SpringCloud(Hoxton SR6)微服务工具集学习笔记
Spring Cloud 微服务工具集(版本: Hoxton SR6)
- Spring Cloud 微服务工具集
-
-
-
- 1.什么是微服务
- 2.为什么是微服务?
-
- 单体应用
- 微服务架构应用
- 架构的演变
- 3.微服务的解决方案
- 4.什么是SpringCloud
-
- 官方定义
- 核心架构及其组件
- 5.环境搭建
-
- 版本命名
- 版本选择
- 环境搭建
- 6.服务注册中心
-
- 什么服务注册中心
- 常用的注册中心
-
- 1.Eureka
- 2.Consul
- 7. 服务间通信方式
-
- 什么是微服务
- 如何解决微服务的服务通信问题?
- 如何在java代码中发起http方式请求?
- 基于RestTemplate的服务调用
-
- RestTemplate 服务调用
- 使用RestTemplate对象实现服务间通信存在问题
- Ribbon负载均衡原理
- 使用Ribbon+RestTemplate实现请求负载均衡
- Ribbon组件实现负载均衡的原理
-
- 面试问题:
- Ribbon组件源码分析
- Ribbon负载均衡策略支持哪些?
- 设置服务间调用负载均衡策略(在用户服务配置文件里写)
- Ribbon组件现在的状态
- 8.OpenFeign组件的使用
-
- 存在问题:
- 说明:
- openFeign 服务调用
- 调用服务并传参
-
- 零散类型参数传递
- 对象类型参数传递
- 数组参数传递
- 集合类型的参数接收
- openfegin的响应处理
- OpenFegin默认超时处理
- OpenFeign调用详细日志展示
- 9.Hystrix组件使用
-
- 服务雪崩
- 服务熔断 =====》Hystrix
- 服务降级
- 降级和熔断总结
- 服务熔断的实现
- 服务降级的实现
- Hystrix Dashboard(仪表盘) NetFlix
- Hystrix停止维护
- 10.Gateway组件使用
-
- 什么是服务网关
- 服务网关组件
-
- zuul 1.x 2.x(netflix 组件)
- gateway (spring) ==**=路由转发+请求过滤**==
- 11.Config组件使用
-
- 什么是Config
-
- 统一配置中心组件流程图
- Config Server 开发(config client --->config server---->远端git仓库)
- Config Client 开发
- 手动配置刷新
- 12.Bus组件的使用
-
- 什么是Bus (AMQP RibbitMQ、Kafka)
- 实现配置刷新原理
- MQ
- 搭建RabbitMQ服务
- 实现自动配置刷新
- 集成webhook(web 钩子)实现自动刷新
- 13.SpringCloud 微服务工具集总结
-
-
Spring Cloud 微服务工具集
- 版本: Hoxton SR6
1.什么是微服务
- 官网: https://www.martinfowler.com/articles/microservices.html
In short, the microservice architectural(架构) style is an approach to developing a single application as a suite(系列) of small services, each running in its own process(进程) and communicating with lightweight mechanisms, often an HTTP resource API. These services are built around business(业务) capabilities(单元) and independently(独立) deployable(部署) by fully automated deployment machinery. There is a bare(基于) minimum of centralized(分布式) management(管理) of these services, which may be written in different programming languages and use different data storage technologies. -----[摘自官网]
- a suite of small services --一系列微小服务
- running in its own process --运行在自己的进程里
- built around business capabilities --围绕自己的业务开发
- independently deployable --独立部署
- bare minimum of centralized management of these services --基于分布式管理
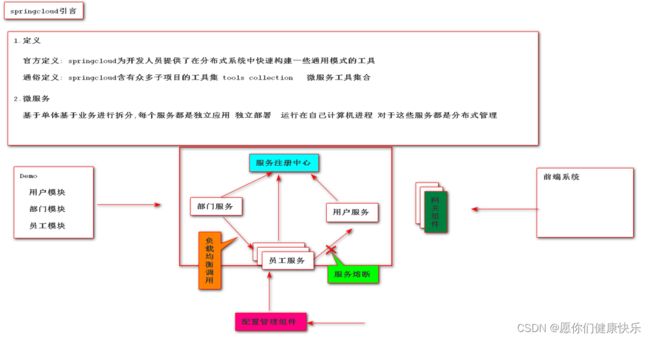
- 官方定义:微服务就是由一系列围绕自己业务开发的微小服务构成,他们独立部署运行在自己的进程里,基于分布式的管理
- 通俗定义:微服务是一种架构,这种架构是将单个的整体应用程序分割成更小的项目关联的独立的服务。一个服务通常实现一组独立的特性或功能,包含自己的业务逻辑和适配器。各个微服务之间的关联通过暴露api来实现。这些独立的微服务不需要部署在同一个虚拟机,同一个系统和同一个应用服务器中。
2.为什么是微服务?
单体应用
# 1.优点
- 单一架构模式在项目初期很小的时候开发方便,测试方便,部署方便,运行良好。
# 2.缺点
- 应用随着时间的推进,加入的功能越来越多,最终会变得巨大,一个项目中很有可能数百万行的代码,
- 互相之间繁琐的jar包。久而久之,开发效率低,代码维护困难
- 还有一个如果想整体应用采用新的技术,新的框架或者语言,那是不可能的。
- 任意模块的漏洞或者错误都会影响这个应用,降低系统的可靠性
微服务架构应用
# 1.优点
- 将服务拆分成多个单一职责的小的服务,进行单独部署,服务之间通过网络进行通信
- 每个服务应该有自己单独的管理团队,高度自治
- 服务各自有自己单独的职责,服务之间松耦合,避免因一个模块的问题导致服务崩溃
# 2.缺点
- 开发人员要处理分布式系统的复杂性
- 多服务运维难度,随着服务的增加,运维的压力也在增大
- 服务治理 和 服务监控 关键
架构的演变
# 1.架构的演变过程
- [单一应用架构] `===>` [垂直应用架构] `===>` [分布式服务架构] `===>` [流动计算架构]||[微服务
架构] `===>` [未知]
# 1. All in One Application 单一架构
- 起初当网站流量很小时,将所有功能都写在一个应用里面,对整个应用进行部署,以减少部署节点和成本。
对于这个架构简化增删改查的工作量的数据访问框架(ORM)是关键。
# 2. Vertical Application 垂直架构
- 当访问量逐渐增大,单一应用增加机器带来的加速度越来越小,提升效率的方法之一是将应用拆成
互不相干的几个应用,以提升效率。此时,用于加速前端页面开发的Web框架(MVC)是关键。
# 3. Distributed Service 分布式服务架构
- 当垂直应用越来越多,应用之间交互不可避免,将核心业务抽取出来,作为独立的服务,逐渐形成
稳定的服务中心,使前端应用能更快速的响应多变的市场需求。此时,用于提高业务复用及整合的分布式
服务框架(RPC)是关键。
# 4. Elastic Computing 流动计算架构即微服务架构
- 当服务越来越多,容量的评估,小服务资源的浪费等问题逐渐显现,此时需增加一个调度中心基于访问
压力实时管理集群容量,提高集群利用率。此时,用于提高机器利用率的资源调度和治理中心(SOA)是关键
- 友情提醒: 好的架构并不是设计出来的,一定是进化来的!!!
3.微服务的解决方案
# 1.Dubbo (阿里系)
- 初出茅庐:2011年末,阿里巴巴在GitHub上开源了基于Java的分布式服务治理框架Dubbo,之后它成为了
国内该类开源项目的佼佼者,许多开发者对其表示青睐。同时,先后有不少公司在实践中基于Dubbo进行
分布式系统架构,目前在GitHub上,它的fork、star数均已破万。Dubbo致力于提供高性能和透明化的
RPC远程服务调用方案,以及SOA服务治理方案,使得应用可通过高性能RPC实现服务的输出、输入功能和
Spring框架无缝集成。Dubbo包含远程通讯、集群容错和自动发现三个核心部分。
- 停止维护:从2012年10月23日Dubbo 2.5.3发布后,在Dubbo开源将满一周年之际,阿里基本停止了对
Dubbo的主要升级。只在之后的2013年和2014年更新过2次对Dubbo 2.4的维护版本,然后停止了所有维护
工作。Dubbo对Srping的支持也停留在了Spring 2.5.6版本上。
- 死而复生:多年漫长的等待,随着微服务的火热兴起,在国内外开发者对阿里不再升级维护Dubbo的吐槽声中,
阿里终于开始重新对Dubbo的升级和维护工作。在2017年9月7日,阿里发布了Dubbo的2.5.4版本,距离上
一个版本2.5.3发布已经接近快5年时间了。在随后的几个月中,阿里Dubbo开发团队以差不多每月一版本
的速度开始快速升级迭代,修补了Dubbo老版本多年来存在的诸多bug,并对Spring等组件的支持进行了
全面升级。
- 2018年1月8日,Dubbo创始人之一梁飞在Dubbo交流群里透露了Dubbo 3.0正在动工的消息。Dubbo 3.0
内核与Dubbo 2.0完全不同,但兼容Dubbo 2.0。Dubbo 3.0将以Streaming为内核,不再是Dubbo 时代
的RPC,但是RPC会在Dubbo 3.0中变成远程Streaming对接的一种可选形态。从Dubbo新版本的路线规划上
可以看出,新版本的Dubbo在原有服务治理的功能基础上,将全面拥抱微服务解决方案。
- 结论:当前由于RPC协议、注册中心元数据不匹配等问题,在面临微服务基础框架选型时Dubbo与Spring Cloud
是只能二选一,这也是为什么大家总是拿Dubbo和Spring Cloud做对比的原因之一。Dubbo之后会积极寻求
适配到Spring Cloud生态,比如作为Spring Cloud的二进制通信方案来发挥Dubbo的性能优势,或者Dubbo
通过模块化以及对http的支持适配到Spring Cloud。
# 2.Spring Cloud:
- Spring Cloud NetFlix
基于美国Netflix公司开源的组件进行封装,提供了微服务一栈式的解决方案。
- Spring Cloud alibaba
在Spring cloud netflix基础上封装了阿里巴巴的微服务解决方案。
- Spring Cloud Spring
目前spring官方趋势正在逐渐吸收Netflix组件的精华,并在此基础进行二次封装优化,打造spring专有
的解决方案
4.什么是SpringCloud
官方定义
- 官方网址: https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/Hoxton.SR5/reference/html/
Spring Cloud provides tools for developers to quickly build some of the common patterns in distributed systems (e.g. configuration management, service discovery, circuit breakers, intelligent routing, micro-proxy, control bus). Coordination of distributed systems leads to boiler plate patterns, and using Spring Cloud developers can quickly stand up services and applications that implement those patterns. -------[摘自官网]
# 1.翻译
- springcloud为开发人员提供了在分布式系统中快速构建一些通用模式的工具(例如配置管理、服务发现、
断路器、智能路由、微代理、控制总线)。分布式系统的协调导致了锅炉板模式,使用springcloud开发
人员可以快速地建立实现这些模式的服务和应用程序。
# 2.通俗理解
- springcloud是一个含概多个子项目的开发工具集,集合了众多的开源框架,他利用了Spring Boot开发的
便利性实现了很多功能,如服务注册,服务注册发现,负载均衡等.SpringCloud在整合过程中主要是针对
Netflix(耐非)开源组件的封装.SpringCloud的出现真正的简化了分布式架构的开发。NetFlix 是美国的
一个在线视频网站,微服务业的翘楚,他是公认的大规模生产级微服务的杰出实践者,NetFlix的开源组件已
经在他大规模分布式微服务环境中经过多年的生产实战验证,因此Spring Cloud中很多组件都是基于
NetFlixspring netflix 维护 闭源
核心架构及其组件
# 1.核心组件说明
- eurekaserver、consul、nacos 服务注册中心组件
- rabbion & openfeign 服务负载均衡 和 服务调用组件
- hystrix & hystrix dashboard 服务断路器 和 服务监控组件
- zuul、gateway 服务网关组件
- config 统一配置中心组件
- bus 消息总线组件
......
5.环境搭建
版本命名
- 官网地址:https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud
Spring Cloud is an umbrella(伞) project consisting of independent projects with, in principle, different release cadences. To manage the portfolio a BOM (Bill of Materials) is published with a curated set of dependencies on the individual project (see below). The release trains have names, not versions, to avoid confusion with the sub-projects. The names are an alphabetic sequence (so you can sort them chronologically) with names of London Tube stations (“Angel” is the first release, “Brixton” is the second). When point releases of the individual projects accumulate to a critical mass, or if there is a critical bug in one of them that needs to be available to everyone, the release train will push out “service releases” with names ending “.SRX”, where “X” is a number. —[摘自官网]
# 1.翻译
- springcloud是一个由众多独立子项目组成的大型综合项目,原则每个子项目上有不同的发布节奏,都维护
自己发布版本号。为了更好的管理springcloud的版本,通过一个资源清单BOM(Bill of Materials),为避免
与子项目的发布号混淆,所以没有采用版本号的方式,而是通过命名的方式。这些名字是按字母顺序排列的。
如伦敦地铁站的名称(“天使”是第一个版本,“布里斯顿”是第二个版本,"卡姆登"是第三个版本)。当单个
项目的点发布累积到一个临界量,或者其中一个项目中有一个关键缺陷需要每个人都可以使用时,发布序列
将推出名称以“.SRX”结尾的“服务发布”,其中“X”是一个数字。
# 2.伦敦地铁站名称 [了解]
- Angel、Brixton、Camden、Dalston、Edgware、Finchley、Greenwich、Hoxton
版本选择
# 1.版本选择官方建议 https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud
- Angel 版本基于springboot1.2.x版本构建与1.3版本不兼容
- Brixton 版本基于springboot1.3.x版本构建与1.2版本不兼容
`2017年Brixton and Angel release官方宣布报废
- Camden 版本基于springboot1.4.x版本构建并在1.5版本通过测试
`2018年Camden release官方宣布报废
- Dalston、Edgware 版本基于springboot1.5.x版本构建目前不能再springboot2.0.x版本中使用
`Dalston(达尔斯顿)将于2018年12月官方宣布报废。Edgware将遵循Spring Boot 1.5.x的生命周期结束。
- Finchley 版本基于springboot2.0.x版本进行构建,不能兼容1.x版本
- Greenwich 版本基于springboot2.1.x版本进行构建,不能兼容1.x版本
- Hoxton 版本基于springboot2.2.x版本进行构建
Spring Cloud Dalston, Edgware, Finchley, and Greenwich have all reached end of life status and are no longer supported.
环境搭建
# 0.说明
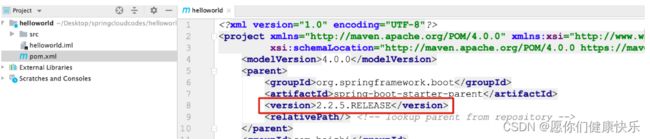
- springboot 2.2.5.RELEASE
- springcloud Hoxton.SR6
- java8
- maven 3.3.9
- idea 2018.3.5
# 1.创建springboot项目 指定版本为 2.2.5版本
# 2.引入springcloud的版本管理
<!--定义springcloud使用版本号-->
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Hoxton.SR6</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<!--全局管理springcloud版本,并不会引入具体依赖-->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
# 3.完成上述操作springboot与springcloud环境搭建完成
- 接下来就是使用到具体的springcloud组件,在项目中引入具体的组件即可
6.服务注册中心
什么服务注册中心
所谓服务注册中心就是在整个的微服务架构中单独提出一个服务,这个服务不完成系统的任何的业务功能,仅仅用来完成对整个微服务系统的服务注册和服务发现,以及对服务健康状态的监控和管理功能。

# 1.服务注册中心
- 可以对所有的微服务的信息进行存储,如微服务的名称、IP、端口等
- 可以在进行服务调用时通过服务发现查询可用的微服务列表及网络地址进行服务调用
- 可以对所有的微服务进行心跳检测,如发现某实例长时间无法访问,就会从服务注册表移除该实例。
常用的注册中心
springcloud支持的多种注册中心Eureka、Consul、Zookeeper、以及阿里巴巴推出Nacos。这些注册中心在本质上都是用来管理服务的注册和发现以及服务状态的检查的。
1.Eureka
# 0.简介
- https://github.com/Netflix/eureka/wiki
- Eureka是Netflix开发的服务发现框架,本身是一个基于REST的服务。SpringCloud将它集成在其子项目spring-cloud-netflix中, 以实现SpringCloud的服务注册和发现功能。
Eureka包含两个组件:Eureka Server和Eureka Client。
开发Eureka Server
1.创建项目并引入eureka server依赖
<!--引入 eureka server-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.编写配置application.yml
server:
port: 8761 #默认端口号
spring:
application:
name: eurekaserver #指定服务名 唯一标识 不能出现下划线 默认服务名不区分大小写 推荐服务名大写
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka #指定服务注册中心的地址 暴露服务地址
细节:在项目启动成功之后默认在eureka server管理界面中出现UNKNOWN 一个位置应用

在微服务架构中服务名称代表服务唯一标识,至关重要,服务名称必须唯一,使用时必须通过如下配置指定服务名成
spring.application.name=EUREKASERVER #指定服务名 唯一标识 不能出现下划线 默认服务名不区分大小写 推荐服务名大写
3.开启Eureka Server,入口类加入注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class Eurekaserver8761Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Eurekaserver8761Application.class, args);
}
}
4.运行


报错问题原因:eureka组件包含 eurekaserver 和 eurekaclient。server是一个服务注册中心,用来接受客户端的注册。client的特性会让当前启动的服务把自己作为eureka的客户端进行服务中心的注册,当项目启动时服务注册中心还没有创建好,所以找我不到服务的客户端组件就直接报错了,当启动成功服务注册中心创建好了,日后client也能进行注册,就不再报错啦!
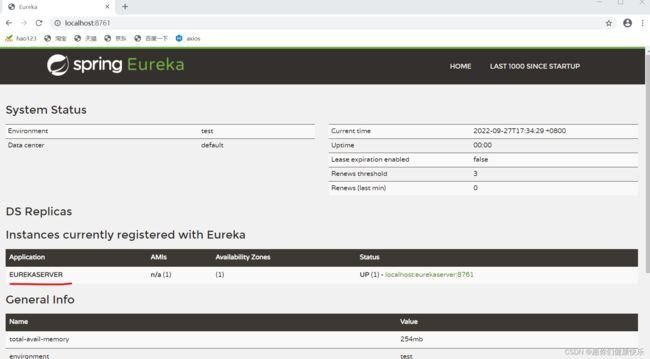
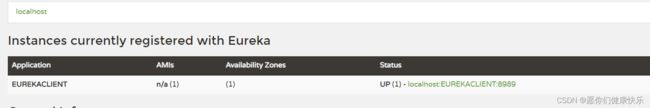
5.访问Eureka的服务注册页面
- http://localhost:8761/
server:
port: 8761 #默认端口号
spring:
application:
name: eurekaserver #指定服务名 不能出现下划线 默认服务名不区分大小写 推荐服务名大写
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka #指定服务注册中心的地址 暴露服务地址
fetch-registry: false #关闭 eureka client的立即注册
register-with-eureka: false #不再将自己同时作为客户端进行注册
再次启动,当前应用就是一个单纯Eureka Server,控制器也不再报错

开发Eureka Client
1.创建项目并引入eureka client依赖
<!--引入eureka client-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.编写配置application.properties
server:
port: 8989
spring:
application:
name: EUREKACLIENT
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka #eureka注册中心地址
3.开启eureka客户端加入注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer //当前应用是一个服务注册中心
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class,args);
}
}
4.启动之前的8761的服务注册中心,在启动eureka客户端服务

5.查看eureka server的服务注册情况

eureka自我保护机制
1. 服务频繁启动时 EurekaServer出现错误
- EMERGENCY! EUREKA MAY BE INCORRECTLY CLAIMING INSTANCES ARE UP WHEN THEY’RE NOT. RENEWALS ARE LESSER THAN THRESHOLD AND HENCE THE INSTANCES ARE NOT BEING EXPIRED JUST TO BE SAFE.
2. 什么是自我保护机制
- 官网地址: https://github.com/Netflix/eureka/wiki/Server-Self-Preservation-Mode
- 默认情况下,如果Eureka Server在一定时间内(默认90秒)没有接收到某个微服务实例的心跳,Eureka Server将会移除该实例。但是当网络分区故障发生时,微服务与Eureka Server之间无法正常通信,而微服务本身是正常运行的,此时不应该移除这个微服务,所以引入了自我保护机制。Eureka Server在运行期间会去统计Eureka 实例正常心跳占比在 15 分钟之内是否低于 85%,如果低于 85%,Eureka Server 会将这些实例保护起来,让这些实例不会过期,自我保护状态一旦开启,除非客户端恢复导致退出自我保护状态,否则实例永不删除。这种设计的哲学原理就是"宁可信其有不可信其无!"。自我保护模式正是一种针对网络异常波动的安全保护措施,使用自我保护模式能使Eureka集群更加的健壮、稳定的运行。
3. 为什么会有自我保护机制?
Eureka服务端为了防止Eureka客户端本身是可以正常访问的,但是由于网路通信故障等原因,造成Eureka服务端失去于客户端的连接,从而形成的不可用。
因为网络通信是可能恢复的,但是Eureka客户端只会在启动时才去服务端注册。如果因为网络的原因而剔除了客户端,将造成客户端无法再注册到服务端。
4. Eureka Server自动进入自我保护机制,此时会出现以下几种情况:
- Eureka Server不再从注册列表中移除因为长时间没收到心跳而应该过期的服务。
- Eureka Server仍然能够接受新服务的注册和查询请求,但是不会被同步到其它节点上,保证当前节点依然可用。
- 当网络稳定时,当前Eureka Server新的注册信息会被同步到其它节点中。
- 心跳正常,退出自我保护状态,客户端恢复。
5. 如何选择关闭还是开启自我保护机制
Eureka服务端默认情况下是会开启自我保护机制的。但我们在不同环境应该选择是否开启保护机制。
一般情况下,我们会选择在 开发环境下关闭自我保护机制,而在生产环境下启动自我保护机制。
开发环境下,我们我们启动的服务数量较少而且会经常修改重启。如果开启自我保护机制,很容易触发Eureka客户端心跳占比低于85%的情况。使得Eureka不会剔除我们的服务,从而在我们访问的时候,会访问到可能已经失效的服务,导致请求失败,影响我们的开发。
在生产环境下,我们启动的服务多且不会反复启动修改。环境也相对稳定,影响服务正常运行的人为情况较少。适合开启自我保护机制,让Eureka进行管理。
6. 如何关闭自我保护机制
服务端:
eureka:
server:
enable-self-preservation: false
eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 3000 #超时3s自动清除。它是清除无效节点的时间间隔
客户端:
eureka:
instance:
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 10
#在接收到上一个心跳之后等待下一个心跳的秒数(默认 90 秒),也就是用来接收心跳的超时时间,若不能在指定时间内收到心跳,则移除此实例,并禁止此实例的流量。
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 5
#指定客户端多久向eureka server发送一次心跳 默认是30s
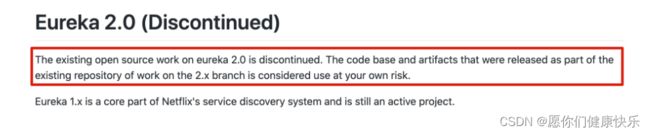
7. eureka 停止更新
在1.x版本项目还是活跃的,但是在2.x版本中停止维护,出现问题后果自负!!!
eureka server集群搭建
测试:这里采用修改虚拟机参数搭建eureka server集群
-
选中一个eureka server复制三个
-
指定服务注册中心的地址,8761要向8762和8763注册,8762要向8761和8763注册,8763要向8761和8762注册
server:
port: 8761 #默认端口号
spring:
application:
name: eurekaserver #指定服务名 不能出现下划线 默认服务名不区分大小写 推荐服务名大写
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8762/eureka,http://localhost:8763/eureka #指定服务注册中心的地址 暴露服务地址
fetch-registry: false #关闭 eureka client的立即注册
register-with-eureka: false #不再将自己同时作为客户端进行注册
server:
enable-self-preservation: false
eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 3000 #超时3s自动清除。它是清除无效节点的时间间隔
解决方法:加个空的config.properties就可以了

启动第二个eureka server(8762,因为虚拟机参数优先于配置文件,所以这里不用在配置文件里修改端口号),修改配置文件,让他向8761,8763注册,第三个同上。
- 启动一个客户端测试一下
注意:如果客户端启动的时候恰好需要注册的这台eureka server宕了,但eureka还有其他的服务注册中心,所以我们在保证server的高可用的时候也要保证client的高可用,所在我们要在配置文件里写上所有的注册中心地址。
server:
port: 8989
spring:
application:
name: EUREKACLIENT
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/,http://localhost:8762/eureka/,http://localhost:8763/eureka/ #eureka注册中心地址
instance:
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 10
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 5
注意:同一个集群,集群的服务名必须一样
小结:不推荐使用eureka服务注册中心。原因有:
- 最新版本停止更新
- 每次必须手动通过代码形式开发服务注册中心
2.Consul
- https://www.consul.io
- consul是一个可以提供服务发现,健康检查,多数据中心,Key/Value存储等功能的分布式服务框架,用于实现分布式系统的服务发现与配置。与其他分布式服务注册与发现的方案,使用起来也较为简单。Consul用Golang实现,因此具有天然可移植性(支持Linux、Windows和Mac OS X);安装包仅包含一个可执行文件,方便部署。
安装consul
- 下载consul
- https://www.consul.io/downloads
-
在指定目录解压缩 注意:不建议含有中文
E:\soft\consul -
启动服务注册中心 在consul安装目录中打开cmd
单节点启动:consul agent -dev
集群启动:consul agent -server -
访问consul 管理界面
http:端口 默认 8500
浏览器:localhost:8500 -
管理界面基本介绍
dcl:数据中心名称 datacenter 默认为:dcl 指定数据中心启动:consul agent -dev -datacenter=aaservices:当前consul服务中注册服务列表 默认:client server同时启动自己注册自己 会出现一个consul服务
nodes:用来查看consul的集群节点
-
推荐配置环境变量
windows:Path=E:\soft\consul(自己机器安装consul目录)
macos、linux:
开发consul 客户端即微服务
- 创建独立springboot应用
- 引入依赖
<!--引入consul依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-consul-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 编写application.properties
server.port=8082
#指定服务名
spring.application.name=CONSULCLIENT
#向consul server服务注册地址
spring.cloud.consul.host=localhost
spring.cloud.consul.post=8500
#指定注册当前服务的服务名称 默认:${spring.application.name} 他会覆盖上面的spring.application.name
#spring.cloud.consul.discovery.service-name=aa
- 在入口类上加入注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient //通用服务注册客户端注解 代表consul client、zk client、nacos client
public class ConsulClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConsulClientApplication.class,args);
}
}
-
直接启动consul client出现以下问题

原因:consul server会检测所有客户端心跳,但是发送心跳时client必须给予响应该服务才能正常使用。但是现有客户端中我们并没有引入健康检查依赖,所以导致健康检查始终不能通过,导致服务不能使用。 -
开启consul健康监控
默认情况consul监控健康是开启的,但是必须依赖健康监控依赖才能正确监控健康状态所以直接启动会显示错误,引入健康监控依赖之后服务正常
<!-- 这个包是用做健康度监控的-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
- consul 关闭健康监控检查
spring.cloud.consul.discovery.register-health-check=false #关闭consu了服务的健康检查[不推荐]
7. 服务间通信方式
什么是微服务
定义:基于单体用用围绕业务进行服务拆分,拆分出来每一个服务独立应用 独立运行 独立部署 运行在自己计算机进程中基于分布式服务管理
如何解决微服务的服务通信问题?
- HTTP Rest 方式 使用http协议进行数据传递 JSON
- RPC 方式 远程过程调用 二进制
OSI: 物理层 数据链路层 网络层 传输层(RPC)回话层 表示层 应用层(Http)
如何在java代码中发起http方式请求?
spring框架提供HttpClient对象 RestTemplate 发起一个请求
基于RestTemplate的服务调用
spring框架提供的RestTemplate类可用于在应用中调用rest服务,它简化了与http服务的通信方式,统一了RESTful的标准,封装了http链接, 我们只需要传入url及返回值类型即可。相较于之前常用的HttpClient,RestTemplate是一种更优雅的调用RESTful服务的方式。
RestTemplate 服务调用
1.创建两个服务并注册到consul注册中心中
users 代表用户服务 端口为 9999
products 代表商品服务 端口为 9998
注意:这里服务仅仅用来测试,没有实际业务意义
2.添加依赖
<!--consul client-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-consul-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--actuator-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.配置两个服务application.properties

4.在入口类中加入服务注解 client注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class UsersApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IRule iRule;
SpringApplication.run(UsersApplication.class,args);
}
}
5.在商品服务中提供服务方法
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class ProductController {
@Value("${server.port}")
private int port;
@GetMapping("/product/findAll")
public Map<String,Object> findAll(){
log.info("商品服务查询所有调用成功,当前服务端口:[{}]",port);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("msg","服务调用成功,服务提供端口为: "+port);
map.put("status",true);
return map;
}
}
6.在用户服务中使用restTemplate进行调用
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/user/findAll")
public String findAll(){
log.info("调用用户服务...");
//1.使用restTemplate调用商品服务
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String forObject = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9998/product/findAll",
String.class);
return forObject;
}
}
9.总结
rest Template是直接基于服务地址调用没有在服务注册中心获取服务,也没有办法完成服务的负载均衡如果需要实现服务的负载均衡需要自己书写服务负载均衡策略。
使用RestTemplate对象实现服务间通信存在问题
1.现有RestTemplate方式通信存在问题?
a.调用服务的路径主机和服务端口直接写死在url中无法实现服务集群时请求负载均衡
b.调用服务的请求路径写死在代码中,日后提供服务服务路径发生变化时不利于后续维护工作
2.解决RestTemplate负载均衡策略问题?
a.自定义负载均衡解决策略
问题:无法实现服务健康检查;负载均衡策略过于单一(随机)
b.使用springcloud提供组件 ribbon解决负载均衡调用 推荐
3.Ribbon springcloud-netflix-ribbbon
作用:负载均衡客户端组件
Ribbon负载均衡原理
使用Ribbon+RestTemplate实现请求负载均衡
1.项目中引入依赖
- 说明:
1.如果使用的是eureka client 和 consul client,无须引入依赖,因为在eureka,consul中默认
集成了ribbon组件
2.如果使用的client中没有ribbon依赖需要显式引入如下依赖
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon
2.使用restTemplate + ribbon进行服务调用
- 使用discovery client 进行客户端调用
- 使用loadBalanceClient 进行客户端调用
- 使用@loadBalanced 进行客户端调用
- 使用discovery Client形式调用(服务发现客户端对象 根据服务id去服务注册中心获取对应服务列表到本地中)
@Configuration //代表这是一个springboot 配置类 spring.xml 工厂 创建对象 bean id class=""
public class BeansConfig {
//工厂中创建restTemplate
@Bean
@LoadBalanced//配合restTemplate使用
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
@Autowired
private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
//获取服务列表
List<ServiceInstance> products = discoveryClient.getInstances("服务ID");
for (ServiceInstance product : products) {
log.info("服务主机:[{}]",product.getHost());
log.info("服务端口:[{}]",product.getPort());
log.info("服务地址:[{}]",product.getUri());
log.info("====================================");
}
String result = restTemplate.getForObject(serviceInstances.get(0).getUri() + "/order", String.class);
//这里的restTemplate对象没有@loadBalanced注解
缺点:没有负载均衡 需要自己实现负载均衡
- 使用loadBalance Client形式调用(负载均衡客户端对象 根据服务id去服务注册中心获取对应服务列表,根据默认负载均衡策略选择列表中一台机器进行返回)
@Autowired
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient;
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
//根据负载均衡策略选取某一个服务调用
ServiceInstance product = loadBalancerClient.choose("服务ID");
log.info("服务主机:[{}]",product.getHost());
log.info("服务端口:[{}]",product.getPort());
log.info("服务地址:[{}]",product.getUri());
String result = restTemplate.getForObject(serviceInstance.getUri() + "/order", String.class);
//这里的restTemplate对象没有@loadBalanced注解
缺点:使用时需要每次先根据服务id获取一个负载均衡机器之后通过restTemplate调用服务
- 使用@loadBalanced + RestTemplate(负载均衡客户端注解)
修饰范围:用在方法上
作用:让当前方法 当前对象具有ribbon负载均衡特性
String result = restTemplate.getForObject("http://ORDERS/order",String.class);
//这里的restTemplate需要@loadBalanced注解
//ORDERS是服务名
但是,使用restTemplate + ribbon进行服务调用还存在问题,restTemplate.getForObject(“http://ORDERS/order”,String.class),路径写死在代码中不利于维护
Ribbon组件实现负载均衡的原理
面试问题:
- 项目中服务间通信都用到什么?
restTemplate - 服务间通信时如何实现负载均衡
使用奈菲封装的ribbon组件实现负载均衡 - ribbon组件原理
根据调用服务的服务id去服务中心获取对应服务id的服务列表,并将服务列表拉去到本地进行缓存,然后在本地通过默认的轮询的负载均衡策略在现有列表中选择一个可用节点提供服务。 - ribbon组件是服务端的负载均衡还是客户端的负载均衡?
它是客户端的负载均衡 - ribbon组件还支持哪些负载均衡策略
通过源码得知Ribbon底层负载均衡策略父接口IRule父接口,在这个父接口中提供很多负载均衡策略 如 轮询 随机 根据响应时间加权 默认是轮询等等。
Ribbon组件源码分析
1.第一步:查看LoadBalancerClient.choose(“ORDERS”) 源码
2.第二步:得知LoadBalancerClient并没有对choose方法做实现,调用的是父接口ServiceInstanceChooser的choose方法,因为如果LoadBalancerClient对choose做了实现,他会直接跳到LoadBalancerClient的源码里
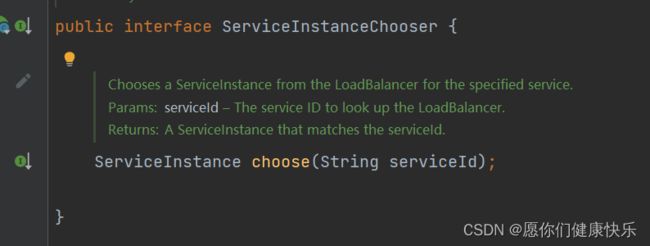
3.第三步:发现有几个实现类(也可用ctrl+h快捷键查看)
得知RibbonLoadBalancerClient是ServiceInstanceChooser choose方法的默认实现。
RibbonLoadBalancerClient中choose方法查看:
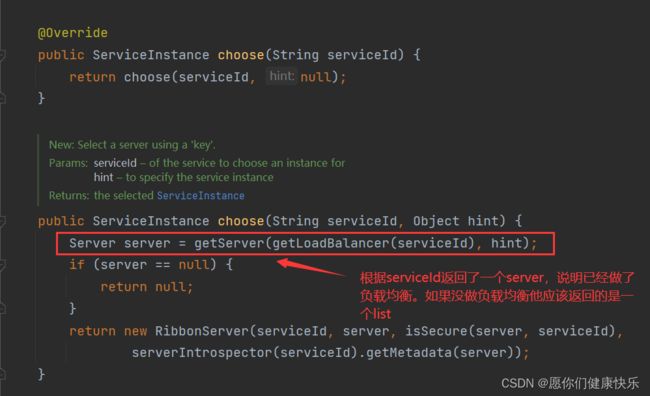
getServer方法查看:
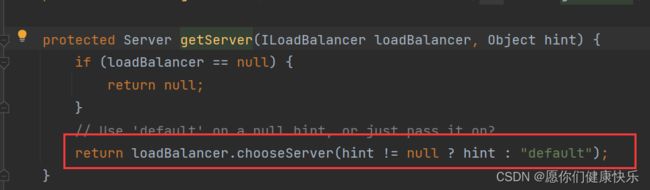
点进去发现进入了父接口ILoadBalancer里

可以发现chooseServer有三个实现类,
不知到该去看那个可以断点调试一下。一般都是Base这个。
断点调试这里,然后进入方法里

,发现它跳进了这个实现类,然后点击下一步,发现他进入了它父类的chooseServer方法
然后我们进入方法,他果然回到了BaseLoadBalancer里

然后下一步下一步,发现真正去做负载均衡的是rule(规则)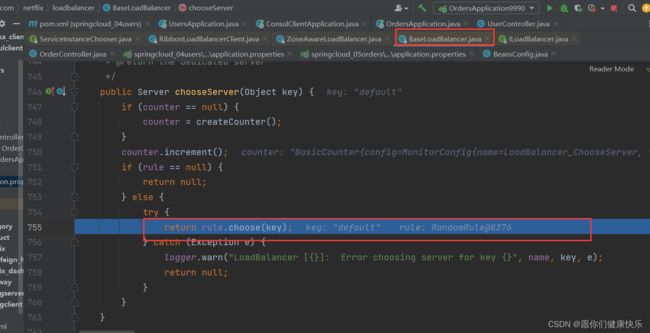
进入rule.choose这个方法,这个key是默认规则,默认轮询这块儿代码在BaseLoadBalancer里面。

我们知道真正去做负载均衡的是rule。rule在BaseLoadBalancer里面是个成员变量。我们去看一下
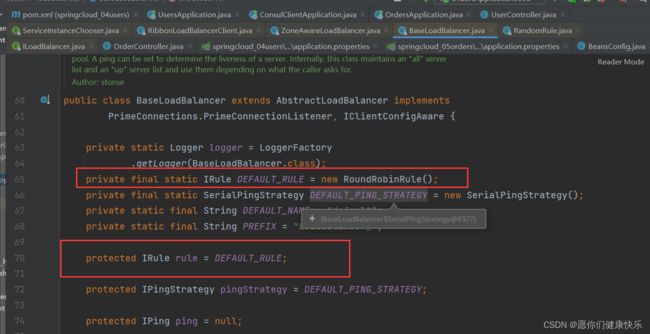
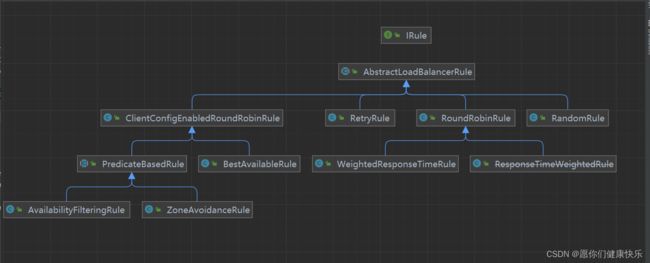
通过源码得知IRule是底层负载均衡父接口
所以我们要想知道负载均衡策略有哪些就是看IRule有哪些实现类。
Ribbon负载均衡策略支持哪些?
# 1.ribbon负载均衡算法
- RoundRobinRule 轮训策略 按顺序循环选择 Server
- RandomRule 随机策略 随机选择 Server
- AvailabilityFilteringRule 可用过滤策略
`会先过滤由于多次访问故障而处于断路器跳闸状态的服务,还有并发的连接数量(tomcat里server.xml写到,tomcat最大的并发线程数是150个)超过阈值的服务,然后对剩余的服务列表按照轮询策略进行访问
- WeightedResponseTimeRule 响应时间加权策略
`根据平均响应的时间计算所有服务的权重,响应时间越快服务权重越大被选中的概率越高,刚启动时如果统计信息不足,则使用
RoundRobinRule策略,等统计信息足够会切换到
- RetryRule 重试策略
`先按照RoundRobinRule的策略获取服务,如果获取失败则在制定时间内进行重试,获取可用的服务。
- BestAviableRule 最低并发策略
`会先过滤掉由于多次访问故障而处于断路器跳闸状态的服务,然后选择一个并发量最小的服务
设置服务间调用负载均衡策略(在用户服务配置文件里写)
服务id.ribbon.NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName=com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule(全限定类名)
Ribbon组件现在的状态
ribbon-core ribbon-loadblance 依然在大规模生产实践中部署,意味着日后如果实现服务间通信负载均衡依然使用ribbon组件
8.OpenFeign组件的使用
- 思考: 使用RestTemplate+ribbon已经可以完成对端的调用,为什么还要使用feign?
String restTemplateForObject = restTemplate.getForObject("http://服务名/url?参数" + name, String.class);
存在问题:
- 1.每次调用服务都需要写这些代码,存在大量的代码冗余
- 2.服务地址如果修改,维护成本增高
- 3.不能自动转换相应结果为对应对象
- 4.必须结成ribbon实现负载均衡
说明:
- https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-openfeign/reference/html/
- Feign是一个声明式的伪Http客户端,它使得写Http客户端变得更简单。使用Feign,只需要创建一个接口并注解。它具有可插拔的注解特性(可以使用springmvc的注解),可使用Feign 注解和JAX-RS注解。Feign支持可插拔的编码器和解码器。Feign默认集成了Ribbon,默认实现了负载均衡的效果并且springcloud为feign添加了springmvc注解的支持。
openFeign 服务调用
1.创建两个独立springboot应用,并注册到服务中心 consul
2.引入服务注册中心依赖
<!--consul client-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-consul-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--actuator-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.修改配置文件
server.port=8787
spring.application.name=CATEGORY
#注册到consul server
spring.cloud.consul.host=localhost
spring.cloud.consul.port=8500
4.入口类加入注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class ProductApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProductApplication.class,args);
}
}
5.使用openfegin进行调用
- 在服务调用方引入OpenFegin依赖
<!--Open Feign依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 在服务调用方入口类加入注解 开启Fegin调用支持
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient//开启服务注册
@EnableFeignClients //开启openfein客户端调用
public class CategoryApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CategoryApplication.class,args);
}
}
- 开发客户端接口
//value属性用来指定:调用服务名称
@FeignClient("PRODUCTS")
public interface ProductClient {
@GetMapping("/product/findAll") //书写服务调用路径
//注意:返回值和参数列表和路径必须一致,方法名随便
String findAll();
}
- 使用feignClient客户端对象调用服务
//注入客户端对象
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
@GetMapping("/user/findAllFeignClient")
public String findAllFeignClient(){
log.info("通过使用OpenFeign组件调用商品服务...");
String msg = productClient.findAll();
return msg;
}
- 访问并测试服务
调用服务并传参
参数传递:
1.传递零散参数类型
2.传递对象类型
3.数组或集合类型参数
零散类型参数传递
1.queryString方式传递参数:?name=xiaochen
1.1 当有一个参数的时候,默认是?方式传参,必须加@RequestParam注解
//定义一个接受零散类型参数接口 queryString
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test(String name){
log.info("name:{} ",name);
return "test ok,当前服务端口为: "+port;
}
@GetMapping("/test")
String test(@RequestParam String name);
1.2 当有两个参数的时候,必须加@RequestParam注解
//定义一个接受零散类型参数接口 queryString
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test(String name, Integer age){
log.info("name:{} age:{}",name,age);
return "test ok,当前服务端口为: "+port;
}
//声明调用商品服务中test?name=xxx&age=23接口传递name,age
@GetMapping("/test")
String test(@RequestParam String name,@RequestParam Integer age);
注意:在openfeign接口声明中必须给参数加入注解@RequestParam
2. 路径传递参数 url/xiaochen/23
//定义一个接受零散类型参数接口 路径传递参数
@GetMapping("/test1/{id}/{name}")
public String test1(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,@PathVariable("name") String name){
log.info("id:{} name:{}",id,name);
return "test1 ok,当前服务端口为: "+port;
}
//声明调用商品服务中test1接口 路径传递数据
@GetMapping("/test1/{id}/{name}")
String test1(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("name") String name);
注意:在openfeign接口声明中必须给参数加入注解@PathVariable
对象类型参数传递
1.application/json方式:推荐
//定义一个接受对象类型参数接口
@PostMapping("/test2")
public String test2(@RequestBody Product product){
log.info("product:{}",product);
return "test2 ok,当前服务端口为: "+port;
}
//声明调用商品服务中test2接口 传递一个商品对象
@PostMapping(value = "/test2")
String test2(@RequestBody Product product);
注意:使用json方式在openfegin接口声明中必须给参数加入注解 @RequestBody注解
数组参数传递
//定义个接口接受数组类型参数
@GetMapping("/test3")
public String test3(String[] ids){
for (String id : ids) {
log.info("id: {}",id);
}
//手动转为list List strings = Arrays.asList(ids);
return "test3 ok,当前服务端口为: "+port;
}
//声明调用商品服务中test3接口 传递一个数组类型 queryString /test3?ids=21&ids=22
@GetMapping("/test3")
String test3(@RequestParam("ids") String[] ids);
集合类型的参数接收
a.服务提供者 商品服务定义
//定义一个接口接受集合类型参数
//springmvc 不能直接接受集合类型参数,如果想要接收集合类型参数必须将集合放入对象中,使用对象的方式接收才行
//oo: oriented(面向) object(对象) 面向对象
// vo(value object): 用来传递数据对象称之为值对象
// dto:(data transfer(传输) object):数据传输对象
@GetMapping("/test4")
public String test4(CollectionVO collectionVO){
collectionVO.getIds().forEach(id-> log.info("id:{} ",id));
return "test4 ok,当前服务端口为: "+port;
}
b.在openfegin中调用
//声明调用商品服务中test4接口 传递一个list集合类型参数 test4?ids=21&ids=22
@GetMapping("/test4")
String test4(@RequestParam("ids") String[] ids);
openfegin的响应处理
1.使用openFegin调用服务,并返回对象
定义一个接口接收id类型参数,返回一个基于id查询的对象
//定义一个接口接收id类型参数,返回一个基于id查询的对象
@GetMapping("/product/{id}")
public Product product(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
log.info("id:{}",id);
return new Product(id,"超短连衣裙",23.23,new Date());
}
声明调用根据id查询商品信息接口
//声明调用根据id查询商品信息接口
@GetMapping("/product/{id}")
Product product(@PathVariable("id") Integer id);
测试
@RestController
public class CategoryController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CategoryController.class);
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
@GetMapping("/category")
public Product category(){
log.info("category service ....");
Product product = productClient.product(21);
return product ;
}
}
2.使用openFegin调用服务,并返回List 集合
定义一个接口接收id类型参数,并返回一个List集合
@GetMapping("/products")
public List<Product> findByCategoryId(Integer categoryId){
log.info("类别id: {}",categoryId);
//调用业务逻辑根据类别id查询商品列表
List<Product> products = new ArrayList<>();
products.add(new Product(1,"短裙",23.23,new Date()));
products.add(new Product(2,"超短裙",23.23,new Date()));
products.add(new Product(3,"超级超短裙",23.23,new Date()));
return products;
}
声明调用商品服务 根据类别id查询一组商品信息
@GetMapping("/products")
List<Product> findByCategoryId(@RequestParam("categoryId") Integer categoryId);
测试
@RestController
public class CategoryController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CategoryController.class);
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
@GetMapping("/category")
public List<Product> category(){
log.info("category service ....");
List<Product> products = productClient.findByCategoryId(1);
products.forEach(product -> log.info("product: {}",product));
return products ;
}
}
3.使用openFegin调用服务,返回Map集合
定义负载数据接口
@GetMapping("/productList")
public Map<String,Object> findByCategoryIdAndPage(Integer page, Integer rows, Integer categoryId){
log.info("当前页: {} 每页显示记录数:{} 当前类别id:{} ",page,rows,categoryId);
//根据类别id分页查询符合当前页集合数据 List select * from t_product where categoryId=? limt ?(page-1)*rows,?(rows)
//根据类别id查询当前类别下总条数 totalCount select count(id) from t_product where categoryId=?
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
List<Product> products = new ArrayList<>();
products.add(new Product(1,"短裙",23.23,new Date()));
products.add(new Product(2,"超短裙",23.23,new Date()));
products.add(new Product(3,"超级超短裙",23.23,new Date()));
int total = 1000;
map.put("rows",products);
map.put("total", total);
return map;
}
在openfegin中处理
第一种
//声明调用商品服务根据类别id查询分页查询商品信息 以及总条数
@GetMapping("/productList")
Map<String,Object> findByCategoryIdAndPage(@RequestParam("page") Integer page,@RequestParam("rows") Integer rows,@RequestParam("categoryId") Integer categoryId);
测试
@RestController
public class CategoryController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CategoryController.class);
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
@GetMapping("/category")
public Map<String,Object> category(){
Map<String, Object> result= productClient.findByCategoryIdAndPage(1, 5, 1);
List<Product> rows = (List<Product>) (result.get("rows"));
rows.forEach(product -> log.info("product:{}",product));
return result;
}
}
如果想要在控制台遍历rows的话不能直接强转,会报错,因为map转json的时候数据丢失了,不知道他是个product。所以这时候需要我们手动序列化。
首先,加个依赖,使用fastjson或jackjson都行。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.76</version>
</dependency>
修改代码为
@RestController
public class CategoryController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CategoryController.class);
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
@GetMapping("/category")
public Map<String,Object> category(){
Map<String, Object> result= productClient.findByCategoryIdAndPage(1, 5, 1);
Object total = result.get("total");
log.info("total:{}",total.toString());
String s = JSONObject.toJSONString(result.get("rows"));
List<Product> products = JSONObject.parseArray(s, Product.class);
products.forEach(product -> log.info("product:{}",product));
return result;
}
}
或者返回值修改为String。因为最后我们不是要返回json字符串。所以我们直接返回string
@RestController
public class CategoryController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CategoryController.class);
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
@GetMapping("/category")
public Map<String,Object> category(){
String result = productClient.findByCategoryIdAndPage(1, 5, 1);
System.out.println(result);
//自定义json反序列化 对象转为json 序列化 on字符串转为对象
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(result);
System.out.println(jsonObject.get("total"));
Object rows = jsonObject.get("rows");
System.out.println(rows);
//二次json反序列化
List<Product> products = jsonObject.parseArray(rows.toString(), Product.class);
products.forEach(product -> {
log.info("product:{}",product);
});
return result;
}
}
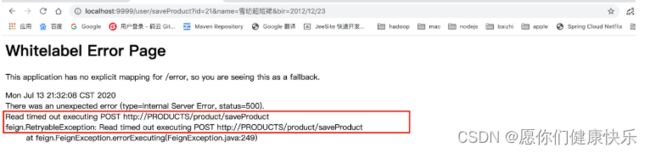
OpenFegin默认超时处理
- 默认情况下,openFiegn在进行服务调用时,要求服务提供方处理业务逻辑时间必须在1S内返回,如果超过1S没有返回则OpenFeign会直接报错,不会等待服务执行,但是往往在处理复杂业务逻辑是可能会超过1S,因此需要修改OpenFeign的默认服务调用超时时间。
1.模拟超时
2.客户端调用
3.修改OpenFeign超时时间
指定服务修改某个服务调用超时时间
feign.client.config.服务id.connectTimeout=5000 #配置指定服务连接超时
feign.client.config.服务id.readTimeout=5000 #配置指定服务等待超时
修改openfegin默认调用所有服务超时时间
#feign.client.config.default.connectTimeout=5000 #配置所有服务连接超时
#feign.client.config.default.readTimeout=5000 #配置所有服务等待超时
OpenFeign调用详细日志展示
日志说明:往往在服务调用时我们需要详细展示feign的日志,默认feign在调用是并不是最详细日志输出,因此在调试程序时应该开启feign的详细日志展示。feign对日志的处理非常灵活可为每个feign客户端指定日志记录策略,每个客户端都会创建一个logger默认情况下logger的名称是feign的全限定名需要注意的是,feign日志的打印只会DEBUG做出响应。
日志使用:
1.展示openfegin日志
logging.level.com.baizhi.feignclients=debug #指定feign调用客户端对象所在包,必须是debug级别
2.fegin每一个客户端提供一个日志对象
`NONE 不记录任何日志
`BASIC 仅仅记录请求方法,url,响应状态代码及执行时间
`HEADERS 记录Basic级别的基础上,记录请求和响应的header
`FULL 记录请求和响应的header,body和元数据
3.设置日志
feign.client.config.PRODUCTS.loggerLevel=full #开启指定服务日志展示
feign.client.config.default.loggerLevel=full #全局开启服务日志展示
9.Hystrix组件使用
微服务中重要的概念:服务雪崩、服务熔断、 服务降级
服务雪崩
在某一时刻微服务系统中所有的微服务均不可用的现象,称之为服务雪崩
服务与服务之间为了完成某种复杂的业务逻辑,他们之间会形成调用链路
图解雪崩效应:
如图存在如下调用链路:
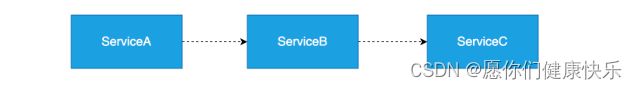 而此时,Service A的流量波动很大,流量经常会突然性增加!那么在这种情况下,就算Service A能扛得住请求,Service B和Service C未必能扛得住这突发的请求。此时,如果Service C因为抗不住请求,变得不可用。那么Service B的请求也会阻塞,慢慢耗尽Service B的线程资源,Service B就会变得不可用。紧接着,Service A也会不可用,这一过程如下图所示
而此时,Service A的流量波动很大,流量经常会突然性增加!那么在这种情况下,就算Service A能扛得住请求,Service B和Service C未必能扛得住这突发的请求。此时,如果Service C因为抗不住请求,变得不可用。那么Service B的请求也会阻塞,慢慢耗尽Service B的线程资源,Service B就会变得不可用。紧接着,Service A也会不可用,这一过程如下图所示

如何解决微服务系统服务雪崩问题?
服务熔断 =====》Hystrix
“熔断器”本身是一种开关装置,当某个服务单元发生故障之后,通过断路器(hystrix)的故障监控,某个异常条件被触发,直接熔断整个服务。向调用方法返回一个符合预期的、可处理的备选响应(FallBack),而不是长时间的等待或者抛出调用方法无法处理的异常,就保证了服务调用方的线程不会被长时间占用,避免故障在分布式系统中蔓延,乃至雪崩。如果目标服务情况好转则恢复调用。服务熔断是解决服务雪崩的重要手段。
熔断机制:所有微服务中必须引入Hystrix组件,一旦引入Hystrix这个组件就具有服务熔断功能。类似于保险丝
服务降级
服务压力剧增的时候根据当前的业务情况及流量对一些服务和页面有策略的降级,以此缓解服务器的压力,以保证核心任务的进行。同时保证部分甚至大部分任务客户能得到正确的响应。也就是当前的请求处理不了了或者出错了,给一个默认的返回。
通俗定义:当网站服务流量突然增加时,为了保证系统核心服务正常运行,有策略关闭系统中边缘服务,以保证核心服务正常运行
降级和熔断总结
1.共同点
- 目的很一致,都是从可用性可靠性着想,为防止系统的整体缓慢甚至崩溃,采用的技术手段;
- 最终表现类似,对于两者来说,最终让用户体验到的是某些功能暂时不可达或不可用;
- 粒度一般都是服务级别,当然,业界也有不少更细粒度的做法,比如做到数据持久层(允许查询,不允许增删改);
- 自治性要求很高,熔断模式一般都是服务基于策略的自动触发,降级虽说可人工干预,但在微服务架构下,完全靠人显然不可能,开关预置、配置中心都是必要手段;sentinel
2.异同点
- 触发原因不太一样,服务熔断一般是某个服务(下游服务)故障引起,而服务降级一般是从整体负荷考虑;
- 管理目标的层次不太一样,熔断其实是一个框架级的处理,每个微服务都需要(无层级之分),而降级一般需要对业务有层级之分(比如降级一般是从最外围服务边缘服务开始)
3.总结
- 熔断必会触发降级,所以熔断也是降级一种,区别在于熔断是对调用链路的保护,而降级是对系统过载的一种保护处理
服务熔断的实现
服务熔断的实现思路
- 引入hystrix依赖,并开启熔断器(断路器)
- 模拟降级方法
- 进行调用测试
1.项目中引入hystrix依赖
<!--引入hystrix-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.开启断路器
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCircuitBreaker //用来开启断路器
public class Products9998Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Products9998Application.class, args);
}
}
3.使用HystrixCommand注解实现断路
//服务熔断
@GetMapping("/product/break")
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "testBreakFall" )
public String testBreak(int id){
log.info("接收的商品id为: "+ id);
if(id<=0){
throw new RuntimeException("数据不合法!!!");
}
return "当前接收商品id: "+id;
}
public String testBreakFall(int id){
//返回值和形参列表必须和上面的一样
return "当前数据不合法: "+id;
}

4.访问测试
正常参数访问
错误参数访问(只要调用失败就会走fallback方法)

5.总结
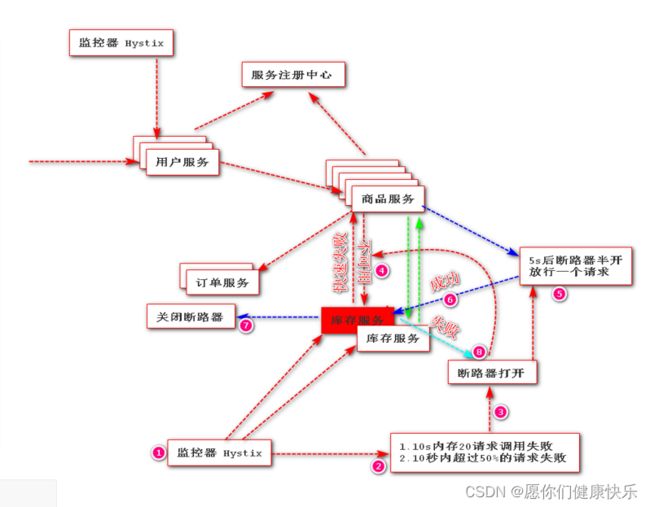
- 从上面演示过程中会发现如果触发一定条件断路器会自动打开,过了一点时间正常之后又会关闭。那么断路器打开条件是什么呢?
6.断路器打开条件
- 官网: https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-netflix/2.2.x/reference/html/#circuit-breaker-spring-cloud-circuit-breaker-with-hystrix
- A service failure in the lower level of services can cause cascading failure all the way up to the user. When calls to a particular service exceed
circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold(default: 20 requests) and the failure percentage is greater thancircuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage(default: >50%) in a rolling window defined bymetrics.rollingStats.timeInMilliseconds(default: 10 seconds), the circuit opens and the call is not made. In cases of error and an open circuit, a fallback can be provided by the developer. --摘自官方 - 原文翻译之后,总结打开关闭的条件:
- 1、 当满足一定的阀值的时候(默认10秒内超过20个请求次数)
- 2、 当失败率达到一定的时候(默认10秒内超过50%的请求失败)
- 3、 到达以上阀值,断路器将会开启
- 4、 当开启的时候,所有请求都不会进行转发
- 5、 一段时间之后(默认是5秒),这个时候断路器是半开状态,会让其中一个请求进行转发。如果成功,断路器会关闭,若失败,继续开启。重复4和5。
断路器流程

整个流程:当Hystrix监控到对该服务接口调用出发1到两个阈值时,会在系统中自动触发熔断器,在熔断器打开期间内,任何到该接口请求均不可用,同时在断路器打开5秒后断路器会处于半开状态,此时断路器允许放行一个请求到该服务接口,如果该请求执行成功,断路器彻底关闭,如果该请求宗兴失败断路器重新打开。
7.默认的服务FallBack处理方法
- 如果为每一个服务方法开发一个降级,对于我们来说,可能会出现大量的代码的冗余,不利于维护,这个时候就需要加入默认服务降级处理方法
@GetMapping("/product/hystrix")
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "testHystrixFallBack") //通过HystrixCommand降级处理 指定出错的方法
public String testHystrix(String name) {
log.info("接收名称为: " + name);
int n = 1/0;
return "服务[" + port + "]响应成功,当前接收名称为:" + name;
}
//服务降级处理
public String testHystrixFallBack(String name) {
return port + "当前服务已经被降级处理!!!,接收名称为: "+name;
}
服务降级的实现
服务降级: 站在系统整体负荷角度 实现: 关闭系统中某些边缘服务 保证系统核心服务运行
Emps 核心服务 Depts 边缘服务
1.客户端openfeign + hystrix实现服务降级实现
- 引入hystrix依赖。注意:openfegin组件底层自动依赖Hystrix依赖项目中无需显示引入
- 配置文件开启feign支持hystrix
- 在feign客户端调用加入fallback指定降级处理
- 开发降级处理方法
2.开启openfeign支持服务降级
feign.hystrix.enabled=true #开启openfeign支持降级
注意:openfegin在调用服务过程中要开启hystrix支持 ,默认没有开启
3.在openfeign客户端中加如Hystrix
@FeignClient(value = "PRODUCTS",fallback = ProductFallBack.class)
public interface ProductClient {
@GetMapping("/product/hystrix")
String testHystrix(@RequestParam("name") String name);
}
4.开发fallback处理类
public class ProductFallBack implements ProductClient {
@Override
public String testHystrix(String name) {
return "我是客户端的Hystrix服务实现!!!";
}
}
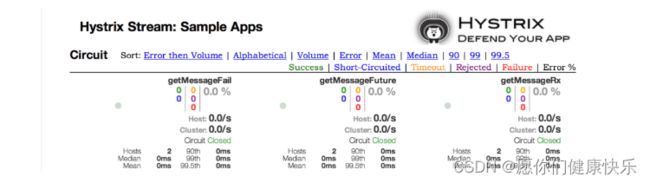
Hystrix Dashboard(仪表盘) NetFlix
- 用来显示状态信息
- 监控每一个@HystrixCommond注解创建一组度量,构建一组信息,然后通过图形化方式展示当前方法@HystrixCommond的状态信息
构建Hystrix DashBoard 仅仅是一个仪表盘应用
1.创建springboot应用
2.引入hystrix dashboard依赖
<!--引入hystrix dashboard 依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.入口类中开启hystrix dashboard
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableHystrixDashboard //开启监控面板
//@EnableDiscoveryClient //注意: 默认只要引入discovery client依赖 该注解无须显示声明 自动注册 consul zk nacos
public class Hystrixdashboard9990Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Hystrixdashboard9990Application.class, args);
}
}
3.启动hystrix dashboard应用并访问监控页面
- http://localhost:9990(dashboard端口)/hystrix
4.监控的项目中入口类中加入监控路径配置[新版本坑],并启动监控项目
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean getServlet() {
HystrixMetricsStreamServlet streamServlet = new HystrixMetricsStreamServlet();
ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(streamServlet);
registrationBean.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registrationBean.addUrlMappings("/hystrix.stream");
registrationBean.setName("HystrixMetricsStreamServlet");
return registrationBean;
}
5.点击监控,一致loading,打开控制台发现报错[特别坑]

# 解决方案
- 新版本中springcloud将jquery版本升级为3.4.1,定位到monitor.ftlh文件中,js的写法如下:
$(window).load(function()
- jquery 3.4.1已经废弃上面写法
- 修改方案 修改monitor.ftlh为如下调用方式:
$(window).on("load",function()
- 编译jar源文件,重新打包引入后,界面正常响应。
Hystrix停止维护
# 官方地址:https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix
- 翻译:Hystrix(版本1.5.18)足够稳定,可以满足Netflix对我们现有应用的需求。同时,我们的
- 重点已经转移到对应用程序的实时性能作出反应的更具适应性的实现,而不是预先配置的设置(例如,
- 通过自适应并发限制)。对于像Hystrix这样的东西有意义的情况,我们打算继续在现有的应用程序中
- 使用Hystrix,并在新的内部项目中利用诸如resilience4j这样的开放和活跃的项目。我们开始建议
- 其他人也这样做。 ----> sentinel 流量卫兵
- Dashboard也被废弃
-
目前状态
- Hystrix不在处于积极开发中,目前处于维护状态
- Hystrix Dashboard 已经被废弃
- 替换产品:Netflix-Skunkworks/hystrix-dashboard
-
日后如何解决服务雪崩
- Hystrix(版本1.5.18)足够稳定,可以满足Netflix对我们现有应用程序的需求
- resilience4j 替换Hystrix 实时自适应系统熔断
- sentinel 流量为病 流量控制 降低策略(根据异常)推荐 Sentinel & sentinel dashboard
10.Gateway组件使用
什么是服务网关
1.说明
- 网关统一服务入口,可方便实现对平台众多服务接口进行管控。
2.网关作用
- 网关统一所有微服务入口。
- 网管可以实现请求路由转发(router dispatcher)以及请求过程负载均衡。
- 访问服务的身份认证、防报文重放与防数据篡改、功能调用的业务鉴权、响应数据的脱敏、流量与并发控制,甚至基于API调用的计量或者计费等等。
服务网关组件
zuul 1.x 2.x(netflix 组件)
- Zuul is the front door for all requests from devices and web sites to the backend of the Netflix streaming application. As an edge service application, Zuul is built to enable dynamic routing, monitoring, resiliency and security.
- https://github.com/Netflix/zuul/wiki
- 原文翻译:zul是从设备和网站到Netflix流媒体应用程序后端的所有请求的前门。作为一个边缘服务应用程序,zul被构建为支持动态路由、监视、弹性和安全性。
zuul版本说明
- 目前zuul组件已经从1.0更新到2.0,但是作为springcloud官方不再推荐使用zuul2.0,但是依然支持zuul2.
springcloud 官方集成zuul文档
- https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-netflix/2.2.x/reference/html/#netflix-zuul-starter
gateway (spring) =路由转发+请求过滤
- This project provides a library for building an API Gateway on top of Spring MVC. Spring Cloud Gateway aims to provide a simple, yet effective way to route to APIs and provide cross cutting concerns to them such as: security, monitoring/metrics, and resiliency.
- https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud-gateway
- 原文翻译:这个项目提供了一个在springmvc之上构建API网关的库。springcloudgateway旨在提供一种简单而有效的方法来路由到api,并为api提供横切关注点,比如:安全性、监控/度量和弹性。
特性
- 基于springboot2.x 和 spring webFlux 和 Reactor 构建 响应式异步非阻塞IO模型
- 动态路由
- 请求过滤
- 统一服务管理
开发网关动态路由
- 网关配置有两种方式一种是快捷方式(Java代码编写网关),一种是完全展开方式(配置文件方式)[推荐]
1.开发独立springboot应用
2.引入网关依赖 注意:去掉项目springboot-start-web依赖,它们存在冲突
<!--引入gateway网关依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
快捷方式配置路由
3.编写网关配置
spring:
application:
name: gateway
cloud:
consul:
host: localhost
port: 8500
gateway:
routes:
- id: user_route # 指定路由唯一标识
uri: http://localhost:9999/ # 指定路由服务的地址
predicates:
- Path=/user/** # 指定路由规则
- id: product_route
uri: http://localhost:9998/
predicates:
- Path=/product/**
server:
port: 8989
4.启动gateway网关项目
java方式配置路由
@Configuration
public class GatewayConfig {
@Bean
public RouteLocator customRouteLocator(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route("order_route", r -> r.path("/order/**")
.uri("http://localhost:9997"))
.build();
}
}
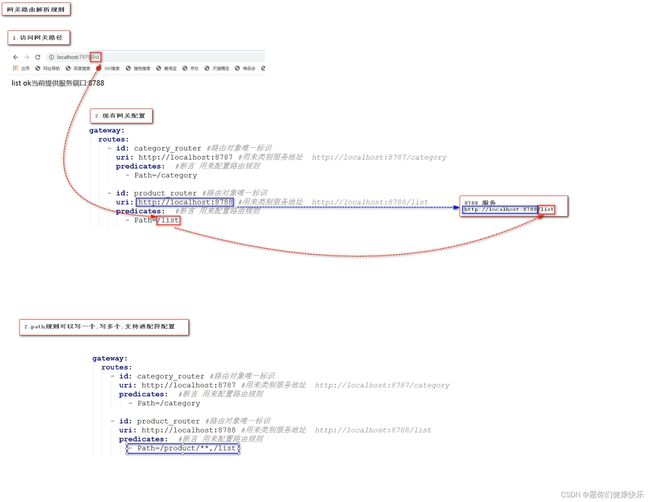
网关路由解析规则
- 现有路由配置方式,都是基于服务地址写死的路由转发,能不能根据服务名称进行路由转发同时实现负载均衡的呢?
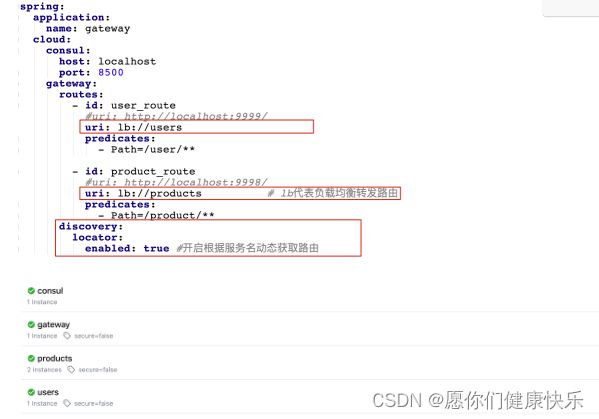
spring:
application:
name: gateway
cloud:
consul:
host: localhost
port: 8500
gateway:
routes:
- id: user_route
#uri: http://localhost:9999/
uri: lb://users # lb代表转发后台服务使用负载均衡,users代表服务注册中心上的服务名
predicates:
- Path=/user/**
- id: product_route
#uri: http://localhost:9998/
uri: lb://products # lb(loadbalance)代表负载均衡转发路由
predicates:
- Path=/product/**
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true #开启根据服务名动态获取路由
常用路由predicate(断言,验证)
网关gateway=断言predicate + 过滤(后置filter)
断言:当请求到达网关时,网关的前置处理满足断言放心请求,不满足断言立即返回
过滤:当请求满足断言的所有条件之后,会向后端服务转发,在向后端服务转发之前会经过一些过滤
断言使用 Route Predicate Factories
- Path=/category 路径断言
- After=2020-07-21T11:33:33.993+08:00[Asia/Shanghai] `代表该路由规则必须在指定时间之后才能生效
- Before=2020-07-21T11:33:33.993+08:00[Asia/Shanghai] `代表该路由规则必须在指定时间之前有效,过了时间失效 代表路由规则在某个时间段有效
- Between=2017-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver], 2017-01-21T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver]
- Cookie=username,chenyn `基于指定cookie的请求进行路由 注意必须配合curl工具使用
- Cookie=username,[A-Za-z0-9]+ `基于指定cookie的请求进行路由
`curl http://localhost:8989/user/findAll --cookie "username=zhangsna"
- Header=X-Request-Id, \d+ `基于请求头中的指定属性的正则匹配路由(这里全是整数)
`curl http://localhost:8989/user/findAll -H "X-Request-Id:11"
- Method=GET,POST `基于指定的请求方式请求进行路由
- 官方更多: https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/spring-cloud-gateway/2.2.3.RELEASE/reference/html/#the-cookie-route-predicate-factory
server:
port: 7979
spring:
application:
name: GATEWAY
cloud:
consul:
host: localhost
port: 8500
gateway:
routes:
- id: product_router #路由对象唯一标识
#uri: http://localhost:8788 #用来类别服务地址 http://localhost:8788/list
uri: lb://PRODUCT #实现请求负载均衡处理 /product/product/list
predicates: #断言 用来配置路由规则
- Path=/product/**,/list
#- After=2021-04-20T10:20:22.124+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]
#- Before=2021-04-20T10:23:22.124+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]
#- Between=2021-04-20T10:23:22.124+08:00[Asia/Shanghai],2021-04-20T10:25:22.124+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]
#- Cookie=name,chenyn
#- Cookie=name,[A-Za-z0-9]+
#- Header=X-Request-Id,\d+
#- Method=GET
常用的Filter以及自定义filter
- 当我们有很多个服务时,比如下图中的user-service、order-service、product-service等服务,客户端请求各个服务的Api时,每个服务都需要做相同的事情,比如鉴权、限流、日志输出等。
- AddRequestHeader=X-Request-red, blue `用来给路由对象的所有转发请求加入指定请求头信息`
- AddRequestParameter=red, blue `用来给路由对象的所有转发请求加入指定请求参数`
- AddResponseHeader=X-Response-Red, AAA `用来给路由对象的所有转发请求的响应加入指定头信息`
- PrefixPath=/emp `用来给路由对象的所有转发请求的url加入指定前缀信息`
- StripPrefix=n `用来给路由对象的所有转发请求的url去掉指定的n个前缀`
自定义全局filter(所有请求都要经过全局filter之后再换发到后端服务)
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class CustomGlobalFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
log.info("进入自定义的filter");
if(exchange.getRequest().getQueryParams().get("username")!=null){
log.info("用户身份信息合法,放行请求继续执行!!!");
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
log.info("非法用户,拒绝访问!!!");
return exchange.getResponse().setComplete();
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return -1;
}
}
- http://localhost:7979/actuator/gateway/routes
查看网关路由规则详细路径必须在网关配置文件中暴露当前路径
11.Config组件使用
什么是Config
-
https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/spring-cloud-config/2.2.3.RELEASE/reference/html/#_spring_cloud_config_server
-
config(配置)又称为 统一配置中心顾名思义,就是将配置统一管理,配置统一管理的好处是在日后大规模集群部署服务应用时相同的服务配置一致,日后再修改配置只需要统一修改全部同步,不需要一个一个服务手动维护
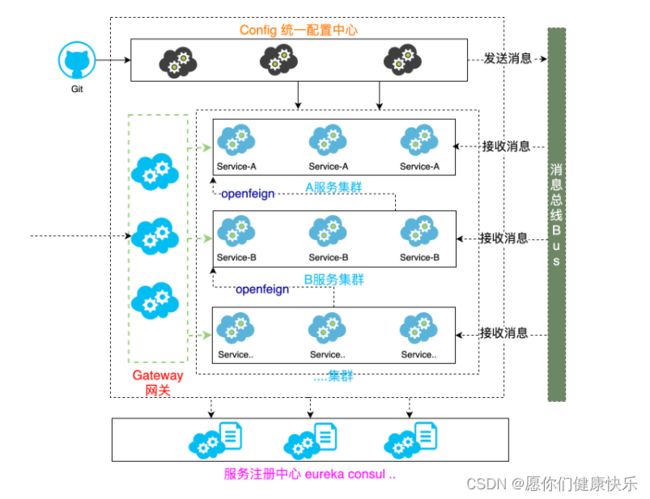
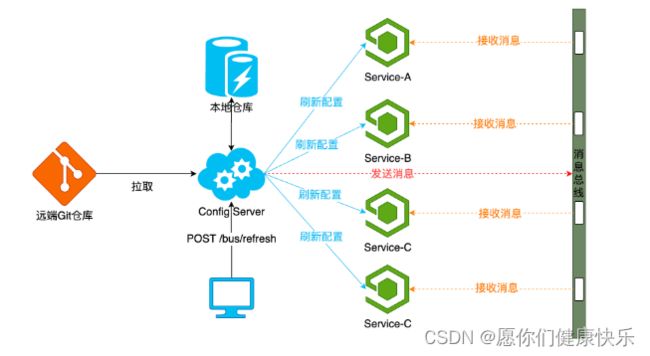
统一配置中心组件流程图
Config Server 开发(config client —>config server---->远端git仓库)
1.选择一个远端git仓库
- 使用github或gitee
- 创建新仓库
- 获取仓库地址
2.搭建config server统一配置中心服务
- 独立springboot应用
- 引入config server依赖
<!--引入统一配置中心-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 配置application .properties 远程仓库地址
spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri=https://github.com/chenyn-java/configservers.git #指定仓库的url
spring.cloud.config.server.git.default-label=master 指定访问的分支
#spring.cloud.config.server.git.username= 私有仓库访问用户名
#spring.cloud.config.server.git.password= 私有仓库访问密码
- 开启统一配置中心 在入口类加入注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class Configserver7878Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Configserver7878Application.class, args);
}
}
- 1. http://localhost:7878/test-xxxx.properties
- 找不到test-xxxx.properties这个文件会找test.properties这个文件,如果找test-dev.properties这个文件找到了的话,会把test.properties文件合并并显示出来
- 2. http://localhost:7878/test-xxxx.json
- 3. http://localhost:7878/test-xxxx.yml
- 拉取远端配置规则
- label/name-profiles.yml|properties|json
`label 代表去那个分支获取 默认使用master分支
`name 代表读取那个具体的配置文件文件名称
`profile 代表读取配置文件环境
- 查看拉取配置详细信息
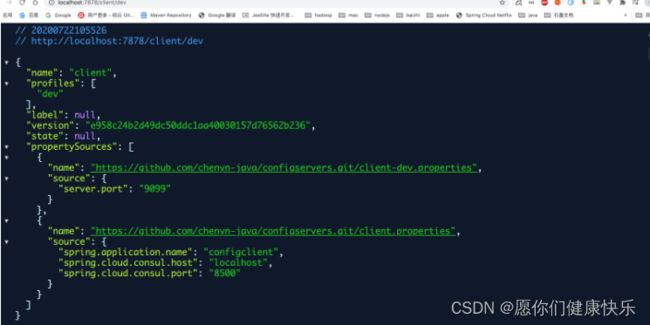
- http://localhost:7878/client/dev [client:代表远端配置名称][dev:代表远程配置的环境]
- 指定分支和本地仓库位置
spring.cloud.config.server.git.basedir=/localresp #一定要是一个空目录,在首次会将该目录清空
spring.cloud.config.server.git.default-label=master
Config Client 开发
- 创建一个独立springboot应用
- 将自身配置交给远端git仓库管理
- client.properties [用来存放公共配置][]
server.port=8990
spring.application.name=CONFIGCLIENT
- client-dev.properties [用来存放研发相关配置]
name=zhangsn
- client-prod.properties [用来存放生产相关配置][]
name=xiaosan
- 引入config client相关依赖(不用加注解)
<!--引入config client-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 配置文件编写
#告诉当前configclient统一配置中心在注册中心服务id
spring.cloud.config.discovery.service-id=CONFIGSERVER
#开启当前configclient 根据服务id去注册中心获取
spring.cloud.config.discovery.enabled=true
#配置注册中心
spring.cloud.consul.host=localhost
spring.cloud.consul.port=8500
#获取那个配置文件 1.确定分支 2.确定文件名 3.确定环境
spring.cloud.config.label=master #可加可不加,因为server里已经写过了
spring.cloud.config.name=configclient
spring.cloud.config.profile=dev
- 启动客户端服务进行远程配置拉取测试
直接启动过程中发现无法启动直接报错
 报错原因
报错原因
项目中目前使用的是application.properties启动项目,使用这个配置文件在springboot项目启动过程中不会等待远程配置拉取,直接根据配置文件中内容启动,因此当需要注册中心,服务端口等信息时,远程配置还没有拉取到,所以直接报错。

解决方案
应该在项目启动时先等待拉取远程配置,拉取远程配置成功之后再根据远程配置信息启动即可,为了完成上述要求springboot官方提供了一种解决方案,就是在使用统一配置中心时应该将微服务的配置文件名修改为bootstrap.(properties|yml),bootstrap.properties作为配置启动项目时,会优先拉取远程配置,远程配置拉取成功之后根据远程配置启动当前应用。

手动配置刷新
当远端git仓库中配置发生变化时,不需要重启微服务就可以直接读取远端修改之后的配置信息,这种就叫做手动配置刷新。
- 在需要刷新代码的类中加入刷新配置的注解
@RestController
@RefreshScope //作用: RefreshScope 用来在不需要重启微服务情况下,将当前scope域中信息刷新为最新配置信息.每个controller都要加
@Slf4j
public class TestController {
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
@GetMapping("/test/test")
public String test(){
log.info("当前加载配置文件信息为:[{}]",name);
return name;
}
}
- 手动调用刷新配置接口(也可以用postman)
curl -X POST http://localhost:9099/actuator/refresh

- 在config client端加入刷新暴露端点
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=* #开启所有web端点暴露。yml文件里是“*”
问题:每一个微服务节点如果要加载最新配置信息,必须向每一个服务手动发送post方式请求,才能加载最新配置
12.Bus组件的使用
什么是Bus (AMQP RibbitMQ、Kafka)
Spring Cloud Bus links nodes of a distributed system with a lightweight message broker. This can then be used to broadcast state changes (e.g. configuration changes) or other management instructions. AMQP and Kafka broker implementations are included with the project. Alternatively, any Spring Cloud Stream binder found on the classpath will work out of the box as a transport. --摘自官网
-
https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud-bus
-
springcloudbus使用轻量级消息代理将分布式系统的节点连接起来。然后,可以使用它来广播状态更改(例如配置更改)或其他管理指令。AMQP和Kafka broker(中间件)实现包含在项目中。或者,在类路径上找到的任何springcloudstream绑定器都可以作为传输使用。
-
通俗定义: bus称之为springcloud中消息总线,主要用来在微服务系统中实现远端配置更新时通过广播形式通知所有客户端刷新配置信息,避免手动重启服务的工作
实现配置刷新原理
MQ
搭建RabbitMQ服务
# 0.下载rabbitmq安装包 [][可以直接使用docker安装更方便]
- 官方安装包下载:https://www.rabbitmq.com/install-rpm.html#downloads
[注意:][这里安装包只能用于centos7.x系统]
# 1.将rabbitmq安装包上传到linux系统中
erlang-22.0.7-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
rabbitmq-server-3.7.18-1.el7.noarch.rpm
# 2.安装Erlang依赖包
rpm -ivh erlang-22.0.7-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
# 3.安装RabbitMQ安装包(需要联网)
yum install -y rabbitmq-server-3.7.18-1.el7.noarch.rpm
注意:默认安装完成后配置文件模板在:/usr/share/doc/rabbitmq-server-3.7.18/rabbitmq.config.example目录中,需要
将配置文件复制到/etc/rabbitmq/目录中,并修改名称为rabbitmq.config
# 4.复制配置文件
cp /usr/share/doc/rabbitmq-server-3.7.18/rabbitmq.config.example /etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.config
# 5.查看配置文件位置
ls /etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.config
# 6.修改配置文件(参见下图:)
vim /etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.config

将上图中配置文件中红色部分去掉%%,以及最后的,逗号 修改为下图:
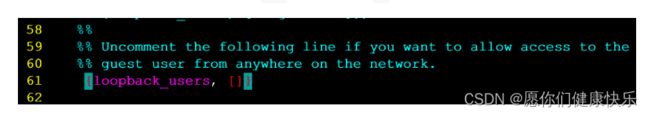
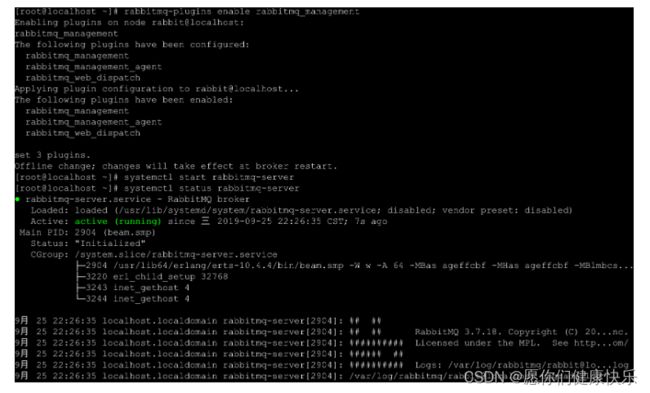
# 7.执行如下命令,启动rabbitmq中的插件管理(可有可无)
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
出现如下说明:
Enabling plugins on node rabbit@localhost:
rabbitmq_management
The following plugins have been configured:
rabbitmq_management
rabbitmq_management_agent
rabbitmq_web_dispatch
Applying plugin configuration to rabbit@localhost...
The following plugins have been enabled:
rabbitmq_management
rabbitmq_management_agent
rabbitmq_web_dispatch
set 3 plugins.
Offline change; changes will take effect at broker restart.
# 8.启动RabbitMQ的服务
systemctl start rabbitmq-server
systemctl restart rabbitmq-server
systemctl stop rabbitmq-server
# 9.查看服务状态(见下图:)
systemctl status rabbitmq-server
● rabbitmq-server.service - RabbitMQ broker
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/rabbitmq-server.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since 三 2019-09-25 22:26:35 CST; 7s ago
Main PID: 2904 (beam.smp)
Status: "Initialized"
CGroup: /system.slice/rabbitmq-server.service
├─2904 /usr/lib64/erlang/erts-10.4.4/bin/beam.smp -W w -A 64 -MBas ageffcbf -MHas ageffcbf -
MBlmbcs...
├─3220 erl_child_setup 32768
├─3243 inet_gethost 4
└─3244 inet_gethost 4
.........
# 10.启动出现如下错误:
- 4月 21 10:10:50 bogon systemd[1]: Starting RabbitMQ broker...
- 4月 21 10:11:11 bogon rabbitmq-server[1772]: ERROR: epmd error for host bogon: address (cannot connect to host/port)
- 4月 21 10:11:11 bogon systemd[1]: rabbitmq-server.service: main process exited, code=exited, status=1/FAILURE
`解决方案`:
1. 修改主机名 vim /etc/hostname 修改为自己注解名 rabbimq 2.修改完必须重启 reboot命令重启
3. vim /etc/hosts 在文件中添加: 127.0.0.1 自己主机名(rabbitmq)
# 10.关闭防火墙服务
systemctl disable firewalld
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/firewalld.service.
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service.
systemctl stop firewalld
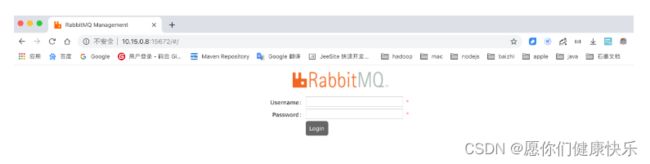
# 11.访问web管理界面
http://10.15.0.8:15672/
# 12.登录管理界面
username: guest
password: guest
# 13.MQ服务搭建成功
实现自动配置刷新
1.启动MQ服务
MQ服务主机:192.168.149.131
MQ:15672端口(Web);5672端口(JAVA)
虚拟主机:/
默认用户:guest
密码:guest
2.配置统一配置中心通过Bus连接到MQ服务
- 配置中心和所有微服务都引入依赖
<!--引入bus依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 远端配置中加入连接mq配置并重启config server
- 加入bus组件之后客户端启动报错

错误原因:引入bus依赖启动立即根据配置文件bus配置连接mq服务器,但是此时mq配置信息都在远端,因此bus连接不到mq直接报错,组织了应用启动
解决方案:允许项目启动时bus组件立即连接mq这个失败,因为获取远端配置之后可以再以远端配置初始化bus组件
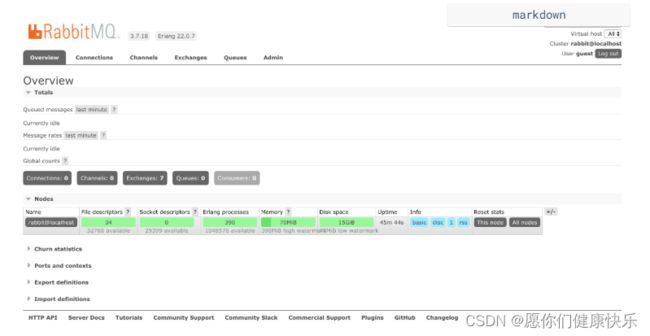
spring.cloud.config.fail-fast=true代表在启动时还没有拉取远端配置完成时的失败都是允许的
3.修改远程配置后在配置中心服务通过执行post接口刷新配置
- 默认情况下使用curl -X POST http://localhost:7878/actuator/bus-refresh这种方式刷新配置是全部广播形式,也就是所有的微服务都能接收到刷新配置通知,但有时我们修改的仅仅是某个服务的配置,这个时候对于其他服务的通知是多余的,因此就需要指定服务进行通知
- 刷新所有服务:
POST http://localhost:7878(server或config地址)/actuator/bus-refresh - 指定端口刷新某个具体服务:
POST http://localhost:7878(server或config地址)/actuator/bus-refresh/configclient:9090 - 指定服务id刷新服务集群节点:
POST http://localhost:7878(server或config地址)/actuator/bus-refresh/configclient - 注意:/actuator/bus-refresh 必须在config server中暴露:
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
集成webhook(web 钩子)实现自动刷新
1.钩子 hooks
根据仓库出发时间执行对应操作
2.webbooks
根据远程仓库出发对应事件发送一个web请求这个请求默认就是POST方式请求
-
说明: git仓库提供一种特有机制: 这种机制就是一个监听机制 监听就是仓库提交事件 … 触发对应事件执行
-
javascript: 事件 事件源 html标签 事件: 触发特定动作click … 事件处理程序:函数
-
添加webhooks
-
在webhooks中添加刷新配置接口
-
内网穿透的网站: https://natapp.cn/


首次配置完成之后config server发送post方式出现400错误,需要在configServer中加入filter配置
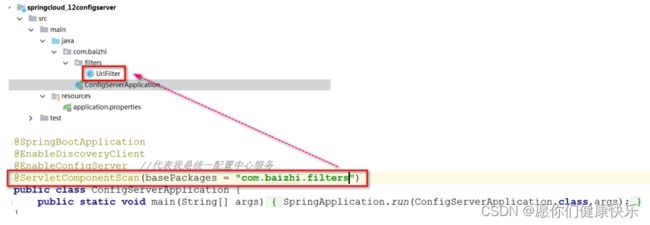
@Component
public class UrlFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest)request;
HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse = (HttpServletResponse)response;
String url = new String(httpServletRequest.getRequestURI());
//只过滤/actuator/bus-refresh请求
if (!url.endsWith("/bus-refresh")) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
//获取原始的body
String body = readAsChars(httpServletRequest);
System.out.println("original body: "+ body);
//使用HttpServletRequest包装原始请求达到修改post请求中body内容的目的
CustometRequestWrapper requestWrapper = new CustometRequestWrapper(httpServletRequest);
chain.doFilter(requestWrapper, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
private class CustometRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
public CustometRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request) {
super(request);
}
@Override
public ServletInputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = new byte[0];
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
return new ServletInputStream() {
@Override
public boolean isFinished() {
return byteArrayInputStream.read() == -1 ? true:false;
}
@Override
public boolean isReady() {
return false;
}
@Override
public void setReadListener(ReadListener readListener) {
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
return byteArrayInputStream.read();
}
};
}
}
public static String readAsChars(HttpServletRequest request)
{
BufferedReader br = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
try
{
br = request.getReader();
String str;
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null)
{
sb.append(str);
}
br.close();
}
catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
if (null != br)
{
try
{
br.close();
}
catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}