最新剑指offer刷题笔记js(含新旧俩版所有题)
目录
一、面试需要的知识()
二、高质量代码
三、解决面试题的思路
四、优化时间和空间效率
五、面试中的各项能力
一、面试需要的知识
数据结构、算法(查找、排序、递归、循环和位运算)
1.求平方根
思路:x的平方根肯定是1~x之间的数,可用二分法在此区间取值mid,若中间值的平方大于x,则右端替换为mid减一,否则左端替换为mid+1。
时间复杂度O(logn)、空间复杂度O(1)
function sqrt(x) {
if (x <= 0) return 0
let left = 1,
right = x
while (true) {
let mid = (left + right) >> 1 // 位运算比除法快
if (mid <= x / mid && (mid + 1) > x / (mid + 1)) return mid // mid*mid可能溢出,所以用除法
else if (x / mid < mid) right = mid - 1
else
left = mid + 1
}
}2.二维数组中的查找
思路:由于Array[m][n]的元素无论横向还是纵向都是增大的,可从左下角开始查找,如果大于target则可以像上搜索,若小则向右;同理从右上角开始也可。
时间复杂度O(n+m);空间复杂度O(1)
function Find(target, array) {
let find = false,
i = array.length - 1,
j = 0
while (i >= 0 && j < array[0].length) {
if (array[i][j] === target)
return true
else if (array[i][j] < target)
j++
else
i--
}
return find
}3.替换空格
思路:初始化新字符串为空,遍历原字符串,若碰到空格则做替换,依次添加到新字符串。
时间、空间复杂度均O(n)
var replaceSpace = function(s) {
let r = ''
for (let i = 0 i < s.length i++) {
if (s[i] === ' ') {
r = r + '%20'
continue
}
r = r + s[i]
}
return r
}4.从尾到头打印链表
思路:将原链表从头到尾依次,从头插入新数组。
时间、空间复杂度均O(n)
var reversePrint = function(head) {
let ans = []
while (head) {
ans.unshift(head.val)
head = head.next
}
return ans
}5.重建二叉树
思路:分治法递归实现;前序遍历序列的首元素为树根,由根元素在中序遍历序列中找到其位置,往左为左子树,往右为右子树;需确认左、右子树的元素在前序、中序遍历序列中的位置区域,分别左右递归重建二叉树。
时间、空间复杂度均O(n)
var buildTree = function(preorder, inorder) {
if (preorder.length === 0 || inorder.length === 0) return null;
const rootnode = preorder[0]
const index = inorder.indexOf(rootnode)
const leftpre = preorder.slice(1, index + 1);
const leftin = inorder.slice(0, index);
const rightpre = preorder.slice(index + 1);
const rightin = inorder.slice(index + 1);
const root = new TreeNode(rootnode)
root.left = buildTree(leftpre, leftin)
root.right = buildTree(rightpre, rightin)
return root
}6.用两个栈实现队列
思路:初始化俩个数组,一个负责进,一个负责出。只有当删除栈为空时才能把插入栈的元素全部转移后再出,方可。
时间、空间复杂度均O(n)
var CQueue = function() {
// 插入栈
this.s1 = []
// 删除栈
this.s2 = []
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {void}
*/
CQueue.prototype.appendTail = function(value) {
//进队
this.s1.push(value)
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
CQueue.prototype.deleteHead = function() {
// 两个栈都没元素,返回 -1
if (!this.s1.length && !this.s2.length) return -1
// 删除栈没元素,从插入栈拿
if (!this.s2.length) {
while (this.s1.length) this.s2.push(this.s1.pop())
}
// 出队
return this.s2.pop()
}7.旋转数组的最小数字
思路:二分法;旋转数组有部分升序的特点,取中间元素与右端值有三种情况:若小于,说明最小值再右侧,则舍弃右端;若大于,则舍去左端;若等说明右端子数组值全相同,则左移(中间值随即左移)。
平均时间复杂度为 O(logn)、空间复杂度O(1)
var minArray = function(numbers) {
let left = 0,
right = numbers.length - 1
while (left < right) {
let mid = (left + right) >> 1
if (numbers[mid] < numbers[right])
right = mid
else if (numbers[mid] > numbers[right])
left = mid + 1
else
right -= 1
}
return numbers[left]
}8.斐波那契数列
思路:滚动窗口;
时间复杂度O(n)、空间复杂度:O(1)
var fib = function(n) {
if (n < 2) return n
let mod = 1e9 + 7
let a = 0,
b = 1,
c = 0
for (let i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
c = a + b
a = b
b = c
b %= mod //防止大数溢出
}
return b
}9.二进制中1的个数
思路:位运算;把一个数减一,再和原来整数做与运算,会把原来的数最右边的一个1变成0。有多少个1即可运算多少次,从而求解。
时间复杂度O(logn)、空间复杂度:O(1)
var hammingWeight = function(n) {
let count = 0
while (n) {
++count
n = (n - 1) & n
}
return count
}10.数值的整数次方
思路:二分法;当n为偶,一个数的n次方等于其n/2次方的平方,若为奇则多乘一次本身;若n为负,则要取倒数。
时间复杂度O(logn)、空间复杂度:O(1)
var myPow = function(x, n) {
if (n === 0) return 1
if (n === -1) return 1 / x
let res = myPow(x, n >> 1)
res *= res
if (n & 1 === 1)
res *= x
return res
}二、高质量代码
代码规范性(命名和布局)、代码完整性(功能测试、边界测试、非法输入测试)
11.打印从1到最大的n位数
思路:考虑大数问题用字符串解决,求得最大值(字符串),再将其转换为数(上界)遍历求解。
时间复杂度O(10^n)、空间复杂度:O(1)
var printNumbers = function(n) {
let res = [],
max = ''
while (n--)
max += '9'
for (let i = 1, m = max - 0; i <= m; i++)
res.push(i)
return res
}12.删除链表的节点
思路:遍历列表,若头节点为要删的,则返回其next;否则遍历链表,若找到则跳过该节点,完成删除。
时间复杂度O(n)、空间复杂度:O(1)
function deleteNode(head, val) {
if (head.val == val) return head.next
let cur = head
while (cur.next) {
if (cur.next.val == val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next
return head
}
cur = cur.next
}
return head
}
//递归
var deleteNode = function(head, val) {
if (head.val == val)
return head.next
/*
* 假设【1,2,3】,目标值是2
* 当前head是1.
* 本来head.next是2,但是调用deletenode函数的时候刚刚好2==2,把2(head)的下一个值3的指针返回
* 所以head.next = 3
* 1->3
*/
head.next = deleteNode(head.next, val)
return head
}13.单词长度的最大乘积
思路:暴力法,双重循环遍历比较。( m 是数组 words 中的单词平均长度,n 是数组 words 的长度)
时间复杂度O(m*n^2)、空间复杂度:O(1)
优化:哈希表空间换时间
时间复杂度O(m+n^2)、空间复杂度:O(n)
// 暴力
var maxProduct = function(words) {
let res = 0
for (let i = 0; i < words.length; i++)
for (let j = i + 1; j < words.length; j++)
if (!isSame(words[i], words[j]))
res = Math.max(res, words[i].length * words[j].length)
return res
}
function isSame(str1, str2) {
for (let i = 0; i < str1.length; i++)
if (str2.includes(str1[i])) return true
}
// 哈希
var maxProduct = function(words) {
let n = words.length
const hash = Array(n).fill(0)
for(let i=0; i14.调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
思路:双指针一个找奇一个找偶数,找到后便交换。
时间复杂度O(n)、空间复杂度:O(1)
//前后指针
var exchange = function(nums) {
let i = 0,
j = nums.length - 1,
tmp
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && nums[i] % 2 == 1) i++
while (i < j && nums[i] % 2 == 0) j--
tmp = nums[i]
nums[i] = nums[j]
nums[j] = tmp
}
return nums
}
//快慢指针
var exchange = function(nums) {
let low = 0,
fast = 0 //搜索奇数
while (fast < nums.length) {
if (nums[fast] & 1) {
[nums[low], nums[fast]] = [nums[fast], nums[low]]
low++ //指向偶数
}
fast++
}
return nums
}15.链表中倒数第k个节点
思路:将第一个指针指向链表的第 k+1 个节点,第二个指针指向链表的第一个节点,此时指针之间刚好间隔 k 个节点。两个指针同步向后走,当第一个指针走到链表的尾部空节点时,则此时第二个指针刚好指向链表的倒数第k个节点。
时间复杂度O(n)、空间复杂度:O(1)
//双指针 推荐该法
var getKthFromEnd = function(head, k) {
let p1 = head,
p2 = head
while (p1 && k) {
k--
p1 = p1.next
}
while (p1) {
p1 = p1.next
p2 = p2.next
}
return p2
}
//第一遍求表长,第二遍找倒数k
var getKthFromEnd = function(head, k) {
let node = head,
n = 0
while (node) {
node = node.next
n++
}
node = head
for (let i = 0; i < n - k; i++)
node = node.next
return node
}16.反转链表
思路:三指针; 时间复杂度O(n)、空间复杂度:O(1)
递归; 时间复杂度O(n)、空间复杂度:O(n)
//三指针
var reverseList = function(head) {
let pre = null,
cur = head
while (cur) {
const next = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = next
}
return pre
}
//递归
var reverseList = function(head) {
return reverse(head, null)
}
function reverse(cur, pre) {
if (cur == null) return pre
let res = reverse(cur.next, cur)
cur.next = pre
return res
}17.合并两个排序的链表
思路:建一个空链表,当俩链表不为空时,比较俩链表节点值,将小的连接到新链表尾;当有一个链表为空时,将另一链表连接上。
时间复杂度O(m+n),m与n为俩链表长度、空间复杂度:O(1)
//循环
var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
const res = new ListNode()
let h = res
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
h.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
} else {
h.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
}
h = h.next
}
h.next = l1 ? l1 : l2
return res.next
}
//递归
var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
if (!l1 || !l2) return l1 || l2
let h = null
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
h = l1
h.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2)
} else {
h = l2
h.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next)
}
return h
}18.树的子结构
思路:前序遍历。当A或B树为空时无子结构,否则判断A树当前节点、左右孩子的子树中是否包含B树;要判断A树某节点的子树是否包含B树,需当前节点值相等且左右节点值均相等。(若B节点为空说明B数已越过叶子节点完成匹配,若A节点为空说明已经越过叶子节点没有找到,或节点A与B的值不相同,即匹配失败。)
时间复杂度O(mn),m与n为树A和B节点数量、空间复杂度:O(m)
var isSubStructure = function(A, B) {
if (!A || !B) return false
return (have(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B) || isSubStructure(A.right, B))
}
function have(A, B) {
if (B == null) return true
if (A == null || A.val != B.val) return false
return have(A.left, B.left) && have(A.right, B.right)
}三、解决面试题的思路
画图分析、举例分析和化繁为简(分步解决(每步一个函数)、分治法)
19.二叉树的镜像
思路:遍历每个节点,若该节点有子节点,就交换,直到交换完所有非叶节点。
时间复杂度O(n)、空间复杂度:O(n)
//前序
var mirrorTree = function(root) {
if (root == null) return null
let t = root.left
root.left = root.right
root.right = t
mirrorTree(root.left)
mirrorTree(root.right)
return root
}
//后序
var mirrorTree = function(root) {
if (root === null) {
return null
}
const left = mirrorTree(root.left)
const right = mirrorTree(root.right)
root.left = right
root.right = left
return root
}20.顺时针打印矩阵
思路:顺时针由外到内遍历矩阵每一圈,将结果压入结果数组:左上角(left,top)开始,从左往右到右上角;从上往下到右下角(right,bottom);当矩阵不只一列一行时,方可从右往左到左下角;从下往上到左上角;每遍历完一圈就缩小范围
时间复杂度O(mn)、空间复杂度:O(1)
var spiralOrder = function(matrix) {
if (!matrix.length || !matrix[0].length) {
return []
}
let row = matrix.length,
col = matrix[0].length
let top = 0,
left = 0,
bottom = row - 1,
right = col - 1
let res = []
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) {
for (let i = left; i <= right; i++)
res.push(matrix[top][i])
for (let j = top + 1; j <= bottom; j++)
res.push(matrix[j][right])
if (top < bottom && left < right) {
for (let i = right - 1; i >= left; i--)
res.push(matrix[bottom][i])
for (let j = bottom - 1; j > top; j--)
res.push(matrix[j][left])
}
[top, right, bottom, left] = [top + 1, right - 1, bottom - 1, left + 1]
}
return res
}21.包含min函数的栈
思路:初始化两个栈,数据栈正常执行,最小栈专门返回最小值。需注意维护最小栈:
入栈时,如果最小栈为空,或者新元素小于或等于最小栈栈顶,则将新元素压入最小栈;
出栈时,如果出栈元素和最小栈栈顶元素值相等,最小栈出栈(若不出栈,则到时返回最小值时,其元素早已出栈了,则出现错误)
时间复杂度O(1)、空间复杂度:O(n)
/**
* initialize your data structure here.
*/
var MinStack = function() {
this.data_stack = []
this.min_stack = []
}
/**
* @param {number} val
* @return {void}
*/
MinStack.prototype.push = function(val) {
this.data_stack.push(val)
// 如果最小栈为空,或者新元素小于或等于最小栈栈顶,则将新元素压入最小栈
if (!this.min_stack.length ||
val <= this.min_stack[this.min_stack.length - 1])
this.min_stack.push(val)
}
/**
* @return {void}
*/
MinStack.prototype.pop = function() {
// 如果出栈元素和最小栈栈顶元素值相等,最小栈出栈
if (this.data_stack[this.data_stack.length - 1] == this.min_stack[this.min_stack.length - 1) this.min_stack.pop() return this.data_stack.pop()
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MinStack.prototype.top = function() {
return this.data_stack[this.data_stack.length - 1]
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MinStack.prototype.min = function() {
return this.min_stack[this.min_stack.length - 1]
}22.栈的压入、弹出序列
思路:借用一个辅助栈 stack模拟进出栈,若能模拟正常模拟则可。按照入栈序列依次 stack压栈,在遇到 “stack栈顶元素 == 弹出序列的当前元素(需记录当前索引)” 就立即执行出栈,若最后栈空则模拟成功;否则,stack全部入栈完成后,有元素无法出栈说明出栈序列不对。
时间复杂度O(n)、空间复杂度:O(n)
var validateStackSequences = function(pushed, popped) {
const stack = []
let index = 0
for (let x of pushed) {
stack.push(x)
while (stack.length && stack[stack.length - 1] == popped[index]) {
stack.pop()
index++
}
}
return stack.length == 0
}23.从上到下打印二叉树
思路:bfs,初始化包含树根节点的队列,当该队列不为空时循环,将队列中节点出队并保存节点值;依次对其左右节点递归。
时间复杂度、空间复杂度均O(n)
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if (!root) return []
const queue = [root],
res = []
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift()
res.push(node.val)
if (node.left) queue.push(node.left)
node.right && queue.push(node.right)
}
return res
}24.二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
思路1:二叉搜索树的特点是左子树的值均比根节点值小,右子树相反;由后续遍历可得根节点,并且划分左右子树;用根节点的值分别与左右子树递归比较即可。
时间复杂度O(n^2):每次调用递归函数减少一个根节点占用O(n),并且最差情况退化为链表,每轮递归需遍历所有节点占用O(n)、空间复杂度O(n)
思路2:倒序遍历 该后序遍历序列(根右左),二叉搜索树某节点中若出现递减,则该节点右边的值必须全小于根节点,否则不是二叉搜索树。
时间、空间复杂度均O(n)
//分治递归
var verifyPostorder = function(postorder) {
if (postorder.length < 2) return true
const val = postorder[postorder.length - 1],
index = postorder.findIndex((n => n > val))
const arr1 = postorder.slice(0, index)
const arr2 = postorder.slice(index, postorder.length - 1)
return (arr1.every(n => n < val) && arr2.every(n => n > val)) &&
verifyPostorder(arr1) &&
verifyPostorder(arr2)
}
//单调栈
var verifyPostorder = function(postorder) {
let stack = [],
root = Number.MAX_VALUE
for (let i = postorder.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (postorder[i] > root) return false
//while循环找逆序节点
while (stack.length > 0 && postorder[i] < stack[stack.length - 1])
root = stack.pop()
stack.push(postorder[i])
}
return true
}25.二叉树中和为某一值的路径
思路:dfs深度优先(先序)遍历,逐个考虑每个节点的值并把满足条件的入栈,边界为到达叶子节点且路径和为目标值,此时便把将路径保存;继续递归其左右节点,若遇到不满足的节点则出栈(回溯)。
时间复杂度O(n^2)、空间复杂度O(n)
// 手动回溯
var pathSum = function(root, target) {
let res = []
function pathTree(root, target, path) {
if (!root) {
return
}
if (!root.left && !root.right && target == root.val) {
path.push(root.val)
res.push(path.slice())
}
path.push(root.val)
pathTree(root.left, target - root.val, path.slice())
pathTree(root.right, target - root.val, path.slice())
path.pop()
}
pathTree(root, target, [])
return res
}
//自动回溯
var pathSum = function(root, target) {
if (root === null) return []
const res = []
const pathTree = (root, target, path) => {
// 到了叶子节点并且当前节点的值跟剩余sum相等,则推入结果集中
if (root.val === target && !root.left && !root.right) {
res.push(path)
}
// 路径中加入当前节点的值
path.push(root.val)
// 递归的去左右子树当中查找路径
if (root.left) pathTree(root.left, target - root.val, path.slice())
if (root.right) pathTree(root.right, target - root.val, path.slice())
}
pathTree(root, target, [])
return res
}26.复杂链表的复制
思路:在原链表每个结点后面新建一个一模一样的结点,然后拆分链表。
第一次遍历原链表时,在每个结点后新建值相同的结点及next,形式如:1->1'->2->2';
第二次遍历原链表时,修改每个新结点的random指向;
第三次遍历原链表时,把新结点逐个拆下构成新链表,并恢复原链表。
时间复杂度O(n)、空间复杂度O(1)
var copyRandomList = function(head) {
if (head === null) {
return null
}
for (let node = head; node !== null; node = node.next.next) {
const nodeNew = new Node(node.val, node.next, null)
node.next = nodeNew
}
for (let node = head; node !== null; node = node.next.next) {
const nodeNew = node.next
nodeNew.random = (node.random !== null) ? node.random.next : null
}
const headNew = head.next
for (let node = head; node !== null; node = node.next) {
const nodeNew = node.next
node.next = node.next.next
nodeNew.next = (nodeNew.next !== null) ? nodeNew.next.next : null
}
return headNew
}27.二叉搜索树与双向链表
思路:中序遍历二叉搜索树可得有序序列,遍历各节点添加前后指针。
时间复杂度O(n)、空间复杂度O(1)
var treeToDoublyList = function(root) {
if (!root) return
let head = null
let preNode = head
const inOrder = (node) => {
if (!node) return //越过了叶子节点 直接返回
inOrder(node.left)
if (!preNode) {
// 遍历到最左边节点,preNode为空,此时节点就是双向链表的head
head = node
} else
// 修改双向节点引用 以下俩句不能调换顺序
preNode.right = node
node.left = preNode
// 进入下一轮之前把上一个节点的指针指向当前节点
preNode = node
inOrder(node.right)
}
inOrder(root)
// 完成中序遍历后,pre指向了最后一个节点,head指向头节点,
head.left = preNode
preNode.right = head
return head
}28.字符串的排列
思路:递归出口:当前字符串长度小于等于1;
当前递归要做的事:依次去掉字符串一个字符,得到剩余字符串的全排列,将去掉的字符与剩余字符串的全排列拼接;
返回上一级的内容:将拼接的所有字符放入数组,并去重,返回这个数组给上一级。
时间复杂度:O(n×n!)、空间复杂度O(1)
const permutation = s => {
if (s.length === 0) return ['']
if (s.length === 1) return [s]
const res = []
const len = s.length
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 取出一个字符为char
const char = s[i]
// newStr=去掉char后剩下的字符
let newStr = s.slice(0, i) + s.slice(i + 1)
// 递归产生newStr的全排列
const next = permutation(newStr)
// 将char与newStr的全排列拼接,放入res
next.forEach(item => {
res.push(char + item)
})
}
// 去重
return [...new Set(res)]
}四、优化时间和空间效率
必要时考虑“以空间换时间”
29.数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
排序法思路:超过一半的数字在排序后必定在中间
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)空间复杂度O(logn)
投票法思路:把众数(出现次数超过一半的数字)记为 +1,把其他数记为 −1,将它们全部加起来,显然和大于 0。
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(1)
//排序法
var majorityElement = function(nums) {
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b)
return nums[Math.floor(nums.length / 2)]
}
//投票法
var majorityElement = function(nums) {
let vote = 0,
selectNum = 0
for (const item of nums) {
if (vote === 0) {
selectNum = item
}
vote += item === selectNum ? 1 : -1
}
return selectNum
}30.最小的k个数
①排序法思路:升序排序后取前K个数
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)空间复杂度O(logn)
②划分法思路:划分之后的index(分隔位置)与k有三种情况 若等于则可返回,若小于则说明第k小的元素在index右边 否则在左边 就继续划分。
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(logn)
//排序法
const getLeastNumbers = (arr, k) => {
arr.sort((a, b) => a - b)
return arr.splice(0, k)
}
//划分法
function partition(arr, l, r) {
let pivot = arr[l] //基准
let index = l
for (let i = l + 1 i <= r i++) {
if (arr[i] > pivot) continue
else{
index++ //小数所在的位置
[arr[i], arr[index]] = [arr[index], arr[i]]
}
}
[arr[l], arr[index]] = [arr[index], arr[l]]
return index
}
var getLeastNumbers = function(arr, k) {
const length = arr.length
if (k >= length) return arr
let left = 0,
right = length - 1
let index = partition(arr, left, right)
while (index !== k) {
if (index < k) {
left = index + 1
index = partition(arr, left, right)
} else if (index > k) {
right = index - 1
index = partition(arr, left, right)
}
}
return arr.slice(0, k)
}31.连续子数组的最大和
思路:动态规划(dp),dp[i] 代表以第 i 个数结尾的「连续子数组的最大和」。对于某一个元素, 如果取:则 dp[i] = dp[i-1] + nums[i];如果不取:则 dp[i] = nums[i](相当于从这个元素作为子区间的新起点,重新算起),所以动态规划转移方程: dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1] + nums[i],nums[i])
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(logn)
//动态规划
var maxSubArray = function(nums) {
let dp = [],
max = dp[0] = nums[0]
for (i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i])
max = Math.max(dp[i], max)
}
return max
}
//贪心
const maxSubArray = nums => {
if (nums.length === 1) return nums[0]
let max = nums[0]
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 如果前一个的累加和小于0,就不要累加了
if (nums[i - 1] > 0) {
nums[i] += nums[i - 1]
}
// 更新max
max = max > nums[i] ? max : nums[i]
}
return max
}32.1~n 整数中 1 出现的次数
思路:把n按其位数,依次分别切分三个部分(左边,当前位和右边),分别计算各部分中含1的次数再累加;计算完分割当前位的情况后,继续往后一位,直至n的位数。
时间复杂度:O(logn)、空间复杂度O(log1)
var countDigitOne = function(n) {
let res = 0,
base = 1 //从个位开始计算
while (base <= n) {
let high = Math.floor(n / base / 10),
cur = Math.floor(n / base % 10),
low = n % base
if (cur > 1) res += (high + 1) * base
else if (cur == 1) res += (high * base + low + 1)
else res += high * base
base *= 10 //依次计算后面各位
}
return res
}
//暴力法:超时
var countDigitOne1 = function(n) {
var num = 0
for (let i = 1 i <= n i++)
while (i) {
if (i % 10 === 1) num++
i = i / 10
}
return num
}33.把数组排成最小的数
思路:排序;
- 若拼接字符串 x + y < y + x ,则 x “小于” y ,意味着x要排在y前面
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)、空间复杂度O(n)
var minNumber = function(nums) {
nums.sort((a, b) => ((a + '' + b) - (b + '' + a)))
return nums.join('')
}
//简写
var minNumber = function(nums) {
return nums.sort((a, b) => `${a}${b}` - `${b}${a}`).join('')
}34.丑数
思路:动态规划
定义数组 dp,其中 dp[i - 1] 表示第 i 个丑数,第 n 个丑数即为 dp[n - 1]
初始值 第 1 个丑数 dp[0] = 1
定义3个指针指向dp下标,p2, p3, p5,表示下一个丑数是当前指针指向的丑数乘以对应的质因数
比较n2,n3,n5,最小值的那个指针+1
最后返回 dp[n - 1]
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(n)
var nthUglyNumber = function(n) {
const dp = [1]
let p2 = 0,
p3 = 0,
p5 = 0
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
let n2 = dp[p2] * 2,
n3 = dp[p3] * 3,
n5 = dp[p5] * 5
dp[i] = Math.min(n2, n3, n5)
dp[i] == n2 && ++p2
dp[i] == n3 && ++p3
dp[i] == n5 && ++p5
}
return dp[n - 1]
}35.第一个只出现一次的字符
思路1:api,第一个只出现一次的字符:第一次出现的位置和最后的位置是否相等
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(1)
思路二:哈希表,第一遍用长度为26的数组保存各字母的出现次数,第二遍检查第一次出现次数为1的字符
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(小写字母字符种类数)
var firstUniqChar = function(s) {
for (let x of s) {
if (s.indexOf(x) === s.lastIndexOf(x)) return x
}
return ' '
}
var firstUniqChar = function(s) {
let count = new Array(26).fill(0)
for (c of s) {
let index = c.charCodeAt() - 97
++count[index]
}
for (c of s) {
let index = c.charCodeAt() - 97
if (count[index] == 1)
return c
}
return ' '
}36.数组中的逆序对
思路:归并排序,记录逆序对。
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)、空间复杂度O(n)
var reversePairs = function(nums) {
function merge_Sort(arr, l, r) {
if (l >= r) return 0
let mid = (l + r) >> 1
let res = merge_Sort(arr, l, mid) + merge_Sort(arr, mid + 1, r)
let i = l,
j = mid + 1
const temp = []
while (i <= mid && j <= r) {
if (arr[i] <= arr[j]) {
temp.push(arr[i])
i++
} else {
temp.push(arr[j])
j++
// 当前i大于j的数字,出现逆序对
res += mid - i + 1
}
}
while (i <= mid) {
temp.push(arr[i])
i++
}
while (j <= r) {
temp.push(arr[j])
j++
}
for (let i = l, j = 0; i <= r; i++, j++)
arr[i] = temp[j]
return res
}
return merge_Sort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1)
}37.两个链表的第一个公共节点
思路:用两个指针 pA,pB 分别指向两个链表 headA,headB 的头结点,然后同时分别逐结点遍历;当 pA 到达链表 headA 的末尾时,重新定位到链表 headB 的头结点;当 pB 到达链表 headB 的末尾时,重新定位到链表 headA 的头结点。这样,当它们相遇时,所指向的结点就是第一个公共结点。
时间复杂度:O(m+n)、空间复杂度O(1)
var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
if (headA === null || headB === null) {
return null
}
let pA = headA,
pB = headB
while (pA !== pB) {
pA = pA !== null ? pA.next : headB
pB = pB !== null ? pB.next : headA
}
return pA
}五、面试中的各项能力
沟通学习、知识迁移(举一反三)、抽象建模(找合适的数据结构)和发散思维
38.编辑距离
思路:动态规划(dp[i][j] 表示以下标i-1为结尾的字符串word1,和以下标j-1为结尾的字符串word2,最近编辑距离为dp[i][j]),俩个单次三种操作方式,本质不同的操作只有三种:A删、B删(即A增)和A替换。分别对应dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + 1、dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] + 1、dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
时间、空间复杂度均为:O(mn)O
const minDistance = (word1, word2) => {
let m = word1.length + 1,
n = word2.length + 1
let dp = Array(m).fill(0).map(() => Array(n).fill(0)) //初始化二维数组
for (let i = 1; i < m; i++) dp[i][0] = i //长度位为i的word1变成长度为0 需要i次(删除)操作
for (let j = 1; j < n; j++) dp[0][j] = j
for (let i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j < n; j++) {
if (word1[i - 1] === word2[j - 1])
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] //不用任何操作
else
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]) + 1
}
}
return dp[m - 1][n - 1]
}39.二叉树的深度
思路:深度遍历,分别统计左右子树的高度取大者;层次遍历,
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(n)
// 深度递归实现
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if (!root) return 0
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1
}
//层次遍历法
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if (!root) return
const queue = []
queue.push(root)
let deep = 0
while (queue.length != 0) { //当队列不为空 开始循环遍历每一层
let size = queue.length //记录当前层的宽度
while (size--) {
let node = queue.shift() // 当前层出队
node.left && queue.push(node.left)
node.right && queue.push(node.right)
}
deep += 1 //每一层 高度加一
}
return deep
}40.只出现一次的数字
思路1:位运算 (此法具有通用性)
a. 对于出现x(=3)次的数字,各二进制位出现的次数和都是 x 的倍数
b. 统计所有数字的各二进制位中 1 的个数,并对x取余,结果为只出现一次的数字
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(1)
思路2:哈希表,统计各数字出现的次数(各数字为index,次数为value),返回次数为一的数字。
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(n)
思路3:参考第一个只出现一次的字符,调用数组api 实现,时间开销大 不推荐
// 位运算
var singleNumber = function(nums) {
let res = 0
// 将所有数字都看成32位
for (let i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
let bit = 0
// 对每一位计算该位上的和 结果为3N或3N+1
for (n of nums)
bit += ((n >> i) & 1)
// 对3取余即为res在该位的值
res += ((bit % 3) << i)
}
return res
}
//哈希表 对象实现
var singleNumber = function(nums) {
let m = {}
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
var key = nums[i]
if (m[key])
m[key] += 1
else
m[key] = 1
}
for (item in m) {
if (m[item] == 1)
return item
}
}
//哈希表 Map实现 api
var singleNumber = function(nums) {
const freq = new Map()
for (const num of nums) {
freq.set(num, (freq.get(num) || 0) + 1)
}
for (const [num, occ] of freq.entries()) {
if (occ === 1)
return num
}
}
// 数组api
var singleNumber = function(nums) {
return nums.filter((item) => nums.indexOf(item) === nums.lastIndexOf(item))[0]
}41.和为s的两个数字 VS 和为s的连续正数序列
思路:双指针分别指向数组的头尾,若小于则头指针向右,若大于则尾指针向前,相等则返回。
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(1)
var twoSum = function(nums, target) {
let i = 0,
j = nums.length - 1
while (i < j) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] < target) i++
else if (nums[i] + nums[j] > target) j--
else
return [nums[i], nums[j]]
}
return []
}思路:求和公式为sum=(首项+尾项)*项数/2,俩指针初始化为最小区间,左指针至多走到target的一半;若和小了,则需要尾指针向右增大区间范围;若和大了,则需要头指针向右减小区间范围;相等时则返回其中一种情况,同时头指针向右寻找其他解。
时间复杂度:O(target)、空间复杂度O(1)
var findContinuousSequence = function(target) {
let [left, right] = [1, 2], mid = target >> 1
let sum = 0
const res = []
while (left <= mid) {
// sum=(首项+尾项)*项数/2
sum = ((left + right) * (right - left + 1)) >> 1
if (sum < target) right++
else if (sum > target) left++
else {
const temp = []
// 将[left,right]中的数都输出
for (let i = left; i <= right; i++) {
temp.push(i)
}
res.push(temp)
left++
}
}
return res
}42.翻转单词顺序 VS 左旋转字符串
思路:去除字符串首尾的空格;维护双指针一个指向单词头,一个指向紧跟单词尾部的空格,将各单词前插入结果数组,最后用空格连接各单词。(数组自身的join()等方法时间复杂度均为O(n) )
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(n)
//手动实现 省空间
var reverseWords = function(s) {
let i = 0,
j = s.length - 1
while (s[i] == ' ') i++
while (s[j] == ' ') j++
s = s.slice(i, j + 1)
i = j = 0
const res = []
while (j < s.length) {
while (j < s.length && s[j] !== ' ') j++
res.unshift(s.slice(i, j))
while (j < s.length && s[j] == ' ') j++
i = j
}
return res.join(' ')
}
//api实现 空间换时间
//split()把字符串分割为字符串数组;trim()去除字符串俩边的字符串;join()以某字符连接字符串
//reverse()反转数组中元素的顺序;filter()过滤数组元素
var reverseWords = function(s) {
if (s == null || !s.length) return s
let arr = s
.split(" ")
.reverse()
.filter((item) => item.trim().length > 0)
return arr.join(" ")
}思路:取前面的字符拼在后面
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(1)
// api实现
var reverseLeftWords = function(s, n) {
return s.slice(n, s.length) + s.slice(0, n)
}
//手动实现
var reverseLeftWords = function(s, n) {
let res = ""
for (let i = n; i < s.length; i++) res += s[i]
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) res += s[i]
return res
}43.n个骰子的点数
思路:动态规划,结果为5n+1个概率值,n=1的结果显然,每次加骰子的结果只与上一次的结果有关且每次增加5个概率值(数组下标+k即可),增加的骰子出现点数的情况有6种,则需要累加并取平均。
时间复杂度:OO(n^2)、空间复杂度O(n)
var dicesProbability = function(n) {
let dp = Array(6).fill(1 / 6)
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
let tmp = Array(5 * i + 1).fill(0)
for (let j = 0; j < dp.length; j++)
for (let k = 0; k < 6; k++)
tmp[j + k] += dp[j] / 6
dp = tmp
}
return dp
}44.扑克牌中的顺子
思路:升序排列数组,统计0的个数,若最大数减除0后面数小于5,说明符合连续;若出现“对子”说明不符合。
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)(n=5)==>O(1) 、空间复杂度O(1)
var isStraight = function(nums) {
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b)
let joker = 0
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++)
if (nums[i] == 0) joker++ //先判断0,后面非0的不能出现相等
else if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) return false
return nums[4] - nums[joker] < 5
}45.圆圈中最后剩下的数字
思路:数学推导(动态转移方程):[n,m] 问题中设m%n=t,第一轮从0开始,因此要删除的数是(m-1)%n;即t-1,且下一轮 [n-1,m] 从t开始。删除第一个数后剩下[0,1,...m-2,m,...n-2] 对应[t,t+1,...n-1,0,...t-2 ],映射关系为 p(x)=(x + t)%n 。由于 [n-1,m] 的结果与[n,m]相等,记结果 f(n)=x=f(n-1),代入映射关系可得 f(n) = (f(n-1) + m%n)%n ==> ( f(n-1)+m ) % n。 因此转移方程即为:f(n) = ( f(n-1) + m) % n。
不妨这样想:n个数时删除第m个数得到n-1个数,反之n-1数时加上第m个数得到n个数;每往后推进都要对当前总个数数取模。
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(1)
function lastRemaining(n, m) {
let last = 0 // 1个人时只有一个编号0
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
last = (last + m) % i
}
return last
}46.求1+2+…+n
思路:递归 递归代替循环,位运算代替条件判断;f(n)=f(n-1)+n
时间、空间复杂度均为O(n)
var sumNums = function(n) {
return n === 1 || (sumNums(n - 1) + n)
}47.不用加减乘除做加法
思路:位运算,0+0结果是0,0+1,1+0的结果都是1都符合异或操作,从而实现加法;唯独忽略了1+1结果会产生进位,通过 与运算和左移解决进位;重复前两步,直到不产生进位为止。
时间、空间复杂度均为 O(1)
var add = function (a, b) {
let sum, carry;
while (b) {
sum = a ^ b // 相加不考虑进位 也即得最后结果的一步
carry = (a & b) << 1 // 考虑进位
a = sum
b = carry // 记录进位情况
}
return a
}48.把字符串转换成整数
思路:去空格,判断正负,判断数字部分(舍弃非数字字符),判断越界。
时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(1)
var strToInt = function(str) {
let i = 0,
sign = 1,
total = 0
const l = str.length,
min = -(2 ** 31),
max = (2 ** 31) - 1
while (str[i] === ' ' && i < l) i++
if (str[i] == '+' || str[i] == '-')
sign = str[i++] == '+' ? 1 : -1
while (i < l) {
if (str.charCodeAt(i) < 48 || str.charCodeAt(i) > 57) break
total = total * 10 + (str[i++] - 0)
}
total *= sign
return total <= min ? min : total >= max ? max : total
}
// 巧用正则 str.trim()空间复杂度O(n)
var strToInt = function(str) {
const num = str.trim().match(/^[+-]?\d+/)
if (!num) return 0
const min = -(2 ** 31),
max = (2 ** 31) - 1
return num <= min ? min : num >= max ? max : num
}49.首个共同祖先
思路:深度遍历,公共祖先有3种情况:
p / q为对方的祖先;p、 q在 root 的异侧;p、 q在 root 的同侧
时间、空间复杂度均为O(n)
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
// 当越过叶节点,则直接返回 null
if (!root) return
// root 为根节点的树找到了p或q (p或q为另一个的祖先)
if (p == root || q == root) return root
// p,q 分别在 root 的异侧
let left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
let right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if (left && right ) return root
//p,q 都在 root 的左子树中(否则在右)
return left ? left : right
}50.只出现一次的数字 III
思路:先对所有数字进行一次异或,得到两个只出现一次的数字的异或值;在异或结果中找到任意(这里取低位)为 1 的位;根据这一位对所有的数字按位 与 即可进行将这俩数分在不同组;同时,在俩个组内进行异或操作,即可得到结果 (只出现一次的数字)。
时间复杂度:O(n)、空间复杂度O(1)
var singleNumber = function(nums) {
let ret = 0,
div = 1
for (n of nums)
ret ^= n // 此时ret是 俩只出现一次的数 异或的结果
while ((div & ret) == 0) // 通过与运算 左移 判断,获取div
div <<= 1 // div是ret最低位为1、其余位是0的二进制数
let a = b = 0
for (n of nums) {
if (n & div)
a ^= n
else
b ^= n
}
return [a, b]
}51.组合
思路:经典回溯
var combine = function(n, k) {
const res = []
const backtrack = (start, path) => { // start是枚举选择的起点 path是当前构建的路径(组合)
if (path.length == k) {
res.push(path.slice()) // 拷贝一份path,推入res
return // 结束当前递归
}
for (let i = start; i <= n; i++) { // 枚举出所有选择
path.push(i) // 选择
backtrack(i + 1, path) // 向下继续选择
path.pop() // 撤销选择
}
};
backtrack(1, []) // 递归的入口,从数字1开始选
return res
}52.矩阵中的路径
思路:深度搜索注意回溯,注意边界条件;遍历某个节点时做好标记(防止重复遍历),递归之后要恢复节点。
时间复杂度 O(3^K * MN) ,空间复杂度 O(K)
var exist = function(board, word) {
const r = board.length,
c = board[0].length
function dfs(i, j, index) {
if (i < 0 || i >= r || j < 0 || j >= c || board[i][j] !== word[index])
return false
if (index == word.length - 1) return true
const temp = board[i][j] //此时board[i][j] == word[index] 没必要用temp暂存
board[i][j] = false //访问标记
const res = dfs(i + 1, j, index + 1) || dfs(i - 1, j, index + 1) ||
dfs(i, j + 1, index + 1) || dfs(i, j - 1, index + 1)
board[i][j] = temp
return res
}
for (let i = 0; i < r; i++)
for (let j = 0; j < c; j++)
if (dfs(i, j, 0))
return true
return false
}53.机器人的运动范围
思路:首先准备 求数位之和 的函数,由于每次机器人只能走一步(不能跳过中间不符合的格子),所以不能用双重循环遍历;则考虑 dfs.
时间、空间复杂度 均为O(MN)
var movingCount = function(m, n, k) {
const sum = (x) => {
let a = 0
while (x) {
a += x % 10
x = Math.floor(x / 10)
}
return a
}
const visited = Array(m).fill(0).map(() => Array(n).fill(0))
const dfs = (x, y) => {
if (x >= m || y >= n || sum(x) + sum(y) > k || visited[x][y])
return 0
visited[x][y] = true
return dfs(x + 1, y) + dfs(x, y + 1) + 1
}
return dfs(0, 0)
}54.剪绳子
本题同 整数拆分 思路见动态规划专题第2题
55.数组中重复的数字
思路1:双层循环遍历判断重复数字.
时间复杂度:O(n^2) ,空间复杂度为O(1)
思路2:哈希表,空间换时间.
时间、空间复杂度均为O(n)
// 双层遍历
var findRepeatNumber = function(nums) {
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
for (let j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++)
if (nums[i] == nums[j])
return nums[i]
}
// 哈希表 array实现
var findRepeatNumber = function(nums) {
const hash = Array(100000).fill(0)
for (n of nums)
hash[n]++
console.log(hash)
for (let i = 0; i < hash.length; i++)
if (hash[i] > 1)
return i
}
// 哈希表 map实现
var findRepeatNumber = function(nums) {
let map = new Map()
for (let i of nums) {
if (map.has(i)) return i
map.set(i, 1)
}
return null
}56.正则表达式匹配
思路:动态规划,dp[i][j] 表示 s 的前 i 个字符能否和p的前 j 个字符匹配,分为四种情况依次处理。
递归法:参考公共子序列
时间、空间复杂度O(mn)
//动态规划
const isMatch = (s, p) => {
if (s == null || p == null) return false
const sLen = s.length,
pLen = p.length
const dp = new Array(sLen + 1)
for (let i = 0; i < dp.length; i++)
dp[i] = new Array(pLen + 1).fill(false) // 将项默认为false
// base case: s和p第0个位置是匹配的
dp[0][0] = true
for (let j = 1; j < pLen + 1; j++)
//情况1:如果p的第j-1个位置是*,则j的状态等于j-2的状态
if (p[j - 1] == "*") dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 2]
// 迭代
for (let i = 1; i < sLen + 1; i++)
for (let j = 1; j < pLen + 1; j++)
//情况2:如果s和p当前字符是相等的 或者p当前位置是. 则s和p都向前看一位 得到当前位前面的所有字符也匹配
if (s[i - 1] == p[j - 1] || p[j - 1] == ".")
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
else if (p[j - 1] == "*") {
//情况3:进入当前字符不匹配的分支 如果当前p是* 则有可能会匹配
if (s[i - 1] == p[j - 2] || p[j - 2] == ".") {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 2] || dp[i - 1][j - 2] || dp[i - 1][j]
} else {
//情况4:s当前位置和p前2个位置不匹配,则相当于*重复了0次
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 2]
}
}
return dp[sLen][pLen] // 长sLen的s串 是否匹配 长pLen的p串
}
// 递归
var isMatch = function(s, p) {
const n = s.length,
m = p.length
function dfs(i, j) {
if (i === n && j === m) return true
if (i > n || j >= m) return false
const isSame = p[j] === '.' || s[i] === p[j]
if (p[j + 1] === '*') return isSame && dfs(i + 1, j) || dfs(i, j + 2)
return isSame && dfs(i + 1, j + 1)
}
return dfs(0, 0)
}57.表示数值的字符串
思路:isNaN(x):如果 x 是非数字值(或者能被转换为这样的值),返回的值就是 true。如果 x 是其他值,则返回 false。所以对其取反可判断数值,注意空格例外。
正则表达式(底层原理为有限状态自动机)
//调用isNaN()函数 注意排除空格
var isNumber = function(s) {
if (s === " ") return false
return !isNaN(s)
}
// 用正则表达式
var isNumber = function(s) {
return /^([+-]?((\d*\.\d+)|\d+|(\d+\.\d*)))([eE][+-]?\d+)?$/.test(s.trim())
//行的开始,符号, 浮点数|整数|浮点数 e 符号 整数 匹配行尾 去掉前后空格
}58.链表中环的入口节点
思路:快慢指针一个每次走一步另一个走俩步,慢指针走k则快指针比其多走k步。相遇必然在环内,此时快指针仍然多走k步,但相遇点到环起点的距离小于(等于)k(慢指针也走了环)记作k-m;也就是说从相遇点走k-m即可到环起点;也即head到环起点也为k-m。所以俩个指针分别从head和相遇点同步出发,会在环起点相遇。
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(1)
var detectCycle = function(head) {
let slow = head
let fast = head
// 快指针走到末尾时停止
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if (slow == fast) {
slow = head
while (slow !== fast) {
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
}
return slow
}
}
return null
}
// 哈希表 但耗费空间O(n)
var detectCycle = function(head) {
let hash = new Set()
while (head) {
if (hash.has(head))
return head
hash.add(head)
head = head.next
}
return null
}59.对称的二叉树
思路:若任意两个对称节点 L 和 R 的值相等,且其左(右)孩子等于右(左)孩子,则为对称二叉树。注意边界:均到达空节点则说明节点均符合;若有只有一个为空或值不等则不符合;剩下俩孩子都在时继续判断。
时间、空间复杂度均为 O(N)
// 递归
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
if (!root) return true
return check(root.left, root.right)
function check(left, right) {
if (!left && !right) return true
else if (!left || !right || left.val !== right.val)
return false
else
return check(left.right, right.left) && check(left.left, right.right)
}
}
//层次遍历 更快
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
if (!root) return true
let st = []
st.push(root.left)
st.push(root.right)
while (st.length) {
let leftNode = st.pop()
let rightNode = st.pop()
if (!leftNode && !rightNode)
continue
if ((!leftNode || !rightNode || (leftNode.val != rightNode.val)))
return false
st.push(leftNode.left)
st.push(rightNode.right)
st.push(leftNode.right)
st.push(rightNode.left)
}
return true
}60.序列化二叉树
思路:前序遍历或者层次遍历。遇到 null 节点也要翻译成特定符号 ’X‘,反序列化时才知道这里是 null。
时间、空间复杂度均为 O(N)
// dfs递归
const serialize = (root) => {
if (root == null) // 遍历到 null 节点
return 'X'
const left = serialize(root.left) // 左子树的序列化结果
const right = serialize(root.right) // 右子树的序列化结果
return root.val + ',' + left + ',' + right // 按 根,左,右 拼接字符串
}
const deserialize = (data) => {
const list = data.split(',') // split成数组
const buildTree = (list) => { // 基于list构建当前子树
const rootVal = list.shift() // 弹出首项,获取它的“数据”
if (rootVal == "X") // 是X,返回null节点
return null
const root = new TreeNode(rootVal) // 不是X,则创建节点
root.left = buildTree(list) // 递归构建左子树
root.right = buildTree(list) // 递归构建右子树
return root // 返回当前构建好的root
}
return buildTree(list) // 构建的入口
}
//bfs
var serialize = function(root) {
const queue = [root]
let res = []
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift()
if (node) {
res.push(node.val)
queue.push(node.left)
queue.push(node.right)
} else
res.push('X')
}
return res
}
var deserialize = function(data) {
if (data == 'X') return null
const root = new TreeNode(data[0])
const queue = [root]
let index = 1
while (index < data.length) {
const node = queue.shift()
const leftVal = data[index]
const rightVal = data[index + 1]
if (leftVal != 'X') {
const leftNode = new TreeNode(leftVal)
node.left = leftNode
queue.push(leftNode)
}
if (rightVal != 'X') {
const rightNode = new TreeNode(rightVal)
node.right = rightNode
queue.push(rightNode)
}
index += 2
}
return root
}61.数据流中的中位数
思路:在添加数的时候,进行二分查找插入保证数组有序;返回中位数时注意奇偶。
添加的时间、空间复杂度均为 O(N),查找的时间、空间复杂度均为 O(1)
var MedianFinder = function() {
this.data = []
}
MedianFinder.prototype.addNum = function(num) {
if (!this.data.length) {
this.data.push(num)
return
}
let left = 0,
right = this.data.length - 1
while (left <= right) {
let mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2)
if (this.data[mid] === num) {
this.data.splice(mid, 0, num)
return
} else if (this.data[mid] < num)
left = mid + 1
else
right = mid - 1
}
this.data.splice(right + 1, 0, num)
}
MedianFinder.prototype.findMedian = function() {
const length = this.data.length
if (!length)
return null
const mid = Math.floor((length - 1) / 2)
if (length % 2)
return this.data[mid]
return (this.data[mid] + this.data[mid + 1]) / 2
}62.数字序列中某一位的数字
思路:找规律
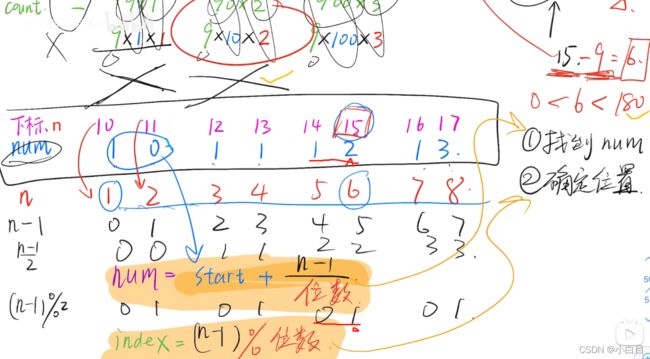
假如n=15, 首先15-9=6<180,确定是digit=2的区间,可以看到15对应实际数字num中的12的末位num[1]。至于怎么求num=12和index=1,公式如上图。
时间、空间复杂度均为 O(logn)
var findNthDigit = function(n) {
//确定区间
let digit = 1,
start = 1,
count = 9
while (n > count) {
n -= count
digit += 1
start *= 10
count = digit * start * 9
}
//求 num
let num = start + Math.floor((n - 1) / digit)
//求 index
return num.toString()[(n - 1) % digit]
}63.把数字翻译成字符串
思路:需先判断什么时候能将相邻的俩个数字一起翻译,然后就类似于动态规划专题的 “打家劫舍”题。
时间、空间复杂度均为O(logn)
// 记忆化搜索
var translateNum = function(num) {
const len = num.toString().length,
memo = new Array(len).fill(0)
const dfs = (str, index) => {
if (index >= str.length - 1) return 1
if (memo[index]) return memo[index]
const cur = Number(str[index] + str[index + 1])
if (cur > 9 && cur < 26)
// 翻译 1 个数,指针走一步,递归调用,返回出剩余数字的翻译方法数。
// 翻译 2 个数,指针走两步,递归调用,返回出剩余数字的翻译方法数。
memo[index] = dfs(str, index + 1) + dfs(str, index + 2)
else
memo[index] = dfs(str, index + 1)
return memo[index]
}
return dfs(num.toString(), 0)
}
// 动态规划
var translateNum = function(num) {
const str = num.toString(),
len = str.length
dp = new Array(len + 1).fill(0)
dp[0] = dp[1] = 1
for (let i = 2; i <= len; i++) {
const cur = Number(str[i - 2] + str[i - 1])
if (cur > 9 && cur < 26)
// dp[i] :翻译前 i 个数的方法数
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]
else
dp[i] = dp[i - 1]
}
return dp[len]
}64.礼物的最大价值
思路:从左上到右下每次向右或者向下移动一格,则到达当前格子最大价值为 f(i,j) = grid(i,j) + Math.max(f(i, j − 1), f(i − 1, j))
时间复杂度:O(mn),空间复杂度:O(1)
var maxValue = function(grid) {
const row = grid.length,
col = grid[0].length
// 初始化首行、首列
// 第一列的元素 只能从上来
for (let i = 1; i < row; i++) grid[i][0] += grid[i - 1][0]
// 第一行的元素 总能从左来
for (let j = 1; j < col; j++) grid[0][j] += grid[0][j - 1]
for (let i = 1; i < row; i++)
for (let j = 1; j < col; j++)
grid[i][j] += Math.max(grid[i - 1][j], grid[i][j - 1])
return grid[row - 1][col - 1]
}65.最长不含重复字符的子字符串
思路:双指针维护滑动窗口,j 负责遍历,i负责调整窗口。
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(1)
var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function(s) {
const map = new Map(); // 记录字串包含的字符和下标
let max = i = 0
for (let j = 0; j < s.length; j++) {
if (map.has(s[j]) && map.get(s[j]) >= i) //如果出现重复
i = map.get(s[j]) + 1 // 就把i移到上次出现的后一位(排除重复)
map.set(s[j], j) //每次记录字符及最后出现的位置
max = Math.max(max, j - i + 1)
}
return max
}66.在排序数组中查找数字 I
思路:对于查找数字的题基本都可以用哈希,但是此方法少不了空间复杂度O(n);由于是一维数组查找,遍历也不过O(n)且空间占用小;因为是排序数组所以可用二分查找优化时间为O(logn)
var search = function(nums, target) {
// 1. 构造哈希表hash value为出现的次数 Time: O(n) Space: O(n)
const hash = Object.create(null)
for (const num of nums) hash[num] ? hash[num]++ : (hash[num] = 1)
return hash[target] || 0
}
var search = function(nums, target) {
// 2. 双端指针队列 向中心收敛 利用有序这一条件 Time: O(n) Space: O(1)
let l = 0,
r = nums.length - 1
while (nums[l] < target) l++
while (nums[r] > target) r--
return r - l >= 0 ? r - l + 1 : 0
}
var search = function(nums, target) { // Time: O(logn) Space: O(1)
// 3. 二分法找target
let [low, high, flag] = [0, nums.length - 1, null]
while (low <= high) {
const mid = (low + high) >> 1
if (nums[mid] > target) high = mid - 1
else if (nums[mid] < target) low = mid + 1
else {
flag = mid
break
}
}
if (flag === null) return 0
// 向俩边找target 确定个数
low = high = flag
while (nums[low - 1] === target) low--
while (nums[high + 1] === target) high++
return high - low + 1
}67.二叉搜索树的第k大节点
思路: 遍历右根左 直接得到第k大的数,无需遍历完所有节点再去倒数第k个
var kthLargest = function(root, k) {
let res
function dfs(root) {
if (root == null || k == 0) return
dfs(root.right)
if (--k == 0) res = root.val
dfs(root.left)
}
dfs(root)
return res
}68.队列的最大值
思路:设置俩个队列,一个负责进出,另一个负责最大值。最大值队列维持非递增,即可每次出队最大值;实现方法只需每次入队时和和最大值队列的队尾元素比较,如果比队尾元素大则弹出,否则压入。出对时,若出队元素和最大值队列的队首元素相同则都出队。
时间复杂度:O(1),空间复杂度:O(n)
var MaxQueue = function() {
this.queue = []
this.maxque = []
}
MaxQueue.prototype.max_value = function() {
if (this.maxque.length) return this.maxque[0]
return -1
}
MaxQueue.prototype.push_back = function(value) {
this.queue.push(value)
while (this.maxque.length && this.maxque[this.maxque.length - 1] < value)
this.maxque.pop()
this.maxque.push(value)
}
MaxQueue.prototype.pop_front = function() {
if (!this.queue.length) return -1
const ans = this.queue.shift()
if (ans == this.maxque[0])
this.maxque.shift()
return ans
}69.股票的最大利润
思路:遍历数组找到其中的相差(利润)最大的俩个数,如果当前值比原来小则更新,否则考虑卖出的利润,如果比原来利润大则更新。
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(1)
var maxProfit = function(prices) {
let min = Number.MAX_VALUE,
maxpro = 0
for (price of prices)
if (price < min)
min = price
else if (price - min > maxpro)
maxpro = price - min
return maxpro
}70.构建乘积数组
思路:从左到右遍历构建当前元素之前的的左边的所有乘积;从右向左遍历,用一个变量来存当前元素右边元素的所有乘积,再乘上左边乘积即可得到结果
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(1)
var constructArr = function(a) {
const len = a.length,
b = new Array(len).fill(1)
// 左边:a[0]*...*a[i-1]
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++)
b[i] = b[i - 1] * a[i - 1]
// 右边:a[n-1]*...*a[i+1]
let r = 1
for (let i = len - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
r *= a[i + 1]
b[i] *= r
}
return b
}