Oracle编程( 其三)(pl/sql&&游标&&存储过程、存储函数&&触发器)
一、PL/SQL编程语言
- pl/编程语言是对sql语言的扩展,使得sql语言具有过程化编译的特性。
- pl/编程语言比一般的过程化编程语言,更加灵活高效。
- pl/编程语言主要用来编写存储过程和存储函数
1、声明方法
赋值操作 : (:=)或者(into查询语句)两种方式赋值。
例:引用型变量(type)和记录型变量(rowtype)的使用
set serveroutput on
declare
i number(2) :=10;
s varchar2(10) :='小明';
ena emp.ename%type;-- 引用型变量
emprow emp%rowtype;--记录型变量
begin
dbms_output.put_line(i);
dbms_output.put_line(s);
select ename into ena from emp where empno=7499;
dbms_output.put_line(ena);
select * into emprow from emp where empno=7499;
dbms_output.put_line(emprow.ename||'的工作为:' ||emprow.job);
end;
2、pl/sql中的if判断语句&&分支结构
2.1、if判断语句
通用句式:(条件语句中必须要以end if结束,并且只有这里加分号、可以省去elsif和else,类似于java)
declare
begin
if then
elsif then
else
end if;
end;
例:
输入小于18的数字,输出未成年
输入小于40大于18的数字,输出中年人
输入大于40的数字,输出老年人
set serveroutput on
declare
x number(3):=&xx;
begin
if x<18 then
dbms_output.put_line('未成年');
elsif x<40 then
dbms_output.put_line('中年人');
else
dbms_output.put_line('老年人');
end if;
end;
declare
args score.grade%type;
case
when
then
when
then
else;
end case;
3、pl/sql中的loop循环
3.1.1、while循环
set serveroutput on
declare
i number(2):=1;
begin
while i<11 loop
dbms_output.put_line(i);
i :=i+1;
end loop;
end;
3.1.2、exit循环(重点掌握)
set serveroutput on
declare
i number(2):=1;
begin
loop
exit when i>10;
dbms_output.put_line(i);
i:=i+1;
end loop;
end;
3.1.3、for循环
set serveroutput on
declare
i number(2):=1;
begin
for i in 1..10 loop
dbms_output.put_line(i);
end loop;
end;
3.2.1、if 循环
declare
args score%rowtype;
n int (10):=1;
v_count int;
begin
select count(*) into v_count from score;
loop
select b.sno,b.cno,b.grade into args from
(select rownum as num,score.* from score) b where b.num=n;
dbms_output.put_line('sno='||args.sno||'cno='||args.cno||'grade='||args.grade);
n :=n+1;
if n>v_count then
exit;
end if;
end loop;
end;
3.2.2、wile循环
declare
args score%rowtype;
n int :=1;
v_count int;
begin
select count(*) into v_count from score;
while n<=v_count
loop
select b.sno,b.cno,b.grade into args from
(select rownum as num,score.* from score) b where b.num=n;
dbms_output.put_line('sno='||args.sno||'cno='||args.cno||'grade='||args.grade);
n :=n+1;
end loop;
end;
3.2.3、for循环
declare
args score%rowtype;
n int;
v_count int;
begin
select count(*) into v_count from score;
for n in 1..v_count loop
select b.sno,b.cno,b.grade into args from
(select rownum as num,score.* from score) b where b.num=n;
dbms_output.put_line('sno='||args.sno||'cno='||args.cno||'grade='||args.grade);
end loop;
end;
二、游标(cursor)&&记录(record)
记录 record 使用:定义数据记录类型
TYPE RECORD_NAME IS RECORD(--声明记录数据类型
V1 DATA_TYPE1 [NOT NULL][:=DEFAULT_VALUE],--定义变量、变量数据类型
V2 DATA_TYPE2 [NOT NULL][:=DEFAULT_VALUE],
VN DATA_TYPEN [NOT NULL][:=DEFAULT_VALUE]);
游标:可以存放多个对象,多行记录。
例:输出emp表中所有员工的姓名。
方法一:
set serveroutput on
declare
cursor c1 is select * from emp;
emprow emp%rowtype;
begin
open c1;
loop
fetch c1 into emprow;
exit when c1%notfound;
dbms_output.put_line(emprow.ename);
end loop;
close c1;
end;
set serveroutput on
declare
cursor c2(eno emp.deptno%type) is select empno from emp where deptno=eno;
en emp.empno%type;
begin
open c2(10);
loop
fetch c2 into en;
exit when c2%notfound;
update emp set sal=sal+100 where empno=en;
commit;
end loop;
close c2;
end;
set serveroutput on
declare
cursor stu_cur is select sno,sage from student where sname='张书贺';
n stu_cur%rowtype;
begin
open stu_cur;
loop
fetch stu_cur into n;
exit when stu_cur%notfound;
stu_ dbms_output.put_line(n.sno||n.sage);
end loop;
close cur;
end;
函数
-
聚合函数
–count(*)和count(1)推荐使用 底层一样,都是查询第一列数量
select count(1) from emp;–查询总数量
select sum(sal) from emp;–工资总和
select max(sal) from emp;–最大工资
select min(sal) from emp;–最低工资
select avg(sal) from emp;–平均工资 -
单行函数
作用于一行,返回一个值 -
多行函数
作用于多行,返回一个值 -
字符函数
select upper('yes') from dual;--YES 小写变大写
select lower('YES') from dual;--yes 大写变小写
select length('aasS') from dual;--字符串长度
select reverse('ssds,dasd'),replace('sasdd,sdad,dsad') from dual;--反转,代替字符串
- 数值函数
select round(26.16,1) from dual;
--四舍五入(26.2),后面表示保留的位数
select trunc(26.16,1) from dual;
--直接截取(26.1),后面表示保留的位数
select mod(10,3) from dual;
--求余数(1)
select power(x,n)
--求x的n次幂
- 日期函数
–查询出emp表中所有员工入职距离现在几天
select sysdate-e.hiredate from emp e;
--现在时间
select sysdate,current_date from dual;
--算出明天此刻
select sysdate+1 from dual;
--查询出emp表中所有员工入职距离现在几月
select months_between(sysdate,e.hiredate) from emp e;
--查询出emp表中所有员工入职距离现在几年
select months_between(sysdate,e.hiredate)/12 from emp e;
--查询出emp表中所有员工入职距离现在几周(四舍五入去掉小数)
select round((sysdate-e.hiredate)/7) from emp e;
- 转换函数
–日期转字符串
select to_char(sysdate,'fm yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') from dual;
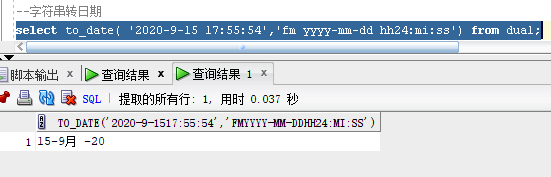
select to_date( '2020-9-15 17:55:54','fm yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') from dual;
- 通用函数
–算出emp表中所有员工的年薪
–奖金里面有null值,null和任意数字进行算数运算,结果都是null
select e.sal*12+nvl(e.comm,0) from emp e;
三、存储过程(procedure)
存储过程:提前已经编译好的一段pl/sql语言,放置在数据库端,可以直接被调用。(这一段pl/sql一般都是固定步骤的业务)
优点:
执行速度快,在服务器端运行
编译一次驻留在缓冲存储器中,可多次执行
保证数据库安全
自动完成需要预先处理的任务
例:给指定员工涨100工资
create or replace procedure p1(eno emp.empno%type)
is
begin
update emp set sal=sal+500 where empno=eno;
commit;
end;
![]()
or replace作用:没有时 --> 创建这个过程。有重名时 --> 替换为现在的。(保证能够每次都创建、使用or replace时,其它用户在该函数上的权限不会丢失和变化)
测试p1:
declare
begin
p1(7499);
end;
out类型参数使用方法:
例:使用存储过程来计算年薪
create or replace procedure p_yearsal(eno emp.empno%type,yealsal out number)
is
s number(10);
c emp.comm%type;
begin
select sal*12,nvl(comm,0) into s,c from emp where empno=eno;
yealsal := s+c;
end;
![]()
测试P_YEARSAL:
declare
yealsal number(10);
begin
p_yearsal(7499,yealsal);
dbms_output.put_line(yealsal);
end;
in 和 out 类型参数的区别是什么?
凡是涉及到into查询语句赋值、:= 操作的参数,都必须使用out来修饰。
例:
1、给定学号删除成绩,自定义异常处理
create or replace procedure p_delscore(psno score.sno%type)
is
err_nodata exception;
begin
delete from score where sno=psno;
if sql%notfound then
raise err_nodata;
else
dbms_output.put_line('delete'||sql%rowcount||'rows');
commit;
end if;
exception
when err_nodata then dbms_output.put_line('nodate');
end;
2、创建存储过程,根据院系编号更新sdept表中院系名称
create or replace procedure p_upsdept(dno sdept.deptno%type,dna sdept.dname%type)
is
begin
update sdept set dname=dna where deptno=dno;
if sql%found then
dbms_output.put_line('update finish');
commit;
else
dbms_output.put_line('no data');
end if;
end;
四、存储函数(function)
存储过程和存储函数的参数都不能带长度
存储函数的返回值类型不能带长度
例:通过存储函数实现计算指定员工的年薪
在oracle中,null与数字相加减,结果为null。所以需要nvl()函数将comm去除null值。
create or replace function f_yearsal(eno emp.empno%type) return number
is
s number(10);
begin
select sal*12+nvl(comm,0) into s from emp where empno =eno;
return s;
end;
![]()
测试函数(F_YEARSAL):
函数在调用的时候,返回值需要接收
declare
s number(10);
begin
s:=f_yearsal(7499);
dbms_output.put_line(s);
end;

例题:
1、创建函数,根据学生的学号获得该学生的选修课程门数
create or replace function f_sumscoure(fsno score.sno%type)
return varchar
is
v_grade score.grade%type;
cursor scgrade_cur is select grade from score where sno=upper(fsno);
begin
open scgrade_cur;
loop
fetch scgrade_cur into v_grade;
exit when scgrade_cur%notfound;
end loop;
if scgrade_cur%rowcount>0 then
return to_char(scgrade_cur%rowcount);
else
raise zero_divide;
end if;
exception
when zero_divide then return '没有选修科目';
end;
select f_sumscoure('0701010135') from dual;
2、根据姓名查询选修分数
create or replace function f_namecc(fsname student.sname%type)
return varchar
is
s_grade course.ccredit%type;
s_sumgrade course.ccredit%type:=0;
err_notdata exception;
cursor scgrade_cur is select ccredit from course where cno in(select cno from score where sno=(select sno from student where sname=upper(fsname)));
begin
for cur in scgrade_cur loop
s_sumgrade:=s_sumgrade+cur.ccredit;
end loop;
if s_sumgrade>0 then
return to_char(s_sumgrade);
else
raise err_notdata;
end if;
exception
when err_notdata then return'没有选修课程';
end;
select f_namecc('张书贺 ') from dual;
create or replace
function
f_numxue(sna student.sname%type)
return varchar
as
cursor cur_credit is select student.sno,sum(ccredit) credit from student,course,score where student.sno=score.sno
and course.cno=score.cno and student.sname=sna group by student.sno;
err_nodata exception;
cur cur_credit%rowtype;
str varchar(100) default null;
begin
open cur_credit;
loop
fetch cur_credit into cur;
if cur_credit%rowcount=0 then
raise err_nodata;
end if;
exit when cur_credit%notfound;
str:=str||cur.sno||cur.credit||';';
end loop;
return str;
close cur_credit;
exception
when err_nodata then return 'no data';
end;
存储过程和存储函数的区别:
- 语法区别:
关键字不一样(存储函数比存储过程多了两个return) - 本质区别:
存储函数有返回值,存储过程没有返回值。
如果存储过程想实现有返回值的业务,我么就必须用out类型的参数。
即便是存储过程使用了out类型的参数,本质也不是真的有了返回值。
而是在存储过程内部给out类型参数赋值,再执行完毕后,我们直接拿到输出类型的值。
案例需求:查询出员工姓名,员工所在部门名称。(我们可以使用存储函数有返回值的特性,来自定义函数.存储过程不能用来自定义函数。)
1、传统方式来实现:
select e.ename,d.dname
from emp e,dept d
where e.deptno=d.deptno;
2、使用存储函数来实现提供一个部门编号,输出一个部门名称。
create or replace function fdna(dno dept.deptno%type) return dept.dname%type
is
dna dept.dname%type;
begin
select dname into dna from dept where deptno=dno;
return dna;
end;
测试(fdna存储函数来实现案例需求):
select e.ename,fdna(e.deptno)
from emp e;
五、触发器(trigger)
指定一个规则,在我们增删改操作的时候只要满足,自动触发,无需调用
触发器三要素:
- 触发事件
- 触发时机
- 触发器功能
例:插入一条记录,输出一个新学生入学
reate or replace trigger t1
after
insert
on student
declare
begin
dbms_output.put_line('一个新员工入职!');
end;
触发t1触发器
insert into student values('1111111','王延新','女',18,'04');
commit;
2、行级触发器:包含for each row
加for each row目的:为了使用: a、 :old 对象、b、:new 对象、c、一行记录。
例:不能给员工降薪
raise_application_error(-20001~-20999之间,‘错误提示信息’);
create or replace trigger t2
before
update
on emp
for each row
declare
begin
if :old.sal>:new.sal then
raise_application_error(-20001,'不能给员工降薪');
end if;
end;
update emp set sal=sal-1 where empno=7499;
commit;
创建触发器,实现在跟新student表中sno的值时,可以级联跟新该列的其他表中的sno的值
create or replace trigger tr_upstu
before
update
of sno on student
for each row
begin
update score set sno=:new.sno where sno=:old.sno;
end;
触发:update student set sno=‘007’ where sno=‘5131’

2、创建触发器,删除数据时,可以级联删除引用该列的其他表中的数据值
delete from course where cno='B002'
create or replace trigger tr_delcour
after
delete
on course
for each row
begin
delete form score where cno:old.cno;
end;
触发器实现主键自增
分析:在用户做插入操作之前,拿到即将插入的数据,给主键列赋值
create or replace trigger auid
before
insert
on student
for each row
declare
begin
select s_person.nextval into :new.pid from dual;
end;
insert into person (pname) value('a');
commit;