MySQL 窗口函数
MySQL的窗口函数是一种特殊类型的聚合函数,使用窗口函数可以计算一些有趣的结果,例如排名、百分比、累计和移动平均值等。
目录
-
- 一、认识窗口函数
-
-
- 1、动态图演示窗口划分和滑动
- 2、窗口函数的适用场景
- 3、窗口函数与分组函数、聚合函数的区别
-
- 二、具体方法
-
-
- 1、排序窗口函数
- 2、聚合窗口函数
- 3、滑动窗口函数
- 4、分布窗口函数
-
- 三、语法
-
-
- 1、窗口函数的两种书写形式:
- 2、注意:
-
- 四、实例
-
-
- 1、窗口、分组、聚合函数的区别和联系
- 2、排序窗口函数
- 3、聚合窗口函数
- 4、滑动窗口函数
-
- (1)固定取值函数
- (2)滑动取值函数
- (3)滑动窗口函数
- 5、分布窗口函数
-
- (1)将数据按照默认规则分组
- (2)窗口的百分位数
-
- 五、 附录
一、认识窗口函数
MySQL 8.0 版本中可以使用窗口函数,它很像分组函数却又区别于分组函数,在使用group by后每组只有一个结果,而窗口函数不论是否分组都是一行一个结果。窗口函数不对数据进行分组,而是按照窗口划分,计算与当前行相关的聚合值,并将计算结果返回给每一行。
注意:
1、窗口的划分并不是通过分组来的,而是通过 over 子句中的 rows between 划分,只不过不加 rows between 的时候,默认的窗口划分形式和分组规则看起来一样(这个一定要理解)。
2、窗口函数通常需要占用比较多的系统资源,因此在使用时需要评估其对性能的影响或采取优化措施。
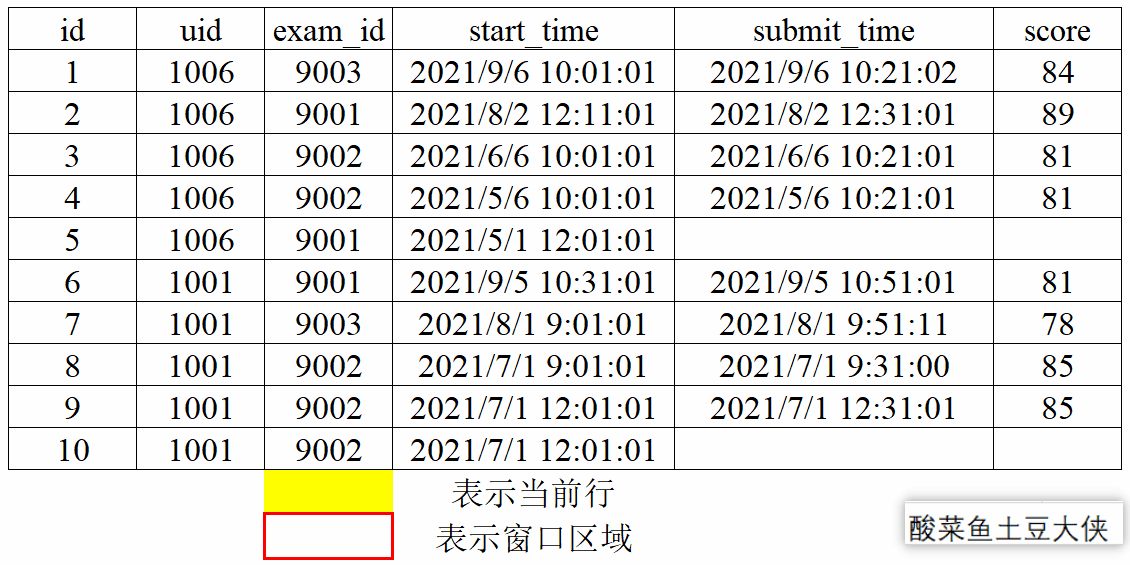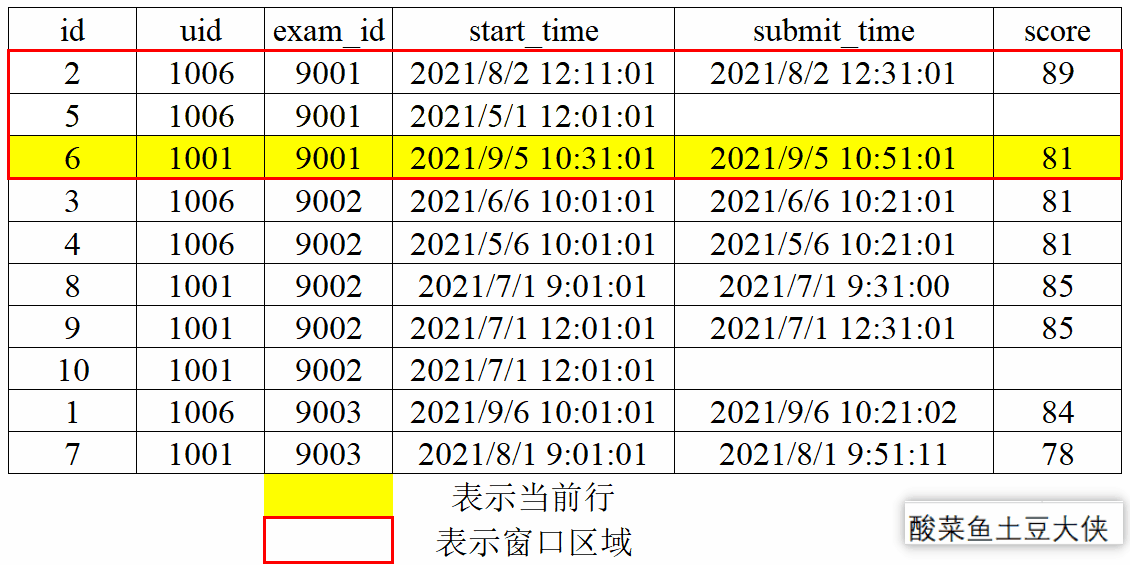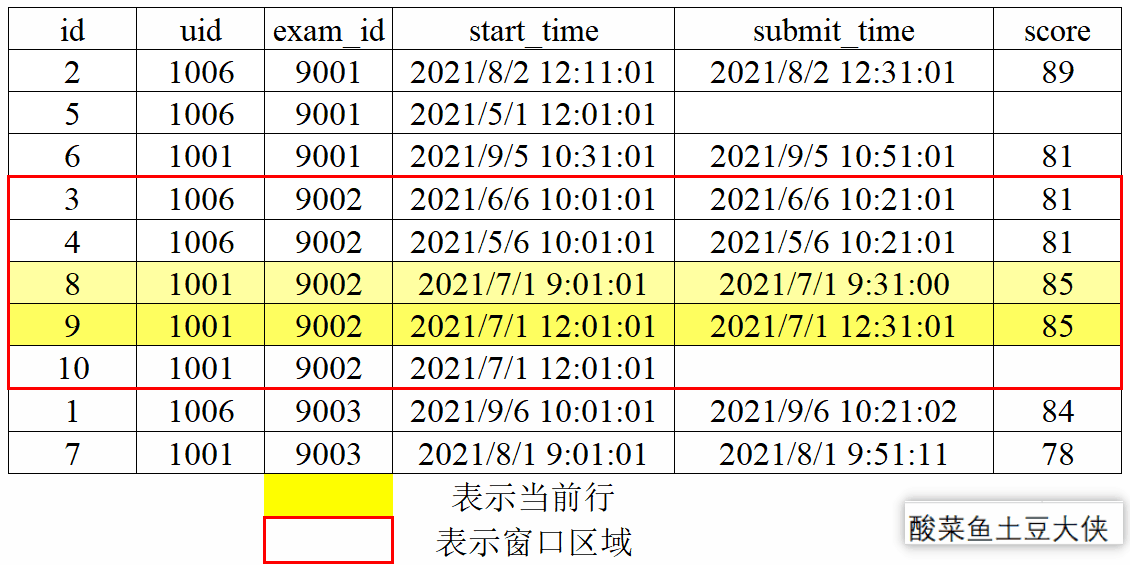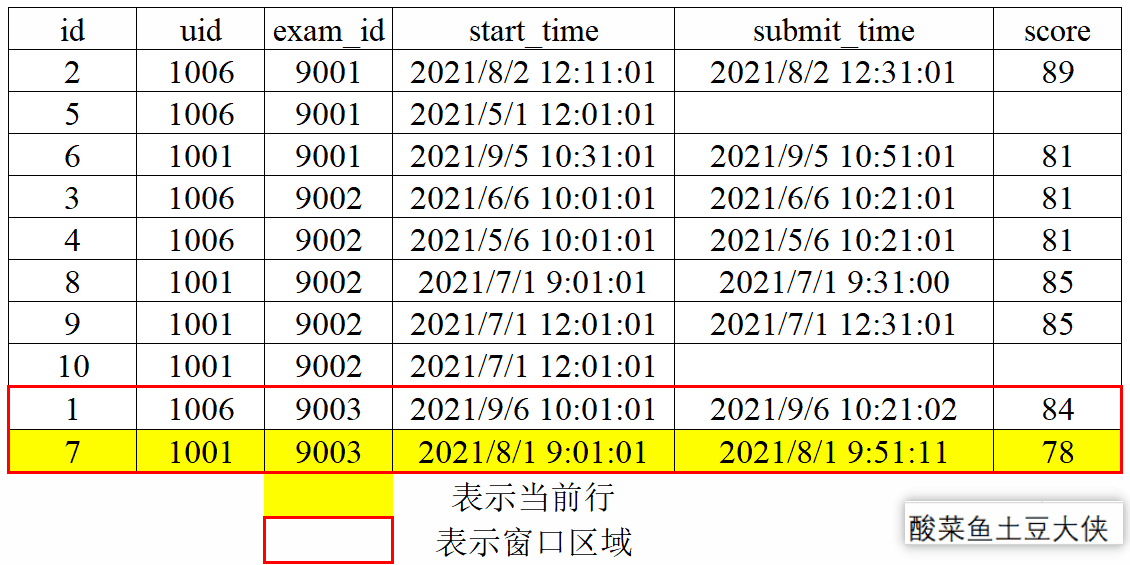
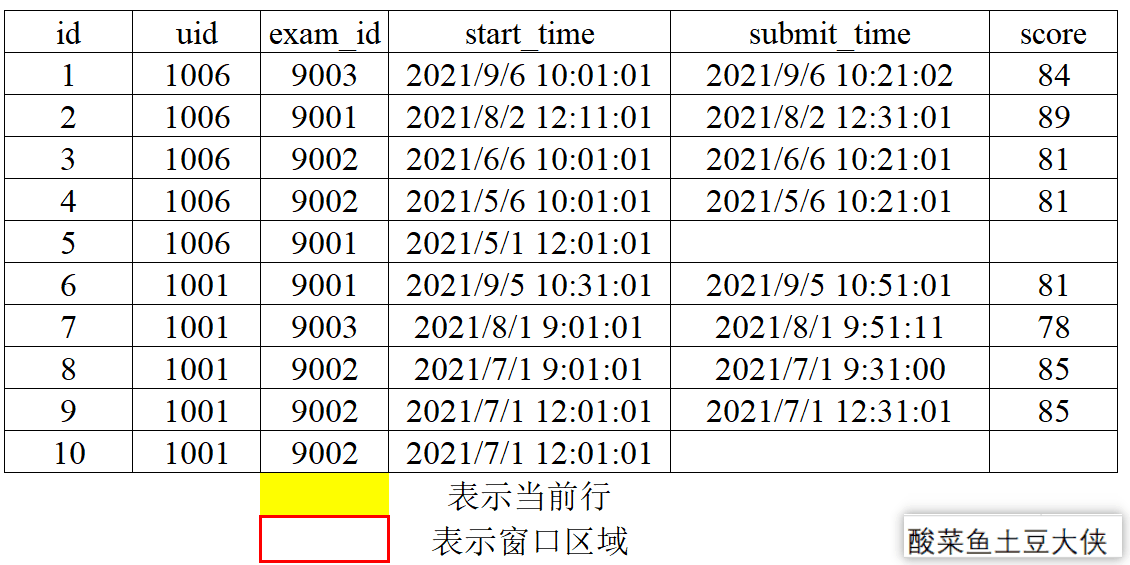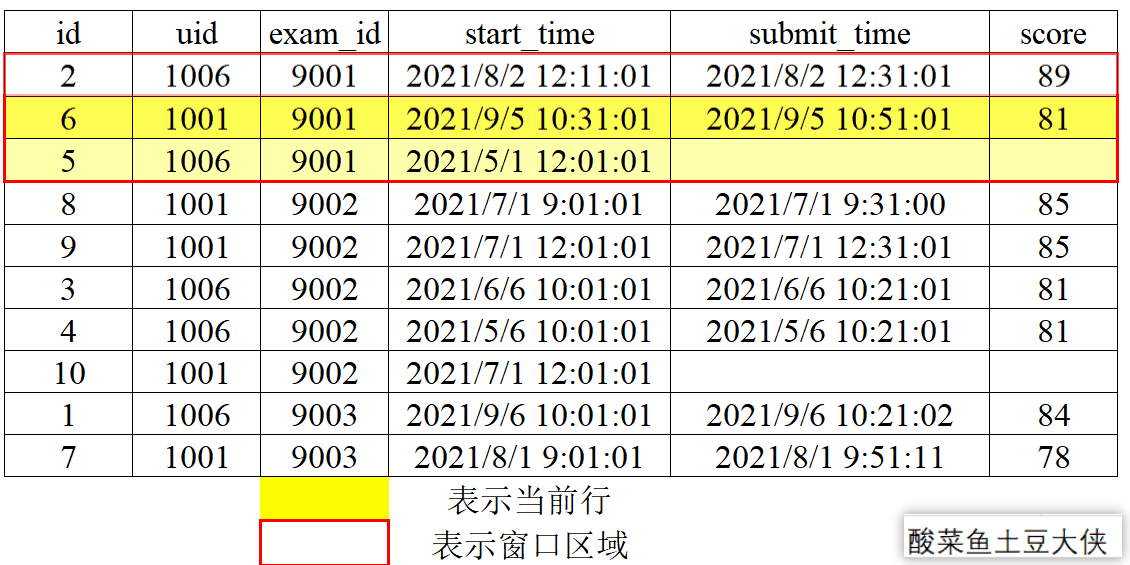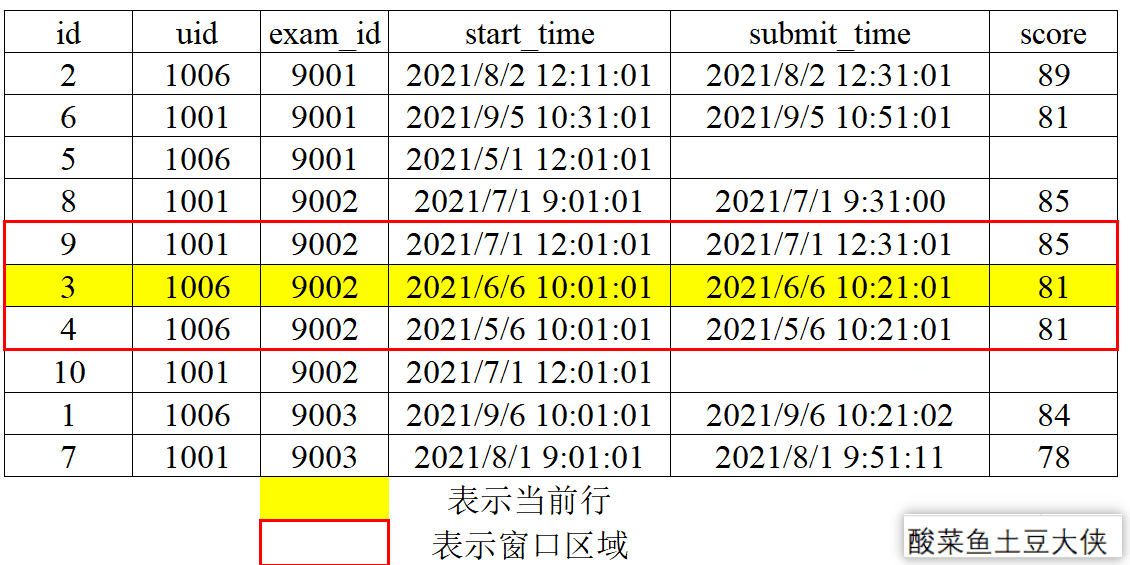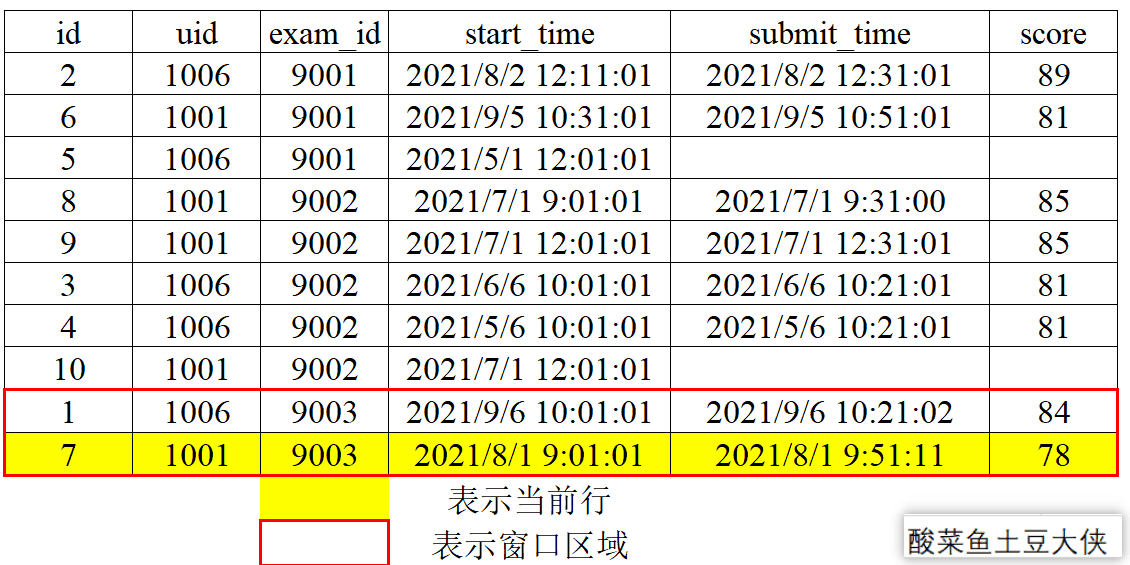
1、动态图演示窗口划分和滑动
- 分组划分
按照exam_id分组来划分窗口。
- 窗口滑动
对exam_id分组后按照score降序,再取分组内当前行及后一行和前一行。
2、窗口函数的适用场景
- 按照某个或某些指标对数据进行排序和排名
例如,使用 rank() 或 dense_rank() 函数计算产品在一个公司的销售额排名,或者使用 row_number() 函数给每个产品进行唯一编号后分类。
- 对某个或某些指标进行聚合计算
例如,使用 sum()、avg()、max() 或 min() 函数对分组内的数据进行计算,并将结果返回给每一行。
- 滑动窗口聚合
例如,获取与当前行相关的前几行或后几行的值,并将它们作为当前行的一部分输出,或者对数据进行累计求和、求滑动平均等。
例如,在一个在线游戏中,我们可能需要计算所有玩家最近一小时内的获得积分总数。
- 分组数据分布情况
窗口函数通过计算每个分组的百分位数,能够反映每个分组的数据分布情况。例如,可以使用 ntile() 函数将每个分组分成n个桶,并返回每个桶的编号。也可以使用 percentile_cont() 函数计算分组内指定列的百分位数。
3、窗口函数与分组函数、聚合函数的区别
实例详见1.1、1.2、1.3。
| 函数 | 与窗口函数的联系 | 与窗口函数的区别 |
|---|---|---|
| 分组函数 | 都可以进行聚合计算 | 处理数据的方式不同。分组函数会根据指定的列对数据进行分组,从而将数据划分为若干个子集进行聚合计算;而窗口函数则不对数据进行分组,而是按照窗口划分,计算与当前行相关的聚合值,并将计算结果返回给每一行。 |
| 聚合函数 | 都是用来对数据进行聚合计算的函数 | 窗口函数可以在不影响原始查询结果的情况下,返回每一行相关的聚合计算结果,而聚合函数只能返回单一的聚合结果。另外,窗口函数可以使用 over 子句来定义分组、排序和滑动窗口等操作,处理数据也更加地灵活。 |
扩展: 分组函数和聚合函数的联系和区别
他们都是用来对数据进行聚合计算的函数,但是两者所处理的粒度不同。
- 分组函数(如GROUP BY)是将数据按照指定的列进行分组,并对每个分组内的数据进行聚合计算,返回每个分组的结果;
- 聚合函数(如SUM、COUNT、AVG、MAX、MIN等)是对整个数据集进行聚合计算,返回一个结果。它可以不分组对整个数据集进行计算。
二、具体方法
MySQL支持多种窗口函数,根据函数功能和使用场景的不同可以将它们分为以下几类:
1、排序窗口函数
| 具体函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| row_number() | 顺序排序,返回无重复值的排名。(本质:为每行生成一个唯一的数字标识符) |
| rank() | 并列排序,返回有间隔重复的排名,例如1,1,3 |
| dense_rank() | 并列排序,返回无间隔重复的排名,例如1,1,2 |
2、聚合窗口函数
| 具体函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| sum(expr) over | 对[窗口内]指定列的expr值进行求和 |
| count(expr) over | 对[窗口内]指定列的expr值进行计数 |
| avg(expr) over | 对[窗口内]指定列的expr值进行平均值计算 |
| max(expr) over | 找到[窗口内]指定列的expr最大值 |
| min(expr) over | 找到[窗口内]指定列的expr最大值 |
以上为常用的聚合函数,其余还有group_concat:将指定列中的值连接为一个字符串;std、stddev或stddev_pop:计算指定列或表中数值列的标准差;var、var_pop或var_samp:计算指定列或表中数值列的方差等。
3、滑动窗口函数
| 分类 | 具体函数或语法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 固定取值函数 | ||
| first_value(expr) | 返回[窗口内]指定列中第一行的expr值 | |
| last_value(expr) | 返回[窗口内]指定列中当前行的expr值 | |
| nth_value(expr,n) | 返回[窗口内]指定列中第n行的expr值 | |
| 滑动取值函数 | ||
| lag(expr,n) | 返回[窗口内]指定列中当前行向前第n行的expr值,不写n,默认n为1 | |
| lead(expr,n) | 返回[窗口内]指定列中当前行向后第n行的expr值,不写n,默认n为1 | |
| 滑动窗口聚合 | rows between frame_start and frame_end | 返回[窗口内]当前行的前几行或后几行的窗口计算值。例和聚合函数一起使用得到移动平均、累计求和等。 |
4、分布窗口函数
| 分类 | 具体函数或语法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 百分比函数 | ||
| percent_rank() | 返回[窗口内]百分比排名值 | |
| cume_dist() | 返回[窗口内]累计分布值 | |
| 默认分组 | ntile(n) | 将行分成n个桶,并返回每个桶的编号 |
三、语法
窗口函数的语法基本上与普通的聚合函数相同,但需要使用 over 子句来指定窗口函数的作用范围,所以使用窗口函数,要在函数后包含一个 over 子句。
1、窗口函数的两种书写形式:
1、窗口直接定义在 over 子句中
函数名([expr]) over (
[partition by <分组的列>, ... ]
[order by <排序的列> [asc|desc], ... ]
[rows between <窗口起始位置 and 窗口结束位置>]
)
2、引用定义在其他地方的命名窗口函数
函数名([expr]) over <窗口函数名称>
...
window <窗口函数名称> as (
[partition by <分组的列>, ... ]
[order by <排序的列> [asc|desc], ... ]
[rows between <窗口起始位置 and 窗口结束位置>]
)
不论是哪种书写形式,over 子句后面圆括号里面的的语法是一样的,具体如下:
function_name:窗口函数的名称,例如row_number、sum、avg等。
expr:可选项,指定窗口函数作用的列或表达式。
partition by:可选的子句,指定分组的列或表达式。
- 如果省略了partition by,则所有查询行为一组,也就是没有分组的概念。
- 标准SQL要求PARTITION BY后面只跟列名。MySQL扩展允许使用表达式,而不仅仅是列名。例如,一个表有一个字段名为 ts 的 timestamp 列,标准SQL允许 partition by ts,但不允许 partition by day(ts),而MySQL两者都允许。具体见例3.2。
order by:可选的子句,指定排序的列及顺序。
- 表达式后面可选地跟着 asc 或 desc 来指示排序方向。如果没有指定方向,默认为 asc。升序时先对空值排序,降序时最后对空值排序;如果排序值为空,则不显示,见例2.1和2.2。
- 如果省略order by,则分区行是无序的,没有暗示处理顺序,所有分区行都是对等的。
- 若有分组,是组内排序。若没有分组,是将结果集作为一个整体进行排序。
rows between:可选的子句(窗口从句),指定滑动窗口的起始和结束位置。
当 order by后面缺少窗口从句条件,窗口规范默认是rows between unbounded preceding and current row,其中,unbounded preceding 表示窗口从第一行开始,而 current row 表示窗口截止到当前行;
当order by和窗口从句都缺失, 窗口规范默认是 rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following。
不同写法及含义,举例:
# 1、取前面2行和当前行 rows between 2 preceding and current row # 2、取当前行前面的所有行和当前行 rows between unbounded preceding and current row # 3、取当前行后面的所有行 rows between current row and unbounded following # 4、取当前行前面的2行和当前行 rows between 2 preceding and current row # 5、取当前行前面的2行和后面2行,总共5行(包括当前行) rows between 2 preceding and 2 following
2、注意:
- 解释
当前行:发生函数求值的行称为当前行。
当前行的窗口:与发生函数求值的当前行相关的查询行组成了当前行的窗口。再次强调窗口函数的本质是按照窗口去计算,而不是对数据分组计算。
- 使用位置
窗口函数只允许出现在 select 列表和 order by 子句中。
- 执行顺序
查询结果行由 where、group by 和 having 处理之后的from子句确定,窗口执行发生在 order by 、limit 和 select distinct 之前。
四、实例
已知试卷作答记录表exam_record(uid:用户ID, exam_id:试卷ID, start_time:开始作答时间, submit_time:交卷时间,为空的话则代表未完成, score:得分):
| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1006 | 9003 | 2021-09-06 10:01:01 | 2021-09-06 10:21:02 | 84 |
| 2 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-08-02 12:11:01 | 2021-08-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
| 3 | 1006 | 9002 | 2021-06-06 10:01:01 | 2021-06-06 10:21:01 | 81 |
| 4 | 1006 | 9002 | 2021-05-06 10:01:01 | 2021-05-06 10:21:01 | 81 |
| 5 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-05-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
| 6 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 10:31:01 | 2021-09-05 10:51:01 | 81 |
| 7 | 1001 | 9003 | 2021-08-01 09:01:01 | 2021-08-01 09:51:11 | 78 |
| 8 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-07-01 09:01:01 | 2021-07-01 09:31:00 | 85 |
| 9 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-07-01 12:01:01 | 2021-07-01 12:31:01 | 85 |
| 10 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-07-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
先通过三个实例看一下窗口函数和分组函数、聚合函数的区别和联系。
1、窗口、分组、聚合函数的区别和联系
- 聚合函数
例1.1 使用 exam_record 表,求所有试卷类型的作答次数。
select
count(exam_id) as count_exam_id
from exam_record;
结果:
| count_exam_id |
|---|
| 10 |
- 分组函数
例1.2 求每类试卷的作答次数;并按试卷类型升序
select
exam_id,
count(exam_id) as count_exam_id
from exam_record
group by exam_id
order by exam_id;
结果:
| exam_id | count_exam_id |
|---|---|
| 9001 | 3 |
| 9002 | 5 |
| 9003 | 2 |
- 窗口函数
例1.3 分别求所有试卷、每类试卷的作答次数;并按试卷类型升序
select
exam_id,
count(exam_id) over() as total_exam_id,
count(exam_id) over(partition by exam_id) as count_exam_id
from exam_record
order by exam_id;
结果:
| exam_id | total_exam_id | count_exam_id |
|---|---|---|
| 9001 | 10 | 3 |
| 9001 | 10 | 3 |
| 9001 | 10 | 3 |
| 9002 | 10 | 5 |
| 9002 | 10 | 5 |
| 9002 | 10 | 5 |
| 9002 | 10 | 5 |
| 9002 | 10 | 5 |
| 9003 | 10 | 2 |
| 9003 | 10 | 2 |
2、排序窗口函数
窗口函数可以很方便地对数据进行排序和排名,在处理排名、排行等相关数据时非常有用。
- row_number() :1、2、3;
- rank() :1、1、3;
- dense_rank() :1、1、2。
例2.1 使用 row_number() 、rank() 、dense_rank() 对 exam_record 表中的答题记录按照得分排序;
# 形式一:
select
score,
row_number() over(order by score desc) as 'row_number',
rank() over(order by score desc) as 'rank',
dense_rank() over(order by score desc) as 'dense_rank'
from exam_record;
# 形式二:
select
score,
row_number() over w as 'row_number',
rank() over w as 'rank',
dense_rank() over w as 'dense_rank'
from exam_record
window w as (order by score desc);
结果:
| score | row_number | rank | dense_rank |
|---|---|---|---|
| 89 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 85 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 85 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| 84 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| 81 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| 81 | 6 | 5 | 4 |
| 81 | 7 | 5 | 4 |
| 78 | 8 | 8 | 5 |
例2.2 使用 row_number() 对 exam_record 表中的每类试卷类型中的记录排序、按照得分排序;
#省略order by 和有order by 的区别
select
exam_id,
score,
row_number() over(partition by exam_id) as row_num1,
row_number() over(partition by exam_id order by score desc) as row_num2
from exam_record;
结果:
| id | exam_id | score | row_num1 | row_num2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 9001 | 89 | 1 | 1 |
| 6 | 9001 | 81 | 3 | 2 |
| 5 | 9001 | None | 2 | 3 |
| 8 | 9002 | 85 | 3 | 1 |
| 9 | 9002 | 85 | 4 | 2 |
| 3 | 9002 | 81 | 1 | 3 |
| 4 | 9002 | 81 | 2 | 4 |
| 10 | 9002 | None | 5 | 5 |
| 1 | 9003 | 84 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 9003 | 78 | 2 | 2 |
省略order by 和有order by 的区别:
省略 order by 默认按照分组内的id升序;
3、聚合窗口函数
窗口函数可以让我们更加灵活地对数据进行聚合计算,避免使用group by 分组后只有一个数据的问题。
- sum(expr) over : 求和
- count(expr) over : 计数
- avg(expr) over : 求平均
- max(expr) over : 求最大值
- min(expr) over : 求最小值
例3.1 查询 exam_record 表中每个试卷类型的记录对应的得分总和、个数、平均值、最大值和最小值,最后按照试卷类型升序;
select
exam_id,
score,
sum(score) over w as 'sum',
count(score) over w as 'count',
avg(score) over w as 'avg',
max(score) over w as 'max',
min(score) over w as 'min'
from exam_record
window w as (partition by exam_id)
order by exam_id;
结果:
| exam_id | score | sum | count | avg | max | min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9001 | 89 | 170 | 2 | 85.0000 | 89 | 81 |
| 9001 | None | 170 | 2 | 85.0000 | 89 | 81 |
| 9001 | 81 | 170 | 2 | 85.0000 | 89 | 81 |
| 9002 | 81 | 332 | 4 | 83.0000 | 85 | 81 |
| 9002 | 81 | 332 | 4 | 83.0000 | 85 | 81 |
| 9002 | 85 | 332 | 4 | 83.0000 | 85 | 81 |
| 9002 | 85 | 332 | 4 | 83.0000 | 85 | 81 |
| 9002 | None | 332 | 4 | 83.0000 | 85 | 81 |
| 9003 | 84 | 162 | 2 | 81.0000 | 84 | 78 |
| 9003 | 78 | 162 | 2 | 81.0000 | 84 | 78 |
partition by 多列分组
除了在 over 子句中指定单个列以便进行分组外,还可以使用 partition by关键字同时指定多个列,从而将输入行分成更小的分组。
例3.2 查询 exam_record 表,按试卷类型和开始作答试卷的日期这两个列进行分组,并计算每个分组内得分最高的记录:
select
exam_id,
date(start_time) as start_date
score,
max(score) over ranking as 'max'
from exam_record
window ranking as (partition by exam_id, date(start_time))
order by exam_id,start_date;
结果:
| exam_id | start_date | score | max |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9001 | 2021-05-01 | None | None |
| 9001 | 2021-08-02 | 89 | 89 |
| 9001 | 2021-09-05 | 81 | 81 |
| 9002 | 2021-05-06 | 81 | 81 |
| 9002 | 2021-06-06 | 81 | 81 |
| 9002 | 2021-07-01 | 85 | 85 |
| 9002 | 2021-07-01 | 85 | 85 |
| 9002 | 2021-07-01 | None | 85 |
| 9003 | 2021-08-01 | 78 | 78 |
| 9003 | 2021-09-06 | 84 | 84 |
4、滑动窗口函数
窗口函数可以很方便地实现滑动窗口聚合,即对当前行及其前几行或后几行所构成的一组连续的行进行聚合计算。
(1)固定取值函数
- first_value(expr) : [窗口内]第一行的值;
- last_value(expr) : [窗口内]当前行的值;
- nth_value(expr,n) : [窗口内]第n行的值。
例4.1 求 exam_record 中每个试卷类型的每个用户与第一名、第二名得分的差值(first_dif、nth_dif)
select
uid,
exam_id,
score,
first_value(score) over (partition by exam_id order by score desc) as first_score,
nth_value(score,2) over (partition by exam_id order by score desc) as nth_score,
last_value(score) over (partition by exam_id order by score desc) as last_score,
last_value(score) over (partition by exam_id order by score desc rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following) as last_score1,
score - first_value(score) over (partition by exam_id order by score desc) as first_dif,
score - nth_value(score,2) over (partition by exam_id order by score desc) as nth_dif
from exam_record;
结果:
| uid | exam_id | score | first_score | nth_score | last_score | last_score2 | first_dif | nth_dif |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1006 | 9001 | 89 | 89 | None | 89 | None | 0 | None |
| 1001 | 9001 | 81 | 89 | 81 | 81 | None | -8 | 0 |
| 1006 | 9001 | None | 89 | 81 | None | None | None | None |
| 1001 | 9002 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | None | 0 | 0 |
| 1001 | 9002 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | None | 0 | 0 |
| 1006 | 9002 | 81 | 85 | 85 | 81 | None | -4 | -4 |
| 1006 | 9002 | 81 | 85 | 85 | 81 | None | -4 | -4 |
| 1001 | 9002 | None | 85 | 85 | None | None | None | None |
| 1006 | 9003 | 84 | 84 | None | 84 | 78 | 0 | None |
| 1001 | 9003 | 78 | 84 | 78 | 78 | 78 | -6 | 0 |
(2)滑动取值函数
lag 和 lead 函数通常用于计算行之间的差异。比如取今天和昨天的某字段差值
- lag(expr) : [窗口内]当前行的前第n行的值;
- lead(expr) : [窗口内]当前行的后第n行的值。
例4.2 求 exam_record 表中每个试卷类型当前用户与上一名用户得分的差值(lag_dif)。
select
uid,
exam_id,
score,
lag(score) over w as lag_score,
lead(score) over w as lead_score,
score - lag(score,1) over w as lag_dif
from exam_record;
window w as (partition by exam_id order by score desc);
结果:
| uid | exam_id | score | lag_score | lead_score | lag_dif |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1006 | 9001 | 89 | None | 81 | None |
| 1001 | 9001 | 81 | 89 | None | -8 |
| 1006 | 9001 | None | 81 | None | None |
| 1001 | 9002 | 85 | None | 85 | None |
| 1001 | 9002 | 85 | 85 | 81 | 0 |
| 1006 | 9002 | 81 | 85 | 81 | -4 |
| 1006 | 9002 | 81 | 81 | None | 0 |
| 1001 | 9002 | None | 81 | None | None |
| 1006 | 9003 | 84 | None | 78 | None |
| 1001 | 9003 | 78 | 84 | None | -6 |
(3)滑动窗口函数
除了计算滑动平均值、累计数外,还可以计算滑动标准差stddev_pop(),他帮助我们更好地掌握数据的变化范围和稳定性。
- 使用滑动窗口:rows between feame_start and frame_end 当前行的前几行或后几行。
已知11月份销售数据表sales_tb(sales_date:销售日期,user_id:用户编号,item_id:货号,sales_num:销售数量,sales_price:销售金额):
| sales_date | user_id | item_id | sales_num | sales_price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-11-01 | 1 | A001 | 1 | 90 |
| 2021-11-01 | 2 | A002 | 2 | 220 |
| 2021-11-01 | 2 | B001 | 1 | 120 |
| 2021-11-02 | 3 | C001 | 2 | 500 |
| 2021-11-02 | 4 | B001 | 1 | 120 |
| 2021-11-03 | 5 | C001 | 1 | 240 |
| 2021-11-03 | 6 | C002 | 1 | 270 |
| 2021-11-04 | 7 | A003 | 1 | 180 |
| 2021-11-04 | 8 | B002 | 1 | 140 |
| 2021-11-04 | 9 | B001 | 1 | 125 |
| 2021-11-05 | 10 | B003 | 1 | 120 |
| 2021-11-05 | 10 | B004 | 1 | 150 |
| 2021-11-05 | 10 | A003 | 1 | 180 |
| 2021-11-06 | 11 | B003 | 1 | 120 |
| 2021-11-06 | 10 | B004 | 1 | 150 |
例4.3 根据销售记录表 sales_tb,计算出11月每天的累计销售额和平均销售单价(为了更好地了解销售趋势)
select
day(sales_date) as 'day',
sales_num as 'num',
sales_price as 'price',
sales_num*sales_price as 'total',
sum(sales_price*sales_num) over w as cumulative_sales,
avg(sales_price*sales_num) over w as avg_unit_price
from sales_tb
window w as (order by day(sales_date) rows between unbounded preceding and current row);
结果:
| day | num | price | total | cumulative_sales | avg_unit_price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90.0000 |
| 1 | 2 | 220 | 440 | 530 | 265.0000 |
| 1 | 1 | 120 | 120 | 650 | 216.6667 |
| 2 | 2 | 500 | 1000 | 1650 | 412.5000 |
| 2 | 1 | 120 | 120 | 1770 | 354.0000 |
| 3 | 1 | 240 | 240 | 2010 | 335.0000 |
| 3 | 1 | 270 | 270 | 2280 | 325.7143 |
| 4 | 1 | 180 | 180 | 2460 | 307.5000 |
| 4 | 1 | 140 | 140 | 2600 | 288.8889 |
| 4 | 1 | 125 | 125 | 2725 | 272.5000 |
| 5 | 1 | 120 | 120 | 2845 | 258.6364 |
| 5 | 1 | 150 | 150 | 2995 | 249.5833 |
| 5 | 1 | 180 | 180 | 3175 | 244.2308 |
| 6 | 1 | 120 | 120 | 3295 | 235.3571 |
| 6 | 1 | 150 | 150 | 3445 | 229.6667 |
5、分布窗口函数
(1)将数据按照默认规则分组
- ntile(n):将行分成n个桶,并返回每个桶的编号。
例5.1 将 exam_scores 表中数据按照成绩分成4组。
select
ntile(4) over (order by score desc) as pack4,
ntile(2) over (partition by exam_id order by score desc) as pack2,
exam_id,
uid,
score
FROM exam_record;
结果:
| pack4 | pack2 | exam_id | uid | score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 9001 | 1006 | 89 |
| 3 | 1 | 9001 | 1001 | 81 |
| 4 | 2 | 9001 | 1006 | None |
| 1 | 1 | 9002 | 1001 | 85 |
| 1 | 1 | 9002 | 1001 | 85 |
| 2 | 1 | 9002 | 1006 | 81 |
| 2 | 2 | 9002 | 1006 | 81 |
| 4 | 2 | 9002 | 1001 | None |
| 2 | 1 | 9003 | 1006 | 84 |
| 3 | 2 | 9003 | 1001 | 78 |
(2)窗口的百分位数
窗口函数可以很方便地计算每个窗口的百分位数,从而更好地反映每个窗口的数据分布情况。
返回窗口值的百分比,返回值范围为 0 到 1。
- cume_dist() : [窗口内]数据分布的累计百分比;
- 计算公式:窗口内 <=当前rank值对应的最大值的行数 / 窗口内总行数
- percent_rank() :[窗口内]rank排名百分比值;
- 计算公式:(窗口内 <=当前rank值的行数 -1) / (窗口内总行数-1)
例5.2 对 exam_record 表中成绩按照升序计算累计百分比和排名百分比。
select
score,
row_number() over w as 'row_num',
rank() over w as 'rank',
cume_dist() over w as 'cume_dist',
percent_rank() over w as 'percent_rank'
from exam_record
window w as (order by score);
结果:
| score | row_num | rank | cume_dist | percent_rank | 解释cume_dist | 解释percent_rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 1 | 1 | 0.200 | 0.000 | 2/10 | (1-1)/(10-1) |
| None | 2 | 1 | 0.200 | 0.000 | 2/10 | (1-1)/(10-1) |
| 78 | 3 | 3 | 0.300 | 0.222 | 3/10 | (3-1)/(10-1) |
| 81 | 4 | 4 | 0.600 | 0.333 | 6/10 | (4-1)/(10-1) |
| 81 | 5 | 4 | 0.600 | 0.333 | 6/10 | (4-1)/(10-1) |
| 81 | 6 | 4 | 0.600 | 0.333 | 6/10 | (4-1)/(10-1) |
| 84 | 7 | 7 | 0.700 | 0.667 | 7/10 | (7-1)/(10-1) |
| 85 | 8 | 8 | 0.900 | 0.778 | 9/10 | (8-1)/(10-1) |
| 85 | 9 | 8 | 0.900 | 0.778 | 9/10 | (8-1)/(10-1) |
| 89 | 10 | 10 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 10/10 | (10-1)/(10-1) |
五、 附录
创建 exam_record 表的代码
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for exam_record
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `exam_record`;
CREATE TABLE `exam_record` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增ID',
`uid` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户ID',
`exam_id` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '试卷ID',
`start_time` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT '开始时间',
`submit_time` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '提交时间',
`score` tinyint(4) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '得分',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 11 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of exam_record
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `exam_record` VALUES (1, 1006, 9003, '2021-09-06 10:01:01', '2021-09-06 10:21:02', 84);
INSERT INTO `exam_record` VALUES (2, 1006, 9001, '2021-08-02 12:11:01', '2021-08-02 12:31:01', 89);
INSERT INTO `exam_record` VALUES (3, 1006, 9002, '2021-06-06 10:01:01', '2021-06-06 10:21:01', 81);
INSERT INTO `exam_record` VALUES (4, 1006, 9002, '2021-05-06 10:01:01', '2021-05-06 10:21:01', 81);
INSERT INTO `exam_record` VALUES (5, 1006, 9001, '2021-05-01 12:01:01', NULL, NULL);
INSERT INTO `exam_record` VALUES (6, 1001, 9001, '2021-09-05 10:31:01', '2021-09-05 10:51:01', 81);
INSERT INTO `exam_record` VALUES (7, 1001, 9003, '2021-08-01 09:01:01', '2021-08-01 09:51:11', 78);
INSERT INTO `exam_record` VALUES (8, 1001, 9002, '2021-07-01 09:01:01', '2021-07-01 09:31:00', 85);
INSERT INTO `exam_record` VALUES (9, 1001, 9002, '2021-07-01 12:01:01', '2021-07-01 12:31:01', 85);
INSERT INTO `exam_record` VALUES (10, 1001, 9002, '2021-07-01 12:01:01', NULL, NULL);
创建 sales_tb 表的代码
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for sales_tb
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `sales_tb`;
CREATE TABLE `sales_tb` (
`sales_date` date NOT NULL,
`user_id` int(10) NOT NULL,
`item_id` char(10) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL,
`sales_num` int(10) NOT NULL,
`sales_price` int(10) NOT NULL
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of sales_tb
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-01', 1, 'A001', 1, 90);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-01', 2, 'A002', 2, 220);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-01', 2, 'B001', 1, 120);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-02', 3, 'C001', 2, 500);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-02', 4, 'B001', 1, 120);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-03', 5, 'C001', 1, 240);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-03', 6, 'C002', 1, 270);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-04', 7, 'A003', 1, 180);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-04', 8, 'B002', 1, 140);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-04', 9, 'B001', 1, 125);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-05', 10, 'B003', 1, 120);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-05', 10, 'B004', 1, 150);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-05', 10, 'A003', 1, 180);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-06', 11, 'B003', 1, 120);
INSERT INTO `sales_tb` VALUES ('2021-11-06', 10, 'B004', 1, 150);