java多域名共享session_同一服务器不同域名session共享
Tomcat下,不同的二级域名之间或根域与子域之间,Session默认是不共享的,因为Cookie名称为JSESSIONID的Cookie根域是默认是没设置 的,访问不同的二级域名,其Cookie就重新生成,而session就是根据这个Cookie来生成的,所以在不同的二级域名下生成的Session也 不一样。找到了其原因,就可根据这个原因对Tomcat在生成Session时进行相应的修改(注:本文针对Tomcat 6.0.18)。
方案一:
修改tomcat源代码 包:catalina.jar
类:org.apache.catalina.connector.Request
protectedvoidconfigureSessionCookie(Cookie cookie) {
cookie.setMaxAge(-1);
String contextPath = null;
if(!connector.getEmptySessionPath() && (getContext() !=null)) {
contextPath = getContext().getEncodedPath();
}
if((contextPath !=null) && (contextPath.length() >0)) {
cookie.setPath(contextPath);
}else{
cookie.setPath("/"); }
String value = System.getProperty("webDomain");
if((null!=value) && (value.length()>0) && (value.indexOf(".") != -1)) {
cookie.setDomain((value.startsWith("."))?value:"."+value);
}
if(isSecure()) {
cookie.setSecure(true); }
重新编译Tomcat:编译tomcat
修改配置:tomcat\conf\catalina.properties,在最后添加一行 webDomain=***.com
方案二:
网上其他方案
Usage:
- compile CrossSubdomainSessionValve & put it in a .jar file
- put that .jar file in $CATALINA_HOME/lib directory
- include a
in
$CATALINA_HOME/conf/server.xml
packageorg.three3s.valves;
importjava.io.*;
importjavax.servlet.*;
importjavax.servlet.http.*;
importorg.apache.catalina.*;
importorg.apache.catalina.connector.*;
importorg.apache.catalina.valves.*;
importorg.apache.tomcat.util.buf.*;
importorg.apache.tomcat.util.http.*;
/**
Replaces the domain of the session cookie generated by Tomcat
with a domain that allows that
* session cookie to be shared across subdomains. This valve digs
down into the response headers
* and replaces the Set-Cookie header for the session cookie, instead
of futilely trying to
* modify an existing Cookie object like the example at
http://www.esus.be/blog/?p=3. That
* approach does not work (at least as of Tomcat 6.0.14) because the
* org.apache.catalina.connector.Response.addCookieInternal
method renders the
* cookie into the Set-Cookie response header immediately, making any
subsequent modifying calls
* on the Cookie object ultimately pointless.
*
*
This results in a single, cross-subdomain session cookie on the
client that allows the
* session to be shared across all subdomains. However, see the
{@link getCookieDomain(Request)}
* method for limits on the subdomains.
*
*
Note though, that this approach will fail if the response has
already been committed. Thus,
* this valve forces Tomcat to generate the session cookie and then
replaces it before invoking
* the next valve in the chain. Hopefully this is early enough in the
valve-processing chain
* that the response will not have already been committed. You are
advised to define this
* valve as early as possible in server.xml to ensure that the
response has not already been
* committed when this valve is invoked.
*
*
We recommend that you define this valve in server.xml
immediately after the Catalina Engine
* as follows:
*
*
*
*
*
*/
publicclassCrossSubdomainSessionValveextendsValveBase
{
publicCrossSubdomainSessionValve()
{
super();
info = "org.three3s.valves.CrossSubdomainSessionValve/1.0";
}
@Override
publicvoidinvoke(Request request, Response response)throws
IOException, ServletException
{
//this will cause Request.doGetSession to create the session
cookie ifnecessary
request.getSession(true);
//replace any Tomcat-generated session cookies with our own
Cookie[] cookies = response.getCookies();
if(cookies !=null)
{
for(inti =0; i
{
Cookie cookie = cookies[i];
containerLog.debug("CrossSubdomainSessionValve: Cookie
name is " + cookie.getName());
if(Globals.SESSION_COOKIE_NAME.equals(cookie.getName()))
replaceCookie(request, response, cookie);
}
}
//process the next valve
getNext().invoke(request, response);
}
/** Replaces the value of the response header used to set the
specified cookie to a value
* with the cookie's domain set to the value returned by
getCookieDomain(request)
*
* @param request
* @param response
* @param cookie cookie to be replaced.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protectedvoidreplaceCookie(Request request, Response response,
Cookie cookie)
{
//copy the existing session cookie, but use a different domain
Cookie newCookie = newCookie(cookie.getName(), cookie.getValue());
if(cookie.getPath() !=null)
newCookie.setPath(cookie.getPath());
newCookie.setDomain(getCookieDomain(request));
newCookie.setMaxAge(cookie.getMaxAge());
newCookie.setVersion(cookie.getVersion());
if(cookie.getComment() !=null)
newCookie.setComment(cookie.getComment());
newCookie.setSecure(cookie.getSecure());
//if the response has already been committed, our replacement
strategy will have no effect
if(response.isCommitted())
containerLog.error("CrossSubdomainSessionValve: response
was already committed!");
//find the Set-Cookie header for the existing cookie and
replace its value with newcookie
MimeHeaders headers = response.getCoyoteResponse().getMimeHeaders();
for(inti =0, size = headers.size(); i
{
if(headers.getName(i).equals("Set-Cookie"))
{
MessageBytes value = headers.getValue(i);
if(value.indexOf(cookie.getName()) >=0)
{
StringBuffer buffer = newStringBuffer();
ServerCookie.appendCookieValue(buffer,
newCookie.getVersion(), newCookie
.getName(), newCookie.getValue(),
newCookie.getPath(), newCookie
.getDomain(), newCookie.getComment(),
newCookie.getMaxAge(), newCookie
.getSecure());
containerLog.debug("CrossSubdomainSessionValve:
old Set-Cookie value: "
+ value.toString());
containerLog.debug("CrossSubdomainSessionValve:
newSet-Cookie value: " + buffer);
value.setString(buffer.toString());
}
}
}
}
/** Returns the last two parts of the specified request's server
name preceded by a dot.
* Using this as the session cookie's domain allows the session to
be shared across subdomains.
* Note that this implies the session can only be used with
domains consisting of two or
* three parts, according to the domain-matching rules specified
in RFC 2109 and RFC 2965.
*
*
Examples:
*
*
foo.com => .foo.com*
www.foo.com => .foo.com*
bar.foo.com => .foo.com*
abc.bar.foo.com => .foo.com - this means cookie won't workon abc.bar.foo.com!
*
*
* @param request provides the server name used to create cookie domain.
* @return the last two parts of the specified request's server
name preceded by a dot.
*/
protectedString getCookieDomain(Request request)
{
String cookieDomain = request.getServerName();
String[] parts = cookieDomain.split("\\.");
if(parts.length >=2)
cookieDomain = parts[parts.length - 2] +"."+
parts[parts.length - 1];
return"."+ cookieDomain;
}
publicString toString()
{
return("CrossSubdomainSessionValve[container="+
container.getName() + ']');
}
}
放入标签中,也可以放到标签中。个人猜想:如果放入标签中应该只是当前项目的主域名和二级域名session共享,如果放到标签中,应该是该tomcat下所有的项目都是主域名和二级域名共享(没有实验)。
方便对于tomcat的二级域名的使用..而导致session失效的解决方法..
需要引用的包是..
下载CrossSubdomainSessionValve包.. 把下载的包,放到$CATALINA_HOME/server/lib 里面
然后修改tomcat的配置文件: $CATALINA_HOME/conf/server.xml
在标签"Engine",中添加依家配置标签..
类似于:
测试发现,,cookie可以共享,另外发现SESSIONID可以共享。但session中的其他内容不能共享。
这是简单方案。 多台服务器的话,还需要配置tomcat的session复制。
方案三:
还有一种巧妙的单机方式
最近在做一个jsp的网站遇到了session共享的问题,下面以一个简单的实例讲解一下其中的细节及解决方法:
网站有两个域名:主域名www.test.com 二级域名xxx.test.com
1、用主域名打开网站,比如访问www.test.com/login.jsp,这时会产生一个session,并将JSESSIONID=XXXXXXXXXX保存到客户端Cookie中;
2、接着进行登陆操作,提交表单到www.test.com/checklogin.jsp, 这两次操作是在同一会话(session)下(假设没关浏览器),why?
因为我们再通过主域访问站点的其他页面时,第一步在客户端生成的JSESSIONID(通过cookie方式,如果cookie被禁了则通过url)会提交到服务端
用于获取对应的session对象,两次JSESSIONID一样,所以两次的会话保持一致
3、登陆成功后去到了www.test.com/index.jsp 页面,页面打印当前的JSESSIONID=XXXXXXXXXX
4、接着通过二级域名访问index.jsp,即xxx.test.com/index.jsp,这时页面打印的JSESSIONID=YYYYYYYYYY,也就是说再通过二级域名访问index.jsp
这个页面时session已经改变了,即刚才的登陆对二级域名下的访问无效了,why?因为通过该二级域名访问index.jsp时,由于无法获取到主域名生成的JSESSIONID
所以会重新生成一个session,并把JSESSIONID=YYYYYYYYYY保存到客户端。
如何解决?
我的解决方法:做一个跳转页面skip.jsp
String JSESSIONID = request.getSession().getId();//获取当前JSESSIONID (不管是从主域还是二级域访问产生)
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("JSESSIONID", JSESSIONID);
cookie.setDomain(".test.com"); //关键在这里,将cookie设成主域名访问,确保不同域之间都能获取到该cookie的值,从而确保session统一
response.addCookie(cookie); //将cookie返回到客户端
request.getRequestDispatcher("indes.jsp").forward(request, response);
%>
方案四:
大型项目出于性能考虑,一般采用session分布式方案,如: 修改session实现+分布式缓存memcached
------------------------------------------other start--------------------------------------------------
让tomcat支持2级域名共享session
最近启用二级域名后,面临一个主域名与二级域名之间 session 不能共享的问题,带来的麻烦就是用户在主域名登陆,但由于二级域名 session 不能共享 ,因此无法进行登陆的操作,对一些功能有一些影响。
问题的原因如下:
Tomcat 下,不同的二级域名,Session 默认是不共享的,因为 Cookie 名称为 JSESSIONID 的 Cookie 根域是默认是没设置的,访问不同的二级域名,其 Cookie 就重新生成,而 session 就是根据这个 Cookie 来生成的,所以在不同的二级域名下生成的 Session 也不一样。
找到了其原因,就可根据这个原因对 Tomcat 在生成 Session 时进行相应的修改。
快速解决方案1:
在项目的/MET-INF/ 目录下创建一个 context.xml 文件,内容为:
1 2
Done!
快速解决方案2:修改 Tomcat 的 server.xml 文件,内容为:
1
Done!
以上两种方案的详细讲解见:http://快速解决方案3:生成一个叫做 crossSubdomainSessionValve.jar 的文件,用的时候放在 Tomcat lib 目录下,然后修改 Tomcat server.xml 文件:
1
原理:取代由 Tomcat 域产生的会话 cookie ,允许该会话 cookie 跨子域共享。
测试发现,JSESSIONID不能共享,但cookie可以共享...
后来使用tomcat7版本测试,cookie可以共享,另外发现SESSIONID可以共享。但session中的其他内容不能共享。
------------------------------------------other end--------------------------------------------------------
方案五:
经过最后, 通过配置tomcat7,和开发时小改动,成功达到共享session的方案如下:
(不过终极方案还是缓存+session管理接口实现)
同一个tomcat多个web应用共享session
tomcat版本:apache-tomcat-6.0.29(次方tomcat6和tomcat7支持)
1.修改D:\apache-tomcat-6.0.29\conf\server.xml文件
由于每个app都有一个唯一的一个ServletContext 实例对象,下面的所有的servlet 共享此ServletContext。
利用ServletContext 中的setAttribute() 方法把Session 传递过去 然后在另外一个app中拿到session实例。
设置为true 说明你可以调用另外一个WEB应用程序 通过ServletContext.getContext() 获得ServletContext ;
然后再调用其getattribute() 得到你要的对象。
2.创建两个web项目
两个项目访问URL为:
http://localhost:8080/app1/
http://localhost:8080/app2/
app1的index.jsp代码如下:
app2的index.jsp代码如下:
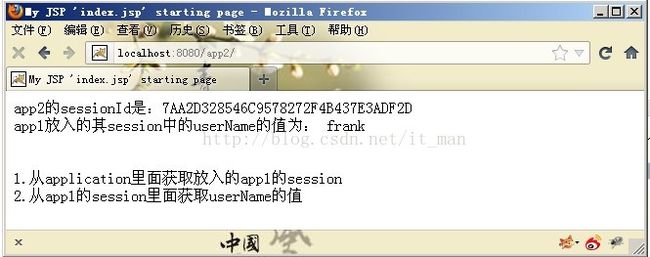
3.访问项目:
4.原理(个人浅见)
全局只用app1的session!
app1使用session时,直接使用;其他app使用session的时候通过application获取app1的session,然后使用。
当浏览器关闭,app1的session也就关闭。application的globalSession的value为null。
获取application
application为jsp的九大内置对象,在jsp里面可以直接使用。在servlet或者struts2的action里面可以通过request.getSession.getServletContext()获取!
APP1的角色
一般app1扮演“首页”角色,初始化。后面的项目使用其session。
设置crossContext = true,让两个应用可以在tomcat中交叉使用上下文环境
------------------------------------------------------------
/
最后,还是得采用基于缓存(Memcache/redis)的Session共享的方式才能实现,以上实现大都不能解决session里的数据共享。
redis实现如下:
tomcat-redis-session-manager.jar的下载地址https://github.com/jcoleman/tomcat-redis-session-manager.git。
放到tomcat的lib目录下(注意此jar依赖的jar也要放到tomcat的lib下)。
修改tomcat6的server.xml文件如下:
unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true"
xmlValidation="false" xmlNamespaceAware="false">
host="172.22.203.115"
port="6379"
database="0"
maxInactiveInterval="60"/>
unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true"
xmlValidation="false" xmlNamespaceAware="false">
host="172.22.203.115"
port="6379"
database="0"
maxInactiveInterval="60"/>