Redis高级之IO多路复用和epoll(十二)
nginx 的反向代理也是采用了IO多路复用
1.是什么
-
I/O
- 网络 I/O
-
多路
- 多个客户端连接(连接就是套接字描述符,即socket 或者 channel),指的是多条 TCP 连接
-
复用
- 用一个进程来处理多条的连接,使用单进程就能实现同时处理多个客户端的连接
-
总结
- 实现了用一个进程来处理大量的用户连接
- IO多路复用类似一个规范和接口,落地实现是由 linux系统的 select -> poll -> epoll
2.Redis如何处理多并发客户端连接
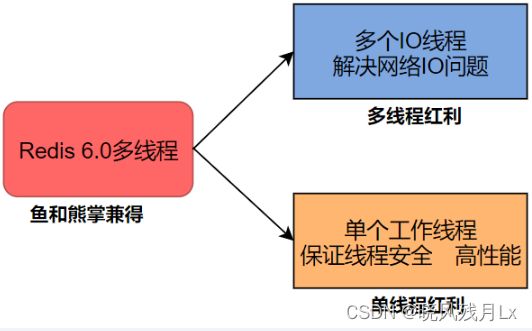
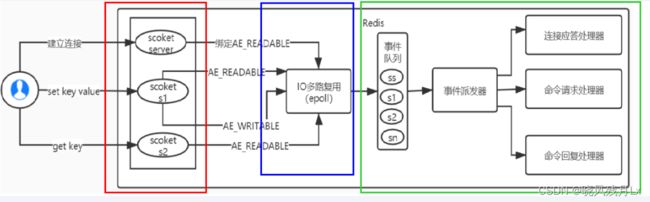
Redis 利用 epoll 来实现 IO多路复用,将连接信息和事件都放到队列中,一次放到文件事件分派器,事件分派器将事件分发给事件处理器
Redis 是跑在单线程中的,所有的操作都是按照顺序线性执行的,但是由于读写操作等待用户输入或输出都是阻塞的,所以 I/O 操作在一般情况下往往不能直接返回,这会导致某一文件的 I/O 阻塞导致整个进程无法对其它客户提供服务,而 I/O 多路复用就是为了解决这个问题而出现
所谓 I/O 多路复用机制,就是说通过一种机制,可以监视多个描述符,一旦某个描述符就绪(一般是读就绪或写就绪),能够通知程序进行相应的读写操作。这种机制的使用需要 select 、 poll 、 epoll 来配合。多个连接共用一个阻塞对象,应用程序只需要在一个阻塞对象上等待,无需阻塞等待所有连接。当某条连接有新的数据可以处理时,操作系统通知应用程序,线程从阻塞状态返回,开始进行业务处理。
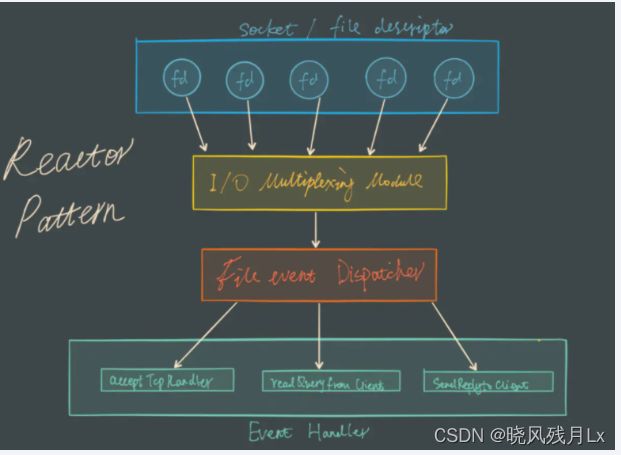
Redis 服务采用 Reactor 的方式来实现文件事件处理器(每一个网络连接其实都对应一个文件描述符)
Redis基于Reactor模式开发了网络事件处理器,这个处理器被称为文件事件处理器。它的组成结构为4部分:
-
多个套接字、
-
IO多路复用程序、
-
文件事件分派器、
-
事件处理器。
因为文件事件分派器队列的消费是单线程的,所以Redis才叫单线程模型
Reactor 模式要求 主线程(I/O 处理单元) 只负责监听文件描述符上是否有事件发生,有的话就立即将该事件通知工作线程(逻辑单元)。除此之外,主线程不做任何其他实质性的工作。 读写数据,接受新的连接,以及处理客户请求均在工作线程中完成。
从Redis6开始,将网络数据读写、请求协议解析通过多个IO线程的来处理 ,对于真正的命令执行来说,仍然使用单线程操作
3.异步、同步、阻塞、非阻塞
-
同步
- 调用者要一直等待调用结果的通知后才能进行后续的执行
-
异步
- 指被调用方先返回应答让调用者先回去,然后再计算调用结果,计算完最终结果后再通知并返回给调用方
- 异步调用要想获得结果一般通过回调
-
同步与异步的理解
- 同步、异步的讨论对象是被调用者(服务提供者),重点在于获得调用结果的消息通知方式上
-
阻塞
- 调用方一直在等待而且别的事情什么都不做,当前线/进程都会被挂起,啥也不干
-
非阻塞
- 调用在发出去后,调用方先去忙别的事情,不会阻塞当前进/线程,而会立即返回
-
阻塞与非阻塞的理解
- 阻塞、非阻塞的讨论对象是调用者(服务请求者),重点在于等消息时候的行为,调用者是否能干其他事
-
总结
- 同步阻塞
- 调用发出后,调用者一直等待调用结果的通知,什么也不干
- 同步非阻塞
- 调用发出后,会立马收到答复,如果得到的不是完整的资源,调用者会周期循环轮询发送IO请求,直到真正获得调用结果的通知,在此期间调用者可以去做别的
- 异步阻塞
- 调用不会马上发出,安排一个时间再发起请求,什么也不干,等待调用结果的通知
- 异步非阻塞
- 调用不会马上发出,安排一个时间再发起请求,当发出请求,可以马上得到答复,如果得到的不是完整的资源,调用者调用者会周期循环轮询发送IO请求,直到真正获得调用结果的通知,在此期间调用者可以去做别的
- 同步阻塞
4. Java验证(模拟redis6379端口)
BIO
accept监听
-
RedisServer
import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.UUID; /** * @author 晓风残月Lx * @date 2023/4/5 9:17 */ public class RedisServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(6379); while(true){ System.out.println("模拟redisServcer启动 -----111 等待连接"); Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); System.out.println("---222 连接成功 " + UUID.randomUUID()); System.out.println(); } } } -
RedisClient01
import java.io.IOException; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author 晓风残月Lx * @date 2023/4/5 9:09 */ public class RedisClient01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("------RedisClient01 start "); Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 6379); System.out.println("------RedisClient01 connection over "); } } -
RedisClient02
import java.io.IOException; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author 晓风残月Lx * @date 2023/4/5 9:09 */ public class RedisClient02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("------RedisClient02 start "); Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 6379); System.out.println("------RedisClient02 connection over "); } } -
测试 先启动redisServer,在启动redisClient
read(读取)
-
单线程模式测试
-
先启动 RedisServerBIO,再启动 RedisClient01 验证后再启动 2号客户端
-
RedisServerBIO
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.UUID; /** * @author 晓风残月Lx * @date 2023/4/5 9:25 */ public class RedisServerBIO { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(6379); while (true) { System.out.println("---111 等待连接"); Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); // 阻塞1,等待客户端连接 System.out.println("---222 成功连接"); InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); int lenth = 1; byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; System.out.println("---333 等待读取"); while ((lenth = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1){ // 阻塞2 等待客户端发送数据 System.out.println("---444 成功读取" + new String(bytes, 0, lenth)); System.out.println("=========" + UUID.randomUUID()); System.out.println(); } inputStream.close(); socket.close(); } } } -
RedisClient01
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.Scanner; /** * @author 晓风残月Lx * @date 2023/4/5 9:22 */ public class RedisClient01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 6379); OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); while (true) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String str = sc.next(); if (str.equalsIgnoreCase("quit")) { break; } socket.getOutputStream().write(str.getBytes()); System.out.println("-----RedisClient01 input quit keyword to finish"); } outputStream.close(); socket.close(); } } -
RedisClient02
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.Scanner; /** * @author 晓风残月Lx * @date 2023/4/5 9:22 */ public class RedisClient02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 6379); OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); while (true) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String str = sc.next(); if (str.equalsIgnoreCase("quit")) { break; } socket.getOutputStream().write(str.getBytes()); System.out.println("-----RedisClient02 input quit keyword to finish"); } outputStream.close(); socket.close(); } } -
测试
- 上述存在很大的问题,如果客户端与服务端建立了连接,如果这个连接的客户端迟迟不乏数据,数据就会一直堵塞再 read() 方法上,这样其他客户端也不能进行连接,也就是一次只能处理一个客户端,对客户很不友好
-
-
多线程模式
- RedisServerBIOMultiThread
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.UUID; /** * @author 晓风残月Lx * @date 2023/4/5 9:25 */ public class RedisServerBIOMultiThread { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(6379); while (true) { System.out.println("--------RedisServerBIOMultiThread 111 等待连接"); Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); // 阻塞1,等待客户端连接 System.out.println("--------RedisServerBIOMultiThread 222 成功连接"); new Thread(() -> { try { InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); int lenth = 1; byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; System.out.println("---333 等待读取"); while ((lenth = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) { // 阻塞2 等待客户端发送数据 System.out.println("---444 成功读取" + new String(bytes, 0, lenth)); System.out.println("=========" + UUID.randomUUID()); System.out.println(); } inputStream.close(); socket.close(); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, Thread.currentThread().getName()).start(); } } }- RedisClient01
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.Scanner; /** * @author 晓风残月Lx * @date 2023/4/5 9:22 */ public class RedisClient01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 6379); OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); while (true) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String str = sc.next(); if (str.equalsIgnoreCase("quit")) { break; } socket.getOutputStream().write(str.getBytes()); System.out.println("-----RedisClient01 input quit keyword to finish"); } outputStream.close(); socket.close(); } }-
RedisClient02
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.Scanner; /** * @author 晓风残月Lx * @date 2023/4/5 9:22 */ public class RedisClient02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 6379); OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); while (true) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String str = sc.next(); if (str.equalsIgnoreCase("quit")) { break; } socket.getOutputStream().write(str.getBytes()); System.out.println("-----RedisClient02 input quit keyword to finish"); } outputStream.close(); socket.close(); } } -
测试
- 存在的问题
- 每来一个客户端,就要开辟一个线程,如果来1万个客户端,那就要开辟1万个线程。在操作系统中用户态不能直接开辟线程,需要调用内核来创建的一个线程,这其中还涉及到用户状态的切换(上下文的切换),十分耗资源。
- 解决方法
- 线程池,在客户端连接少的情况下可以使用,但是用户量大的清况下,你不知道线程池要设置多大,内存可能不够
- NIO(非阻塞式IO)
- 存在的问题
NIO
-
在NIO模式中,一切都是非阻塞的:
- accept()方法是非阻塞的,如果没有客户端连接,就返回无连接标识
- read()方法是非阻塞的,如果read()方法读取不到数据就返回空闲中标识,如果读取到数据时只阻塞read()方法读数据的时间
-
在NIO模式中,只有一个线程:
-
当一个客户端与服务端进行连接,这个socket就会加入到一个数组中,隔一段时间遍历一次
看这个socket的read()方法能否读到数据,这样一个线程就能处理多个客户端的连接和读取了
-
-
非阻塞在java中使用 ServerSocketChannel类
-
RedisServerNIO
import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.util.ArrayList; /** * @author 晓风残月Lx * @date 2023/4/5 10:07 */ public class RedisServerNIO { static ArrayList<SocketChannel> socketList = new ArrayList<>(); static ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("---------RedisServerNIO 启动等待中......"); ServerSocketChannel serverSocket = ServerSocketChannel.open(); serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 6379)); serverSocket.configureBlocking(false);//设置为非阻塞模式 while (true) { for (SocketChannel element : socketList) { int read = element.read(byteBuffer); if (read > 0) { System.out.println("-----读取数据: " + read); byteBuffer.flip(); byte[] bytes = new byte[read]; byteBuffer.get(bytes); System.out.println(new String(bytes)); byteBuffer.clear(); } } SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocket.accept(); if (socketChannel != null) { System.out.println("-----成功连接: "); socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);//设置为非阻塞模式 socketList.add(socketChannel); System.out.println("-----socketList size: " + socketList.size()); } } } } -
RedisClient01
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.Scanner; /** * @author 晓风残月Lx * @date 2023/4/5 9:22 */ public class RedisClient01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 6379); OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); while (true) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String str = sc.next(); if (str.equalsIgnoreCase("quit")) { break; } socket.getOutputStream().write(str.getBytes()); System.out.println("-----RedisClient01 input quit keyword to finish"); } outputStream.close(); socket.close(); } } -
RedisClient02
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.Scanner; /** * @author 晓风残月Lx * @date 2023/4/5 9:22 */ public class RedisClient02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 6379); OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); while (true) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String str = sc.next(); if (str.equalsIgnoreCase("quit")) { break; } socket.getOutputStream().write(str.getBytes()); System.out.println("-----RedisClient02 input quit keyword to finish"); } outputStream.close(); socket.close(); } }
-
-
测试
- 存在的问题
- 如何用单线程处理大量的链接
- 非阻塞IO就是请求发出,如果资源没有完成,不断轮询该请求
- 存在的问题
5.IO多路复用详解
5.1 Redis为什么那么快
Redis利用epoll来实现IO多路复用,将连接信息和事件放到队列中,依次放到事件分派器,事件分派器将事件分发给事件处理器。
Redis 服务采用 Reactor 的方式来实现文件事件处理器(每一个网络连接其实都对应一个文件描述符)
所谓 I/O 多路复用机制,就是说通过一种机制,可以监视多个描述符,一旦某个描述符就绪(一般是读就绪或写就绪),能够通知程序进行相应的读写操作。这种机制的使用需要 select 、 poll 、 epoll 来配合。多个连接共用一个阻塞对象,应用程序只需要在一个阻塞对象上等待,无需阻塞等待所有连接。当某条连接有新的数据可以处理时,操作系统通知应用程序,线程从阻塞状态返回,开始进行业务处理。
5.2 Reator设计模式
基于 I/O 复用模型:多个连接共用一个阻塞对象,应用程序只需要在一个阻塞对象上等待,无需阻塞等待所有连接。当某条连接有新的数据可以处理时,操作系统通知应用程序,线程从阻塞状态返回,开始进行业务处理。
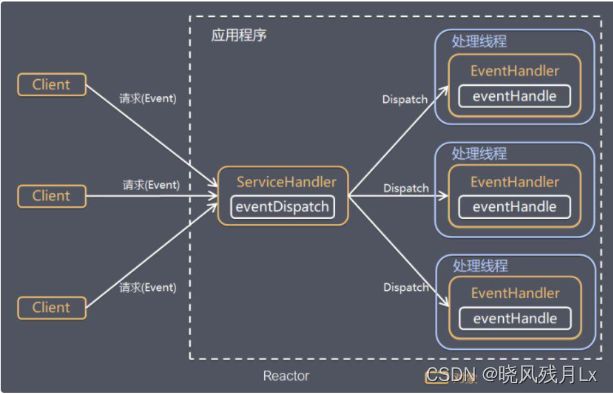
Reactor 模式,是指通过一个或多个输入同时传递给服务处理器的服务请求的事件驱动处理模式。服务端程序处理传入多路请求,并将它们同步分派给请求对应的处理线程,Reactor 模式也叫 Dispatcher 模式。即 I/O 多了复用统一监听事件,收到事件后分发(Dispatch 给某进程),是编写高性能网络服务器的必备技术!
Reactor 模式中有 2 个关键组成:
1)Reactor:Reactor 在一个单独的线程中运行,负责监听和分发事件,分发给适当的处理程序来对 IO 事件做出反应。 它就像公司的电话接线员,它接听来自客户的电话并将线路转移到适当的联系人;
2)Handlers:处理程序执行 I/O 事件要完成的实际事件,类似于客户想要与之交谈的公司中的实际办理人。Reactor 通过调度适当的处理程序来响应 I/O 事件,处理程序执行非阻塞操作。
Redis 服务采用 Reactor 的方式来实现文件事件处理器(每一个网络连接其实都对应一个文件描述符)
Redis基于Reactor模式开发了网络事件处理器,这个处理器被称为文件事件处理器。
它的组成结构为4部分:
多个套接字、
IO多路复用程序、
文件事件分派器、
事件处理器。因为文件事件分派器队列的消费是单线程的,所以Redis才叫单线程模型
select、poll、epoll 都是 I/O 多路服用的具体的实现
5.3 select 方法
我们自己写的java代码的思想(用户态)
/**
* select 其实就是把NIO 中用户态要遍历的fd(文件描述符)数组(我们的每一个socket链接,安装进ArrayList 里面的那个)拷贝到了内核态,
* 让内核态来遍历,因为用户态判断socket是否有数据还是要调用内核态的,所有拷贝到内核态后,这样遍历和判断的时候就不用一直用户态和内核态频繁切换
*/
while (true) {
for (SocketChannel element : socketList) {
int read = element.read(byteBuffer);
if (read > 0) {
System.out.println("-----读取数据: " + read);
byteBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[read];
byteBuffer.get(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
byteBuffer.clear();
}
}
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocket.accept();
if (socketChannel != null) {
System.out.println("-----成功连接: ");
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);//设置为非阻塞模式
socketList.add(socketChannel);
System.out.println("-----socketList size: " + socketList.size());
}
}
C语言代码
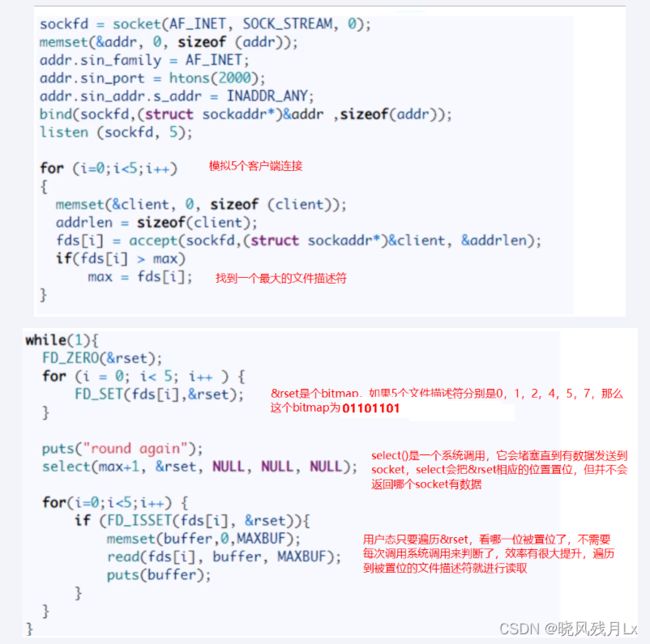
select函数的执行分析流程
- select是一个阻塞函数,当没有数据时,会一直阻塞在select那一行
- 当有数据时会将reset中对应的那一位置为1
- select函数返回,不再阻塞
- 遍历文件描述符数组,判断哪个fd被置位了
- 读取数据,然后处理
优缺点
- 优点
- select 其实就是把NIO中用户态要遍历的fd数组(我们的每一个socket链接,安装进ArrayList里面的那个)拷贝到了内核态,让内核态来遍历,因为用户态判断socket是否有数据还是要调用内核态的,所有拷贝到内核态后,这样遍历判断的时候就不用一直用户态和内核态频繁切换了
- 从代码中可以看出,select系统调用后,返回了一个置位后的&rset,这样用户态只需进行很简单的二进制比较,就能很快知道哪些socket需要read数据,有效提高了效率
- 缺点
- bitmap最大1024位,一个进程最多只能处理1024个客户端
- &rset不可重用,每次socket有数据就相应的位会被置位
- 文件描述符数组拷贝到了内核态(只不过无系统调用切换上下文的开销。(内核层可优化为异步事件通知)),仍然有开销。select 调用需要传入 fd 数组,需要拷贝一份到内核,高并发场景下这样的拷贝消耗的资源是惊人的。(可优化为不复制)
- select并没有通知用户态哪一个socket有数据,仍然需要O(n)的遍历。select 仅仅返回可读文件描述符的个数,具体哪个可读还是要用户自己遍历。(可优化为只返回给用户就绪的文件描述符,无需用户做无效的遍历)
总结
select方式,既做到了一个线程处理多个客户端连接(文件描述符),又减少了系统调用的开销(多个文件描述符只有一次 select 的系统调用 + N次就绪状态的文件描述符的 read 系统调用
5.4 poll 方法
C语言代码
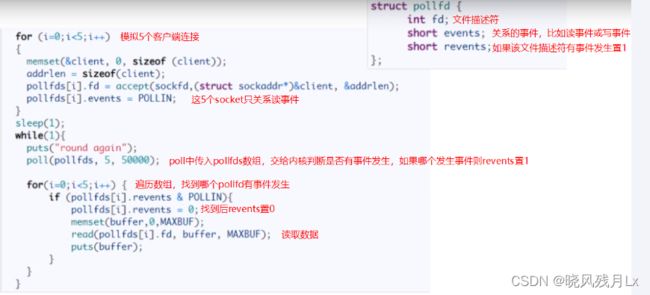
执行流程分析
- 将五个fd从用户态拷贝到内核态
- poll为阻塞方法,执行poll方法,如果有数据会将fd对应的revents置为POLLIN
- poll方法返回
- 循环遍历,查看哪个fd被置位为POLLIN了
- 将revents重置为0,便于复用
- 对置位的fd进行读取和处理
优点
1、poll使用pollfd数组来代替select中的bitmap,数组没有1024的限制,可以一次管理更多的client。它和 select 的主要区别就是,去掉了 select 只能监听 1024 个文件描述符的限制。
2、当pollfds数组中有事件发生,相应的revents置位为1,遍历的时候又置位回零,实现了pollfd数组的重用
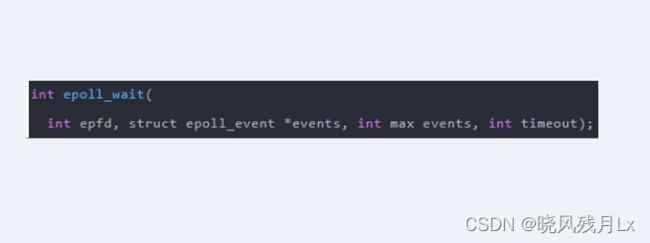
5.5 epoll方法
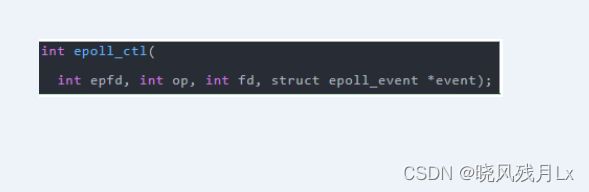
三步调用
C语言代码
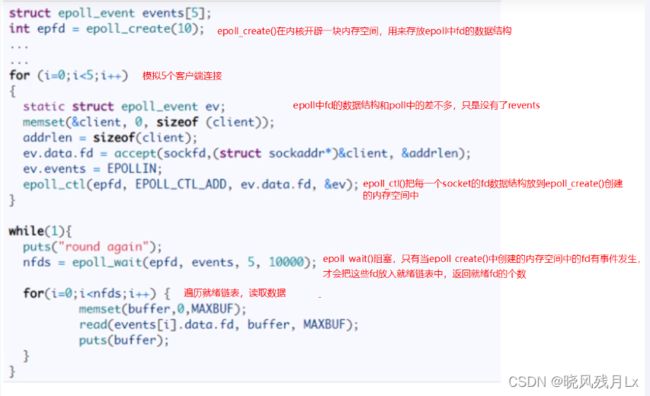
执行流程(epoll非阻塞的)
- 当有数据的时候,会把相应的文件描述符 “置位”,但是epool没有revent标志为,所以并不是真正的置位。这时候会把有数据的文件描述符放到队首。
- epoll会返回有数据的文件描述符的个数
- 根据返回的个数,读取前N个文件描述符即可
- 读取、处理
结论
多路复用快的原因在于,操作系统提供了这样的系统调用,使得原来的 while 循环里多次系统调用,变成了一次系统调用 + 内核层遍历这些文件描述符。
epoll是现在最先进的IO多路复用器,Redis、Nginx,linux中的Java NIO都使用的是epoll。
这里“多路”指的是多个网络连接,“复用”指的是复用同一个线程。
1、一个socket的生命周期中只有一次从用户态拷贝到内核态的过程,开销小
2、使用event事件通知机制,每次socket中有数据会主动通知内核,并加入到就绪链表中,不需要遍历所有的socket
在多路复用IO模型中,会有一个内核线程不断地去轮询多个 socket 的状态,只有当真正读写事件发送时,才真正调用实际的IO读写操作。因为在多路复用IO模型中,只需要使用一个线程就可以管理多个socket,系统不需要建立新的进程或者线程,也不必维护这些线程和进程,并且只有真正有读写事件进行时,才会使用IO资源,所以它大大减少来资源占用。多路I/O复用模型是利用 select、poll、epoll 可以同时监察多个流的 I/O 事件的能力,在空闲的时候,会把当前线程阻塞掉,当有一个或多个流有 I/O 事件时,就从阻塞态中唤醒,于是程序就会轮询一遍所有的流(epoll 是只轮询那些真正发出了事件的流),并且只依次顺序的处理就绪的流,这种做法就避免了大量的无用操作。 采用多路 I/O 复用技术可以让单个线程高效的处理多个连接请求(尽量减少网络 IO 的时间消耗),且 Redis 在内存中操作数据的速度非常快,也就是说内存内的操作不会成为影响Redis性能的瓶颈
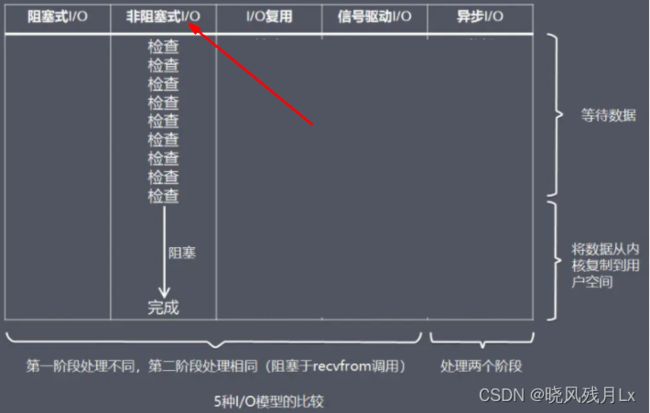
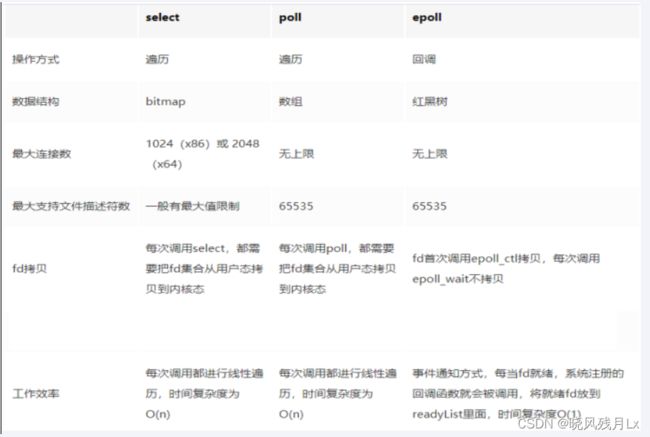
5.6 三方法对比
PS: 尽量不要用 windows 的redis,只能调用select()方法,时间复杂度是O(n), Linux是用epoll(),时间复杂度O(1),所以 Linux 的 redis 会比 windows 的快!!!