java高级注解与反射的使用与思考
不知道java注解与反射的同学,可以先学习一下我的另一篇博客注解与反射
下面让我们来简单回顾一下,什么是注解、反射
1.注解
什么是注解
//什么是注解
public class Demo01_Annotation extends Object {
//@Override就是一个注解
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
}
内置注解
// 什么是注解
public class Demo01_Annotation extends Object {
// @Override就是一个注解
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
// @Deprecated不推荐程序员使用,但是可以使用,或者存在更好的更新方式
@Deprecated
public static void test() {
System.out.println("Deprecated");
}
// @SuppressWarnings 镇压警告
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public void test01(){
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
}
}
自定义注解,元注解
//测试元注解
@MyAnnotation
public class Demo02_MetaAnnotation {
@MyAnnotation
public void test() {
}
}
//定义一个注解
//@Target可以用在什么地方
//ElementType.METHOD方法上有效 ElementType.TYPE类上有效
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
//@Retention在什么地方有效
//RUNTIME>CLASS>SOURCES
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//@Documented 表示是否将我们的注解生成在Javadoc中
@Documented
//@Inherited 子类可以继承父类的注解
@Inherited
@interface MyAnnotation { }
//自定义注解
public class Demo03_CustomAnnotation {
//注解可以显示赋值,如果没有默认值,就必须给注解赋值
@MyAnnotation2(name = "张三")
public void test() {
}
}
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation2 {
//注解的参数:参数类型+参数名()
//String name();
String name() default "";
int age() default 0;
int id() default -1;//-1代表不存在
String[] schools() default {"西部开源","清华大学"};
2.反射机制
Java反射机制概念
静态 & 动态语言
反射机制概念
反射机制研究与应用
反射机制优缺点
实现
//什么叫反射
public class Demo04_Reflection {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 通过反射获取类的class对象
Class<?> c = Class.forName("cn.doris.reflection.User");
System.out.println(c);
Class<?> c1 = Class.forName("cn.doris.reflection.User");
Class<?> c2 = Class.forName("cn.doris.reflection.User");
Class<?> c3 = Class.forName("cn.doris.reflection.User");
Class<?> c4 = Class.forName("cn.doris.reflection.User");
// 一个类在内存中只有一个Class对象
// 一个类被加载后,类的整个结构都会被封装在Class对象中
/**
* public native int hashCode();返回该对象的hash码值
* 注:哈希值是根据哈希算法算出来的一个值,这个值跟地址值有关,但不是实际地址值。
*/
System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
System.out.println(c4.hashCode());
}
}
//实体类
class User {
private String name;
private int id;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int id, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
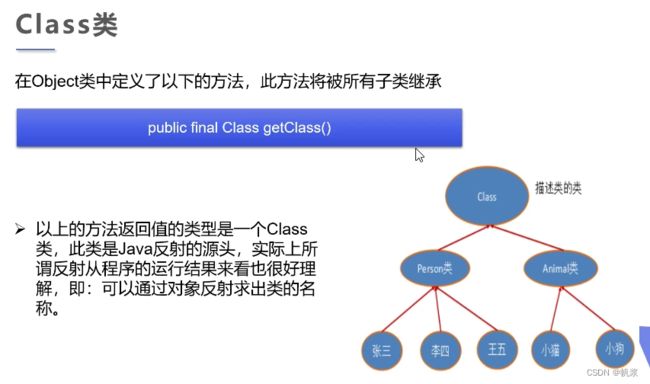
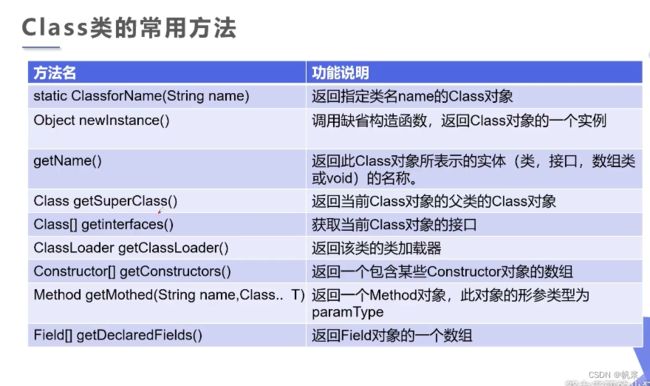
理解Class类并获取Class实例
class类介绍
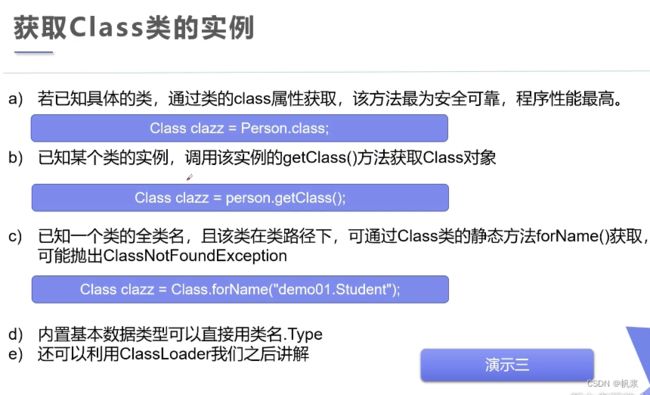
获取Class类的实例
//测试class类的创建方式有哪些
public class Demo05_CreateClass {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Person person = new Student();
System.out.println("这个人是:"+person.name);
//方式一:通过对象查询
Class c1 = person.getClass();
System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
//方式二:forname获得
Class c2 = Class.forName("cn.doris.reflection.Student");
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
//方式三:通过类名.class获得
Class c3 = Student.class;
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
//方式四,基本类型的包装类都有一个Type
Class c4 = Integer.TYPE;
System.out.println(c4);
//获得父类类型
Class c5 = c1.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(c5);
}
}
class Person {
String name;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name=" + name +
'}';
}
}
class Student extends Person {
public Student() {
this.name = "学生";
}
}
class Teacher extends Person {
public Teacher() {
this.name = "老师";
}
}
哪些类型可以有Class对象
//所有类型的Class
public class Demo06_AllTypeClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class c1 = Object.class; //类
Class c2 = Comparable.class; //接口
Class c3 = String[].class; //一维数组
Class c4 = int[][].class; //二维数组
Class c5 = Override.class; //注解
Class c6 = ElementType.class; //美剧
Class c7 = Integer.class; //基本数据类型
Class c8 = void.class; //void
Class c9 = Class.class; //class
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c3);
System.out.println(c4);
System.out.println(c5);
System.out.println(c6);
System.out.println(c7);
System.out.println(c8);
System.out.println(c9);
//只要元素类型与维度一样,就是同一个Class
int[] a = new int[10];
int[] b = new int[100];
System.out.println(a.getClass().hashCode());
System.out.println(b.getClass().hashCode());
}
}
3.我的思考与实现demo
不知道你看到这里对反射与注解有没有更新的思考,这里我分享一下我的感悟(都在代码里)
思考demo1
1.定义属于我们自己的注解
可以看到这里我自定义了 一个类名注解 和 一个属性注解
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//类名注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface TableDoris {
String value();//值
}
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//属性注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface FiledDoris {
//在该interface当中所定义的所有属性,都是该注解所携带的属性
//形式为 @FiledDoris(columnName = "", type = "", length = )
String columnName();//列表
String type();//类型
int length();//长度
}
2.定义实体类 在实体类上使用我们所定义的注解
类名注解 我们就用在类名上,属性注解,我们就用于属性上
package com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
//通过查看注解 @TableDoris 发现该注解中只有一个属性为value的值
//我们这里传入的“db_student” 就是传递给该值得
//因为只有一个value 所以不需要使用 value = "db_student"
@TableDoris("db_student")
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
class Student2 {
@FiledDoris(columnName = "db_id", type = "int", length = 10)
private int id;
@FiledDoris(columnName = "db_age", type = "int", length = 3)
private int age;
@FiledDoris(columnName = "db_name", type = "varchar", length = 200)
private String name;
}
3.编写测试类
package com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
//练习反射操作注解
//我们想要的是 通过注解的反射来 拿到注解的值
public class Demo14_ORM {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
//使用 forName 获取反射
Class c1 = Class.forName("com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection.Student2");
System.out.println(c1 + "获取的反射");
//通过反射获取注解
Annotation[] annotations = c1.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation + "获取的注解值");
}
//获得注解value
TableDoris tableDoris = (TableDoris) c1.getAnnotation(TableDoris.class);
String value = tableDoris.value();
System.out.println(value);
//获得类指定的注解
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
FiledDoris annotation = name.getAnnotation(FiledDoris.class);
System.out.println(annotation.columnName());
System.out.println(annotation.type());
System.out.println(annotation.length());
System.out.println("===========================");
//根据 类名.class 获得来进行反射
Class<Student2> c2 = Student2.class;
//根据反射来获取注解
Annotation[] c2Annotations = c2.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotationc2:c2Annotations) {
System.out.println(annotationc2);
}
//使用具体的注解名称,来获取注解反射到的类()
TableDoris tableDorisc2 = c2.getAnnotation(TableDoris.class);
String valuec2 = tableDorisc2.value();
System.out.println(valuec2);
//获取反射类中的指点字段
Field age = c1.getDeclaredField("age");
FiledDoris annotationc2 = age.getAnnotation(FiledDoris.class);
System.out.println(annotationc2.columnName());
System.out.println(annotationc2.type());
System.out.println(annotationc2.length());
}
}
测试结果:可以看到我们通过,反射与注解的使用拿到了定义在注解上的值
com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection.Demo14_ORM
class com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection.Student2获取的反射
@com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection.TableDoris(value=db_student)获取的注解值
db_student
db_name
varchar
200
===========================
@com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection.TableDoris(value=db_student)
db_student
db_age
int
3
Process finished with exit code 0
思考实现通过自定义注解实现字典项的转换
1.老规矩先定义属于我们自己的注解
这里我们自定义一个字典项注解 、一个字典项类型注解
package com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//字典类型注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Dict {
//字典类型值
String value();
}
package com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//字典项注解
@Component
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Iswhl {
String name();//名称
int sort();//排序
String readConverterExp();//具体字典值
}
2.编写实体类,在实体类中使用我们自己的注解
package com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
//使用自定义注解
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class MyDict {
@Dict("d_field01")
@Iswhl(name = "field_01",sort = 1,readConverterExp = "0=是,1=否")
private String field01;
@Dict("d_field02")
@Iswhl(name = "field_02",sort = 2,readConverterExp = "0=是,1=否")
private String field02;
@Dict("d_field03")
@Iswhl(name = "field_03",sort = 3,readConverterExp = "0=是,1=否")
private String field03;
}
3.编写测试类
package com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class<MyDict> aClass = MyDict.class;
Annotation[] annotations = aClass.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation ano:
annotations) {
System.out.println(ano);
}
//获取全部的field 这里拿到是Dict 中配置的value值
Field[] fields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
for (Field field:
fields) {
System.out.println(field);
Dict dict = field.getAnnotation(Dict.class);
Iswhl iswhl = field.getAnnotation(Iswhl.class);
System.out.println(dict.value());
String[] splits = iswhl.readConverterExp().split(",");
for (String str:
splits) {
String[] split = str.split("=");
map.put(split[0],split[1]);
}
}
for (Map.Entry<String, String> s:
map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(s.getKey() +":"+ s.getValue());
}
//我们来测试一下我们所写的字典项转换注释
MyDict myDict = new MyDict("0","1","0");
// myDict是目标对象
try{
//通过getDeclaredFields()方法获取对象类中的所有属性(含私有)
Field[] field = myDict.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : field) {
//设置允许通过反射访问私有变量
f.setAccessible(true);
//获取字段的值
String value = f.get(myDict).toString();
//获取字段属性名称
String name = f.getName();
System.out.println("原始字典项:"+name+":"+value);
//其他自定义操作
for (Map.Entry<String, String> s:
map.entrySet()) {
if (value.equals(s.getKey())){
value = s.getValue();
}
}
System.out.println("字典转换后的字典项为:"+name+":"+value);
}
}
catch (Exception ex){
//处理异常
}
System.out.println(stringBuffer.toString());
}
}
运行结果:
private java.lang.String com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection.MyDict.field01
d_field01
private java.lang.String com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection.MyDict.field02
d_field02
private java.lang.String com.iswhl.AnnotationAndReflection.MyDict.field03
d_field03
0:是
1:否
原始字典项:field01:0
字典转换后的字典项为:field01:是
原始字典项:field02:1
字典转换后的字典项为:field02:否
原始字典项:field03:0
字典转换后的字典项为:field03:是