Linux信号sigaction / signal
Linux信号sigaction / signal
文章目录
- Linux信号sigaction / signal
-
- 目的
- 函数原型
- struct sigaction
- 信号枚举值
-
- ISO C99 signals.
- Historical signals specified by POSIX.
- New(er) POSIX signals (1003.1-2008, 1003.1-2013).
- Nonstandard signals found in all modern POSIX systems(including both BSD and Linux).
- 测试
-
- 1 处理信号后重启系统调用
- 2 处理信号后不重启系统调用
- 3 使用 sigaction 函数为 SIGUSR1 和 SIGUSR2 信号注册处理函数
- 实际代码框架
-
- 1. signal
- 2 将程序放入线程中
- 终端间通过kill发送信号
- Reference
目的
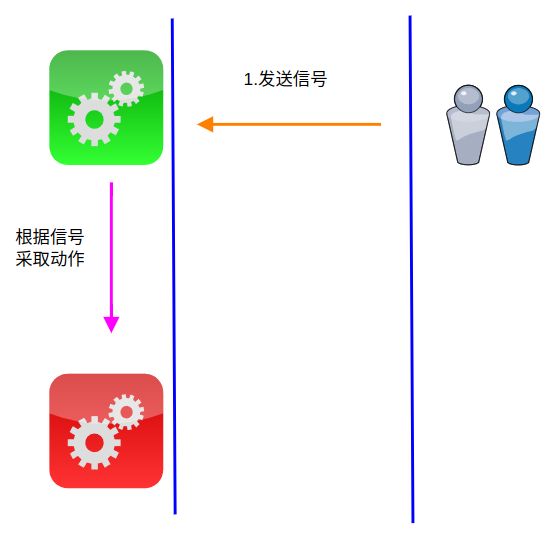
我们可以通过sigaction函数或者signal指定某种特定信号,在程序执行过程中,通过发送信号,达到改变程序运行状态的目的,比如让程序停止等。
函数原型
获取或者设定与指定信号相关联的处理动作。
/* Get and/or set the action for signal SIG. */
extern int sigaction (int __sig, const struct sigaction *__restrict __act,
struct sigaction *__restrict __oact) __THROW;
extern __sighandler_t signal (int __sig, __sighandler_t __handler)
__THROW;
sigaction函数执行信号处理程序时,会把当前信号加入到进程的信号屏蔽字中,从而防止在进行信号处理期间信号丢失。
对signal(),Linux默认会自动重启动被中断的系统调用;
而对于 sigaction(),Linux默认并不会自动重启动,所以如果希望执行信号处理后自动重启动先前中断的系统调用,就需要为sa_flags指定 SA_RESTART标志。
struct sigaction
当信号到达时,用于描述采取的动作的结构
/* Structure describing the action to be taken when a signal arrives. */
struct sigaction
{
/* Signal handler. */
#if defined __USE_POSIX199309 || defined __USE_XOPEN_EXTENDED
union
{
/* Used if SA_SIGINFO is not set. */
__sighandler_t sa_handler;
/* Used if SA_SIGINFO is set. */
void (*sa_sigaction) (int, siginfo_t *, void *);
}
__sigaction_handler;
# define sa_handler __sigaction_handler.sa_handler
# define sa_sigaction __sigaction_handler.sa_sigaction
#else
__sighandler_t sa_handler;
#endif
/* Additional set of signals to be blocked. */
__sigset_t sa_mask;
/* Special flags. */
int sa_flags;
/* Restore handler. */
void (*sa_restorer) (void);
};
- sa_handler 和signal()的参数__handler相同,代表新的信号处理函数
- sa_mask 表示处理信号时,需要阻止的信号集
- sa_flags 处理信号时的标志位
- SA_RESETHAND:在调用处理函数前,将信号的处理函数重置为缺省值(即SIG_IGN)
- SA_RESTART:执行信号处理后,自动重启先前中断的系统调用
- SA_NODEFER :一般情况下, 当信号处理函数运行时,内核将阻塞该给定信号。但是如果设置了 SA_NODEFER标记, 那么在该信号处理函数运行时,内核将不会阻塞该信号
- SA_ONSTACK:使用由sigaltstack()安装的备选栈
- SA_SIGINFO:调用信号处理程序时携带了额外参数(提供了关于信号的深入信息)
信号枚举值
ISO C99 signals.
| 符号 | 数值 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| SIGINT | 2 | Interactive attention signal. |
| SIGILL | 4 | Illegal instruction. |
| SIGABRT | 6 | Abnormal termination. |
| SIGFPE | 8 | Erroneous arithmetic operation. |
| SIGSEGV | 11 | Invalid access to storage. |
| SIGTERM | 15 | Termination request. |
Historical signals specified by POSIX.
| 符号 | 数值 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| SIGHUP | 1 | Hangup. |
| SIGQUIT | 3 | Quit. |
| SIGTRAP | 5 | Trace/breakpoint trap. |
| SIGKILL | 9 | Killed. |
| SIGBUS | 10 | Bus error. |
| SIGSYS | 12 | Bad system call. |
| SIGPIPE | 13 | Broken pipe. |
| SIGALRM | 14 | Alarm clock. |
New(er) POSIX signals (1003.1-2008, 1003.1-2013).
| 符号 | 数值 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| SIGURG | 16 | Urgent data is available at a socket. |
| SIGSTOP | 17 | Stop, unblockable. |
| SIGTSTP | 18 | Keyboard stop. |
| SIGCONT | 19 | Continue. |
| SIGCHLD | 20 | Child terminated or stopped. |
| SIGTTIN | 21 | Background read from control terminal. |
| SIGTTOU | 22 | Background write to control terminal. |
| SIGPOLL | 23 | Pollable event occurred (System V). |
| SIGXCPU | 24 | CPU time limit exceeded. |
| SIGXFSZ | 25 | File size limit exceeded. |
| SIGVTALRM | 26 | Virtual timer expired. |
| SIGPROF | 27 | Profiling timer expired. |
| SIGUSR1 | 30 | User-defined signal 1. |
| SIGUSR2 | 31 | User-defined signal 2. |
Nonstandard signals found in all modern POSIX systems(including both BSD and Linux).
| 符号 | 数值 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| SIGWINCH | 28 | Window size change (4.3 BSD, Sun). |
测试
1 处理信号后重启系统调用
#include 当按下 CTRL + c时,会一直打印。
$ ./main
^CSIGINT recived
^CSIGINT recived
^CSIGINT recived
2 处理信号后不重启系统调用
#include 程序起来后,控制台输入CTRL + c,能够接收到信号。再次输入时,程序退出。
(base) qiancj@qiancj-Dell-G15-5510:~/codes/test/build$ ./main
sleeping 0
sleeping 1
^CI got signal 2
i = 0
i = 1
i = 2
i = 3
i = 4
sleeping 2
^C
(base) qiancj@qiancj-Dell-G15-5510:~/codes/test/build$
3 使用 sigaction 函数为 SIGUSR1 和 SIGUSR2 信号注册处理函数
#include 当一个终端启动程序,获取当前PID号(13770),另一个终端输入kill -USR1 32230或者kill -USR2 32230,第一个终端就会收到中断信号
(base) qiancj@qiancj-Dell-G15-5510:~/codes/test/build$ ./main
My PID is 32230n
SIGUSR1 received
read is interrupted by signal
SIGUSR2 received
read is interrupted by signal
实际代码框架
当程序需要一直运行时,需要人为中断停止时,可以使用信号函数,具体框架可以设置为以下2种:
1. signal
#include 2 将程序放入线程中
#include 终端间通过kill发送信号
(base) qiancj@qiancj-Dell-G15-5510:~$ kill --help
kill: kill [-s sigspec | -n signum | -sigspec] pid | jobspec ... or kill -l [sigspec]
Send a signal to a job.
Send the processes identified by PID or JOBSPEC the signal named by
SIGSPEC or SIGNUM. If neither SIGSPEC nor SIGNUM is present, then
SIGTERM is assumed.
Options:
-s sig SIG is a signal name
-n sig SIG is a signal number
-l list the signal names; if arguments follow `-l' they are
assumed to be signal numbers for which names should be listed
-L synonym for -l
Kill is a shell builtin for two reasons: it allows job IDs to be used
instead of process IDs, and allows processes to be killed if the limit
on processes that you can create is reached.
Exit Status:
Returns success unless an invalid option is given or an error occurs.
信号种类
(base) qiancj@qiancj-Dell-G15-5510:~$ kill -l
1) SIGHUP 2) SIGINT 3) SIGQUIT 4) SIGILL 5) SIGTRAP
6) SIGABRT 7) SIGBUS 8) SIGFPE 9) SIGKILL 10) SIGUSR1
11) SIGSEGV 12) SIGUSR2 13) SIGPIPE 14) SIGALRM 15) SIGTERM
16) SIGSTKFLT 17) SIGCHLD 18) SIGCONT 19) SIGSTOP 20) SIGTSTP
21) SIGTTIN 22) SIGTTOU 23) SIGURG 24) SIGXCPU 25) SIGXFSZ
26) SIGVTALRM 27) SIGPROF 28) SIGWINCH 29) SIGIO 30) SIGPWR
31) SIGSYS 34) SIGRTMIN 35) SIGRTMIN+1 36) SIGRTMIN+2 37) SIGRTMIN+3
38) SIGRTMIN+4 39) SIGRTMIN+5 40) SIGRTMIN+6 41) SIGRTMIN+7 42) SIGRTMIN+8
43) SIGRTMIN+9 44) SIGRTMIN+10 45) SIGRTMIN+11 46) SIGRTMIN+12 47) SIGRTMIN+13
48) SIGRTMIN+14 49) SIGRTMIN+15 50) SIGRTMAX-14 51) SIGRTMAX-13 52) SIGRTMAX-12
53) SIGRTMAX-11 54) SIGRTMAX-10 55) SIGRTMAX-9 56) SIGRTMAX-8 57) SIGRTMAX-7
58) SIGRTMAX-6 59) SIGRTMAX-5 60) SIGRTMAX-4 61) SIGRTMAX-3 62) SIGRTMAX-2
63) SIGRTMAX-1 64) SIGRTMAX
Reference
- linux中sigaction函数详解
- sigaction详细解析