日撸 Java 三百行day21-22
文章目录
- 说明
- day21 二叉树的深度遍历的递归实现
-
- 1. 二叉树的遍历
- 2. 二叉树深度,结点数
- 3. 代码
- day 22 二叉树的存储
-
- 1. 思路
- 2.层次遍历代码
- 3.代码
说明
闵老师的文章链接: 日撸 Java 三百行(总述)_minfanphd的博客-CSDN博客
自己也把手敲的代码放在了github上维护:https://github.com/fulisha-ok/sampledata
day21 二叉树的深度遍历的递归实现
1. 二叉树的遍历
- 前序遍历:根-左子树-右子树;
- 中序遍历:左子树-根-右子树;
- 后序遍历:左子树-右子树-根;
在实现二叉树的遍历时,使用递归把把复杂的问题转化为与原来问题相似的但规模较小的问题去解决。对于二叉树采用递归是好理解的,如果二叉树的深度高了 那递归不见得就是一个高效的算法。
2. 二叉树深度,结点数
对于一颗二叉树,用递归去求二叉树的深度和结点数,不管他有多少结点,我们在理解时都把他当成一个根结点,右边一个“右结点”,左边一个“左结点”,求深度我们只需要知道是一个根结点+(看左右结点是否存在来加1),求二叉树的结点数也是,只需要关注我这个结点左右结点是否有结点。
3. 代码
package main.java.datastructure.tree;
import java.time.OffsetDateTime;
public class BinaryCharTree {
/**
* The value in char
*/
char value;
/**
* The left child
*/
BinaryCharTree leftChild;
/**
* The right child
*/
BinaryCharTree rightChild;
/**
* The first constructor
* @param paraName
*/
public BinaryCharTree(char paraName){
value = paraName;
leftChild = null;
rightChild = null;
}
/**
* manually construct a tree.
*
* @return
*/
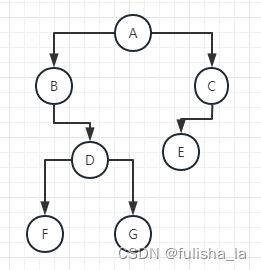
public static BinaryCharTree manualConstructTree(){
// Step 1. Construct a tree with only one node.
BinaryCharTree resultTree = new BinaryCharTree('a');
//Step 2. Construct all nodes. The first node is the root.
BinaryCharTree tempTreeB = new BinaryCharTree('b');
BinaryCharTree tempTreeC = new BinaryCharTree('c');
BinaryCharTree tempTreeD = new BinaryCharTree('d');
BinaryCharTree tempTreeE = new BinaryCharTree('e');
BinaryCharTree tempTreeF = new BinaryCharTree('f');
BinaryCharTree tempTreeG = new BinaryCharTree('g');
// Step 3. Link all nodes.
resultTree.leftChild = tempTreeB;
resultTree.rightChild = tempTreeC;
tempTreeB.rightChild = tempTreeD;
tempTreeC.leftChild = tempTreeE;
tempTreeD.leftChild = tempTreeF;
tempTreeD.rightChild = tempTreeG;
return resultTree;
}
/**
* pre-order visit
*/
public void preOrderVisit(){
System.out.print("" + value + " ");
if (leftChild != null){
leftChild.preOrderVisit();
}
if (rightChild != null){
rightChild.preOrderVisit();
}
}
/**
* in-order visit
*/
public void inOrderVisit(){
if (leftChild != null){
leftChild.inOrderVisit();
}
System.out.print("" + value + " ");
if (rightChild != null) {
rightChild.inOrderVisit();
}
}
/**
* Post-order visit.
*/
public void postOrderVisit(){
if (leftChild != null) {
leftChild.postOrderVisit();
}
if (rightChild != null) {
rightChild.postOrderVisit();
}
System.out.print("" + value + " ");
}
public int getDepth(){
// It is a leaf.
if ((leftChild == null) && (rightChild == null)) {
return 1;
}
// The depth of the left child.
int tempLeftDepth = 0;
if (leftChild != null){
tempLeftDepth = leftChild.getDepth();
}
int tempRighDepth = 0;
if (rightChild != null){
tempRighDepth = rightChild.getDepth();
}
if (tempLeftDepth >= tempRighDepth) {
return tempLeftDepth + 1;
}else {
return tempRighDepth + 1;
}
}
/**
* get the number of nodes
* @return
*/
public int getNumNodes(){
if (leftChild == null && rightChild == null){
return 1;
}
int tempLeftNodes = 0;
if (leftChild != null){
tempLeftNodes = leftChild.getNumNodes();
}
int tempRightNodes = 0;
if (rightChild != null) {
tempRightNodes = rightChild.getNumNodes();
}
return tempLeftNodes + tempRightNodes + 1;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
BinaryCharTree tempTree = manualConstructTree();
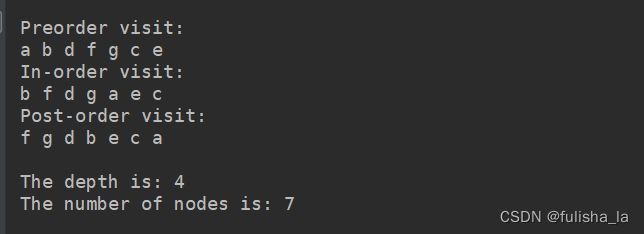
System.out.println("\r\nPreorder visit:");
tempTree.preOrderVisit();
System.out.println("\r\nIn-order visit:");
tempTree.inOrderVisit();
System.out.println("\r\nPost-order visit:");
tempTree.postOrderVisit();
System.out.println("\r\n\r\nThe depth is: " + tempTree.getDepth());
System.out.println("The number of nodes is: " + tempTree.getNumNodes());
}
}
day 22 二叉树的存储
1. 思路
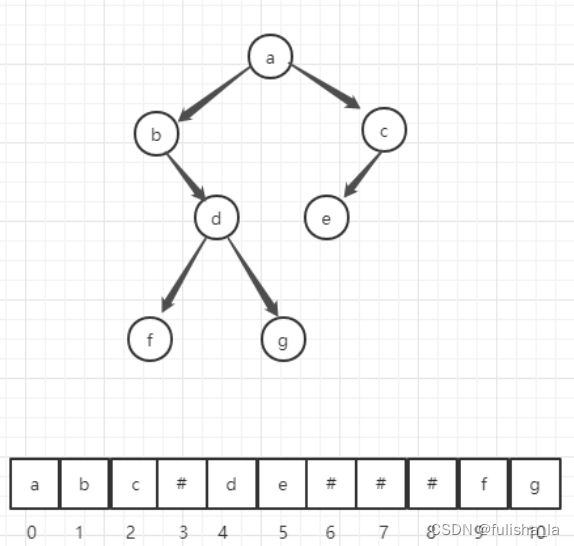
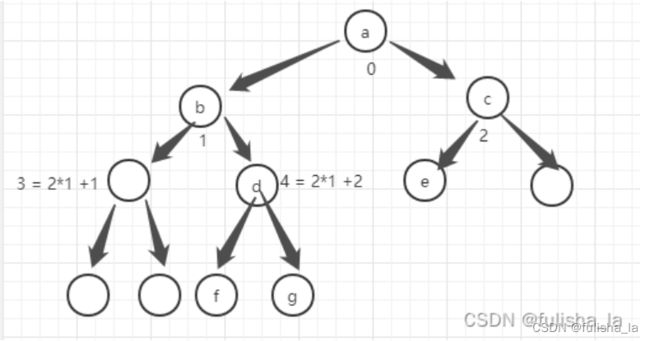
(结合下图来理解将二叉树存入数组中)以完全二叉树来计算结点存储索引位置,则当双亲结点为i,则左子树存储的索引为2i+1;右子树为2i+2;如果对于稀疏的二叉树而言,用这样的存储方式显然会很浪费大量的存储空间,而文章中的第二个方法则是把存储值和存储索引分开,一个数组存储结点的值,一个数组存储结点对应的索引值,这个索引值也是根据完全二叉树计算方式算出来的,这样就可以相比于第一种方法这样可以节省空间。
2.层次遍历代码
在看了本题的存储思路主要是采用存储遍历的方式来存储二叉树的存储,所以只要层次遍历的方式明白就可以理解文章中的代码,层次遍历主要就是借助队列来实现的。以下是自己结合文章写出的层次遍历算法。
/**
* Level-order visit.
*/
public void levelOderVisit(){
CircleObjectQueue tempQueue = new CircleObjectQueue();
tempQueue.enqueue(this);
BinaryCharTree tempTree = (BinaryCharTree) tempQueue.dequeue();
while (tempTree != null){
System.out.print("" + tempTree.value + " ");
if (tempTree.leftChild != null) {
tempQueue.enqueue(tempTree.leftChild);
}
if (tempTree.rightChild != null) {
tempQueue.enqueue(tempTree.rightChild);
}
tempTree = (BinaryCharTree) tempQueue.dequeue();
}
}
3.代码
我发现用前中后序遍历去实现两个队列存储貌似有点麻烦,用这个层次遍历要方便点。
public void toDataArrays(){
int tempLength = getNumNodes();
valuesArray = new char[tempLength];
indicesArray = new int[tempLength];
int i = 0;
//Traverse and convert at the same time.
CircleObjectQueue tempQueue = new CircleObjectQueue();
tempQueue.enqueue(this);
CircleIntQueue tempIntQueue = new CircleIntQueue();
tempIntQueue.enqueue(0);
BinaryCharTree tempTree = (BinaryCharTree) tempQueue.dequeue();
int tempIndex = tempIntQueue.dequeue();
while (tempTree != null){
valuesArray[i] = tempTree.value;
indicesArray[i] = tempIndex;
i++;
if (tempTree.leftChild != null) {
tempQueue.enqueue(tempTree.leftChild);
tempIntQueue.enqueue(tempIndex * 2 + 1);
}
if (tempTree.rightChild != null) {
tempQueue.enqueue(tempTree.rightChild);
tempIntQueue.enqueue(tempIndex * 2 + 2);
}
tempTree = (BinaryCharTree) tempQueue.dequeue();
tempIndex = tempIntQueue.dequeue();
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
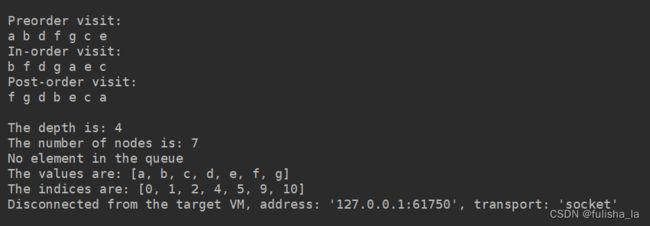
BinaryCharTree tempTree = manualConstructTree();
System.out.println("\r\nPreorder visit:");
tempTree.preOrderVisit();
System.out.println("\r\nIn-order visit:");
tempTree.inOrderVisit();
System.out.println("\r\nPost-order visit:");
tempTree.postOrderVisit();
System.out.println("\r\n\r\nThe depth is: " + tempTree.getDepth());
System.out.println("The number of nodes is: " + tempTree.getNumNodes());
tempTree.toDataArrays();
System.out.println("The values are: " + Arrays.toString(tempTree.valuesArray));
System.out.println("The indices are: " + Arrays.toString(tempTree.indicesArray));
}
}