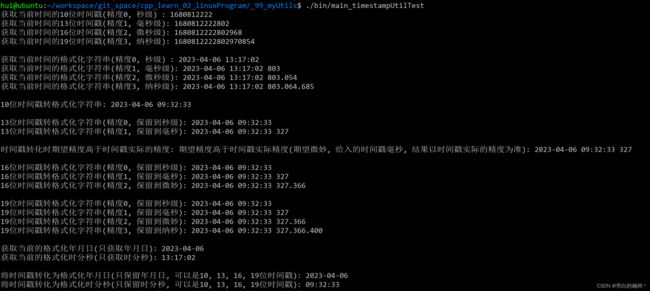
基于c++11的时间戳工具类, (TimestampUtil) 支持10位时间戳, 13位时间戳, 16位时间戳, 和19位时间戳的获取与转为格式化时间字符串
C++ 时间戳工具类 timestampUtil 基于c++11
- 前言/工具类说明
- 头文件(TimestampUtil.h)
- 源文件(TimestampUtil.cpp文件)
- 测试代码/使用示例
- 测试结果
前言/工具类说明
最近学习c++, 发现网络上几乎没有用c++编写的时间戳工具类(TimestampUtil). 今天在CSDN上参考了一些大佬的代码, 了解了c++11中获取和使用时间戳的步骤和方式, 总结后自己写了一个时间戳工具类. 基本覆盖日常编程中, 获取时间戳, 和将时间戳转化为格式化日期时间(字符串)的功能.
- 考虑到跨平台的需求, 工具类中只使用了c++的时间库, 主要是chrono 和iomanip这两个库, 已避免使用任何C库函数. 以确保工具类可以在windows, linux等操作系统上正常编译和运行, 确保代码复制即用, 无需考虑系统差异(已测试无问题)
- 接口函数注释较为详细, 根据头文件中的函数说明和测试代码中的示例使用
- 由于是工具类, 已禁止继承和实例化. 所有函数均为static, 只能通过类名调用
- 由于std:localtime函数是线程不安全的. 所以通过条件编译的方法, 在windows下使用std::localtime_s函数, linux以及类unix系统中使用localtime_r函数. 来规避localtime. 因此本类是线程安全的, 可以在多线程程序中使用.
- 工具类基于c++11标准, 确保你的编译器最低支持c++11
头文件(TimestampUtil.h)
头文件中主要包含TimestampUtil类的声明, 你可以根据注释, 通过类名调用public权限中的函数来使用本工具类
#pragma once
#include 源文件(TimestampUtil.cpp文件)
TimestampUtil.cpp文件为TimestampUtil.h的代码实现, 你可以删除TimestampUtil.cpp文件中的第一行(删掉include行), 并将其余所有的代码复制到TimestampUtil.h的最后面, 实现header-only, 以方便在你的程序中更加快速的使用这个工具类
#include "TimestampUtil.h" // 你可以将该行删除, 然后把本文其余的所有代码全部复制到TimestampUtil.h(头文件)的最后面. 之后就可以直接声明TimestampUtil.h来使用这个工具类
int
TimestampUtil::checkBitLength(time_t timestamp)
{
int bit=0;
if(timestamp == 0) return 1;
while(timestamp)
{
bit++;
timestamp/=10;
}
return bit;
}
system_clock::time_point
TimestampUtil::_getNow()
{
return system_clock::now();
}
int
TimestampUtil::getTimeLevel(const time_t ×tamp)
{
int timestampLen = checkBitLength(timestamp);
int time_level = -1;
switch (timestampLen)
{
case 10:
time_level = 0;
break;
case 13:
time_level = 1;
break;
case 16:
time_level = 2;
break;
case 19:
time_level = 3;
break;
default:
break;
}
return time_level;
}
void TimestampUtil::setFormatData(int time_level, const string &formatType, struct __timeData &timedata)
{
time_t timestamp = timedata.timestamp;
int ms;
int cs;
int ns;
time_t timestamp_sec;
stringstream formatTime;
switch (time_level)
{
case 0:
timestamp_sec = timestamp;
break;
case 1:
timestamp_sec = timestamp / 1000;
timedata.ms = timestamp % 1000;
break;
case 2:
timestamp_sec = timestamp / 1000 / 1000;
timedata.cs = timestamp % 1000;
timedata.ms = timestamp / 1000 % 1000;
break;
case 3:
timestamp_sec = timestamp / 1000 / 1000 / 1000;
timedata.ns = timestamp % 1000;
timedata.cs = timestamp / 1000 % 1000;
timedata.ms = timestamp / 1000 / 1000 % 1000;
break;
default:
return;
}
tm timeInfo;
#if defined(WIN32) || defined(_WIN32) || defined(__WIN32__)
localtime_s(&timeInfo, ×tamp_sec);
#elif defined(linux) || defined(__linux) || defined(__linux__)
localtime_r(×tamp_sec, &timeInfo);
#elif defined(unix) || defined(__unix) || defined(__unix__)
localtime_r(×tamp_sec, &timeInfo);
#endif
formatTime << put_time(&timeInfo, formatType.c_str());
timedata.formatDatatime = formatTime.str();
}
string
TimestampUtil::buildFormatString(struct __timeData &timedata)
{
stringstream formatString;
formatString << timedata.formatDatatime;
if (timedata.ms == -1)
{
return formatString.str();
}
formatString << " " << setw(3) << setfill('0') << timedata.ms;
if (timedata.cs == -1)
{
return formatString.str();
}
formatString << "." << setw(3) << setfill('0') << timedata.cs;
if (timedata.ns == -1)
{
return formatString.str();
}
formatString << "." << setw(3) << setfill('0') << timedata.ns;
return formatString.str();
}
time_t
TimestampUtil::getCurrentTimestamp(int time_level)
{
auto timeinfo = _getNow().time_since_epoch();
time_t current_time_stamp;
switch (time_level)
{
case 0:
current_time_stamp = duration_cast<seconds>(timeinfo).count();
break;
case 1:
current_time_stamp = duration_cast<milliseconds>(timeinfo).count();
break;
case 2:
current_time_stamp = duration_cast<microseconds>(timeinfo).count();
break;
case 3:
current_time_stamp = duration_cast<nanoseconds>(timeinfo).count();
break;
default:
current_time_stamp = -1;
break;
}
return current_time_stamp;
}
string
TimestampUtil::getCurrentFormatDatetime(int time_level)
{
struct __timeData timedata;
timedata.timestamp = getCurrentTimestamp(time_level);
setFormatData(time_level, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", timedata);
return buildFormatString(timedata);
}
string
TimestampUtil::getCurrentFormatDate()
{
struct __timeData timedata;
timedata.timestamp = getCurrentTimestamp(0);
setFormatData(0, "%Y-%m-%d", timedata);
return buildFormatString(timedata);
}
string
TimestampUtil::getCurrentFormatTime()
{
struct __timeData timedata;
timedata.timestamp = getCurrentTimestamp(0);
setFormatData(0, "%H:%M:%S", timedata);
return buildFormatString(timedata);
}
string
TimestampUtil::getFormatData(const time_t timestamp)
{
struct __timeData timedata;
int time_level = getTimeLevel(timestamp);
timedata.timestamp = timestamp;
time_level = 0;
time_level = timestampGabFix(time_level, timedata);
setFormatData(time_level, "%Y-%m-%d", timedata);
return buildFormatString(timedata);
}
string
TimestampUtil::getFormatTime(const time_t timestamp)
{
struct __timeData timedata;
int time_level = getTimeLevel(timestamp);
timedata.timestamp = timestamp;
time_level = 0;
time_level = timestampGabFix(time_level, timedata);
setFormatData(time_level, "%H:%M:%S", timedata);
return buildFormatString(timedata);
}
string
TimestampUtil::getFormatDataTime(time_t timestamp, int time_level)
{
if (time_level > 3 || time_level < 0)
{
return nullptr;
}
struct __timeData timedata;
timedata.timestamp = timestamp;
// timestamp和time_level的精度拟合修复函数
time_level = timestampGabFix(time_level, timedata);
setFormatData(time_level, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", timedata);
return buildFormatString(timedata);
}
int
TimestampUtil::timestampGabFix(int input_level, __timeData &timedata)
{
int time_level_gab; // 拟合值
time_t timestamp = timedata.timestamp;
int timestamp_time_level = getTimeLevel(timestamp);
if (timestamp_time_level < 0)
{
return -1;
}
int time_level = -1;
// 时间戳精度大于输入精度, 时间戳根据拟合值删减
if (timestamp_time_level > input_level)
{
time_level_gab = timestamp_time_level - input_level;
timestamp = timestamp / pow(1000, time_level_gab); // 时间戳截取
time_level = input_level; // 使用输入的精度
}
// 时间戳精度小于输入精度, 以时间戳精度为准
else
{
time_level = timestamp_time_level;
}
timedata.timestamp = timestamp;
return time_level;
}
测试代码/使用示例
测试代码中调用了工具类中public权限所有的函数, 并已经通过注释和打印字符串的方式给出了详细的说明. 你可以根据测试代码中的函数调用方式, 来使用这个工具类.
#include "TimestampUtil.h"
int main()
{
/* 当前时间时间戳获取 */
cout << "获取当前时间的10位时间戳(精度0, 秒级) : " << TimestampUtil::getCurrentTimestamp(0) << endl;
cout << "获取当前时间的13位时间戳(精度1, 毫秒级): " << TimestampUtil::getCurrentTimestamp(1) << endl; // 也可以写为 TimestampUtil::getCurrentTimestamp();
cout << "获取当前时间的16位时间戳(精度2, 微秒级): " << TimestampUtil::getCurrentTimestamp(2) << endl;
cout << "获取当前时间的19位时间戳(精度3, 纳秒级): " << TimestampUtil::getCurrentTimestamp(3) << endl << endl;
/* 当前格式化获取 */
cout << "获取当前时间的格式化字符串(精度0, 秒级) : " << TimestampUtil::getCurrentFormatDatetime(0) << endl; // TimestampUtil::getCurrentFormatDatetime();
cout << "获取当前时间的格式化字符串(精度1, 毫秒级): " << TimestampUtil::getCurrentFormatDatetime(1) << endl;
cout << "获取当前时间的格式化字符串(精度2, 微秒级): " << TimestampUtil::getCurrentFormatDatetime(2) << endl;
cout << "获取当前时间的格式化字符串(精度3, 纳秒级): " << TimestampUtil::getCurrentFormatDatetime(3) << endl << endl;
time_t testTimestamp_10 = 1680798753; // 测试用的10位时间戳, 精确到秒
time_t testTimestamp_13 = 1680798753327; // 测试用的13位时间戳, 精确到毫秒
time_t testTimestamp_16 = 1680798753327366; // 测试用的16位时间戳, 精确到微妙
time_t testTimestamp_19 = 1680798753327366400; // 测试用的19位时间戳, 精确到纳秒
// 将10位时间戳转为格式化字符串
cout << "10位时间戳转格式化字符串: " << TimestampUtil::getFormatDataTime(testTimestamp_10) << endl << endl;
// 将13位时间戳转为格式化字符串
cout << "13位时间戳转格式化字符串(精度0, 保留到秒级): " << TimestampUtil::getFormatDataTime(testTimestamp_13) << endl;
cout << "13位时间戳转格式化字符串(精度1, 保留到毫秒): " << TimestampUtil::getFormatDataTime(testTimestamp_13, 1) << endl << endl;
/*
时间戳转为格式化字符串时, 如果期望精度高于时间戳实际的精度, 结果以时间戳实际的精度为准. 如下面的示例:
给入的时间戳位数为13(对应精度1, 毫秒级), 期望的精度为3(纳秒级), 结果以时间戳实际的精度为准
*/
cout << "时间戳转化时格式化字符串时, 如果期望精度高于时间戳实际的精度: 例如期望纳妙, 给入的时间戳为毫秒级, 结果以时间戳实际的精度为准): " << TimestampUtil::getFormatDataTime(testTimestamp_13, 3) << endl << endl;
// 将16位时间戳转为格式化字符串
cout << "16位时间戳转格式化字符串(精度0, 保留到秒级): " << TimestampUtil::getFormatDataTime(testTimestamp_16) << endl;
cout << "16位时间戳转格式化字符串(精度1, 保留到毫秒): " << TimestampUtil::getFormatDataTime(testTimestamp_16, 1) << endl;
cout << "16位时间戳转格式化字符串(精度2, 保留到微妙): " << TimestampUtil::getFormatDataTime(testTimestamp_16, 2) << endl << endl;
// 将19位时间戳转为格式化字符串
cout << "19位时间戳转格式化字符串(精度0, 保留到秒级): " << TimestampUtil::getFormatDataTime(testTimestamp_19) << endl;
cout << "19位时间戳转格式化字符串(精度1, 保留到毫秒): " << TimestampUtil::getFormatDataTime(testTimestamp_19, 1) << endl;
cout << "19位时间戳转格式化字符串(精度2, 保留到微妙): " << TimestampUtil::getFormatDataTime(testTimestamp_19, 2) << endl;
cout << "19位时间戳转格式化字符串(精度3, 保留到纳秒): " << TimestampUtil::getFormatDataTime(testTimestamp_19, 3) << endl << endl;
/* 当前格式化年月日获取(只获取年月日) */
cout << "获取当前的格式化年月日(只获取年月日): " << TimestampUtil::getCurrentFormatDate() << endl;
/* 当前格式化时分秒获取(只获取时分秒) */
cout << "获取当前的格式化时分秒(只获取时分秒): " << TimestampUtil::getCurrentFormatTime() << endl << endl;
cout << "将时间戳转化为格式化年月日(只保留年月日, 可以是10, 13, 16, 19位时间戳): " << TimestampUtil::getFormatData(testTimestamp_19) << endl;
cout << "将时间戳转化为格式化时分秒(只保留时分秒, 可以是10, 13, 16, 19位时间戳): " << TimestampUtil::getFormatTime(testTimestamp_19) << endl;
return 0;
}