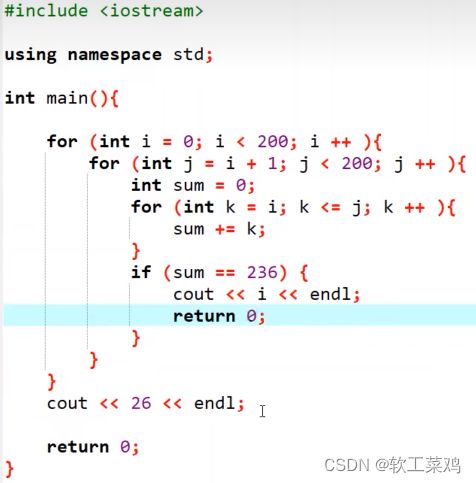
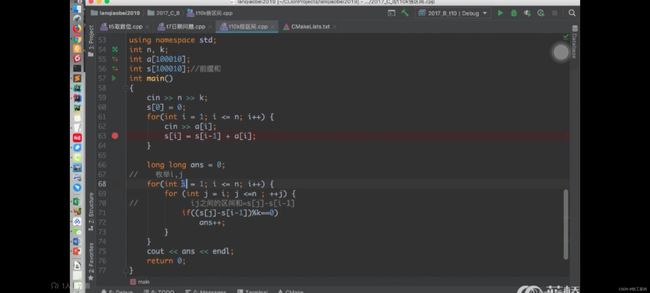
K倍区间
技巧11.5:计算1~n用 t--,别用fori
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t-- > 0){}递增三元组
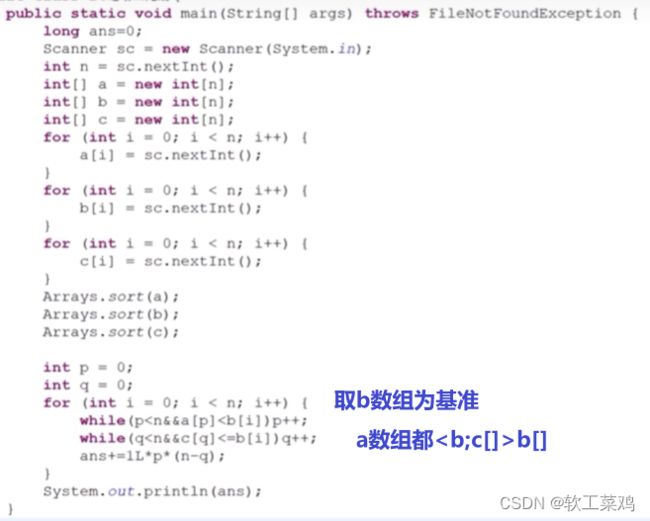
public class Main {//自己写的三重暴力拿了62.5的分数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=scan.nextInt();
scan.nextLine();//吞掉第一行的剩下的东西
int[][] arr=new int[3][n];
String s0=scan.nextLine();
String s1=scan.nextLine();
String s2=scan.nextLine();
//System.out.println(s0);
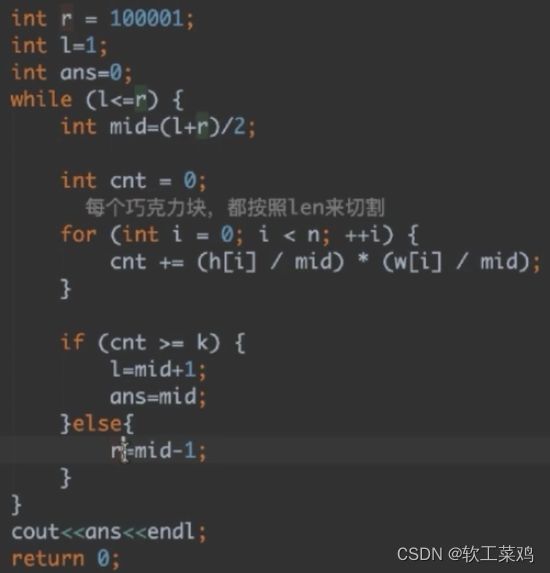
for(int i=0;i分巧克力 用二分优化暴力
从 int len=100000;开始 用二分法 找最大的切割块
技巧14:区间树(线段树)优化区间和的查询,也可用于求区间最值
!他的优化也是数组赋值,快速识别!我差了一点捏
九进制转十进制_2022
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String rs="2022";
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt(rs,9));
}
}常见错误解析
//感觉今年好难特别是填空题!