2.SpringBoot2开发实用篇①
1.热部署
1.1 手动启动热部署
使用图书管理项目(springboot_books)
修改books.html的修改方法
//修改
handleEdit() {
axios.put("/books",this.formData).then((res)=>{
//判断当前操作是否成功
if(res.data.flag){
//1.关闭弹层
this.dialogFormVisible4Edit = false;
this.$message.success(res.data.msg);
}else{
this.$message.error(es.data.msg);
}
}).finally(()=>{
//2.重新加载数据
this.getAll();
});
}
① 添加开发者工具的依赖坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
dependency>
② 激活热部署:Ctrl + F9
也就是build ==> build poject
关于热部署
重启(Restart):自定义开发代码,包含类、页面、配置文件等,加载位置restart类加载器
重载(ReLoad):jar包,加载位置base类加载器
1.2 自动启动热部署
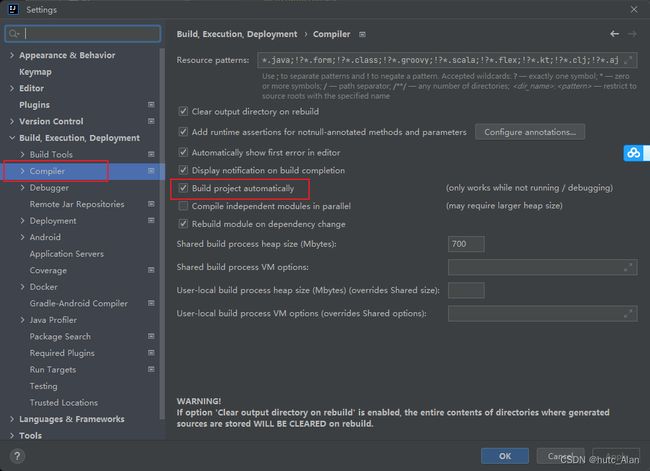
第二步:
旧版是:ctrl+shift+Alt+/ 快捷键弹出窗口选择Registry,然后勾选compiler.automake.allow.when.app.running
新版设置如下:

激活方式:idea失去焦点5秒后启动热部署
1.3 热部署范围配置
默认不触发启动的目录列表
/META-INF/maven
/META-INF/resources
/resources
/static
/public
/templates
自定义不参与重启排除项
spring:
devtools:
restart:
#设置不参与热部署的文件或文件夹
exclude: public/**,static/**
1.4 关闭热部署
关闭热部署
方式一:
spring:
devtools:
restart:
enabled: false
方式二:
设置高优先级属性禁用热部署
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootBooksApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("spring.devtools.restart.enabled","false");
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootBooksApplication.class, args);
}
}
2.配置高级
创建一个新的springboot项目,不使用web
springboot使用2.5.4版本
2.1 @ConfigurationPoperties
属性绑定
① 添加lombok依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
dependency>
② 添加配置
servers:
ipAddress: 192.168.0.1
port: 1234
timeout: -1
③ 添加ServersConfig类
package com.example.config;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers")
public class ServersConfig {
private String ipAddress;
private int port;
private long timeout;
}
④ 测试
package com.example;
import com.example.config.ServersConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Spingboot03Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(Spingboot03Application.class, args);
ServersConfig bean = ctx.getBean(ServersConfig.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
}
使用@ConfigurationPoperties为第三方bean绑定属性
① 添加druid依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.16version>
dependency>
② 在配置文件中添加
datasource:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jc.jdbc.Driver456789
③ 测试
package com.example;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.example.config.ServersConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Spingboot03Application {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "datasource")
public DruidDataSource datasource(){
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
return ds;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(Spingboot03Application.class, args);
ServersConfig bean = ctx.getBean(ServersConfig.class);
System.out.println(bean);
DruidDataSource ds = ctx.getBean(DruidDataSource.class);
System.out.println(ds.getDriverClassName());
}
}
注解:@EnableConfigurationProperties
@EnableConfigurationProperties注解可以将使用@ConfigurationProperties注解对应的类加入Spring容器
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerConfig.class)
public class DemoApplication {
}
//@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers")
public class ServerConfig {
}
注意事项:@EnableConfigurationProperties与@Component不能同时使用
解除使用@ConfigurationProperties注释警告
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
dependency>
2.2 宽松绑定/松散绑定
@ConfigurationProperties绑定属性支持属性名宽松绑定
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers")
public class ServersConfig {
private String ipAddress;
private int port;
private long timeout;
}
servers:
# ipAddress: 192.168.0.1 # 驼峰
# ipaddress: 192.168.0.2
# ip_address: 192.168.0.3 # unline
ip-address: 192.168.0.4 # 烤肉串模式:0-0-0-0
# IPADDRESS: 192.168.0.5
# IP_ADDRESS: 192.168.0.6 #常量
# IP_ADD_R-ES_S: 192.168.0.7
port: 1234
timeout: -1
注意事项:
宽松绑定不支持注解@Value引用单个属性的方式
绑定前缀名命名规范:仅能使用纯小写字母、数字、下划线作为合法的字符
2.3 常用计量单位绑定
SpringBoot支持JDK8提供的时间与空间计量单位
package com.example.config;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.convert.DataSizeUnit;
import org.springframework.boot.convert.DurationUnit;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.unit.DataSize;
import org.springframework.util.unit.DataUnit;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers")
public class ServersConfig {
private String ipAddress;
private int port;
private long timeout;
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.HOURS)
private Duration serverTimeOut;
@DataSizeUnit(DataUnit.MEGABYTES)
private DataSize dataSize;
}
配置文件
servers:
ip-address: 192.168.0.4
port: 1234
timeout: -1
serverTimeOut: 3
# dataSize: 10MB
dataSize: 10
2.4 数据校验
开启数据校验有助于系统安全性,J2EE规范中JSR303规范定义了一组有关数据校验的API
实验
1.导入JSR303规范坐标与Hibernate校验框架对应坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.validationgroupId>
<artifactId>validation-apiartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validatorgroupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validatorartifactId>
dependency>
2.对bean开启校验功能及设置效验规则
package com.example.config;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.convert.DataSizeUnit;
import org.springframework.boot.convert.DurationUnit;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.unit.DataSize;
import org.springframework.util.unit.DataUnit;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers")
//2.开启对当前bean的属性注入校验
@Validated
public class ServersConfig {
private String ipAddress;
//3.设置具体的规则
@Max(value = 8888,message = "最大值不能超过8888")
@Min(value = 202,message = "最小值不能小于202")
private int port;
private long timeout;
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.HOURS)
private Duration serverTimeOut;
@DataSizeUnit(DataUnit.MEGABYTES)
private DataSize dataSize;
}
2.5 补充
yaml语法规则
字面值表达方式
boolean: TRUE #TRUE,true,True,FALSE,false,False均可
float: 3.14 #6.8523015e+5 #支持科学计数法
int: 123 #0b1010_0111_0100_1010_1110 #支持二进制、八进制、十六进制
null: ~ #使用~表示null
string: HelloWorld #字符串可以直接书写
string2: "Hello World" #可以使用双引号包裹特殊字符
date: 2018-02-17 #日期必须使用yyyy-MM-dd格式
datetime: 2018-02-17T15:02:31+08:00 #时间和日期之间使用T连接,最后使用+代表时区
3.测试
3.1 加载测试专用属性
① 在启动测试环境时可以通过properties参数设置测试环境专用的属性
优势:比多环境开发中的测试环境影响范围更小,仅对当前测试类有效
② 在启动测试环境时可以通过args参数设置测试环境专用的传入参数
测试类
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
//properties属性可以为当前测试用例添加临时的属性配置
//@SpringBootTest(properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"})
//args属性可以为当前测试用例添加临时的命令行参数
//@SpringBootTest(args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"})
//args覆盖properties
@SpringBootTest(args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"},properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"})
public class PropertiesAndArgsTest {
@Value("${test.prop}")
private String msg;
@Test
void testProperties(){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
3.2 加载测试专用配置
使用@Import注解加载当前测试类专用的配置
实验
在测试包下创建
MsgConfig
package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MsgConfig {
@Bean
public String msg(){
return "bean msg";
}
}
ConfigurationTest
package com.example;
import com.example.config.MsgConfig;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@SpringBootTest
@Import(MsgConfig.class)
public class ConfigurationTest {
@Autowired
private String msg;
@Test
void testConfiguration(){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
3.3 Web环境模拟测试
将pom.xml中的spring-boot-starter依赖改为spring-boot-starter-web
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
模拟端口
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
//RANDOM_PORT随机端口 DEFINED_PORT默认端口(8080)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class WebTest {
@Test
void test(){
}
}
虚拟请求
main包下创建controller类
package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@GetMapping
public String getById(){
System.out.println("getById is running ...");
return "springboot";
}
}
虚拟请求测试
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockHttpServletRequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
//RANDOM_PORT随机端口 DEFINED_PORT默认端口
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
//开启虚拟MVC调用
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class WebTest {
@Test
void test(){
}
@Test
void testWeb(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
//创建虚拟请求,当前访问/books
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
//执行对应的请求
mvc.perform(builder);
}
}
虚拟请求状态匹配
@Test
void testStatus(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
// MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books1");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
//设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过,失败测试失败
//定义本次调用的预期值
StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status();
//预计本次调用成功的:状态200
ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk();
//添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(ok);
}
虚拟请求体匹配
@Test
void testBody(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
//设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过,失败测试失败
//定义本次调用的预期值
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
//预计本次调用成功的预期结果
// ResultMatcher result = content.string("springboot");
ResultMatcher result = content.string("springboot2");
//添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(result);
}
虚拟请求体(json)匹配
实体类
package com.example.domain;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Book {
private int id;
private String name;
private String type;
private String Description;
}
controller类模拟数据
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.domain.Book;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@GetMapping
public Book getById(){
System.out.println("getById is running ...");
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(1);
book.setName("springboot");
book.setType("springboot");
book.setDescription("springboot");
return book;
}
}
测试
@Test
void testJson(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
//设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过,失败测试失败
//定义本次调用的预期值
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
//预计本次调用成功的预期结果
// ResultMatcher result = content.string("{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"springboot\",\"type\":\"springboot\",\"description\":\"springboot\"}");
ResultMatcher result = content.string("{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"springboot\",\"type\":\"springboot\",\"description\":\"springboot2\"}");
//添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(result);
}
虚拟请求响应头匹配
@Test
void testContentType(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
//设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过,失败测试失败
//定义本次调用的预期值
HeaderResultMatchers header = MockMvcResultMatchers.header();
//预计本次调用成功的预期结果
ResultMatcher contentType = header.string("Content-Type","application/json");
//添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(contentType);
}
模拟测试
@Test
void testGetById(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder);
StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status();
ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk();
action.andExpect(ok);
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
ResultMatcher result = content.string("{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"springboot\",\"type\":\"springboot\",\"description\":\"springboot2\"}");
action.andExpect(result);
HeaderResultMatchers header = MockMvcResultMatchers.header();
ResultMatcher contentType = header.string("Content-Type","application/json");
action.andExpect(contentType);
}
3.4 数据层测试回滚
在图书管理项目中实验
1.为测试用例添加事务,SpringBoot会对测试用例对应的事务提交操作进行回滚
2.如果想在测试用例中提交事务,可以通过@Rollback注释设置
package com.example;
import com.example.domain.Book;
import com.example.service.BookService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.annotation.Rollback;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@SpringBootTest
//@Transactional默认发生回滚即@Rollback(true)
@Transactional
//@Rollback(false)
public class ServiceTest {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@Test
void testSave(){
Book book = new Book();
book.setName("springboot");
book.setType("springboot");
book.setDescription("springboot");
bookService.save(book);
}
}
3.5 测试用例数据设定
测试用例数据通常采用随机值进行测试,使用SpringBoot提供的随机数为其赋值
① 在配置文件中添加
testcase:
book:
id: ${random.int}
id2: ${random.int(10)} # 随机生成10以内的值
name: ${random.value}
uuid: ${random.uuid}
publishTime: ${random.long}
② 实体类
package com.example.testcase.domain;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "testcase.book")
public class BookCase {
private int id;
private int id2;
private String name;
private String uuid;
private long publishTime;
}
③ 测试随机赋值
package com.example.testcase.domain;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
public class BookCaseTest {
@Autowired
private BookCase bookCase;
@Test
void testProperties(){
System.out.println(bookCase);
}
}
补充:
- ${random.int}表示随机整数
- ${random.int(10)}表示10以内的随机数
- ${random.int(10,20)}表示10到20的随机数
- 其中()可以是任意字符,例如[],!!均可
4.数据层解决方案
4.1 SQL
现有数据层解决方案技术选型
Druid + MyBatis-Plus + MySQL
数据源:DruidDataSource
持久化技术:MyBatis-Plus / MyBatis
数据库:MySQL
数据源配置格式
格式一
spring:
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.224:3306/ssm_db
username: root
password: 123456
格式二
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.224:3306/ssm_db
username: root
password: 123456
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
4.1.1 内置数据源
数据源配置
- SpringBoot提供了3种内嵌的数据源对象供开发者选择
- HikariCP:默认内置数据源对象
- Tomcat提供DataSource:HikariCP不可用的情况下,且在web环境中,将使用tomcat服务器配置的数据源对象
- Commons DBCP:Hikari不可用,tomcat数据源也不可用,将使用dbcp数据源
spring:
datasource:
hikari:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: 123456
maximum-pool-size: 50
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.224:3306/ssm_db
4.1.2 内置持久化解决方案——jdbcTemplate
内置持久化解决方案——jdbcTemplate
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
测试
package com.example;
import com.example.domain.Book;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringBootSqlTest {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
void testJdbcTemplateSave(){
String sql = "insert into tbl_book values(2,'springboot2','springboot2','springboot2')";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
}
@Test
void testJdbc(){
String sql = "select * from tbl_book where id = 1";
List<Book> query = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new RowMapper<Book>() {
@Override
public Book mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Book temp = new Book();
temp.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
temp.setName(rs.getString("name"));
temp.setType(rs.getString("type"));
temp.setDescription(rs.getString("description"));
return temp;
}
});
System.out.println(query);
}
}
JdbcTemplate配置
spring:
jdbc:
template:
query-timeout: -1 # 查询超时时间
max-rows: 500 # 最大行数
fetch-size: -1 # 缓存行数
4.1.3 内嵌数据库
内嵌数据库
- SpringBoot提供了3种内嵌数据库供开发者选择,提高开发测试效率
- H2
- HSQL
- Derby
① 导入H2相关坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2databasegroupId>
<artifactId>h2artifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
② 设置当前项目为web工程,并配置H2管理控制台参数
访问用户名sa,默认密码123456
server:
port: 80
spring:
h2:
console:
enabled: true
path: /h2
datasource:
hikari:
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
username: sa
password: 123456
url: jdbc:h2:~/test
③ 浏览器访问:http://localhost/h2
输入密码登录
操作数据库(创建表)
create table tbl_book (id int,name varchar,type varchar,description varchar);
insert into tbl_book values(1,'springboot','springboot','springboot');
select * from tbl_book;
运行SpringBootSqlTest测试类
H2数据库控制台仅用于开发阶段,线上项目请务必关闭控制台功能
spring:
h2:
console:
enabled: false
path: /h2
SpringBoot可以根据url地址自动识别数据库种类,在保障驱动类存在的情况下,可以省略配置
server:
port: 80
spring:
h2:
console:
enabled: true
path: /h2
datasource:
hikari:
# driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
username: sa
password: 123456
url: jdbc:h2:~/test
4.2 NoSQL
市场上常见的NoSQL解决方案
Redis
Mongo
ES
说明:上述技术通常在Linux西永中安装部署,为降低学习者压力,下面内容是基于Windows版本的
4.2.1 Redis
-
Redis是一款key-value存储结构的内存级NoSQL数据库
- 支持多种数据存储格式
- 支持持久化
- 支持集群
-
Redis下载( Windows版)
- https://github.com/tporadowski/redis/releases
- Redis-x64-5.0.14.msi(链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1sp2qwD-_0J_eVzU6DsJsjw 提取码:02uy)
-
Redis安装与启动(Windows版)
- Windows解压安装或一键式安装
- 服务端启动
redis-server.exe redis.windows.conf - 客户端启动命令
redis-cli.exe
Redis启动
Windows版本存在bug,执行redis-cli.exe --> shutdown --> exit --> redis-server.exe redis.windows.conf 启动Redis
D:\tools\redis>redis-cli.exe
127.0.0.1:6379> shutdown
not connected> exit
D:\tools\redis>redis-server.exe redis.windows.conf
[25480] 03 Jun 15:39:45.243 # oO0OoO0OoO0Oo Redis is starting oO0OoO0OoO0Oo
[25480] 03 Jun 15:39:45.243 # Redis version=5.0.14.1, bits=64, commit=ec77f72d, modified=0, pid=25480, just started
[25480] 03 Jun 15:39:45.243 # Configuration loaded
_._
_.-``__ ''-._
_.-`` `. `_. ''-._ Redis 5.0.14.1 (ec77f72d/0) 64 bit
.-`` .-```. ```\/ _.,_ ''-._
( ' , .-` | `, ) Running in standalone mode
|`-._`-...-` __...-.``-._|'` _.-'| Port: 6379
| `-._ `._ / _.-' | PID: 25480
`-._ `-._ `-./ _.-' _.-'
|`-._`-._ `-.__.-' _.-'_.-'|
| `-._`-._ _.-'_.-' | http://redis.io
`-._ `-._`-.__.-'_.-' _.-'
|`-._`-._ `-.__.-' _.-'_.-'|
| `-._`-._ _.-'_.-' |
`-._ `-._`-.__.-'_.-' _.-'
`-._ `-.__.-' _.-'
`-._ _.-'
`-.__.-'
[25480] 03 Jun 15:39:45.246 # Server initialized
[25480] 03 Jun 15:39:45.248 * DB loaded from disk: 0.000 seconds
[25480] 03 Jun 15:39:45.249 * Ready to accept connections
Redis最基本的操作
D:\tools\redis>Redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> set name test
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get name
"test"
127.0.0.1:6379> set name2 test2
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "name2"
2) "name"
127.0.0.1:6379> hset keya a1 aa1
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> hset keya a2 aa2
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> hget keya a1
"aa1"
127.0.0.1:6379> hget keya a2
"aa2"
想要了解更多可以去找Redis课程学习
4.2.2 SpringBoot整合Redis
新建SpringBoot项目,勾选Spring Data Redis(Access + Driver)
SpringBoot版本选择2.5.4
① 配置Redis(采用默认配置)
# 使用默认地址和端口号可以不进行配置(内部已经配置)
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
② RedisTemplate提供操作各种数据存储类型的接口API
客户端:RedisTemplate以对象作为key和value,内部对数据进行序列化
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.HashOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootRedisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void set() {
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set("age",41);
}
@Test
void get(){
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Object age = ops.get("age");
System.out.println(age);
}
@Test
void hset() {
HashOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
ops.put("info","a","aa");
}
@Test
void hget(){
HashOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Object val = ops.get("info","a");
System.out.println(val);
}
}
客户端:StringRedisTemplate以字符串作为key和value,与Redis客户端操作等效
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
@SpringBootTest
public class StringRedisTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Test
void get(){
ValueOperations<String, String> ops = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
String name = ops.get("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
}
SpringBoot操作Redis客户端的技术切换(jdeis)
① 导入jdeis坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clientsgroupId>
<artifactId>jedisartifactId>
dependency>
② 添加配置
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
client-type: jedis
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 16
lettcus与jedis区别
- jedis连接Redis服务器是直连模式,当多线程模式下使用jedis会存在线程安全问题,解决方案可以通过配置连接池使每个连接专用,这样整体性能就大受影响。
- lettcus基于Netty框架进行与Redis服务器连接,底层设计中采用StatefulRedisConnection。 StatefulRedisConnection自身是线程安全的,可以保障并发访问安全问题,所以一个连接可以被多线程复用。当然lettcus也支持多连接实例一起工作。
4.2.3 MongoDB
MongoDB是一个开源、高性能、无模式的文档型数据库。NoSQL数据库产品中的一种,是最像关系型数据库的非关系型数据库
应用场景
- 淘宝用户数据
- 存储位置:数据库
- 特征:永久性存储,修改频度极低
- 游戏装备数据、游戏道具数据
- 存储位置:数据库、Mongodb
- 特征:永久性存储与临时存储相结合、修改频度较高
- 直播数据、打赏数据、粉丝数据
- 存储位置:数据库、Mongodb
- 特征:永久性存储与临时存储相结合,修改频度极高
- 物联网数据
- 存储位置:Mongodb
- 特征:临时存储,修改频度飞速
- 其他数据……
安装和启动
Windows版MongDB下载:
官网:https://www.mongodb.com/try/download
可以选择一键式安装或者解压缩(链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1-hRy0X-fKDKvO4vyzhzIaA 提取码:f6e6)
Windows版Mongo安装:
解压缩后设置数据目录(data\db)
Windows版Mongo启动:
服务端启动:
mongod --dbpath=..\data\db
客户端启动:
mongo --host=127.0.0.1 --port=27017
推荐可视化客户端Robo3T(链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1cpl_zE62YmR8-xkrm1byQA 提取码:n0cs)
Robo3T的使用
基础操作
3. 添加
//添加数据(文档)
db.book.save({"name":"springboot"})
db.book.save({"name":"springboot",type:"springboot"})
- 查询
//db.getCollection('book').find({})
//db.book.find()
db.book.find({type:"springboot"})
- 删除
//删除操作(不加条件相当于删除表)
db.book.remove({type:"springboot"})
- 修改
//修改操作
//只修改第一个符合条件的数据
db.book.update({name:"springboot"},{$set:{name:"springboot2"}})
//修改所有符合条件的数据
db.book.updateMany({name:"springboot2"},{$set:{name:"springboot"}})
MongoDB基础CRUD
- 基础查询
- 查询全部:db.集合.find();
- 查第一条:db.集合.findOne()
- 查询指定数量文档:db.集合.find().limit(10) //查10条文档
- 跳过指定数量文档:db.集合.find().skip(20) //跳过20条文档
- 统计:db.集合.count()
- 排序:db.集合.sort({age:1}) //按age升序排序
- 投影:db.集合名称.find(条件,{name:1,age:1}) //仅保留name与age域
- 条件查询
- 基本格式:db.集合.find({条件})
- 模糊查询:db.集合.find({域名:/正则表达式/}) //等同SQL中的like,比like强大,可以执行正则所有规则
- 条件比较运算:db.集合.find({域名:{$gt:值}}) //等同SQL中的数值比较操作,例如:name>18
- 包含查询:db.集合.find({域名:{$in:[值1,值2]}}) //等同于SQL中的in
- 条件连接查询:db.集合.find({$and:[{条件1},{条件2}]}) //等同于SQL中的and、or
4.2.4 SpringBoot整合MongoDB
1 创建的springboot项目,勾选Spring Data MongoDB,修改springboot版本为2.5.4
或者导坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodbartifactId>
dependency>
- 导入lombok坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
dependency>
- 创建实体类Book
java
package com.example.domain;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Book {
private int id;
private String name;
private String type;
private String Description;
}
- 配置客户端
spring:
data:
mongodb:
uri: mongodb://localhost/test
- 客户端读写MongoDB
package com.example;
import com.example.domain.Book;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.MongoTemplate;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootMongodbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
@Test
void testSave() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(1);
book.setName("springboot");
book.setType("springboot");
book.setDescription("springboot");
mongoTemplate.save(book);
}
@Test
void testFind(){
List<Book> all = mongoTemplate.findAll(Book.class);
System.out.println(all);
}
}
如果测试find报错,则将id不是int型的数据删除
4.2.5 Elasticsearch(ES)
ES是一个分布式全文搜索引擎
倒排索引:指的是将文档内容中的单词作为索引,将包含该词的文档 ID 作为记录的结构。
Windows版ES下载:
下载网址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/elasticsearch
(链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1bW19luc5qZ64SrAhWjDJBQ 提取码:5n29)
Windows版ES安装与启动:
运行bin\elasticsearch.bat
使用postman测试
添加数据:发送put请求:http://localhost:9200/books
获取数据:发送get请求:http://localhost:9200/books
删除数据:发送delete请求:http://localhost:9200/books
注:如果send卡住,重启ES
IK分词器
下载地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases
将elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.16.2.zip解压缩到plugins包中
发送put请求:http://localhost:9200/books
创建索引并指定规则(请求体中添加json格式数据)
{
"mappings":{
"properties":{
"id":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"name":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word",
"copy_to":"all"
},
"type":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"description":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word",
"copy_to":"all"
},
"all":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
4.2.6 ES文档操作
1.创建文档
请求体
{
"name":"springboot",
"type":"springboot",
"description":"springboot"
}
发送post请求
http://localhost:9200/books/_doc #使用系统生成id
http://localhost:9200/books/_doc/1 #使用指定id,不存在创建,存在更新(版本递增)
http://localhost:9200/books/_create/1 #使用指定id
2.查询文档
发送get请求
http://localhost:9200/books/_doc/1 #查询单个文档
http://localhost:9200/books/_search #查询全部文档
3.条件查询
发送get请求
http://localhost:9200/books/_search?q=name:springboot
4.删除文档
发送delete请求
http://localhost:9200/books/_doc/1
5.修改文档(全量修改)
发送put请求
http://localhost:9200/books/_doc/1
请求体包含内容
{
"name":"springboot",
"type":"springboot",
"description":"springboot"
}
6.修改文档(部分修改)
发送post请求
http://localhost:9200/books/_update/1
请求体内容为
{
"doc":{
"name":"springboot"
}
}
4.2.7 SpringBoot整合ES客户端操作
低级别的客户端
- 创建新的springboot项目,勾选Spring Data Elasticsearch(Access+Driver)
或者添加坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearchartifactId>
dependency>
- 配置
spring:
elasticsearch:
rest:
uris: http://localhost:9200
- 客户端
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.ElasticsearchRestTemplate;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootEsApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchRestTemplate template;
}
高级别的客户端
高版本的springboot已经整合了
- 添加依赖坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.clientgroupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-clientartifactId>
dependency>
- 客户端
package com.example;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClientBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.io.IOException;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootEsApplicationTests {
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
HttpHost host = HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200");
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(host);
client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws IOException {
client.close();
}
@Test
void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
}
- 添加文档
添加相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.78version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
dependency>
测试添加文档
package com.example;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import lombok.Data;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.action.admin.indices.delete.DeleteIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClientBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootEsApplicationTests {
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
HttpHost host = HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200");
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(host);
client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws IOException {
client.close();
}
@Test
void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
@Test
void testCreateIndexByIK() throws IOException {
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
String json = "{\n" +
" \"mappings\":{\n" +
" \"properties\":{\n" +
" \"id\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\":\"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\":\"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"type\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"description\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\":\"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\":\"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"all\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\":\"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
//设置请求中的参数
request.source(json, XContentType.JSON);
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
//添加文档
@Test
void testCreateDoc() throws IOException {
//数据实际上来自于数据库
//Book book = bookDao.selectById(1);
//String json = JSON.toJSONString(book);
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("books").id("1");
//模拟数据
String json = "{\n" +
" \"name\":\"springboot\",\n" +
" \"type\":\"springboot\",\n" +
" \"description\":\"springboot\"\n" +
"}";
request.source(json,XContentType.JSON);
client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
//批量添加文档
@Test
void testCreateDocAll() throws IOException {
//从数据库中读取
// List bookList = bookDao.selectList(null);
//模拟数据
List<Book> bookList = new ArrayList<>();
Book book1 = new Book();
book1.setId(1);
book1.setName("springboot");
book1.setType("springboot");
book1.setDescription("springboot");
Book book2 = new Book();
book2.setId(2);
book2.setName("springboot2");
book2.setType("springboot2");
book2.setDescription("springboot2");
bookList.add(book1);
bookList.add(book2);
BulkRequest bulk = new BulkRequest();
for (Book book : bookList) {
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("books").id(Integer.toString(book.getId()));
String json = JSON.toJSONString(book);
request.source(json,XContentType.JSON);
bulk.add(request);
}
client.bulk(bulk,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
@Data
public static class Book {
private int id;
private String name;
private String type;
private String Description;
}
}
- 查询文档
//按id查询
@Test
void testGet() throws IOException {
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("books","1");
GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
String json = response.getSourceAsString();
System.out.println(json);
}
//按条件查询
@Test
void testSearch() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("books");
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
builder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("all","springboot"));
request.source(builder);
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
String json = hit.getSourceAsString();
// System.out.println(json);
Book book = JSON.parseObject(json,Book.class);
System.out.println(book);
}
}